A real-time instance is created from the data that is generated after a real-time task is submitted to the Operation Center. Dataphin lets you view data from real-time tasks and manage real-time instances. Management operations include viewing tasks, instance code, and instance parameters. This topic describes the statuses of real-time instances and explains how to manage them.
Go to the real-time instance page
In the top navigation bar of the Dataphin homepage, choose Develop > O&M.
In the top navigation bar, select the production or development environment.
In the navigation pane on the left, choose Instance O&M > Real-time Instance to go to the Real-time Instance page.
Introduction to the real-time instance page
The Real-time Instance page lists the real-time instances that the system has generated. You can perform operations and maintenance (O&M) on this page.
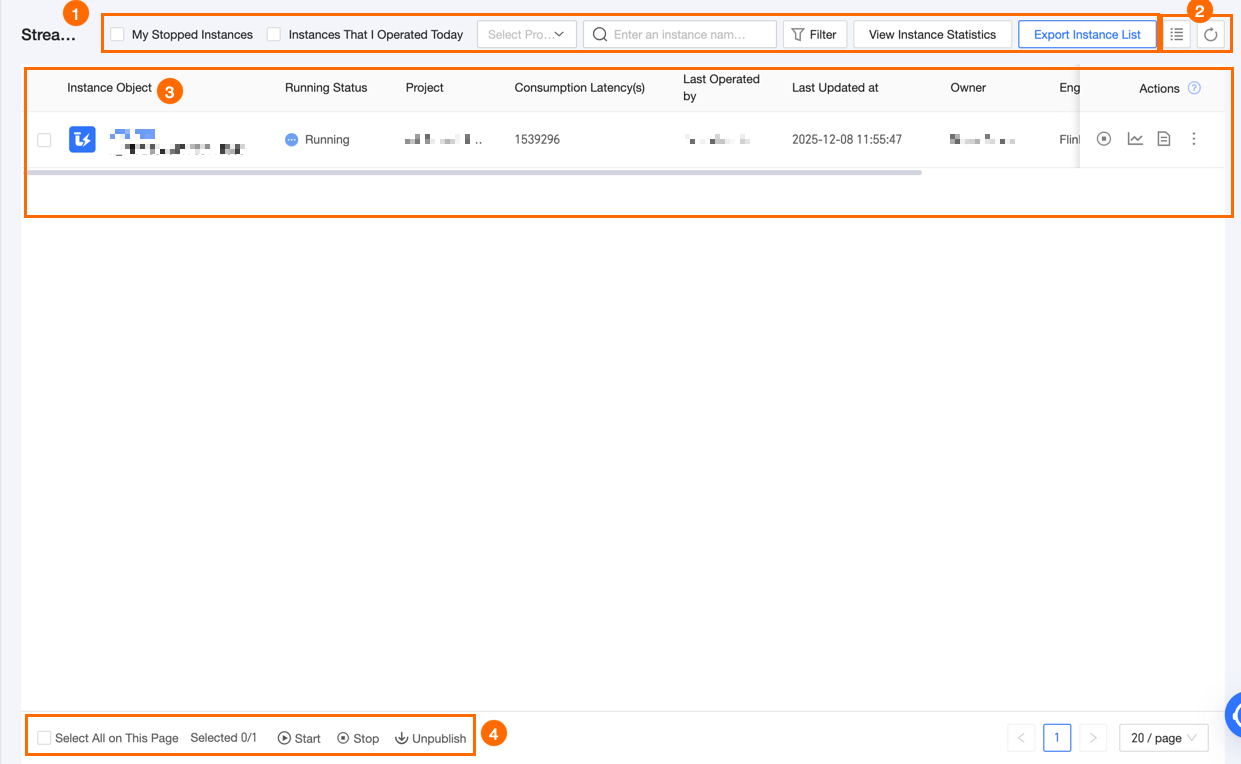
Block | Description |
① Filter and search area | Enter an instance object name or ID to search for a real-time instance. This feature is useful for quick searches when you know the real-time object name or ID.
|
② List operations |
|
③ Real-time instance list | The Real-time Instance page lists the real-time instances that the system has generated. The list includes information such as instance object, running status, last operator, last update time, owner, and project.
The Actions column in the list displays the O&M operations supported for real-time instances. For information about individual O&M operations, see Individual operations. |
④ Batch operations | Use the Start, Stop, and Unpublish functions in the batch operations area to process real-time instances in batches. This improves operational efficiency. For information about batch O&M operations, see Batch operations. |
Real-time instance running status description
Status icon | Status | Description |
| Completed | The instance that processes bounded stream data is complete. |
| Starting | The instance has started, but its operating system is not running. |
| Running | The instance is running. |
| Stopping | The stop operation has been triggered, and the system is stopping the instance. |
| Stop | The running instance is stopped. |
| Failed | The instance failed to run. |
| Startup Failed | The instance failed to start. |
Manage real-time instances
Single operation
Operation | Description |
Start | In the Actions column of the target real-time instance, click the |
Stop | In the Actions column of the target real-time instance, click the
Note
|
Unpublish | In the Actions column of the target real-time instance, click the |
View Running Analysis | In the Actions column of the target real-time instance, click the The compute engine is Apache Flink. For more information, see View running analysis. For real-time instances that use the Ververica Flink or Blink real-time engine, see View job details. |
View Real-time Task | In the Actions column of the target real-time instance, click the |
View Instance Code | In the Actions column of the target real-time instance, click the If the compute engine is Flink, click Logical Code or Physical Code to switch between views.
|
View Instance Parameters | In the Actions column of the target real-time instance, click the |
View Sync Objects | In the Actions column of the target real-time instance, click the
Note This feature is supported only for real-time integration instances that use the incremental and full synchronization solution in the development environment. |
Refresh Sync Objects | In the Actions column of the target real-time instance, click the
Note This feature is supported only for real-time integration instances that use the incremental and full synchronization solution, are in the Running state, and have updated synchronization content. |
Batch operations
Operation | Description |
Start | Note The instance statuses that support the start operation vary based on the real-time engine.
