If you want to optimize write and query performance when you use MySQL to process a large dataset, you can use DataWorks Data Integration to synchronize the data to a MySQL partitioned table. This topic describes the best practice for synchronizing data to a MySQL partitioned table by using DataWorks Data Integration.
Prerequisites
A MySQL database is prepared and added to DataWorks as a data source. For more information, see MySQL data source.
Preparations
Create a source table named user_tb1. DataWorks Data Integration reads data from the source table.
CREATE TABLE `user_tb1` ( `id` bigint(20) unsigned NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT COMMENT 'id', `name` varchar(100) COLLATE utf8mb4_unicode_ci DEFAULT NULL COMMENT 'Name', `update_time` datetime DEFAULT NULL, PRIMARY KEY (`id`) ); INSERT INTO user_tb1 (name, update_time) VALUES ('u1', '2023-12-28 09:52:05'); INSERT INTO user_tb1 (name, update_time) VALUES ('u2', '2023-12-25 09:52:05'); INSERT INTO user_tb1 (name, update_time) VALUES ('u3', '2023-12-26 09:52:05'); INSERT INTO user_tb1 (name, update_time) VALUES ('u3', '2023-12-27 09:52:05'); INSERT INTO user_tb1 (name, update_time) VALUES ('u4', '2023-12-28 09:52:05'); INSERT INTO user_tb1 (name, update_time) VALUES ('u5', '2023-12-28 09:52:05'); INSERT INTO user_tb1 (name, update_time) VALUES ('u6', '2023-12-28 09:52:05'); INSERT INTO user_tb1 (name, update_time) VALUES ('u7', '2023-12-28 09:52:05');Create destination partitioned tables. The destination partitioned tables are used to store the data that is synchronized from the source table.
In this example, the source data is written to a range partitioned table and a key partitioned table. You must separately create the tables.
Create a range partitioned table
CREATE TABLE `pt_write_test_tb1` ( `id` bigint(20) unsigned NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT COMMENT 'id', `name` varchar(100) COMMENT 'Name', `update_time` datetime COMMENT 'Update time', PRIMARY KEY (`id`,`update_time`), KEY `idx_update_time` (`update_time`) ) PARTITION BY RANGE COLUMNS(update_time) ( PARTITION pt20231216 VALUES LESS THAN ('20231216'), PARTITION pt20231217 VALUES LESS THAN ('20231217'), PARTITION pt20231218 VALUES LESS THAN ('20231218'), PARTITION pt20231219 VALUES LESS THAN ('20231219'), PARTITION pt20231220 VALUES LESS THAN ('20231220'), PARTITION pt20231221 VALUES LESS THAN ('20231221'), PARTITION pt20231222 VALUES LESS THAN ('20231222'), PARTITION pt20231223 VALUES LESS THAN ('20231223'), PARTITION pt20231224 VALUES LESS THAN ('20231224'), PARTITION pt20231225 VALUES LESS THAN ('20231225'), PARTITION pt20231226 VALUES LESS THAN ('20231226'), PARTITION pt20231227 VALUES LESS THAN ('20231227'), PARTITION pt20231228 VALUES LESS THAN ('20231228'), PARTITION pt20231229 VALUES LESS THAN ('20231229') );Create a key partitioned table
CREATE TABLE `pt_write_test_tb2` ( `id` bigint(20) unsigned NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT COMMENT 'id', `name` varchar(100) COMMENT 'Name', `update_time` datetime COMMENT 'Update time', PRIMARY KEY (`id`) ) PARTITION BY KEY(`id`) PARTITIONS 16;
Synchronize the source data to the partitioned tables
Synchronize the source data to the range partitioned table
In this example, the update_time field is used as the range partitioning condition to show how to synchronize the source data to a MySQL range partitioned table.
