With the Gateway with Inference Extension component, you can implement replacement, update of the foundation model or canary update of multiple Low-Rank Adaptation (LoRA) models in generative AI inference services. This minimizes service interruption time. This topic describes how to use the Gateway with Inference Extension component to implement canary releases of generative AI inference services.
Before reading this topic, make sure you understand the concepts of InferencePool and InferenceModel.
Prerequisites
An ACK managed cluster with a GPU node pool is created. You can also install the ACK Virtual Node component in the ACK managed cluster to use ACS GPU compute power.
ACK Gateway with Inference Extension is installed and Enable Gateway API Inference Extension is selected when you create the cluster. For more information, see Step 2: Install the Gateway with Inference Extension component.
Preparations
Before performing a progressive canary release of an inference service, you must deploy and validate the model.
Deploy an inference service from the Qwen-2.5-7B-Instruct model.
Deploy an InferencePool and an InferenceModel.
kubectl apply -f- <<EOF apiVersion: inference.networking.x-k8s.io/v1alpha2 kind: InferencePool metadata: name: mymodel-pool-v1 namespace: default spec: extensionRef: group: "" kind: Service name: mymodel-v1-ext-proc selector: app: custom-serving release: qwen targetPortNumber: 8000 --- apiVersion: inference.networking.x-k8s.io/v1alpha2 kind: InferenceModel metadata: name: mymodel-v1 spec: criticality: Critical modelName: mymodel poolRef: group: inference.networking.x-k8s.io kind: InferencePool name: mymodel-pool-v1 targetModels: - name: mymodel weight: 100 EOFDeploy a gateway and configure gateway routing rules.
kubectl apply -f- <<EOF apiVersion: gateway.networking.k8s.io/v1 kind: GatewayClass metadata: name: inference-gateway spec: controllerName: gateway.envoyproxy.io/gatewayclass-controller --- apiVersion: gateway.networking.k8s.io/v1 kind: Gateway metadata: name: inference-gateway spec: gatewayClassName: inference-gateway listeners: - name: llm-gw protocol: HTTP port: 8080 --- apiVersion: gateway.networking.k8s.io/v1 kind: HTTPRoute metadata: name: inference-route spec: parentRefs: - group: gateway.networking.k8s.io kind: Gateway name: inference-gateway sectionName: llm-gw rules: - backendRefs: - group: inference.networking.x-k8s.io kind: InferencePool name: mymodel-pool-v1 weight: 1 matches: - path: type: PathPrefix value: /v1/completions - path: type: PathPrefix value: /v1/chat/completions --- apiVersion: gateway.envoyproxy.io/v1alpha1 kind: ClientTrafficPolicy metadata: name: client-buffer-limit spec: connection: bufferLimit: 20Mi targetRefs: - group: gateway.networking.k8s.io kind: Gateway name: inference-gateway --- apiVersion: gateway.envoyproxy.io/v1alpha1 kind: BackendTrafficPolicy metadata: name: backend-timeout spec: timeout: http: requestTimeout: 24h targetRef: group: gateway.networking.k8s.io kind: Gateway name: inference-gateway EOFObtain the gateway IP address.
export GATEWAY_IP=$(kubectl get gateway/inference-gateway -o jsonpath='{.status.addresses[0].value}')Check the inference service.
curl -X POST ${GATEWAY_IP}:8080/v1/chat/completions -H 'Content-Type: application/json' -d '{ "model": "mymodel", "temperature": 0, "messages": [ { "role": "user", "content": "Who are you?" } ] }'Expected output:
The expected output indicates that the inference service is providing service externally normally by using Gateway with Inference Extension.
Scenario 1: Canary releases of infrastructure and foundation model through updating InferencePool
In real scenarios, you can implement canary releases of model services by updating InferencePool. For example, you can configure two InferencePools that have the same InferenceModel definition and model name but run on different computing configurations, GPU nodes, or foundation models. The following scenarios are suitable:
Infrastructure canary update: Create a new InferencePool, use a new GPU node type or new model configuration, and gradually migrate workloads through canary release. Complete node hardware upgrades, driver updates, or security issue resolutions without interrupting inference request traffic.
Foundation model canary update: Create a new InferencePool, load a new model architecture or fine-tuned model weights, and gradually publish the new inference model through canary release to improve inference service performance or resolve foundation model-related issues.
The following figure shows the procedure of the canary release.