Start Real-time Integration Instances:
Start Real-time Development Instances:
|
Stop | Note The stop operation is supported only for instances in the Failed, Running, Startup Failed, Resume Failed, or Completed state. Stop Real-time Integration Instances:
Stop Real-time Development Instances:
|
Unpublish | Unpublish the selected real-time instances from the production environment. Note You can unpublish only real-time instances that are in the Stopped state. |
Real-time instance DAG
Click the name of an instance object in the instance list. A directed acyclic graph (DAG) appears on the right side of the page with the current node as the central node. By default, the DAG shows one level of parent and child nodes. You can also adjust the display of the DAG:
Click the
 icon to hide the real-time instance list and enlarge the DAG.
icon to hide the real-time instance list and enlarge the DAG.Click the
 icon to hide the DAG.
icon to hide the DAG.Hover over the
 icon and drag to expand or shrink the DAG display area.
icon and drag to expand or shrink the DAG display area.
The DAG provides a dynamic visualization of the node's upstream and downstream dependencies. It also supports O&M operations on upstream and downstream nodes:

Section | Description |
① Node information bar | Displays summary information for the selected node. Click View Node Details to see more information. Ververica Flink real-time engine: Includes node details, sync objects (supported only by real-time instances generated from incremental and full real-time integration nodes), running logs, operation logs, node code, and task parameters (supported only by compute task instances). Flink real-time engine: Includes node details, sync objects (supported only by real-time instances generated from incremental and full real-time integration nodes), running analysis, logs, operation logs, node code, and task parameters (supported only by compute task instances).
|
② Node search and filter area | Quickly set the number of upstream and downstream levels to expand from the central node. If many nodes are expanded and difficult to view, you can search for a node name to quickly locate a specific node within the current DAG display range. |
③ Scheduling dependency graph | Displays the scheduling dependency graph of the instance. You can expand more upstream and downstream nodes. You can also perform O&M operations on upstream and downstream nodes. Hover over a node in the DAG to view its name, type, scheduling cycle, owner, and description. |
④ Canvas adjustment area | Quickly adjust the DAG display ratio. You can set a specific ratio (default is 100%), zoom in (up to 200%), zoom out (down to 20%), fit to canvas, and enter full screen. This area also displays the node ID and node name of the central node in the current DAG. |
Operations supported by real-time instance DAG nodes
Operation | Description |
Expand Parent Nodes | Expand dependency nodes at different levels from the central node in the DAG. |
Expand Child Nodes | |
View Real-time Task | Go to the task node DAG that generated the current instance node. You can view task node details, upstream and downstream node information, and perform O&M on task nodes. For more information, see View and manage real-time tasks. |
View Node Code | You can view the task code that generated the current instance. If the compute engine is Flink, click Logical Code or Physical Code to switch between views. Logical Code: The node code that was written. Physical Code: The compiled code that is executable on the Flink engine.
|
View Running Logs | View the running logs of the instance node. If the node has dirty data, click Download Dirty Data File to download the dirty data to your computer. The file includes the generation time, error content, and error cause of the dirty data. By default, the file is retained for 7 days. If the compute engine is Flink, you can view the startup logs, running logs, and error messages separately to help locate and troubleshoot errors.
|
View Task Parameters | View the task parameters of the current instance node, such as |
Edit Development Node | Go to the node editing page in the Dev project for the node that generated the current instance. This is applicable only to the Dev-Prod development mode. |
Edit Node | Go to the node editing page for the node that generated the current instance. This is applicable only to the Basic mode. |
View Generated Node | View the node configuration in the Prod project for the node that generated the current instance. |
View Operation Logs | View the operation logs of the current instance. The logs include the Operation Time, Operator, and Operation content. |
View Running Analysis | View the running information, data curves, Failover, and other parameters of the current real-time instance. For real-time instances that use the Ververica Flink or Alibaba Blink real-time engine, see View job details. For real-time instances that use the Flink real-time engine, see View running analysis. |
View Sync Objects | In the Sync Objects tab of the current real-time instance details, view the sync object details, including Incremental synchronization and Full synchronization. For field details, see View Sync Objects in the Individual operations section. Note This operation is supported only by real-time instances generated from incremental and full real-time integration nodes. |
Refresh Sync Objects | Click Refresh Sync Objects. In the Refresh Sync Objects dialog box, click OK to run the current real-time instance based on the new synchronization scope. For field details, see Refresh Sync Objects in the Individual operations section. Note This operation is supported only by real-time instances generated from incremental and full real-time integration nodes. |
Start | Start the current real-time instance. For more information, see Start a real-time instance. |
Stop | Stop the current real-time instance. This operation applies to instances in the Running or Completed state. For Completed instances, only stateless stop is supported. Two stop modes are available: Stateless Stop and Stop And Retain Current State.
Note The Blink real-time computing engine does not support the Stateless Stop and Stop And Retain Current State modes. |
Unpublish | Unpublish the real-time instance from the production environment. You can unpublish instances that are in the Stopped state. |
 icon and select View Real-time Task. You are navigated to the node page that generated the current instance. On this page, you can view the details of the real-time task.
icon and select View Real-time Task. You are navigated to the node page that generated the current instance. On this page, you can view the details of the real-time task.
