Data Disaster Recovery allows you to restore terabytes of data within 10 seconds based on technologies such as database physical backup and snapshot mounting. Data Disaster Recovery can provide read and write capabilities and meet the requirements of data restoration for incorrect operations, restoration rehearsals, emergency disaster recovery, DevOps, and data analysis.
Prerequisites
An Oracle database is backed up by using Data Disaster Recovery. For more information, see Back up an Oracle instance. When the Oracle database is backed up, the Backup Storage Type parameter is set to DBS built-in storage. For more information about how to select storage types, see Built-in storage and OSS.
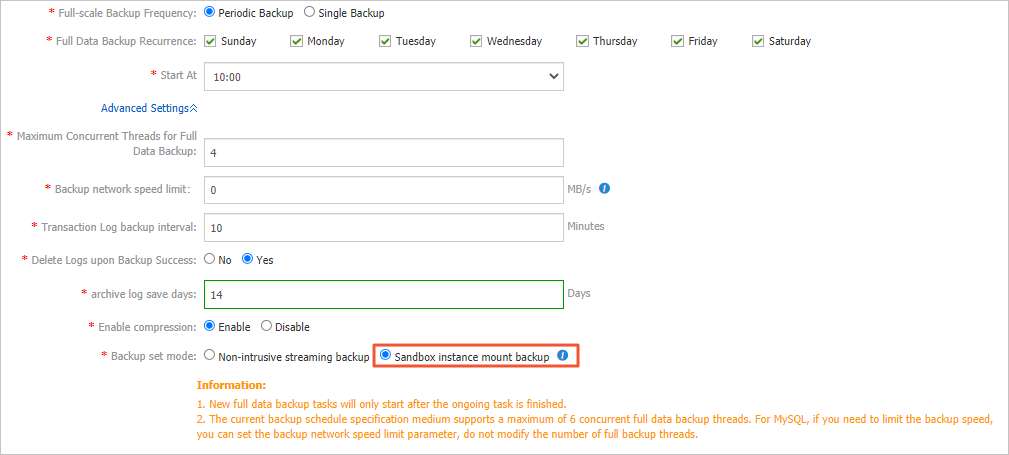
When the Oracle database is backed up, the Backup set mode parameter is set to Sandbox instance mount backup. For more information, see Set the backup set mode to Sandbox instance mount backup of this topic.
The FUSE module is installed on the server where the destination database resides.
The destination database is a self-managed database that is hosted on an Elastic Compute Service (ECS) instance.
NoteThe ECS instance resides in a virtual private cloud (VPC). For more information about how to create a VPC, see Create and manage a VPC.
Precautions
You can switch between the two backup set modes that are supported by Data Disaster Recovery. After you switch the backup set mode, Data Disaster Recovery creates a full backup task and an incremental backup task, and a gap occurs in the time range available to restore backup sets. We recommend that you do not change the backup set mode frequently.
Set the backup set mode to Sandbox instance mount backup
Data Disaster Recovery supports the following backup set modes for backing up an Oracle database:
Non-intrusive streaming backup: uses the Oracle System Backup to Tape (SBT) interface to back up data. Backed up data is stored as backup sets on a virtual tape before the data is streamed to the cloud. This method uses less storage space and does not negatively impact the source database.
Sandbox instance mount backup: uses mount points to back up data. This method negatively impacts the destination environment. Make sure that the FUSE module is installed on the server where the destination database resides. If the Oracle database you want to restore was backed up by using the Sandbox instance mount backup mode, you can skip this step.
If the Oracle database you want to restore was backed up by using the Non-intrusive streaming backup mode, perform the following operations to switch the backup set mode to Sandbox instance mount backup:
Log on to the DMS console V5.0.
In the top navigation bar, choose .
NoteIf you use the DMS console in simple mode, move the pointer over the
 icon in the upper-left corner of the DMS console and choose .
icon in the upper-left corner of the DMS console and choose . On the Backup Schedules page, find the backup schedule that you want to manage and click Manage in the Actions column.
On the Configure Task page, click Backup Time and Advanced Settings in the upper-right corner of the Basic Information section.
On the Edit Backup Source page, set Backup set mode to Sandbox instance mount backup and click Save.
Enable second-level restoration
Log on to the DMS console V5.0.
In the top navigation bar, choose .
NoteIf you use the DMS console in simple mode, move the pointer over the
 icon in the upper-left corner of the DMS console and choose .
icon in the upper-left corner of the DMS console and choose . On the Backup Schedules page, find the backup schedule that you want to use and click Manage in the Actions column.
On the Configure Task page, click Set up second level recovery in the upper-right corner of the Task Running Information section.
In the Set up second level recovery dialog box, set Second level recovery to Enable and click OK.
NoteAfter you enable second-level restoration, the value of the Second recovery time range parameter is Data preparing. Wait until the value changes to a time range available to restore backup sets.
Start a second-level restoration task
Log on to the DMS console V5.0.
In the top navigation bar, choose .
NoteIf you use the DMS console in simple mode, move the pointer over the
 icon in the upper-left corner of the DMS console and choose .
icon in the upper-left corner of the DMS console and choose . On the Backup Schedules page, find the backup schedule that you want to manage and click Manage in the Actions column.
On the Configure Task page, click Second level recovery database in the upper-right corner.
On the Create second level recovery task page, set the parameters as described in the following table.
Section
Parameter
Description
N/A
Task Name
The name of the task. Data Disaster Recovery automatically generates a task name. We recommend that you specify a descriptive name for easy identification. You do not need to specify a unique task name.
Set Time Restored To
Time Range Available to Restore
The time range that is available to restore the backup data. Data Disaster Recovery displays the available time range.
Restore To
The point in time to which you want to restore the backup data. The value must be within the time range that is specified by the Time Range Available to Restore parameter.
Second level recovery information settings
Instance Region
The region where the destination database resides.
Peer VPC
The ID of the VPC where the backup gateway of the destination database resides.
Peer vSwitch
The vSwitch that is connected to the backup gateway of the destination database.
Backup Gateway
The backup gateway that is installed to back up data. To avoid restoring a database to the production environment, you cannot restore data to the same server where the backup data is stored. Therefore, you cannot install the backup gateway to restore data on the same server where the backup gateway to back up data is installed.
Address
The endpoint used to connect to the destination database. Default value:
localhost.Port Number
The port number used to connect to the destination database. Default value:
1521.SID
The system identifier (SID) of the destination database.
Database program directory
The program directory of the database that you want to restore. In this example, set this parameter to the absolute path that is specified by the ORACLE_HOME variable.
Click Recover immediately.
NoteTo view the task ID and task running information about the second-level restoration task you created, click Second level recovery task in the left-side navigation pane.