This topic describes what merge nodes are, how to create them, and how to define their merging logic. It also provides an example of how to configure the scheduling properties for a merge node and view its run details.
Node introduction
A merge node is a logical control node in DataStudio that merges the run statuses of its ancestor nodes. This helps resolve issues related to dependency attachment and run triggers for the descendant nodes of a branch node.
In the logic definition of a merge node, you cannot select a run status for the merge node itself. You can only define conditions that, if met, result in a successful state for the merge node. This allows descendant nodes to depend directly on the merge node.
For example, assume that a branch node C has two logically mutually exclusive branches, C1 and C2. These branches use different logic to write data to the same MaxCompute table. If a descendant node B depends on the output from this MaxCompute table, you must use a merge node J to merge the branches first. Then, you must set the merge node J as an upstream dependency for node B. If you attach node B directly to branches C1 and C2, one of the branches will always fail to meet its condition, and its instance status will be Branch Not Selected. As a result, node B will also have the status Branch Not Selected because one of its upstream dependencies was skipped. The node will then be in a dry-run state and will not be executed. The same applies to all of its descendant nodes.
Prerequisites
The RAM user that you want to use is added to your workspace.
If you want to use a RAM user to develop tasks, you must add the RAM user to your workspace as a member and assign the Develop or Workspace Administrator role to the RAM user. The Workspace Administrator role has more permissions than necessary. Exercise caution when you assign the Workspace Administrator role. For more information about how to add a member and assign roles to the member, see Add workspace members and assign roles to them.
A serverless resource group is associated with your workspace. For more information, see the topics in the Use serverless resource groups directory.
You must create the merge node before you can develop it. For more information, see Create an auto triggered task.
Precautions
You can use merge nodes only in DataWorks Standard Edition or a more advanced edition. For more information about how to purchase or upgrade DataWorks, see DataWorks editions.
Step 1: Develop a merge node
After you create a merge node, go to the node configuration tab to define its merging logic. The following steps describe how to configure the node:
In the merge logic definition section, search for and add the nodes that you want to merge. You can search for branch nodes by node output, node ID, or node name.
After you find the nodes to merge, click the
 icon to add the nodes to the merge condition settings.Note
icon to add the nodes to the merge condition settings.NoteTo merge multiple branch nodes, repeat this step for each node.
In the Merge Condition Settings section, configure the merge conditions for the branch nodes.
The following merge logic conditions are available:
AND: The merge node is marked as successful, as specified in the Result Settings section, only if all upstream branch nodes have finished running and meet their specified run statuses.
OR: The merge node is marked as successful, as specified in the Result Settings section, if all upstream nodes have finished running and at least one branch node meets its specified run status.
The following run statuses are available for a completed node:
Successful: The node ran successfully.
Failed: The node failed to run.
Branch Not Run: The node was not selected to run and is in a dry-run state. In this state, the node is considered to have run successfully, but the task was not executed.
NoteThis status takes effect only if the ancestor node is a branch node.
In the Result Settings section, set the run status for the current node.
NoteYou can only set the run status of the current node to Successful.
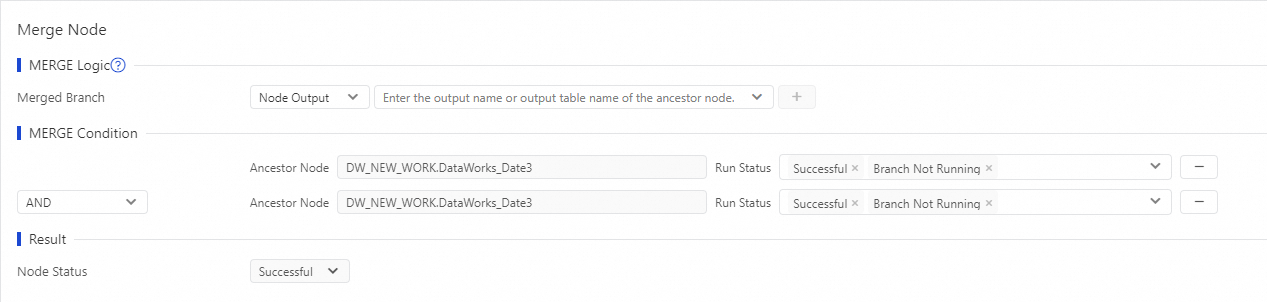
Refer to the figure above.
Nodes
Branch 1andBranch 2are added as the ancestor nodes of the current merge node.The condition for node
Branch 1is met if its status is Successful, Branch Not Run, or Failed. This means that the condition is met as long as nodeBranch 1has finished running, regardless of the outcome.The condition for node
Branch 2is met if its status is Successful or Branch Not Run. This means that nodeBranch 2must finish running without failing.The merge logic condition is set to AND.
Based on these settings, the current merge node is marked as Successful only if node
Branch 1has finished running and nodeBranch 2has finished running without failing.After you configure the merge logic, click Scheduling Properties in the right-side pane of the node configuration tab to set the scheduling properties for the node. For more information, see Configure scheduling properties.
Step 2: Deploy the node and perform O&M
After you configure the scheduling properties, submit and publish the completed merge node to the production environment. For more information, see Deploy a node or workflow.
After a task is published, it runs periodically based on your scheduling configurations. You can go to to view published auto triggered tasks and perform O&M operations. For more information, see Get started with Operation Center.