To bind an IP address to a domain name, point a domain name to a website server, or bind a domain name to an email service, you must add a DNS record for the domain name. Public Zone uses DNS records to guide internet users or systems to the correct resources, such as websites, email services, or URLs.
Use cases
Use case 1
You own the domain name example.com. To allow users to access your website at www.example.com and a demo service at playground.example.com, create DNS records with the hostnames www and playground.
Use case 2
You own the domain name example.com and want www.example.com to be the only entry point. All other subdomains, such as a.example.com and b.example.com, must redirect to www.example.com instead of failing to resolve. To achieve this, create a DNS record with hostname www. Then, create a wildcard DNS record with hostname * and record type Explicit URL Forwarding. This redirects all unconfigured hostnames.
Use case 3
You purchased Alibaba Cloud Enterprise Email. Users must log in to email using <userId>@example.com. To do this, configure DNS records for your email service.
Use case 4
You configured a custom domain name for an OSS bucket, added an accelerated domain name in CDN, added WAF protection for your website, or configured an ingest domain name for live streaming. In each case, you added a domain name (such as demo.example.com) in the corresponding service. That service then generated a CNAME record (such as on-premises-dns.aliyun.com). To complete the setup, create a DNS record with hostname demo and record type CNAME. This points resolution to the corresponding service, which provides the final service endpoint.
Select a record type
Record types supported by Alibaba Cloud DNS and their common use cases:
Record type | Description | How common |
A record | Resolves a domain name to a specified IPv4 address. Commonly used for website domain resolution. | 5 out of 5. The most basic record type. Almost every domain name requires it. |
CNAME record | Resolves a domain name to another domain name. Commonly used for website resolution, CDN acceleration, enterprise email, and Global Traffic Manager integration. | 5 out of 5. Widely used for aliasing. Common for CDN and cloud services. |
MX record | Specifies the mail server for a domain name and sorts servers by priority. | 4 out of 5. Required for email-related services. Not needed if you do not use email. |
AAAA record | Resolves a domain name to a specified IPv6 address. Commonly used when accessing websites over IPv6. | 4 out of 5. IPv6 adoption is accelerating. Most cloud services now support IPv6 by default. |
TXT record | Identifies and describes a domain name. Commonly used for domain ownership verification, digital certificate issuance, SPF records (anti-spam), and domain recovery. | 5 out of 5. Used for many verification tasks, such as SSL, SPF, email, and DNS verification. |
ALIAS record | Flattens CNAME records. Solves conflicts between CNAME and other record types. For example, use ALIAS when you need both MX and CNAME records for a root domain. | 2 out of 5. Use only when CNAME conflicts with MX, TXT, or other records. |
Explicit and implicite URL forwarding | Points a domain name to an existing website. | 2 points: Supported only by certain DNS resolvers and primarily used for domain redirection. |
NS record | Specifies DNS servers that manage DNS configuration for a domain name. Commonly used when delegating subdomain resolution to other DNS providers. | 3 out of 5. Common for subdomain-level settings. Rarely changed in daily operations. |
SRV record | Identifies which server hosts a specific service. Commonly used in Microsoft directory management. | 2 out of 5. Needed for instant messaging and enterprise service protocols. Rarely used for standard websites. |
CAA record | Specifies authorized certification authorities (CAs) allowed to issue HTTPS certificates for a domain name. Prevents unauthorized certificate issuance and improves website security. | 2 out of 5. Enhances SSL/TLS certificate management security. Used in specific scenarios. |
PTR record | Maps an IP address to a domain name. Verifies whether an IP address corresponds to a specific domain name. | 1 out of 5. Used mainly for reverse DNS lookup, such as for email servers. Rarely used for standard websites. |
SVCB record | Improves service discovery by providing protocol and endpoint information. Optimizes client connection decisions to improve performance and security. | 1 out of 5. An emerging protocol. Used with HTTP/3 and QUIC. Currently uncommon. |
HTTPS record | An HTTPS record is a specialized SVCB record designed specifically for HTTPS services. | Point 1: The new HTTPS optimization standard is gradually gaining browser support but is not yet widely adopted by general websites. |
Add a DNS record
A record
An A record points a domain name to a static IP address. It is commonly used for website domain resolution. For example, if you have built a website accessible over the public internet and own a domain name, set up an A record. After the record takes effect, users can access your website using the domain name.
Limits
Obtain the public IPv4 address of the target server. Example:
192.0.2.1.If you use Alibaba Cloud ECS, you can view the public IP address in the Alibaba Cloud ECS console.
If you use a non-Alibaba Cloud server, contact your service provider to obtain the public IP address.
If the hostname is not
@, A records conflict with NS, CNAME, ALIAS, or URL records when the hostname and resolution line are identical. If you receive a conflict error when adding an A record, delete the conflicting record or change the hostname. For more information, see DNS record conflict rules.
How to set up
On the Alibaba Cloud DNS – Public Zone page, click the target domain name to go to the Settings page.
Click the Add Record button.
Fill in the form fields.
Field
Description
Recommended value
Record Type
Different record types require different record values.
Select A from the drop-down list. Resolves the domain name to a specified IPv4 address.
Hostname
Usually the prefix of a subdomain.
If the domain name is
www.example.com, enterwww.If the domain name is
example.com, enter@.If the domain name is
demo.example.com, enterdemo.If the domain name is
test.blog.example.com, entertest.blog.
Query Source
Specifies the source of DNS queries. Select Default unless you need to return different record values based on the user’s location. For example, use smart resolution lines such as carriers or regions outside China. For details, see Smart resolution and Custom resolution lines.
ImportantAlways set one record with the resolution line Default. This acts as a fallback to prevent resolution failures when no matching resolution line exists.
If you have no special requirements, keep Default.
For requests from Beijing and nearby cities, select
China_North.For requests from China Telecom, select
China Telecom.
TTL
The time that DNS resolvers cache the resolution result. We recommend setting TTL to 10 minutes. Smaller TTL values make changes take effect faster for end users. For more information, see How to configure TTL.
Edition
Free Edition
Personal Edition
Enterprise Ultimate Edition & Premium Edition
Minimum TTL value
600 seconds (10 minutes)
600 seconds (10 minutes)
1 second
Maximum TTL value
86400 seconds (24 hours)
86400 seconds (24 hours)
86400 seconds (24 hours)
Record Values Load Strategy
Round Robin:
For A, AAAA, NS, MX, and TXT records, Alibaba Cloud DNS returns all records for the selected resolution line. The local DNS resolver selects the response. If the local DNS resolver returns all addresses, the end user selects randomly.
Ratio:
Returns the Record Values based on the configured weights. For configuration steps, see Configure weights.
Round Robin
Record Values
Usually the public IPv4 address of the website server. You can add multiple addresses.
When Record Values Load Strategy is set to Ratio, set the Ratio next to each record value. When responding to queries, Alibaba Cloud DNS returns record values based on the preset weight ratio.
If you use Alibaba Cloud ECS: View the public IP address in the Alibaba Cloud ECS console.
If you use a non-Alibaba Cloud server: Contact your service provider to get the public IP address.
Example

FAQ
CNAME record
A CNAME (Canonical Name) record points a domain name to another domain name. The other domain name then provides the IP address. Common use cases include CDN, enterprise email, and Global Traffic Manager.
Resolution flow
For example, the CNAME record for www.example.com points to app.cloud-example.net. When users visit www.example.com, the full CNAME resolution flow is as follows:
The user enters
www.example.comin a browser or an application connects to this domain name.The user’s computer checks its local cache. If the record is not found, it queries a recursive DNS server (such as 114.114.114.114 or 8.8.8.8).
If the recursive DNS server does not have the record cached, it performs a standard DNS resolution:
It asks the root DNS server: “Who manages the .com top-level domain?”
The root server returns the address of the .com top-level domain (TLD) DNS server.
The recursive DNS server asks the TLD server: “Who manages example.com?”
The TLD server returns the authoritative DNS server for example.com.
The recursive DNS server asks the authoritative DNS server: “What is the DNS record for www.example.com?”
The authoritative DNS server finds that
www.example.comhas a CNAME record pointing toapp.cloud-example.net. It replies to the recursive DNS server: “www.example.comis equivalent toapp.cloud-example.net. You should query the latter.”
