Add a subdomain to Public Zone. Then configure and manage the subdomain and its DNS records independently. This provides flexible, efficient, and isolated control. Use this feature when your business requires subdomain autonomy, delegated permissions, or decoupling across teams.
Subdomain delegation
By default, the entire primary domain (such as example.com) uses one set of NS servers for DNS resolution. However, the DNS standard lets you assign a separate set of NS records to a subdomain. This is called subdomain delegation. For example, abc.example.com can use a different set of NS servers than its parent domain. Its control and DNS rules become fully independent. If you are not familiar with primary domains and subdomains, read the domain hierarchy.
Scenarios
Distributed business isolation and O&M autonomy
-
SaaS providers, multi-line-of-business enterprises, and conglomerates often have separate O&M teams for each business. Each team can manage DNS for
product.example.comwithout affecting the primary domain or other subdomains. -
You can manage DNS resources for the staging environment
test-env.example.comseparately. This prevents accidental changes from affecting production in the primary domain.
Decoupling across clouds, data centers, or CDN platforms
-
Government, enterprise, and finance customers often run their own DNS servers. However, building and maintaining them is expensive. You can delegate a subdomain to Alibaba Cloud DNS for standalone management.
-
Your primary domain uses a third-party DNS provider. You cannot migrate all DNS records to Alibaba Cloud DNS immediately. Instead, start by migrating only the subdomain to Alibaba Cloud DNS.
Feature details
|
Type |
Details |
|
Instance version limits |
If the primary domain uses a third-party DNS provider and the subdomain uses Alibaba Cloud DNS, you can bind the subdomain to the paid edition of Alibaba Cloud DNS. To use security protection features, enable them separately. |
|
If both the primary domain and subdomain use Alibaba Cloud DNS, they must use the same edition—either both Free Edition or both paid edition. The edition refers only to Free Edition versus paid edition. Paid editions do not restrict specific versions. |
|
|
Inter-account domain name transfer |
Transferring the primary domain moves only its DNS records to the new account. Subdomains remain unaffected. |
|
DNS provider or account limits |
A primary domain and its subdomain can use different DNS providers. They can also belong to different Alibaba Cloud accounts—or the same Alibaba Cloud account. |
|
Subdomain level limits for primary and subdomains |
Free Edition: Supports up to 5 levels. For example, if your subdomain is Paid Edition: Supports up to 10 levels. |
Add a subdomain

Primary domain uses a third-party DNS provider. Subdomain uses Alibaba Cloud DNS.
-
Go to the Alibaba Cloud DNS – Public Authoritative DNS page. Click Add Zone.
-
In the Add Zone dialog box, enter the subdomain—for example,
demo.example.com. Click Verify TXT Record.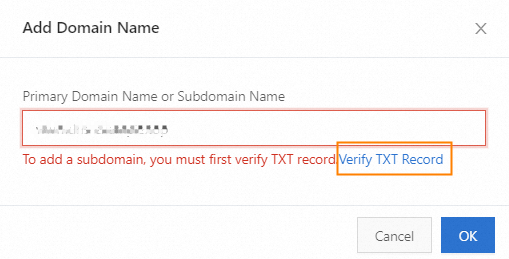
-
In the domain registrant verification dialog box, copy the host record and record value.

-
Go to your third-party DNS provider. On the primary domain’s DNS settings page, add a TXT record using the host record and record value from the domain registrant verification step.
-
Return to the dialog box from step 3. Click Verify. The TXT verification passes.
ImportantRegistrant identity verification lets you copy the Hostname and Record Value. Before you click the Verify button, you can close this dialog box. The Record Value for TXT record validation is valid for 1 day. If you click Verify, you can perform validation up to three times. If all three attempts fail, the TXT record value is reset. After you add the TXT record to the root domain, click the Verify button to perform TXT validation.
-
The subdomain appears in the DNS record list. View the DNS Server IP Address for the subdomain. This is the DNS address that Alibaba Cloud DNS assigned to it.

-
(Optional) Skip this step if the subdomain has no active DNS records. If the subdomain already has active DNS records, add them again in Alibaba Cloud DNS before continuing.
-
Go to your third-party DNS provider. On the primary domain’s DNS settings page, add an NS record for the subdomain. Point it to the DNS server addresses that Alibaba Cloud DNS assigned to the subdomain. For example, if your subdomain is
test.example.com:Host record
Record type
Record value
testNS
ns1.alidns.com
testNS
ns2.alidns.com
Both primary domain and subdomain use Alibaba Cloud DNS.
The primary domain and subdomain can belong to different Alibaba Cloud accounts—or the same Alibaba Cloud account.
-
Go to the Alibaba Cloud DNS – Public Authoritative DNS page. Click Add Zone.
-
In the Add Zone dialog box, enter the subdomain. Click Verify TXT Record.
-
In the Registrant Verification dialog box, copy the Hostname and Record Value.
ImportantRegistrant identity verification lets you copy the Hostname and Record Value. Before you click the Verify button, you can close this dialog box. The Record Value for TXT record validation is valid for 1 day. If you click Verify, you can perform validation up to three times. If all three attempts fail, the TXT record value is reset. After you add the TXT record to the root domain, click the Verify button to perform TXT validation.
-
Log in to the Alibaba Cloud account that owns the primary domain. Go to the DNS settings page. Add a TXT record using the Hostname and Record Value from the domain registrant verification step.
-
After the TXT record takes effect, return to the Registrant Verification dialog box from step 3. Click Verify.
-
After the TXT verification passes, add the subdomain. The subdomain appears automatically in the DNS record list. Click the subdomain to open its DNS settings page. Alibaba Cloud DNS automatically syncs DNS records for the subdomain from the primary domain. For full sync rules, see Sync rules for DNS records when both primary and subdomains use Alibaba Cloud DNS.
-
The subdomain appears in the DNS record list. View the DNS Server IP Address for the subdomain. This is the DNS address that Alibaba Cloud DNS assigned to it.