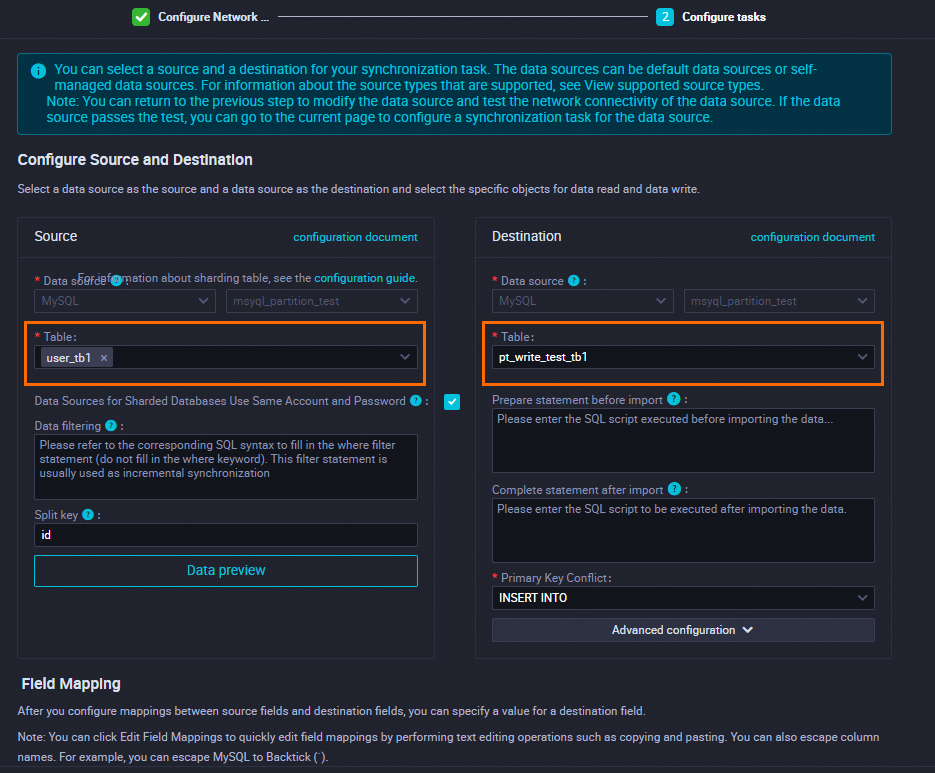
Configure a batch synchronization task.
When you configure a batch synchronization task, take note of the following items:
Specify
user_tb1as the source table.Specify
pt_write_test_tb1as the destination range partitioned table.
 Note
NoteWhen you configure the destination, you can specify an SQL statement in the Prepare statement before import field to enable the system to first create a partition used to store data on the current day before the batch synchronization task starts to write data to the destination:
Prepare a scheduling parameter, such as
pt_date=$[yyyymmdd].Specify the following SQL statement in the Prepare statement before import field:
ALTER TABLE `pt_write_test_tb1` ADD PARTITION (PARTITION pt${pt_date} VALUES LESS THAN ('${pt_date}'));
Query data in the destination table.
Query all data in the table.
SELECT * FROM pt_write_test_tb1;Sample returned result:
+----+------+---------------------+ | id | name | update_time | +----+------+---------------------+ | 2 | u2 | 2023-12-25 09:52:05 | | 3 | u3 | 2023-12-26 09:52:05 | | 4 | u3 | 2023-12-27 09:52:05 | | 1 | u1 | 2023-12-28 09:52:05 | | 5 | u4 | 2023-12-28 09:52:05 | | 6 | u5 | 2023-12-28 09:52:05 | | 7 | u6 | 2023-12-28 09:52:05 | | 8 | u7 | 2023-12-28 09:52:05 | +----+------+---------------------+ 8 rows in set (0.01 sec)Query data in a single partition of the table.
SELECT * FROM pt_write_test_tb1 partition (pt20231229);Sample returned result:
+----+------+---------------------+ | id | name | update_time | +----+------+---------------------+ | 1 | u1 | 2023-12-28 09:52:05 | | 5 | u4 | 2023-12-28 09:52:05 | | 6 | u5 | 2023-12-28 09:52:05 | | 7 | u6 | 2023-12-28 09:52:05 | | 8 | u7 | 2023-12-28 09:52:05 | +----+------+---------------------+ 5 rows in set (0.00 sec)
Synchronize the source data to the key partitioned table
In this example, the id field is used as the key partitioning condition to show how to synchronize the source data to a MySQL key partitioned table.