The recursive DNS server receives
app.cloud-example.netand repeats the resolution process (or uses a cached result). It usually finds the A record (IP address) forapp.cloud-example.netor encounters another CNAME (in theory, CNAMEs can chain, but we recommend no more than two levels).The recursive DNS server continues until it obtains the final IP address.
Limits
If you add a CNAME record on the default resolution line and add A or AAAA records on smart resolution lines, smart resolution may not work correctly.
If the hostname is not
@, CNAME records conflict with other record types when the hostname and resolution line are identical. If you receive a conflict error when adding a CNAME record, delete the conflicting record or change the hostname. For more information, see DNS record conflict rules.
How to set up
On the Alibaba Cloud DNS – Public Zone page, click the target domain name to go to the Settings page.
Click the Add Record button.
Fill in the form fields.
Form field
Description
Recommended value
Record Type
Different record types require different record values.
Select CNAME from the drop-down list. This points the domain name to another domain name, which then resolves to an IP address.
Hostname
Usually the prefix of a subdomain.
If the domain name is
www.example.com, enterwww.If the domain name is
example.com, enter@.If the domain name is
demo.example.com, enterdemo.If the domain name is
test.blog.example.com, entertest.blog.
Query Source
Specifies the source of DNS queries. Select Default unless you need to return different record values based on the user’s location. For example, use smart resolution lines such as carriers or regions outside China. For details, see Smart resolution and Custom resolution lines.
ImportantAlways set one record with the resolution line Default. This acts as a fallback to prevent resolution failures when no matching resolution line exists.
If you have no special requirements, keep Default.
For requests from Beijing and nearby cities, select
China_North.For requests from China Telecom, select
China Telecom.
TTL
The time that DNS resolvers cache the resolution result. We recommend setting TTL to 10 minutes. Smaller TTL values make changes take effect faster for end users. For more information, see How to configure TTL.
Edition
Free Edition
Personal Edition
Enterprise Ultimate Edition & Premium Edition
Minimum TTL value
600 seconds (10 minutes)
600 seconds (10 minutes)
1 second
Maximum TTL value
86400 seconds (24 hours)
86400 seconds (24 hours)
86400 seconds (24 hours)
Record Values Load Strategy
Only Ratio is supported. For configuration steps, see Configure weights.
Ratio
Record Values
A domain name that provides the target IP address. You can add multiple domain names.
When Record Values Load Strategy is set to Ratio, set the Ratio next to each record value. When responding to queries, Alibaba Cloud DNS returns record values based on the preset weight ratio.
Example:
aliyundoc.com.Example

FAQ
MX record
To ensure your email service receives messages, add an MX record. MX stands for mail exchanger. Email systems use MX records to locate mail servers based on the domain part of an email address. For example, when someone sends an email to vincen@example.com, the system resolves the MX record for example.com. If an MX record exists, the system forwards the message to the mail server specified in the MX record, sorted by priority. To quickly add email resolution, see Add email resolution.
Limits
You have deployed an email server and obtained the domain name from your email service provider.
If the hostname is not
@, MX records conflict with NS or CNAME records when the hostname and resolution line are identical. If you receive a conflict error when adding an MX record, delete the conflicting record or change the hostname. For more information, see DNS record conflict rules.
How to set up
The following example shows the (mailbox) (record)s that you must configure for Alibaba Cloud Enterprise Mailbox:
On the Alibaba Cloud DNS – Public Zone page, click the target domain name to go to the Settings page.
Click the Add Record button.
Fill in the form fields.
Form field
Description
Recommended value
Record Type
Different record types require different record values.
Select MX from the drop-down list. MX stands for mail exchanger. Email systems use MX records to locate mail servers based on the domain part of an email address.
Hostname
Usually the prefix of a subdomain.
If the domain name is
www.example.com, enterwww.If the domain name is
example.com, enter@.If the domain name is
demo.example.com, enterdemo.If the domain name is
test.blog.example.com, entertest.blog.
Query Source
Specifies the source of DNS queries. Select Default unless you need to return different record values based on the user’s location. For example, use smart resolution lines such as carriers or regions outside China. For details, see Smart resolution and Custom resolution lines.
ImportantAlways set one record with the resolution line Default. This acts as a fallback to prevent resolution failures when no matching resolution line exists.
If you have no special requirements, keep Default.
For requests from Beijing and nearby cities, select
China_North.For requests from China Telecom, select
China Telecom.
TTL
The time that DNS resolvers cache the resolution result. We recommend setting TTL to 10 minutes. Smaller TTL values make changes take effect faster for end users. For more information, see How to configure TTL.
Edition
Free Edition
Personal Edition
Enterprise Ultimate Edition & Premium Edition
Minimum TTL value
600 seconds (10 minutes)
600 seconds (10 minutes)
1 second
Maximum TTL value
86400 seconds (24 hours)
86400 seconds (24 hours)
86400 seconds (24 hours)
Record Values Load Strategy
Only Round Robin is supported.
For A, AAAA, NS, MX, and TXT records, Alibaba Cloud DNS returns all records for the selected resolution line. The local DNS resolver selects the response. If the local DNS resolver returns all addresses, the end user selects randomly.
Round Robin
Record Values
Record Value:
Obtain this from your email service provider. You can add multiple values. Example: For Alibaba Cloud Email, the required record value is
mx1.qiye.aliyun.com.Priority:
Lower priority numbers indicate higher priority. For example, email is first sent to
5(mx1.qiye.aliyun.com). If that fails, email is sent to10(mx2.qiye.aliyun.com).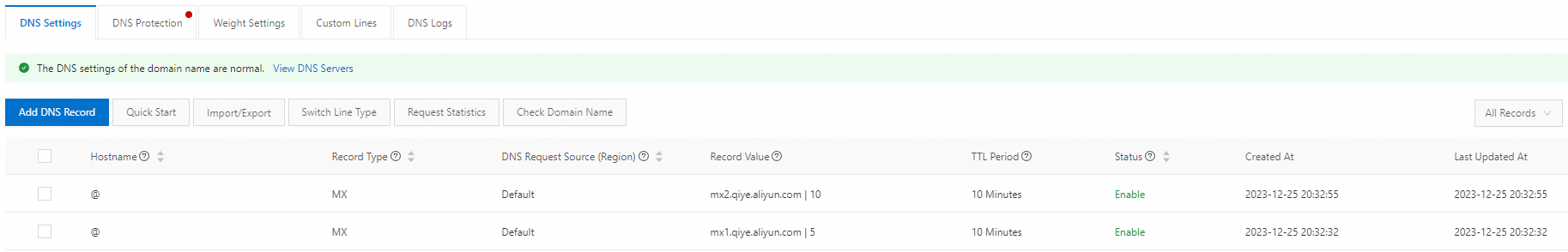
Example:
aliyundoc.com 5.ImportantThe above shows how to set up an MX record. To fully set up email, you also need CNAME and TXT records. Contact your email provider for the exact records you need. If you use Alibaba Cloud Email, see Add email resolution.
Example

FAQ
AAAA record
Use an AAAA record to point a domain name to a static IPv6 address. This is commonly used when configuring DNS resolution for websites that support IPv6.
Limits
Obtain the IPv6 address of the target server in advance. Example: ff03:0:0:0:0:0:0:c1.
If the hostname is not
@, AAAA records conflict with NS, CNAME, ALIAS, or URL records when the hostname and resolution line are identical. If you receive a conflict error when adding an AAAA record, delete the conflicting record or change the hostname. For more information, see DNS record conflict rules.
How to set up
On the Alibaba Cloud DNS – Public Zone page, click the target domain name to go to the Settings page.
Click the Add Record button.
Fill in the form fields.
Form field
Description
Recommended value
Record Type
Different record types require different record values.
Select AAAA from the drop-down list to point the domain name to an IPv6 address, usually the IPv6 address of the website server, such as ff03:0:0:0:0:0:0:c1.
Hostname
Usually the prefix of a subdomain.
If the domain name is
www.example.com, enterwww.If the domain name is
example.com, enter@.If the domain name is
demo.example.com, enterdemo.If the domain name is
test.blog.example.com, entertest.blog.
