In DataWorks, you can create various types of database nodes to develop SQL tasks, schedule them to run periodically, and integrate them with other jobs.
Prerequisites
A RAM user is added to the workspace (optional).
The RAM user you use for task development must be added to the workspace and granted the Developer or Workspace Administrator role. The Workspace Administrator role grants extensive permissions, so assign it with caution. For more information about adding members and granting permissions, see Add members to a workspace.
A DataWorks data source is created.
Ensure that the serverless resource group for the data source has network connectivity. For more information, see Network connectivity solutions.
Ensure that the data source is created using a JDBC connection string. For more information, see Data Source Management.
Ensure that the data source supports creating database nodes. For more information, see Supported data sources.
You must create a database node before you can develop it. For more information, see Create a node for a scheduled workflow.
Step 1: Develop the database node
After you create a database node, you can start developing it.
Select a data source.
In the Select Data Source drop-down list, click
 to open the dialog box. In the dialog box, select the data source that you want to use for task development. If the data source you need is not available, click Add Data Source to add it.
to open the dialog box. In the dialog box, select the data source that you want to use for task development. If the data source you need is not available, click Add Data Source to add it.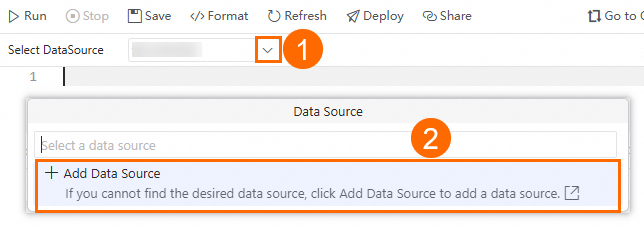 Note
NoteIn a workspace in Standard mode, the list displays only data sources that are configured for both the development and production environments.
Database nodes support only data sources created using a JDBC connection string.
Develop the SQL script.
In the SQL editor, write SQL statements for your task. The following code provides a simple query example.
SELECT * FROM your_table_name; --Query the table. SELECT '${var}'; --Configure a placeholder parameter.NoteYou can write executable statements based on the SQL syntax supported by your configured data source.
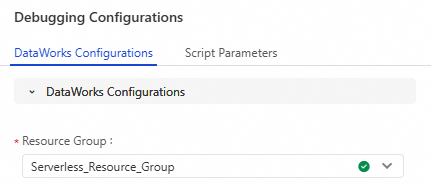
Configure the resource group for debugging.
Click Run Configuration. From the drop-down list, select a serverless resource group with network connectivity to your data source.
 Note
NoteTo access a data source in a public network or VPC, use a scheduling resource group that passes the connectivity test for the data source. For more information, see Network connectivity solutions.
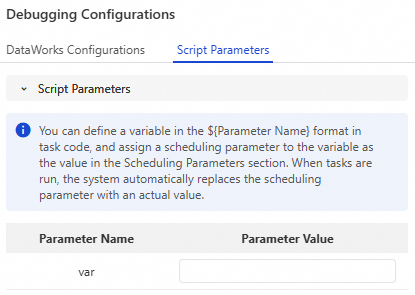
Configure parameters for debugging.
Click Run Configuration. In the Script Parameter section, you can assign values to the parameters configured in the node's script.
After you complete the configuration, click
 to save the configured SQL node. Then, click
to save the configured SQL node. Then, click  to run the SQL script and verify that it works as expected.
to run the SQL script and verify that it works as expected.
After you finish debugging the SQL script, click scheduling configuration on the right side of the SQL editor to configure the node's schedule. For more information, see Node scheduling configuration.
Step 2: Publish and maintain the node
After you configure scheduling, you can submit and publish the database node to the production environment. For more information, see Node and workflow deployment.
After a task is published, it runs periodically according to its scheduling configuration. You can go to to view the task and perform maintenance operations. For more information, see Getting started with Operation Center.
Supported data sources
DataWorks supports creating database nodes for the following data sources:
Data sources for database nodes must be created using a JDBC connection string.
Some databases natively support stored procedures, but DataWorks script development does not currently support them.