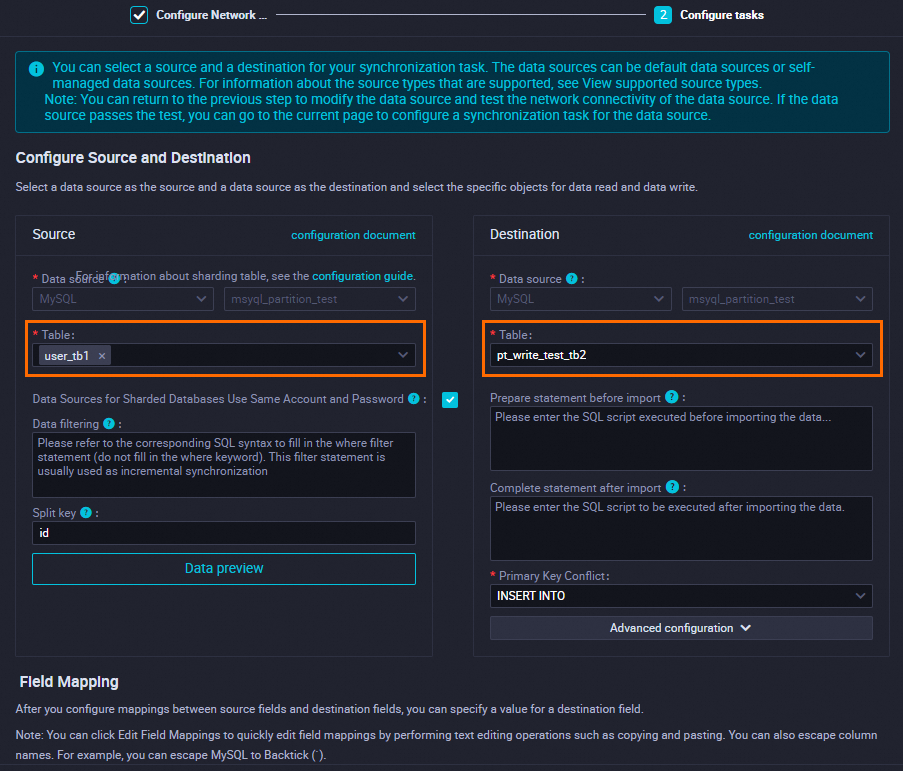
Configure a batch synchronization task.
When you configure a batch synchronization task, take note of the following items:
Specify
user_tb1as the source table.Specify
pt_write_test_tb2as the destination key partitioned table.
Query data in the destination table.
Query all data in the table.
select * from pt_write_test_tb2 order by id;Sample returned result:
+----+------+---------------------+ | id | name | update_time | +----+------+---------------------+ | 1 | u1 | 2023-12-28 09:52:05 | | 2 | u2 | 2023-12-25 09:52:05 | | 3 | u3 | 2023-12-26 09:52:05 | | 4 | u3 | 2023-12-27 09:52:05 | | 5 | u4 | 2023-12-28 09:52:05 | | 6 | u5 | 2023-12-28 09:52:05 | | 7 | u6 | 2023-12-28 09:52:05 | | 8 | u7 | 2023-12-28 09:52:05 | +----+------+---------------------+ 8 rows in set (0.00 sec)Query data in specific partitions.
SELECT TABLE_NAME , PARTITION_NAME , TABLE_ROWS, UPDATE_TIME FROM information_schema.partitions WHERE TABLE_NAME = 'pt_write_test_tb2';Sample returned result:
+-------------------+----------------+------------+---------------------+ | TABLE_NAME | PARTITION_NAME | TABLE_ROWS | UPDATE_TIME | +-------------------+----------------+------------+---------------------+ | pt_write_test_tb2 | p0 | 0 | NULL | | pt_write_test_tb2 | p1 | 0 | NULL | | pt_write_test_tb2 | p10 | 0 | NULL | | pt_write_test_tb2 | p11 | 1 | 2024-02-29 14:49:14 | | pt_write_test_tb2 | p12 | 0 | NULL | | pt_write_test_tb2 | p13 | 0 | NULL | | pt_write_test_tb2 | p14 | 1 | 2024-02-29 14:49:15 | | pt_write_test_tb2 | p15 | 1 | 2024-02-29 14:49:16 | | pt_write_test_tb2 | p2 | 1 | 2024-02-29 14:49:17 | | pt_write_test_tb2 | p3 | 0 | NULL | | pt_write_test_tb2 | p4 | 1 | 2024-02-29 14:49:14 | | pt_write_test_tb2 | p5 | 1 | 2024-02-29 14:49:15 | | pt_write_test_tb2 | p6 | 0 | NULL | | pt_write_test_tb2 | p7 | 0 | NULL | | pt_write_test_tb2 | p8 | 1 | 2024-02-29 14:49:16 | | pt_write_test_tb2 | p9 | 1 | 2024-02-29 14:49:17 | +-------------------+----------------+------------+---------------------+ 16 rows in set (0.01 sec)