Query Source
Specifies the source of DNS queries. Select Default unless you need to return different record values based on the user’s location. For example, use smart resolution lines such as carriers or regions outside China. For details, see Smart resolution and Custom resolution lines.
ImportantAlways set one record with the resolution line Default. This acts as a fallback to prevent resolution failures when no matching resolution line exists.
If you have no special requirements, keep Default.
For requests from Beijing and nearby cities, select
China_North.For requests from China Telecom, select
China Telecom.
TTL
The time that DNS resolvers cache the resolution result. We recommend setting TTL to 10 minutes. Smaller TTL values make changes take effect faster for end users. For more information, see How to configure TTL.
Edition
Free Edition
Personal Edition
Enterprise Ultimate Edition & Premium Edition
Minimum TTL value
600 seconds (10 minutes)
600 seconds (10 minutes)
1 second
Maximum TTL value
86400 seconds (24 hours)
86400 seconds (24 hours)
86400 seconds (24 hours)
Record Values Load Strategy
Round Robin:
For A, AAAA, NS, MX, and TXT records, Alibaba Cloud DNS returns all records for the selected resolution line. The local DNS resolver selects the response. If the local DNS resolver returns all addresses, the end user selects randomly.
Ratio:
Returns the Record Values based on the configured weights. For configuration steps, see Configure weights.
Round Robin
Record Values
Usually the IPv6 address of the website server. You can enter multiple addresses.
When Record Values Load Strategy is set to Ratio, set the Ratio next to each record value. When responding to queries, Alibaba Cloud DNS returns record values based on the preset weight ratio.
Example: ff03:0:0:0:0:0:0:c1.
Example

FAQ
TXT record
Use a TXT record to identify or describe a domain name. TXT records are commonly used for digital certificate issuance and SPF records (anti-spam).
Limits
If the hostname is not
@, TXT records conflict with NS or CNAME records when the hostname and resolution line are identical. If you receive a conflict error when adding a TXT record, delete the conflicting record or change the hostname. For more information, see DNS record conflict rules.The maximum length of a TXT record value is 8192 characters.
How to set up
On the Alibaba Cloud DNS – Public Zone page, click the target domain name to go to the Settings page.
Click the Add Record button.
Fill in the form fields.
Form field
Description
Recommended value
Record Type
The required record value varies based on the record type.
Select TXT from the drop-down list. TXT records are commonly used for tasks such as SSL certificate validation and creating Sender Policy Framework (SPF) records to prevent spam.
Hostname
The prefix of the subdomain.
If the domain name is
www.example.com, enterwww.If the domain name is
example.com, enter@.If the domain name is
demo.example.com, enterdemo.If the domain name is
test.blog.example.com, entertest.blog.
Query Source
Specifies the source of DNS queries. Select Default unless you need to return different record values based on the user’s location. For example, use smart resolution lines such as carriers or regions outside China. For details, see Smart resolution and Custom resolution lines.
ImportantAlways set one record with the resolution line Default. This acts as a fallback to prevent resolution failures when no matching resolution line exists.
If you have no special requirements, keep Default.
For requests from Beijing and nearby cities, select
China_North.For requests from China Telecom, select
China Telecom.
TTL
The time that DNS resolvers cache the resolution result. We recommend setting TTL to 10 minutes. Smaller TTL values make changes take effect faster for end users. For more information, see How to configure TTL.
Edition
Free Edition
Personal Edition
Enterprise Ultimate Edition & Premium Edition
Minimum TTL value
600 seconds (10 minutes)
600 seconds (10 minutes)
1 second
Maximum TTL value
86400 seconds (24 hours)
86400 seconds (24 hours)
86400 seconds (24 hours)
Record Values Load Strategy
Only Round Robin is supported.
For A, AAAA, NS, MX, and TXT records, Alibaba Cloud DNS returns all records that match the selected resolution line. The local DNS resolver then determines which record to use. If the local DNS resolver returns all the record values, the end user's client randomly selects one.
Round Robin
Record Values
TXT records are commonly used for verification. Obtain the required record value from your certificate service or email service provider. For example, you may need to add a TXT record to verify ownership of a subdomain. You can add multiple TXT records.
NoteDuring routine operations and maintenance (O&M), you should clean up unused TXT records. An excessive number of TXT records for a single subdomain can exceed response size limits, which may cause resolution failures on some carrier recursive DNS servers.
Example:
5d597b2c12464a7a8d0dde6b858ce543.Example
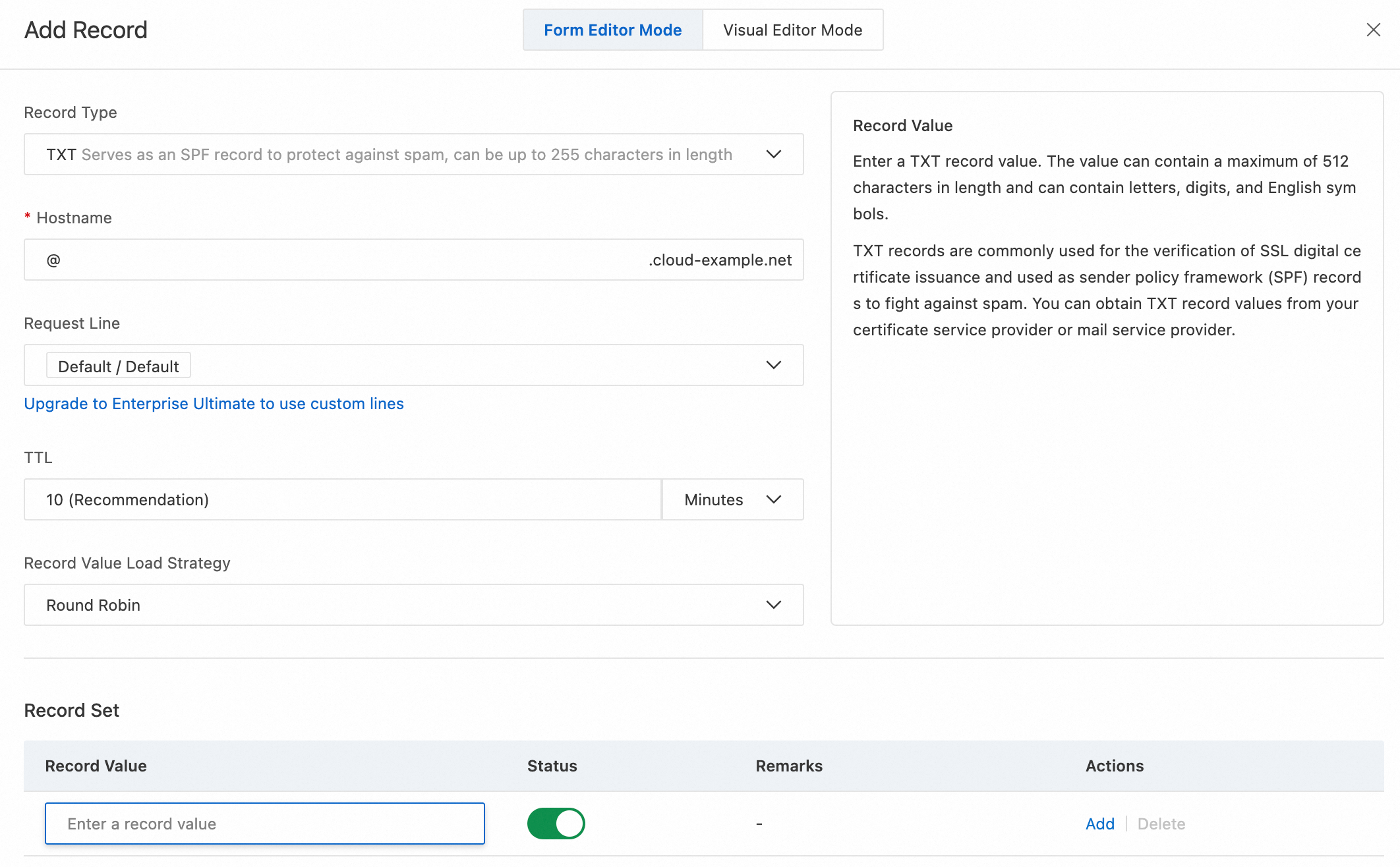
FAQ
ALIAS record
Background information
According to DNS protocol specifications, CNAME records have the highest priority. If a domain name has both CNAME and MX or TXT records, recursive DNS servers return the CNAME record when queried for MX records. To prevent misconfiguration, Alibaba Cloud DNS blocks conflicting records during creation. For more information, see DNS record conflict rules.
