You must synchronize raw data to MaxCompute during data preparation.
Prerequisites
A MaxCompute data source is added. For more information, see Add a MaxCompute data source.
Prepare a data source
Create an ApsaraDB RDS for MySQL instance in the ApsaraDB RDS console and record the instance ID. For more information, see Step 1: Create an ApsaraDB RDS for MySQL instance and configure databases.
Configure a whitelist for the ApsaraDB RDS for MySQL instance in the ApsaraDB RDS console.
NoteWhen you use a serverless resource group to run a data synchronization task, take note of the following items:
If you want to access a data source over a VPC, you must add the CIDR block of the vSwitch with which the resource group is associated to the IP address whitelist of the data source.
If you want to access the data source over the Internet, you must add the EIP configured for the VPC with which the serverless resource group is associated to the IP address whitelist of the data source. If you use an old-version resource group, add the EIP of the resource group to the IP address whitelist.
For more information, see Network connectivity solutions.
Download the raw data required in this tutorial: indicators_data, steal_flag_data, and trend_data.
Upload the raw data to the ApsaraDB RDS for MySQL instance. For more information, see Import data from an Excel file to ApsaraDB RDS for MySQL.
Add a data source
In this example, you must add an ApsaraDB RDS for MySQL data source.
Go to the Management Center page.
Log on to the DataWorks console. In the top navigation bar, select the desired region. In the left-side navigation pane, choose . On the page that appears, select the desired workspace from the drop-down list and click Go to Management Center.
Add a MySQL data source.
In the left-side navigation pane, choose to go to the Data Sources page.
In the upper-left corner of the Data Sources page, click Add Data Source. In the Add Data Source dialog box, click MySQL.
Configure information about the MySQL data source.
On the Add MySQL Data Source page, configure the parameters. In this example, set the Configuration Mode parameter to Alibaba Cloud Instance Mode.
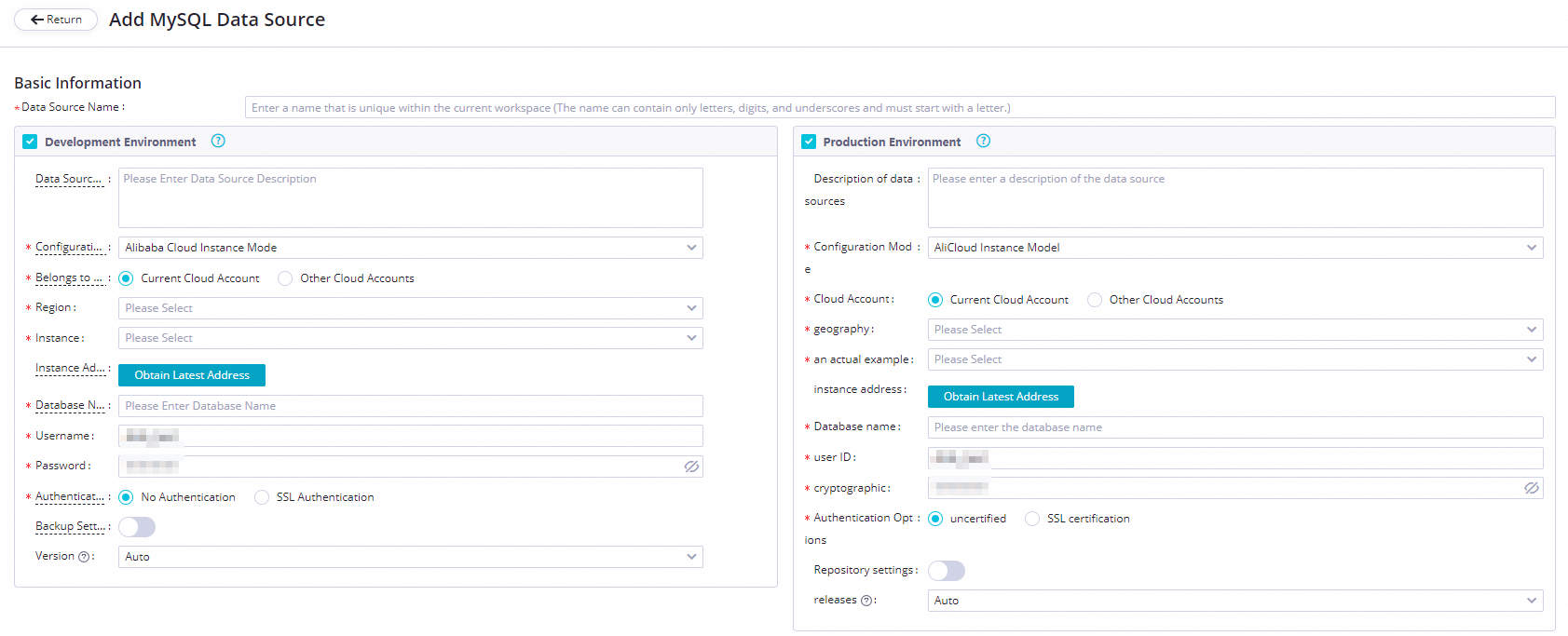
The following table describes the parameters.