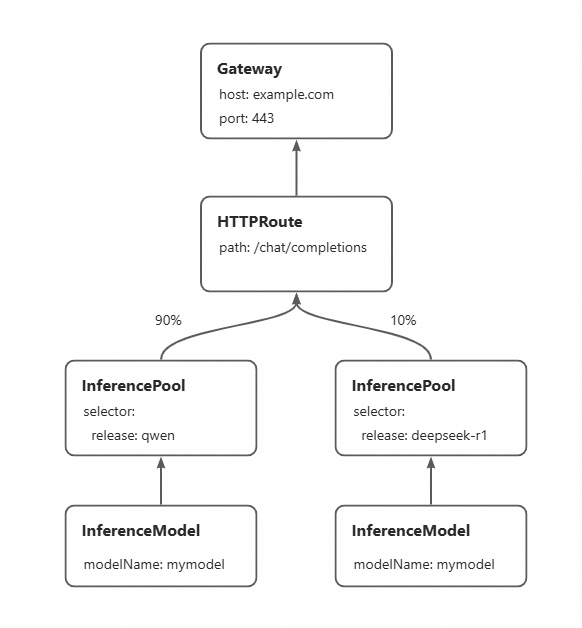
By creating a new InferencePool for the new foundation model and configuring HTTPRoute to allocate traffic proportions between different InferencePools, traffic can be gradually shifted to the new inference service represented by the new InferencePool. In this way, the foundation model can be updated without interruption. The following steps describe how to gradually update the deployed Qwen-2.5-7B-Instruct foundation model service to DeepSeek-R1-Distill-Qwen-7B. You can experience the complete switch of the foundation model by updating the traffic proportion in HTTPRoute.
Deploy an inference service based on the DeepSeek-R1-Distill-Qwen-7B foundation model.
Configure an InferencePool and an InferenceModel for the new inference service. InferencePool
mymodel-pool-v2selects the inference service based on the DeepSeek-R1-Distill-Qwen-7B foundation model through new labels, and declares an InferenceModel with the same model namemymodel.kubectl apply -f- <<EOF apiVersion: inference.networking.x-k8s.io/v1alpha2 kind: InferencePool metadata: name: mymodel-pool-v2 namespace: default spec: extensionRef: group: "" kind: Service name: mymodel-v2-ext-proc selector: app: custom-serving release: deepseek-r1 targetPortNumber: 8000 --- apiVersion: inference.networking.x-k8s.io/v1alpha2 kind: InferenceModel metadata: name: mymodel-v2 spec: criticality: Critical modelName: mymodel poolRef: group: inference.networking.x-k8s.io kind: InferencePool name: mymodel-pool-v2 targetModels: - name: mymodel weight: 100 EOFConfigure the traffic canary strategy.
Configure HTTPRoute to distribute traffic between the existing InferencePool (
mymodel-pool-v1) and the new InferencePool (mymodel-pool-v2). ThebackendRefsweight field controls the percentage of traffic allocated to each InferencePool. The following example configures the model traffic weight as 9:1, which indicates 10% of traffic is forwarded to the DeepSeek-R1-Distill-Qwen-7B foundation service corresponding tomymodel-pool-v2.kubectl apply -f- <<EOF apiVersion: gateway.networking.k8s.io/v1 kind: HTTPRoute metadata: name: inference-route spec: parentRefs: - group: gateway.networking.k8s.io kind: Gateway name: inference-gateway sectionName: llm-gw rules: - backendRefs: - group: inference.networking.x-k8s.io kind: InferencePool name: mymodel-pool-v1 port: 8000 weight: 90 - group: inference.networking.x-k8s.io kind: InferencePool name: mymodel-pool-v2 weight: 10 matches: - path: type: PathPrefix value: / EOFVerify the canary release.
Repeatedly execute the following command to verify the canary effect of the foundation model through the model outputs:
curl -X POST ${GATEWAY_IP}:8080/v1/chat/completions -H 'Content-Type: application/json' -d '{ "model": "mymodel", "temperature": 0, "messages": [ { "role": "user", "content": "Who are you?" } ] }'Expected output for most requests:
{"id":"chatcmpl-6bd37f84-55e0-4278-8f16-7b7bf04c6513","object":"chat.completion","created":1744364930,"model":"mymodel","choices":[{"index":0,"message":{"role":"assistant","reasoning_content":null,"content":"I am Qwen, a large language model created by Alibaba Cloud. I am designed to assist with a wide range of tasks, from answering questions and providing information to helping with creative projects and more. How can I assist you today?","tool_calls":[]},"logprobs":null,"finish_reason":"stop","stop_reason":null}],"usage":{"prompt_tokens":32,"total_tokens":74,"completion_tokens":42,"prompt_tokens_details":null},"prompt_logprobs":null}Expected output for about 10% of requests:
{"id":"chatcmpl-9e3cda6e-b284-43a9-9625-2e8fcd1fe0c7","object":"chat.completion","created":1744601333,"model":"mymodel","choices":[{"index":0,"message":{"role":"assistant","reasoning_content":null,"content":"Hello! I'm an AI assistant created by DeepSeek, here to help with information, answer questions, and provide suggestions. I can assist you with learning, advice, or even just casual conversation. How can I help you today?","tool_calls":[]},"logprobs":null,"finish_reason":"stop","stop_reason":null}],"usage":{"prompt_tokens":8,"total_tokens":81,"completion_tokens":73,"prompt_tokens_details":null},"prompt_logprobs":null}As you can see, most inference requests are still served by the old Qwen-2.5-7B-Instruct foundation model, and a small portion of requests are served by the new DeepSeek-R1-Distill-Qwen-7B foundation model.