Function introduction
An ALIAS record implements CNAME flattening. Its value is a domain name. The system automatically performs recursive resolution and returns the final IP address. This reduces DNS lookups, speeds up resolution, and solves conflicts between CNAME and other record types. For example, use ALIAS when you have a CNAME record for WAF or CDN but also need MX records for email. This feature is available only in the Ultimate Edition and Premium Edition.
ALIAS vs. CNAME
Similarities: Both record types use another domain name as the record value.
Differences:
CNAME | ALIAS |

| 
|
Limits
The ALIAS record type is available only in the Ultimate Edition and Premium Edition.
In the Ultimate Edition, you can configure up to 10 ALIAS records per domain name. In the Premium Edition, there is no limit* on the number of ALIAS records. For more information, see Edition comparison.
*Unlimited: If you exceed the default system limit during actual use, you can request a parameter limit increase, provided the product remains stable and secure.
If you downgrade from a paid edition to the Personal Edition or Free Edition, ALIAS records remain but become inactive. If you downgrade from the Premium Edition to the Ultimate Edition and have more than 10 ALIAS records, the records remain active, but you cannot modify them. To modify existing ALIAS records, delete excess records to reduce the total to 10 or fewer.
The ALIAS record type conflicts with DNSSEC. To use ALIAS records, you must first disable DNSSEC for the domain name.
ALIAS records conflict with A, AAAA, or CNAME records but not with other record types. For more information, see DNS record conflict rules.
ALIAS records are supported only in public authoritative DNS resolution. Global Traffic Manager does not support ALIAS records.
Usage notes
Because ALIAS records rely on public recursive DNS servers, network fluctuations or recursive server failures can cause resolution failures. Therefore, Alibaba Cloud does not guarantee SLA for ALIAS record resolution.
When performing iterative resolution for ALIAS records, public authoritative DNS resolution uses the
ECSfield to pass the local DNS server’s source IP address to the recursive server. If the recursive server supports ECS, it can return smart resolution results.CDN providers may display an error saying “CNAME record not configured” after you set up an ALIAS record. Report this to the provider and ask them to update their validation logic.
The TTL for ALIAS record responses is based on the TTL configured for the ALIAS record itself, not the TTL of the external recursive resolution result.
How to set up
On the Alibaba Cloud DNS – Public Zone page, click the target domain name to go to the Settings page.
Click the Add Record button.
Fill in the form fields.
Form field
Description
Recommended value
Record Type
Different record types require different record values.
Select ALIAS from the drop-down list. This record type points a domain name to another domain name. Alibaba Cloud DNS automatically performs recursive resolution and returns the final IP address.
Hostname
Usually the prefix of a subdomain.
If the domain name is
www.example.com, enterwww.If the domain name is
example.com, enter@.If the domain name is
demo.example.com, enterdemo.If the domain name is
test.blog.example.com, entertest.blog.
Query Source
Specifies the source of DNS queries. Select Default unless you need to return different record values based on the user’s location. For example, use smart resolution lines such as carriers or regions outside China. For details, see Smart resolution and Custom resolution lines.
ImportantAlways set one record with the resolution line Default. This acts as a fallback to prevent resolution failures when no matching resolution line exists.
If you have no special requirements, keep Default.
For requests from Beijing and nearby cities, select
China_North.For requests from China Telecom, select
China Telecom.
TTL
The time that DNS resolvers cache the resolution result. We recommend setting TTL to 10 minutes. Smaller TTL values make changes take effect faster for end users. For more information, see How to configure TTL.
Edition
Free Edition
Personal Edition
Enterprise Ultimate Edition & Premium Edition
Minimum TTL value
600 seconds (10 minutes)
600 seconds (10 minutes)
1 second
Maximum TTL value
86400 seconds (24 hours)
86400 seconds (24 hours)
86400 seconds (24 hours)
Record Values Load Strategy
Only Ratio is supported. For configuration steps, see Configure weights.
Ratio
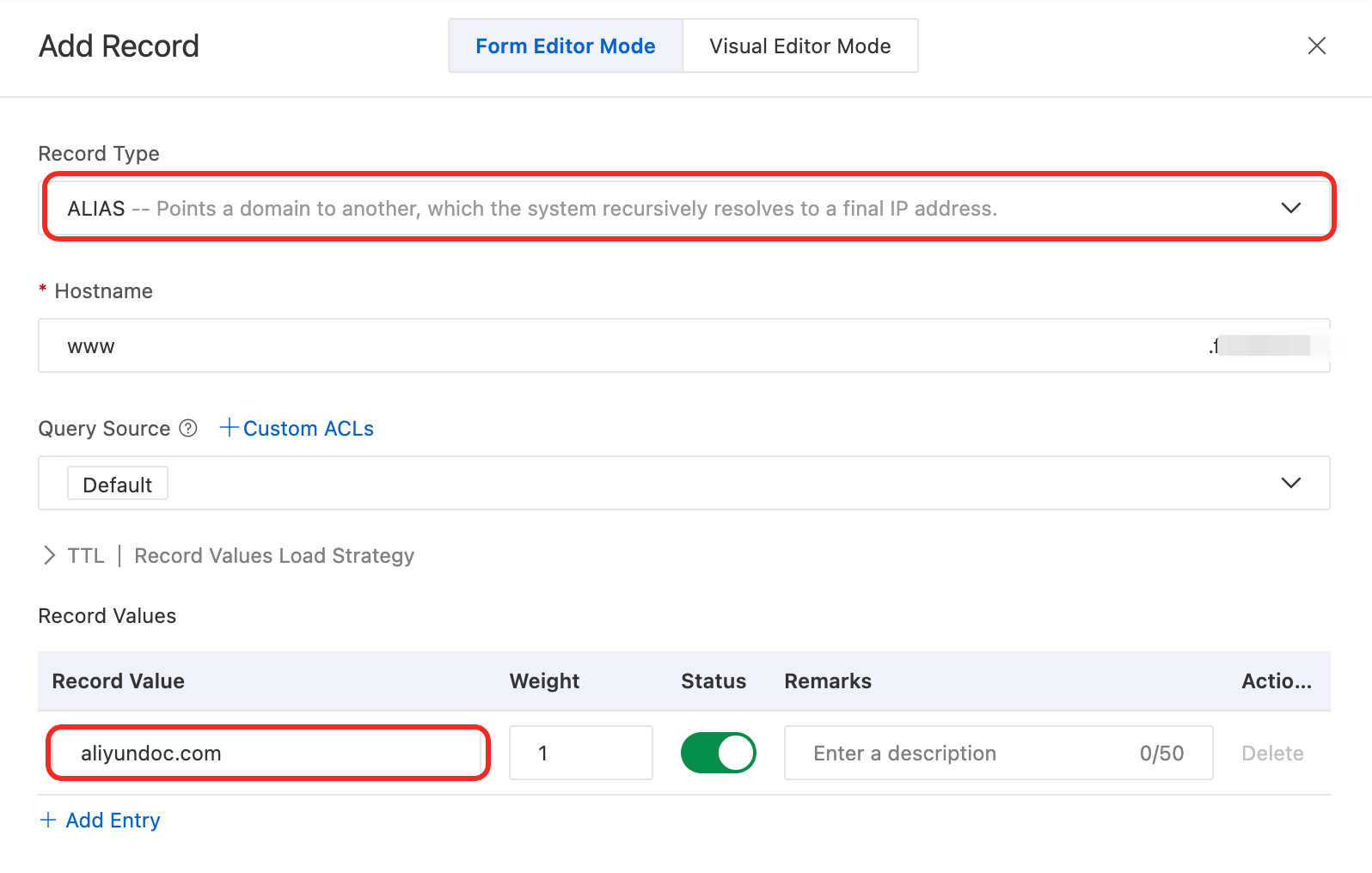
Record Values
The target domain name. You can add multiple domain names.