Parameter
Description
Applicable environment
The environment in which the data source is used. Valid values: Development Environment and Production Environment.
Configuration Mode
The mode in which you want to add the data source. Select Alibaba Cloud Instance Mode.
Belongs to Cloud Account
Select Current Cloud Account.
Region
The region in which the data source resides.
Instance
Select the ApsaraDB RDS for MySQL instance that you create. After you select the instance, you can click Obtain Latest Address to view the information about the instance.
If no instance is available, you can create an instance in the ApsaraDB RDS console.
Database Name, Username, and Password
The name of the default ApsaraDB RDS for MySQL database, and the username and password that are used to log on to the database. Do not use at signs (@) in the password.
The following descriptions provide instructions for you to configure a synchronization task that uses a MySQL data source:
When you configure a database-level real-time or batch synchronization task that uses a MySQL data source, you can select one or more databases on which you have access permissions in the ApsaraDB RDS for MySQL instance.
If you select multiple databases when you configure a batch synchronization task, you must add a data source for each database.
Authentication Options
Select No Authentication.
Backup Settings
If the ApsaraDB RDS for MySQL instance is a primary instance and has a secondary read-only instance, you can turn on Backup Settings, and select the ID of the secondary instance. This prevents the primary instance from being affected and ensures the performance of the primary instance. If the primary instance has multiple secondary read-only instances, only the data of one of the read-only instances is read.
NoteIf you turn on Backup Settings, you can use only an exclusive resource group to run the task that uses the data source.
Test network connectivity between the data source and resource groups that you select.
Separately click Data Integration and Data Scheduling in the Connection Configuration section, find the resource group for Data Integration and the resource group for scheduling that you want to use, and then click Test Network Connectivity in the Connection Status column. If the connectivity status is Connected, the resource groups are connected to the data source.
NoteA synchronization task can use only one resource group of a specific type.
To ensure that your synchronization task can be run as expected, you must test network connectivity between the data source and all types of resource groups on which your synchronization task will be run.
If the data source passes the network connectivity test, click Complete Creation.
Create a workflow
In the upper-left corner of the SettingCenter page, click the
 icon and choose .
icon and choose . On the page that appears, right-click Business Flow and select Create Workflow.
In the Create Workflow dialog box, configure Workflow Name and Description.
NoteThe workflow name cannot exceed 128 characters in length and can contain only letters, digits, underscores (_), and periods (.).
Click Create.
On the workflow configuration tab that appears, drag one zero load node and three offline synchronization nodes to the canvas, name the zero load node start, configure the related settings for the nodes, and click Submit. The offline synchronization nodes are used to synchronize electricity usage trend data, electricity-stealing flag data, and metric data.
Draw lines between nodes and configure the start node as the ancestor node of the three offline synchronization nodes.
Configure the start node
Double-click the start node. In the right-side navigation pane of the configuration tab of the start node, click the Properties tab.
Configure the root node of the workspace as the ancestor node of the start node.
In the latest version of DataWorks, each node must have its ancestor and descendant nodes. Therefore, you must specify an ancestor node for the start node. In this example, the root node of the workspace is specified as the ancestor node of the start node. The root node of the workspace is named in the Workspace name_root format.
After the configuration is complete, click the
 icon in the upper-left corner.
icon in the upper-left corner.
Create tables
Right-click the created workflow and choose .
In the Create Table dialog box, configure the Engine Instance, Path, and Name parameters and click Create.
Create three tables named trend_data, indicators_data, and steal_flag_data. The trend_data table is used to store electricity usage trend data, the indicators_data table is used to store metric data, and the steal_flag_data table is used to store electricity-stealing flag data.
NoteThe table name cannot exceed 64 characters in length. The table name must start with a letter and cannot contain special characters.