-
If the primary domain has DNS records for the subdomain, those records stop working after you delegate the subdomain. Delete them from the primary domain. Then configure DNS records on the subdomain’s DNS settings page. Skip this step if the primary domain has no subdomain records.
ImportantThe primary domain and subdomain must use the same edition of Alibaba Cloud DNS. For example, if the primary domain uses the paid edition, the subdomain must also use the paid edition. If the primary domain uses the paid edition, first bind the subdomain to the paid edition. Then add the NS records on the primary domain.
Recover a subdomain
If another Alibaba Cloud account added your subdomain as a managed subdomain, use the Retrieve Zone feature to move management rights and DNS records back to your current account.
-
Go to the Alibaba Cloud DNS – Public Authoritative DNS page. Click Add Zone.
-
In the Add Zone dialog box, enter the subdomain. Click Retrieve Zone.
-
In the Registrant Verification dialog box, copy the Hostname and Record Value.
ImportantRegistrant identity verification lets you copy the Hostname and Record Value. Before you click the Verify button, you can close this dialog box. The Record Value for TXT record validation is valid for 1 day. If you click Verify, you can perform validation up to three times. If all three attempts fail, the TXT record value is reset. After you add the TXT record to the root domain, click the Verify button to perform TXT validation.
-
After domain registrant verification passes, the subdomain and its DNS records appear automatically in your account.
Delete a subdomain
If you no longer need to manage a subdomain separately, delete it. All DNS records under the subdomain are deleted permanently.
Before you unregister, delete, or transfer a domain—especially one registered with Alibaba Cloud and managed by Alibaba Cloud DNS—change its DNS servers (NS records) to a non-Alibaba Cloud provider. Otherwise, after deletion or release, someone else might register the domain and add it directly to Alibaba Cloud DNS. This creates risks such as abuse, impersonation, or phishing.
-
Go to the Alibaba Cloud DNS – Public Authoritative DNS page. In the Actions column, click Delete.

Appendix
Sync rules for DNS records when both primary and subdomains use Alibaba Cloud DNS
After you add a subdomain, any DNS records for that subdomain on the primary domain are synced automatically. Records added to the primary domain after you add the subdomain are not synced. Full rules follow.
Example 1: No wildcard DNS
The primary domain is a.com. You want to manage c.b.a.com independently. When the primary domain has these DNS records:
|
Record type |
Host record |
Routing line |
Record value |
|
A |
c.b |
Default |
1.1.XX.XX |
The synced DNS records for subdomain c.b.a.com are:
|
Record type |
Host record |
Parse Line |
Record value |
|
A |
@ |
Default |
1.1.XX.XX |
Example 2: Wildcard DNS – 1
The primary domain is a.com. You want to manage c.b.a.com independently. When the primary domain has these DNS records:
|
Record type |
Host record |
Routing line |
Record value |
|
A |
d.c.b |
Default |
1.1.XX.XX |
|
A |
*.c.b |
Default |
2.2.XX.XX |
The synced DNS records for subdomain c.b.a.com are:
|
Record type |
Host record |
Routing line |
Record value |
|
A |
d |
Default |
1.1.XX.XX |
|
A |
* |
Default |
2.2.XX.XX |
Example 3: Wildcard DNS – 2
The primary domain is a.com. You want to manage c.b.a.com independently. When the primary domain has these DNS records:
|
Record type |
Host record |
Routing line |
Record value |
|
A |
*.b |
Default |
1.1.XX.XX |
The synced DNS records for subdomain c.b.a.com are:
|
Record type |
Host record |
Parsing Lines |
Record value |
|
A |
* |
Default |
1.1.XX.XX |
|
A |
@ |
Default |
1.1.XX.XX |
Example 4: Wildcard DNS – 3
The primary domain is a.com. You want to manage c.b.a.com independently. When the primary domain has these DNS records:
|
Record type |
Host record |
Line Parsing |
Record value |
|
A |
*.b |
Default |
1.1.XX.XX |
|
A |
* |
Default |
2.2.XX.XX |
The synced DNS records for subdomain c.b.a.com are:
|
Record type |
Host record |
Routing line |
Record value |
|
A |
* |
Default |
1.1.XX.XX |
|
A |
@ |
Default |
1.1.XX.XX |
The @ record follows the longest-match rule. After syncing, the effective record for the subdomain comes from the primary domain’s *.b record.