When Record Values Load Strategy is set to Ratio, set the Ratio next to each record value. When responding to queries, Alibaba Cloud DNS returns record values based on the preset weight ratio.
Example:
aliyundoc.com.Example
URL forwarding
URL forwarding includes Explicit URL Forwarding and Implicit URL. It points a domain name to an existing website. The process resolves the domain name to an Alibaba Cloud forwarding server, which then forwards traffic to the target site. Alibaba Cloud DNS automatically adds an A record pointing to the forwarding server address. So if you see an A record with IP address 203.107.XX.XX when running dig, this is normal.
Explicit URL Forwarding: Uses HTTP 301 (permanent redirect) or 302 (temporary redirect). The browser address bar shows the target URL, and the page content matches the target site.
Implicit URL forwarding: Implicit URL Forwarding forwarding uses iframe technology. The domain name in the browser's address bar remains unchanged, but the displayed content is from the target website.
URL forwarding does not guarantee SLA for resolution availability. For guaranteed stability, use self-hosted Nginx reverse proxy for HTTPS forwarding and port hiding.
Prerequisites
URL forwarding works by resolving the domain name to an Alibaba Cloud forwarding server, which then handles the forwarding. Alibaba Cloud forwarding servers are deployed in the Chinese mainland. Therefore, the domain name must complete ICP filing (filing does not need to be done through Alibaba Cloud). To file with Alibaba Cloud, see ICP filing process.
Limits
The record value cannot be an IP address.
The domain name before forwarding cannot contain underscores (_).
Wildcard resolution is not supported for URL forwarding.
The target domain name for URL forwarding cannot be a Chinese domain name.
The domain name before forwarding supports HTTP only, not HTTPS. The target URL supports both HTTP and HTTPS.
If the hostname is not
@, URL records conflict with NS, CNAME, A, or AAAA records when the hostname and resolution line are identical. If you receive a conflict error when adding a URL record, delete the conflicting record or change the hostname. For more information, see DNS record conflict rules.URL forwarding is a special feature. Alibaba Cloud DNS does not provide attack prevention. If your domain enters black hole mode because of attacks, URL forwarding will not work. In this case, configure the hostname as an A or CNAME record instead.
How to set up
On the Alibaba Cloud DNS – Public Zone page, click the target domain name to go to the Settings page.
Click the Add Record button.
Fill in the form fields.
Form field
Description
Recommended value
Record Type
Explicit URL Forwarding forwarding displays the target URL in the browser address bar and loads the target site’s content.
Implicit URL Forwarding forwarding means that when you access a domain name configured with Implicit URL Forwarding forwarding, the domain name in the browser address bar remains unchanged, but the displayed website content originates from the target website.
Select Explicit URL Forwarding or Implicit URL Forwarding from the drop-down list.
Hostname
The prefix of a subdomain.
If the domain name is
www.example.com, enterwww.If the domain name is
example.com, enter@.If the domain name is
demo.example.com, enterdemo.If the domain name is
test.blog.example.com, entertest.blog.
Query Source
Specifies the source of DNS queries. Select Default unless you need to return different record values based on the user’s location. For example, use smart resolution lines such as carriers or regions outside China. For details, see Smart resolution and Custom resolution lines.
ImportantAlways set one record with the resolution line Default. This acts as a fallback to prevent resolution failures when no matching resolution line exists.
If you have no special requirements, keep Default.
For requests from Beijing and nearby cities, select
China_North.For requests from China Telecom, select
China Telecom.
TTL
The time that DNS resolvers cache the resolution result. We recommend setting TTL to 10 minutes. Smaller TTL values make changes take effect faster for end users. For more information, see How to configure TTL.
Edition
Free Edition
Personal Edition
Enterprise Ultimate Edition & Premium Edition
Minimum TTL value
600 seconds (10 minutes)
600 seconds (10 minutes)
1 second
Maximum TTL value
86400 seconds (24 hours)
86400 seconds (24 hours)
86400 seconds (24 hours)
Record Values Load Strategy
Only Round Robin is supported.
Round Robin
Record Values
An existing website.
NoteFor Explicit URL Forwarding:
Supports
301permanent redirects and302temporary redirects.A 301 status indicates that the resource at the old address A has been permanently moved. Search engines crawl the new content and replace the old URL with the redirected URL.
A 302 status indicates that the resource at the old address A remains accessible. This redirect is temporary, moving from old address A to new address B. Search engines crawl the new content but retain the old URL.
Example:
www.aliyun.com.Example
Explicit URL Forwarding