On the configuration tab of each table, click DDL and enter the following CREATE TABLE statements:
-- Create a table to store electricity usage trend data. CREATE TABLE trend_data ( uid BIGINT, trend BIGINT ) PARTITIONED BY (dt string);-- Create a table to store metric data. CREATE TABLE indicators_data ( uid BIGINT, xiansun BIGINT, warnindicator BIGINT ) COMMENT '*' PARTITIONED BY (ds string) LIFECYCLE 36000;-- Create a table to store electricity-stealing flag data. CREATE TABLE steal_flag_data ( uid BIGINT, flag BIGINT ) COMMENT '*' PARTITIONED BY (ds string) LIFECYCLE 36000;After you enter the CREATE TABLE statements, click Generate Table Schema. Then, click OK.
On the configuration tab of each table, enter the display name in the General section.
After the configuration is complete, click Commit to Development Environment and Commit to Production Environment in sequence.
Configure the offline synchronization nodes
Configure the node to synchronize electricity usage trend data.
Double-click the node to go to the node configuration tab.
Configure a source.
Parameter
Description
Connection
Select in sequence.
Table
Select the trending table from which data is to be synchronized.
Filter
The condition used to filter the data that you want to synchronize. Filtering based on the LIMIT keyword is not supported. The SQL syntax is determined based on the selected data source. This parameter is optional.
Shard Key
If you configure this parameter, data sharding is performed based on the value of this parameter, and parallel threads can be used to read data. This improves data synchronization efficiency. This parameter is optional.
Configure a destination.
Parameter
Description
Connection
Select ODPS and then the MaxCompute data source that you add.
Table
Select the trend_data table to store the source data.
Partition Key Column
Enter the partition key column to be synchronized. Default value:
dt=${bdp.system.bizdate}.Writing Rule
Select Write with Original Data Deleted (Insert Overwrite).
Convert Empty Strings to Null
Select No.
Configure the mappings between fields in the source and destination.
Configure parameters in the Channel section.
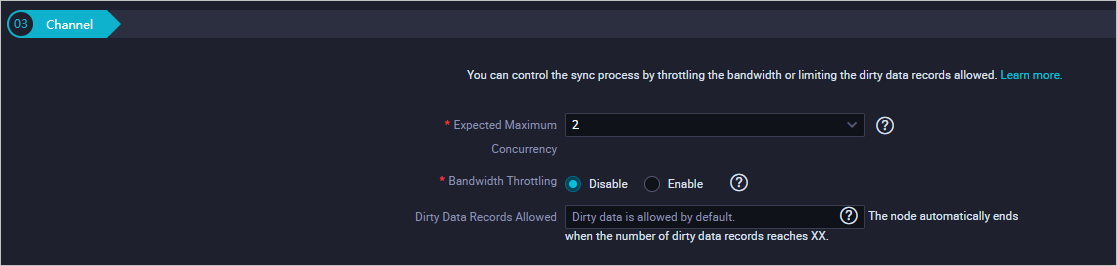
Parameter
Description
Expected Maximum Concurrency
The maximum number of parallel threads that the synchronization node can use to read data from the source or write data to the destination. You can configure the parallelism for the data synchronization node on the codeless UI.
Bandwidth Throttling
Specifies whether to enable throttling. You can enable throttling and specify a maximum transmission rate to prevent heavy read workloads on the source. We recommend that you enable bandwidth throttling and set the maximum transmission rate to an appropriate value based on the configurations of the source.
Dirty Data Records Allowed
The maximum number of dirty data records allowed.
Verify that the preceding configurations are correct and click the
 icon in the upper-left corner.
icon in the upper-left corner.
Commit a workflow
Go to the workflow configuration tab and click the
 icon in the upper-left corner.
icon in the upper-left corner. In the Commit dialog box, select the nodes to be committed, enter your comments in the Change description field, and then select Ignore I/O Inconsistency Alerts.
Click Commit. The Committed successfully message appears.
Check whether data is synchronized to MaxCompute
In the left-side navigation pane, click Ad-Hoc Query. The Ad-Hoc Query pane appears.
In the Ad-Hoc Query pane, right-click Ad-Hoc Query and choose .
Write and execute SQL statements to query the number of data records synchronized to the trend_data, indicators_data, and steal_flag_data tables.
Execute the following SQL statements. In each statement, change the partition key value to the data timestamp of the node. For example, if the scheduling time of the node is August 9, 2019, the data timestamp is 20190808, which is one day before the node is run.
-- Check whether the data is written to MaxCompute. SELECT COUNT(*) FROM trend_data WHERE dt=Data timestamp of the ad hoc query node; SELECT COUNT(*) FROM indicators_data WHERE ds==Data timestamp of the ad hoc query node; SELECT COUNT(*) FROM steal_flag_data WHERE ds=Data timestamp of the ad hoc query node;
Additional information
You understand how to collect and synchronize data. You can now proceed with the next tutorial. The next tutorial describes how to compute and analyze collected data.