Scenario 2: Canary release of LoRA model through configuring InferenceModel
In Multi-LoRA scenarios, Gateway with Inference Extension allows you to deploy multiple versions of LoRA models on the same foundation large model at the same time. You can flexibly allocate traffic for canary testing and verify the effects of each version on performance optimization, bug fixes, or feature iterations.
The following example uses two LoRA versions fine-tuned from Qwen-2.5-7B-Instruct to demonstrate how to implement canary releases of LoRA models by using InferenceModel.
Before the canary release of LoRA models, make sure that an inference service is deployed from the later version of the LoRA model. In this example, the basic service has pre-mounted two LoRA models:travel-helper-v1andtravel-helper-v2.
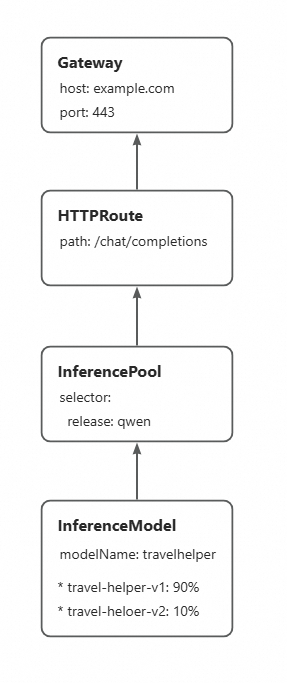
By updating the traffic proportion between different LoRA models in InferenceModel, you can gradually increase the traffic weight of the new version LoRA model, and gradually update to the new LoRA model without interrupting traffic.
Deploy InferenceModel configuration, define multiple versions of LoRA models and specify the traffic proportion between LoRA models. After configuration, when requesting the travelhelper model, the traffic proportion between different versions of LoRA models in the backend is set to 90:10 in the example. That is, 90% of traffic goes to the
travel-helper-v1model, and 10% goes to thetravel-helper-v2model.kubectl apply -f- <<EOF apiVersion: inference.networking.x-k8s.io/v1alpha2 kind: InferenceModel metadata: name: loramodel spec: criticality: Critical modelName: travelhelper poolRef: group: inference.networking.x-k8s.io kind: InferencePool name: mymodel-pool-v1 targetModels: - name: travel-helper-v1 weight: 90 - name: travel-helper-v2 weight: 10 EOFVerify the canary effect.
Repeatedly execute the following command to verify the canary effect of the LoRA model through the model outputs:
curl -X POST ${GATEWAY_IP}:8080/v1/chat/completions -H 'Content-Type: application/json' -d '{ "model": "travelhelper", "temperature": 0, "messages": [ { "role": "user", "content": "I just arrived in Beijing, please recommend a tourist attraction" } ] }'Expected output for most requests:
{"id":"chatcmpl-2343f2ec-b03f-4882-a601-aca9e88d45ef","object":"chat.completion","created":1744602234,"model":"travel-helper-v1","choices":[{"index":0,"message":{"role":"assistant","reasoning_content":null,"content":"Sure, I'd be happy to recommend a place for you. If you're new to Beijing and want to experience its rich history and culture, I highly suggest visiting the Forbidden City (also known as the Palace Museum). It's one of the most iconic landmarks in Beijing and was once the home of emperors during the Ming and Qing dynasties. The architecture is magnificent and it houses an extensive collection of ancient Chinese art and artifacts. You'll definitely get a sense of China's imperial past by visiting there. Enjoy your trip!","tool_calls":[]},"logprobs":null,"finish_reason":"stop","stop_reason":null}],"usage":{"prompt_tokens":38,"total_tokens":288,"completion_tokens":250,"prompt_tokens_details":null},"prompt_logprobs":null}Expected output for about 10% of requests:
{"id":"chatcmpl-c6df57e9-ff95-41d6-8b35-19978f40525f","object":"chat.completion","created":1744602223,"model":"travel-helper-v2","choices":[{"index":0,"message":{"role":"assistant","reasoning_content":null,"content":"Welcome to Beijing! One of the must-visit attractions in Beijing is the Forbidden City, also known as the Imperial Palace. It was the imperial court of the Ming and Qing dynasties and is one of the largest and best-preserved ancient palaces in the world. The architecture, history, and cultural significance make it a fantastic place to explore. I recommend visiting early in the morning to avoid the crowds, and make sure to book your tickets in advance, especially during peak seasons. Enjoy your trip!","tool_calls":[]},"logprobs":null,"finish_reason":"stop","stop_reason":null}],"usage":{"prompt_tokens":38,"total_tokens":244,"completion_tokens":206,"prompt_tokens_details":null},"prompt_logprobs":null}As you can see, most inference requests are served by the
travel-helper-v1LoRA model, and a small portion of requests are served by thetravel-helper-v2LoRA model.