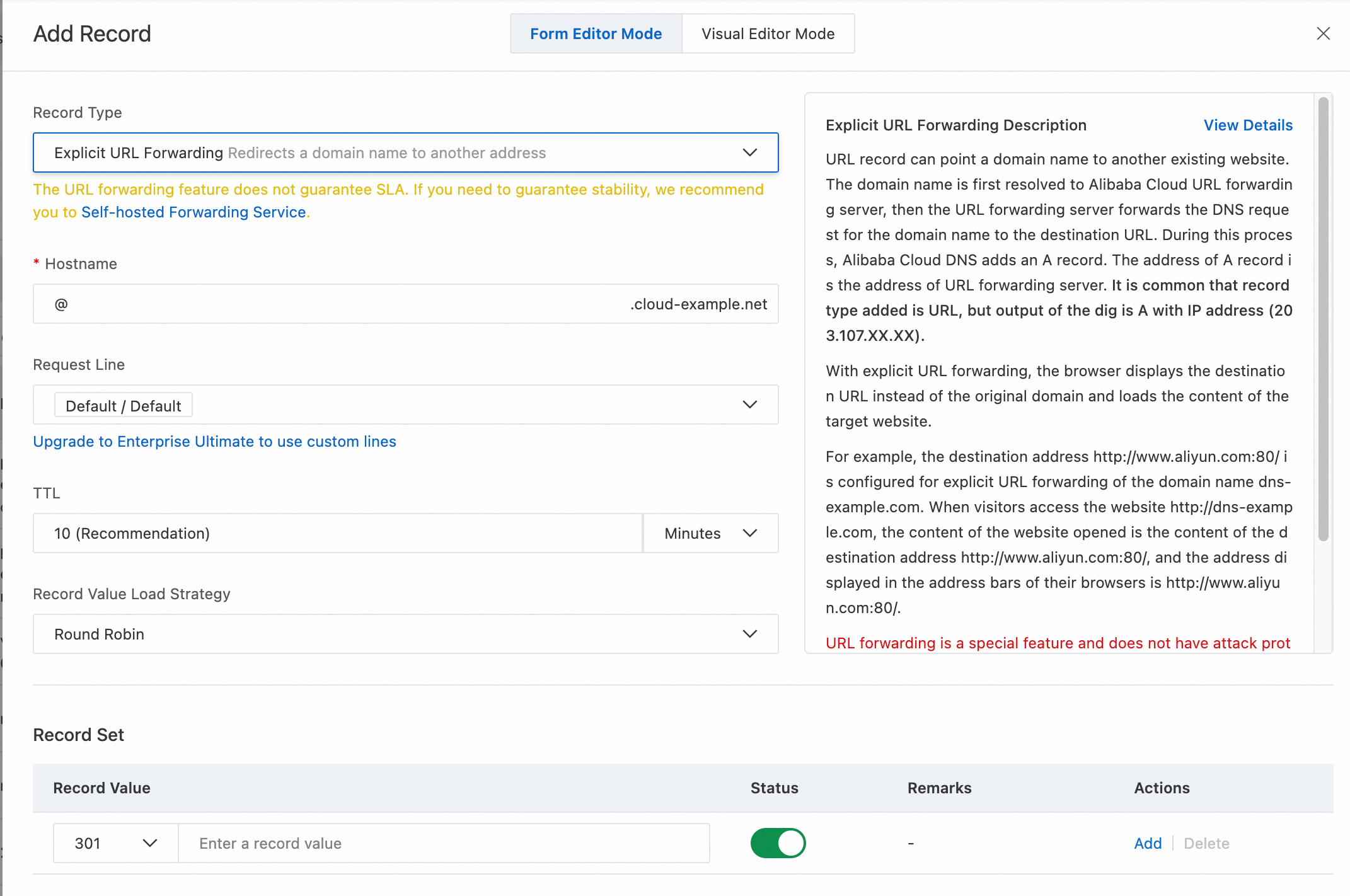
Implicit URL Forwarding

FAQ
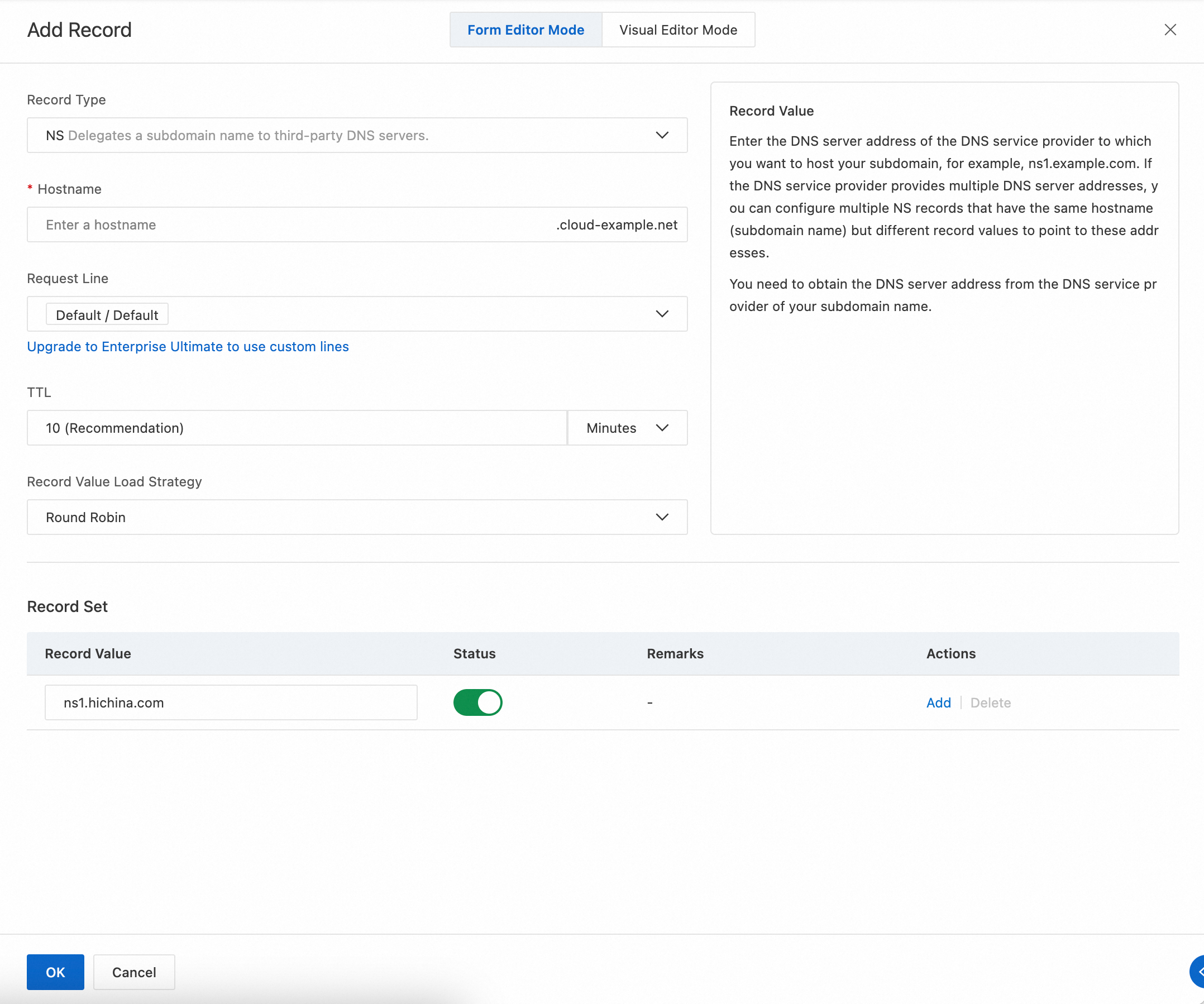
NS record
To delegate subdomain resolution to another DNS provider or to let subsidiaries, departments, or business units manage their own subdomains independently, add an NS record to the root domain. For subdomain delegation scenarios, see Subdomain management.
Limits
Root domain delegation is not supported (the hostname cannot be set to @). To delegate the root domain to another DNS provider, update the DNS server addresses directly at your domain registrar. For more information, see Modify domain name DNS servers.
If the hostname is not
@, NS records conflict with other record types when the hostname and resolution line are identical. If you receive a conflict error when adding an NS record, delete the conflicting record or change the hostname. For more information, see DNS record conflict rules.
How to set up
Add the subdomain to Alibaba Cloud DNS and obtain the DNS server addresses assigned to the subdomain. For steps, see Subdomain management.
Go to the authoritative DNS server for the root domain and modify the subdomain’s DNS records. For example, using Alibaba Cloud public authoritative DNS: Go to the Alibaba Cloud DNS – Public Zone page, click the target domain name to go to the Settings page.
Click the Add Record button.
Fill in the form fields.
Form field
Description
Recommended value
Record Type
To delegate subdomain resolution to another DNS provider, add an NS record.
Select NS from the drop-down list.
Hostname
Usually the prefix of a subdomain.
If the domain name is
www.example.com, enterwww.If the domain name is
example.com, enter@.If the domain name is
demo.example.com, enterdemo.If the domain name is
test.blog.example.com, entertest.blog.
Query Source
Specifies the source of DNS queries. Select Default unless you need to return different record values based on the user’s location. For example, use smart resolution lines such as carriers or regions outside China. For details, see Smart resolution and Custom resolution lines.
ImportantAlways set one record with the resolution line Default. This acts as a fallback to prevent resolution failures when no matching resolution line exists.
If you have no special requirements, keep Default.
For requests from Beijing and nearby cities, select
China_North.For requests from China Telecom, select
China Telecom.
TTL
The time that DNS resolvers cache the resolution result. We recommend setting TTL to 10 minutes. Smaller TTL values make changes take effect faster for end users. For more information, see How to configure TTL.
Edition
Free Edition
Personal Edition
Enterprise Ultimate Edition & Premium Edition
Minimum TTL value
600 seconds (10 minutes)
600 seconds (10 minutes)
1 second
Maximum TTL value
86400 seconds (24 hours)
86400 seconds (24 hours)
86400 seconds (24 hours)
Record Values Load Strategy
Only Round Robin is supported.
For A, AAAA, NS, MX, and TXT records, Alibaba Cloud DNS returns all records for the selected resolution line. The local DNS resolver selects the response. If the local DNS resolver returns all addresses, the end user selects randomly.
Round Robin
Record Values
The record value is the domain name of the DNS server you want to authorize.
NoteOther DNS providers usually provide multiple DNS server addresses. Configure multiple NS records with the same hostname but different record values.
Example: Tencent Cloud DNS server domain name
ns3.dnspod.net.Example
SRV record
An SRV record identifies which server hosts a specific service. It is commonly used in Microsoft directory management.
Limits
If the hostname is not
@, SRV records conflict with NS or CNAME records when the hostname and resolution line are identical. If you receive a conflict error when adding an SRV record, delete the conflicting record or change the hostname. For more information, see DNS record conflict rules.
How to set up
On the Alibaba Cloud DNS – Public Zone page, click the target domain name to go to the Settings page.
Click the Add Record button.
Fill in the form fields.
Form field
Description
Recommended value
Record Type
An SRV record identifies which server provides a specific service. It also provides the service’s address, port, priority, and weight.
Select SRV from the drop-down list. This option points the domain name to another domain name, which then provides the IP address.
Hostname
The hostname format for an SRV record is usually “service name.protocol type”.
Example: _sip._tcp
Query Source
Specifies the source of DNS queries. Select Default unless you need to return different record values based on the user’s location. For example, use smart resolution lines such as carriers or regions outside China. For details, see Smart resolution and Custom resolution lines.
ImportantAlways set one record with the resolution line Default. This acts as a fallback to prevent resolution failures when no matching resolution line exists.
If you have no special requirements, keep Default.
For requests from Beijing and nearby cities, select
China_North.For requests from China Telecom, select
China Telecom.
TTL
The time that DNS resolvers cache the resolution result. We recommend setting TTL to 10 minutes. Smaller TTL values make changes take effect faster for end users. For more information, see How to configure TTL.
Edition
Free Edition
Personal Edition
Enterprise Ultimate Edition & Premium Edition
Minimum TTL value
600 seconds (10 minutes)
600 seconds (10 minutes)
1 second
Maximum TTL value
86400 seconds (24 hours)
86400 seconds (24 hours)
86400 seconds (24 hours)
Record Values Load Strategy
Only Round Robin is supported.
Round Robin
Record Values
Format:
PriorityWeightPortTarget domainExample: 0 5 5060 www.cloud-example.com.
Example

CAA record
CAA (Certificate Authority Authorization) is an optional DNS record type. By creating CAA resource records, you specify which certification authorities (CAs) may issue certificates for your domain name. Unauthorized third parties attempting to obtain SSL/TLS certificates for your domain from other CAs will be rejected.
Setting a CAA record lets you authorize specific CAs to issue certificates for your domain. This prevents incorrect certificate issuance and improves website security.
Limits
If the hostname is not
@, CAA records conflict with NS or CNAME records when the hostname and resolution line are identical. If you receive a conflict error when adding a CAA record, delete the conflicting record or change the hostname. For more information, see DNS record conflict rules.
How to set up
On the Alibaba Cloud DNS – Public Zone page, click the target domain name to go to the Settings page.
Click the Add Record button.
Fill in the form fields.
Form field
Description
Recommended value
Record Type
CAA records let domain owners specify which certificate authorities (CAs) may issue SSL/TLS certificates for their domain. This prevents unauthorized third parties from obtaining certificates for the domain from other CAs, avoids incorrect certificate issuance, and improves website security.
Select CAA from the drop-down list.
Hostname
Usually the prefix of a subdomain.
If the domain name is
www.example.com, enterwww.If the domain name is
example.com, enter@.If the domain name is
demo.example.com, enterdemo.If the domain name is
test.blog.example.com, entertest.blog.
Query Source
Specifies the source of DNS queries. Select Default unless you need to return different record values based on the user’s location. For example, use smart resolution lines such as carriers or regions outside China. For details, see Smart resolution and Custom resolution lines.
ImportantAlways set one record with the resolution line Default. This acts as a fallback to prevent resolution failures when no matching resolution line exists.
If you have no special requirements, keep Default.
For requests from Beijing and nearby cities, select
China_North.For requests from China Telecom, select
China Telecom.
TTL
The time that DNS resolvers cache the resolution result. We recommend setting TTL to 10 minutes. Smaller TTL values make changes take effect faster for end users. For more information, see How to configure TTL.
Edition
Free Edition
Personal Edition
Enterprise Ultimate Edition & Premium Edition
Minimum TTL value
600 seconds (10 minutes)
600 seconds (10 minutes)
1 second
Maximum TTL value
86400 seconds (24 hours)
86400 seconds (24 hours)
86400 seconds (24 hours)
Record Values Load Strategy
Only Round Robin is supported.
Round Robin
Record Values
flag: Default is 0. If a CA does not recognize this record, it ignores it.
tag: Supports three values: issue, issuewild, and iodef.
issue: Authorizes a single CA to issue any type of certificate for the domain.
issuewild: Authorizes a single CA to issue wildcard certificates for the domain.
iodef: Sends violation reports to an email address.
value: Enter the CA’s domain name or an email address for violation notifications. Example: "ca.cloud-example.com". (Include double quotes.)
Example: 0 issue "ca.cloud-example.com"
Example

PTR record
Reverse DNS lookup: Maps an IP address to a domain name. Unlike forward DNS lookup (A or AAAA records), PTR records verify whether an IP address corresponds to a specific domain name.
How to set up:
Alibaba Cloud DNS provides a Reverse DNS Lookup feature that lets you configure PTR records for the public IP addresses (elastic IP addresses (EIPs) or ECS static public IP addresses) under your current Alibaba Cloud account. These records are used for reverse DNS lookups of the IP addresses. For more information, see What is reverse DNS lookup?
You can obtain public IP addresses that are not provided by Alibaba Cloud from an IDC data center or a hosting service provider.
SVCB record
An SVCB (Service Binding) record improves service discovery by providing clients with extra parameters about a service before connection. These include supported protocols and endpoint details. SVCB records work with various transport protocols and are closely related to HTTPS records.
SVCB records allow DNS to provide more flexible and detailed configuration information. Clients can make smarter decisions before connecting, improving performance, security, and user experience.
Limits
If the hostname is not @, SVCB records conflict with NS or CNAME records when the hostname and resolution line are identical. SVCB records also conflict between alias mode and service mode. If you receive a conflict error when adding an SVCB record, delete the conflicting record or change the hostname. For more information, see DNS record conflict rules.
How to set up
On the Alibaba Cloud DNS – Public Zone page, click the target domain name to go to the Settings page.
Click the Add Record button.
Fill in the form fields.
Form field
Description
Recommended value
Record Type
An SVCB record is a service binding record. It discloses supported protocols and Service Parameters for service discovery.
Select SVCB from the drop-down list.
Hostname
Usually the prefix of a subdomain.
If the domain name is
www.example.com, enterwww.If the domain name is
example.com, enter@.If the domain name is
demo.example.com, enterdemo.If the domain name is
test.blog.example.com, entertest.blog.
Query Source
Specifies the source of DNS queries. Select Default unless you need to return different record values based on the user’s location. For example, use smart resolution lines such as carriers or regions outside China. For details, see Smart resolution and Custom resolution lines.
ImportantAlways set one record with the resolution line Default. This acts as a fallback to prevent resolution failures when no matching resolution line exists.
If you have no special requirements, keep Default.
For requests from Beijing and nearby cities, select
China_North.For requests from China Telecom, select
China Telecom.
TTL
The time that DNS resolvers cache the resolution result. We recommend setting TTL to 10 minutes. Smaller TTL values make changes take effect faster for end users. For more information, see How to configure TTL.
Edition
Free Edition
Personal Edition
Enterprise Ultimate Edition & Premium Edition
Minimum TTL value
600 seconds (10 minutes)
600 seconds (10 minutes)
1 second
Maximum TTL value
86400 seconds (24 hours)
86400 seconds (24 hours)
86400 seconds (24 hours)
Record Values
Priority: A non-negative integer (0–65535) that specifies which SVCB record to try first. Lower numbers indicate higher priority. If a service has multiple SVCB records, clients sort them by priority and start with the highest priority (lowest number). Similar to the priority parameter in MX records for email.
NotePriority 0: Alias mode. Do not set Service Parameters. Similar to a CNAME record, it points to another service name.
Non-zero priority: Service mode. Define service parameters.
Destination Zone Name: The domain name of the server the client should connect to.
In alias mode (priority 0), the target domain is another service name the client should resolve.
In service mode, the target domain is usually the hostname of the actual service. The client resolves this domain to obtain the service’s IP address. Example:
www.example.com.
Service Parameters: Key-value pairs that define service configuration and required features. These include protocol versions, application-layer protocol lists (such as ALPN), transport layer security requirements (such as TLS version), transport parameters, and IP address hints.
Service Parameters give service providers a way to guide clients and provide pre-connection information to optimize performance and security. Example:
alpn="h2" ipv4hint="223.5.5.5" port="443" ech="MTIzNDU2Nzg="NoteCommon Service Parameters:
alpn="h3,h2": Supports HTTP/2 and HTTP/3.
ipv4hint="223.5.XX.XX": IPv4 address hint for the target domain.
ipv6hint="2400:3200::XX": IPv6 address hint for the target domain.
port="443": Port number.
ech="MTIzNDU2Nzg=": Base64-encoded ECH configuration string.
mandatory="alpn,port": List of required parameters.
no-default-alpn: No default application-layer protocol. If present, alpn must be specified.
dohpath="/dns-query{?dns}": URI template for DNS over HTTPS (DoH) access.
Separate key-value pairs with spaces. Maximum length is 1024 characters.
Example

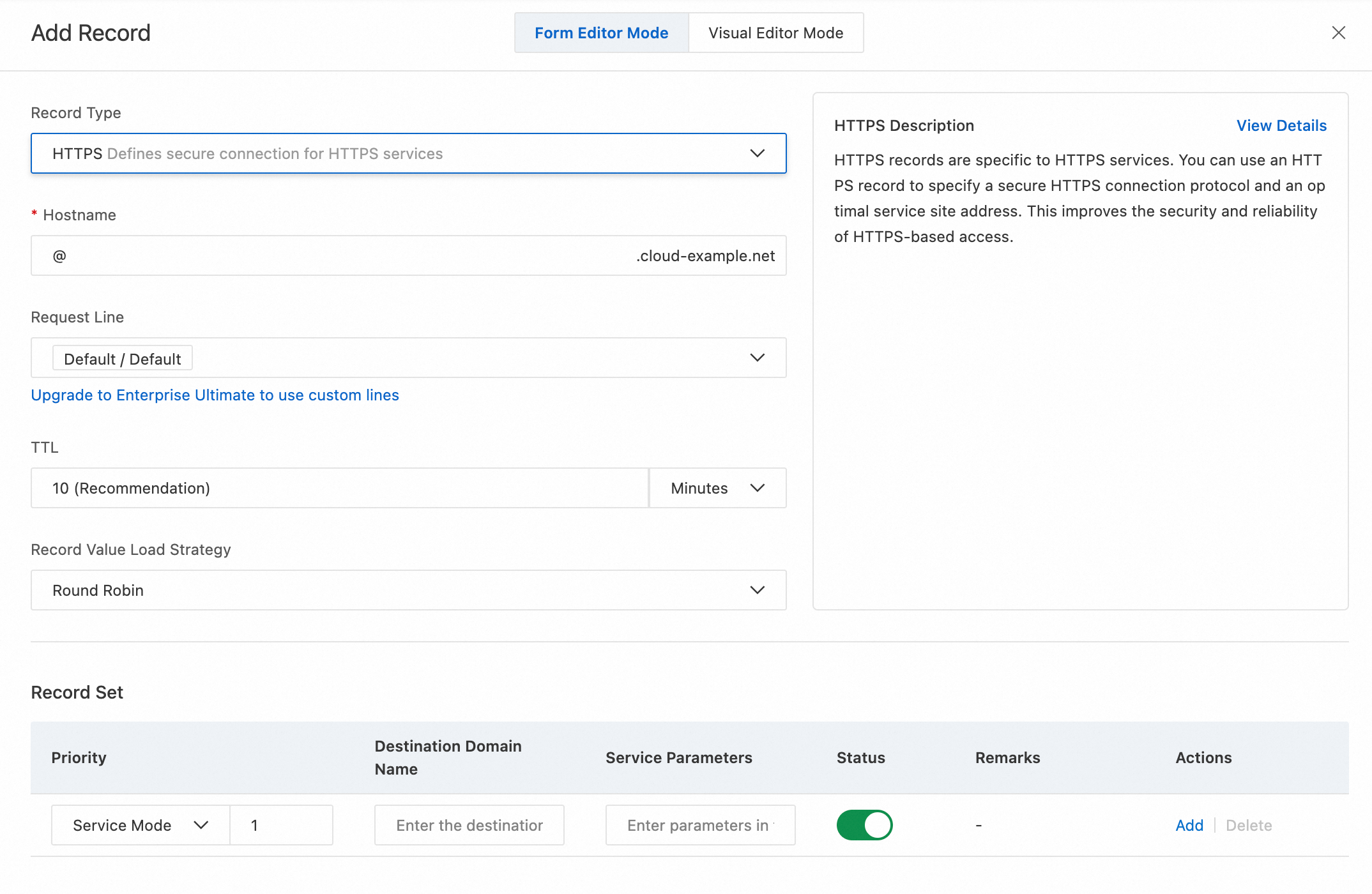
HTTPS record
An HTTPS record is a specialized SVCB record designed specifically for HTTPS services. HTTPS records support the same key-value parameters as SVCB records, but they are interpreted and processed assuming the service protocol is HTTPS.
HTTPS records let website operators provide more detailed information about their HTTPS service, including available IP addresses and supported protocols or service parameters. This ensures clients use the best configuration on first connection, reducing handshake latency, lowering connection failure rates, and enhancing user privacy.
Limits
If the hostname is not @, HTTPS records conflict with NS or CNAME records when the hostname and resolution line are identical. HTTPS records also conflict between alias mode and service mode. If you receive a conflict error when adding an HTTPS record, delete the conflicting record or change the hostname.
How to set up
On the Alibaba Cloud DNS – Public Zone page, click the target domain name to go to the Settings page.
Click the Add Record button.
Fill in the form fields.
Form field
Description
Recommended value
Record Type
An HTTPS record is a specialized DNS record for HTTPS services. It enables clients to negotiate secure HTTPS connection protocols and select optimal service endpoints, improving the security and reliability of HTTPS access.
Select HTTPS from the drop-down list.
Hostname
Usually the prefix of a subdomain.
If the domain name is
www.example.com, enterwww.If the domain name is
example.com, enter@.If the domain name is
demo.example.com, enterdemo.If the domain name is
test.blog.example.com, entertest.blog.
Query Source
Specifies the source of DNS queries. Select Default unless you need to return different record values based on the user’s location. For example, use smart resolution lines such as carriers or regions outside China. For details, see Smart resolution and Custom resolution lines.
ImportantAlways set one record with the resolution line Default. This acts as a fallback to prevent resolution failures when no matching resolution line exists.
If you have no special requirements, keep Default.
For requests from Beijing and nearby cities, select
China_North.For requests from China Telecom, select
China Telecom.
Record Values
Priority: A non-negative integer (0–65535) that specifies which HTTPS record to try first. Lower numbers indicate higher priority. If a service has multiple HTTPS records, clients sort them by priority and start with the highest priority (lowest number). This works similarly to the priority parameter in MX records for email.
NotePriority 0: Alias mode. Do not define service parameters. Like a CNAME record, it points to another service name.
Non-zero priority: Service mode. Define service parameters.
Destination Zone Name: The domain name of the server the client should connect to.
In alias mode (priority 0), the target domain is another service name the client should resolve.
In service mode, the target domain is usually the hostname of the actual service. The client resolves this domain to obtain the service’s IP address. Example:
www.example.com.Service Parameters: Key-value pairs that define service configuration and required features. These include protocol versions, application-layer protocol lists (such as ALPN), transport layer security requirements (such as TLS version), transport parameters, and IP address hints.
Service Parameters give service providers a way to guide clients and provide pre-connection information to optimize performance and security. Example:
alpn="h2,h3" ipv4hint="223.5.XX.XX" ipv6hint="2400:3200::XX" port="443"NoteExamples:
alpn="h3,h2": Supports HTTP/2 and HTTP/3.
ipv4hint="223.5.XX.XX": IPv4 address hint for the target domain.
ipv6hint="2400:3200::XX": IPv6 address hint for the target domain.
port="443": Port number.
mandatory="alpn,port": List of required parameters.
no-default-alpn: No default application-layer protocol. If present, alpn must be specified.
dohpath="/dns-query{?dns}": URI template for DNS over HTTPS (DoH) access.
Separate key-value pairs with spaces. Maximum length is 1024 characters.
Example:
aliyundoc.com.TTL
The time that DNS resolvers cache the resolution result. We recommend setting TTL to 10 minutes. Smaller TTL values make changes take effect faster for end users. For more information, see How to configure TTL.
Edition
Free Edition
Personal Edition
Enterprise Ultimate Edition & Premium Edition
Minimum TTL value
600 seconds (10 minutes)
600 seconds (10 minutes)
1 second
Maximum TTL value
86400 seconds (24 hours)
86400 seconds (24 hours)
86400 seconds (24 hours)
Example
Verify effects
You can learn how TTL works. Confirm the configuration after DNS resolution takes effect.
In addition to accessing the URL directly, use DNS resolution testing methods to verify. If resolution fails, see Quick troubleshooting for failed DNS resolution.
References
If you receive a conflict error when adding a record, you can learn about DNS record conflict rules.
To add a wildcard DNS record with hostname *, you can learn about Wildcard DNS resolution.
If you encounter issues during setup, see these documents: