For large language model (LLM) inference services in Kubernetes clusters, traditional load balancing methods often rely on simple traffic allocation, which cannot handle the complex requests and dynamic traffic loads during the LLM inference process. This topic describes how to configure inference service extensions by using Gateway with Inference Extension to achieve intelligent routing and efficient traffic management.
Background information
Large language model (LLM)
Large language models (LLMs) are neural network-based language models with billions of parameters, exemplified by GPT, Qwen, and Llama. These models are trained on diverse and extensive pre-training datasets, including web text, professional literature, and code, and are primarily used for text generation tasks such as completion and dialogue.
To leverage LLMs for building applications, you can:
Utilize external LLM API services from platforms like OpenAI, Alibaba Cloud Model Studio, or Moonshot.
Build your own LLM inference services using open-source or proprietary models and frameworks such as vLLM, and deploy them in a Kubernetes cluster. This approach is suitable for scenarios requiring control over the inference service or high customization of LLM inference capabilities.
vLLM
vLLM is a framework designed for efficient and user-friendly construction of LLM inference services. It supports various large language models, including Qwen, and optimizes LLM inference efficiency through techniques like PagedAttention, dynamic batch inference (Continuous Batching), and model quantization.
KV cache
Procedure
The following figure is a flowchart.

In the inference-gateway, port 8080 is set up with a standard HTTP route to forward requests to the backend inference service. Port 8081 routes requests to the inference service extension (LLM Route), which then forwards the requests to the backend inference service.
In the HTTP Route, the InferencePool resource is used to declare a group of LLM inference service workloads in the cluster. Configure the InferenceModel to specify the traffic distribution policy for the selected model within the InferencePool. In this way, requests routed through port 8081 of the inference-gateway component are directed to the inference service workloads specified by InferencePool by using an enhanced load balancing algorithm designed for inference services.
Prerequisites
An ACK managed cluster with a GPU node pool is created. You can install the ACK Virtual Node component in the ACK managed cluster to use the computing power of ACS in ACK Pro clusters.
Procedure
Step 1: Deploy sample inference service
Create a file named vllm-service.yaml and copy the following content to the file:
NoteFor the image used in this topic, we recommend that you use A10 cards for ACK clusters and GN8IS (8th-gen GPU B) cards for Alibaba Cloud Container Compute Service (ACS) GPU computing power.
Due to the large size of the LLM image, we recommend that you transfer it to Container Registry in advance and pull it using the internal network address. The speed of pulling from the public network depends on the bandwidth configuration of the cluster elastic IP address (EIP), which may result in longer wait times.
Deploy the sample inference service.
kubectl apply -f vllm-service.yaml
Step 2: Install the Gateway with Inference Extension component
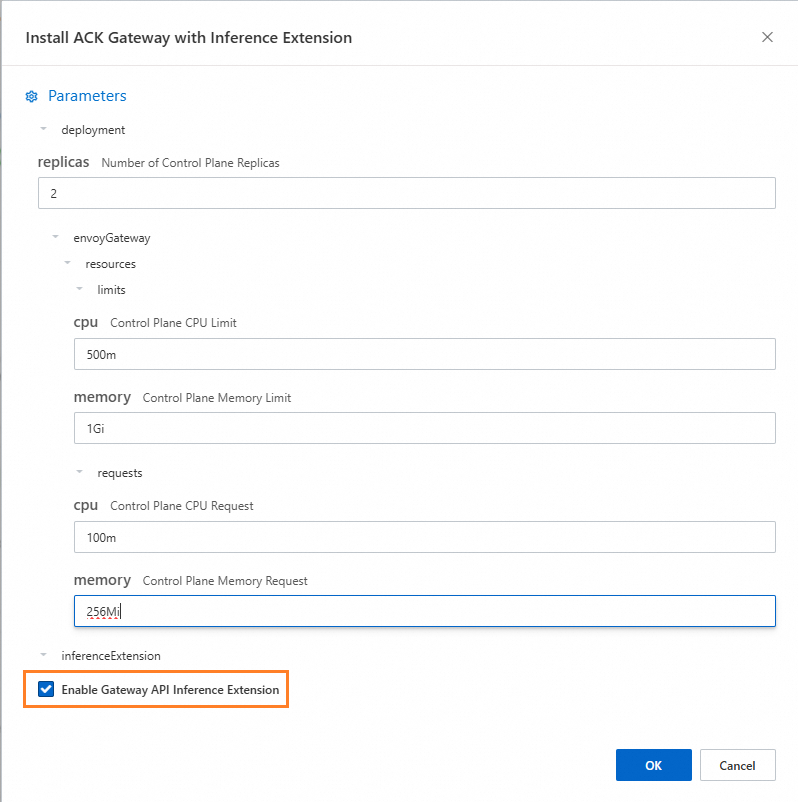
Install the ACK Gateway with Inference Extension component and select Enable Gateway API Inference Extension.
Step 3: Deploy inference routing
This step involves creating the InferencePool and InferenceModel resources.
Create a file named inference-pool.yaml.
apiVersion: inference.networking.x-k8s.io/v1alpha2 kind: InferencePool metadata: name: vllm-qwen-pool spec: targetPortNumber: 8000 selector: app: qwen extensionRef: name: inference-gateway-ext-proc --- apiVersion: inference.networking.x-k8s.io/v1alpha2 kind: InferenceModel metadata: name: inferencemodel-qwen spec: modelName: /model/qwen criticality: Critical poolRef: group: inference.networking.x-k8s.io kind: InferencePool name: vllm-qwen-pool targetModels: - name: /model/qwen weight: 100Deploy inference routing.
kubectl apply -f inference-gateway-llm.yaml
Step 4: Deploy and verify the gateway
This step creates a gateway that includes ports 8080 and 8081.
Create a file named inference-gateway.yaml.
apiVersion: gateway.networking.k8s.io/v1 kind: GatewayClass metadata: name: qwen-inference-gateway-class spec: controllerName: gateway.envoyproxy.io/gatewayclass-controller --- apiVersion: gateway.networking.k8s.io/v1 kind: Gateway metadata: name: qwen-inference-gateway spec: gatewayClassName: qwen-inference-gateway-class listeners: - name: http protocol: HTTP port: 8080 - name: llm-gw protocol: HTTP port: 8081 --- apiVersion: gateway.networking.k8s.io/v1 kind: HTTPRoute metadata: name: qwen-backend spec: parentRefs: - name: qwen-inference-gateway sectionName: llm-gw rules: - backendRefs: - group: inference.networking.x-k8s.io kind: InferencePool name: vllm-qwen-pool matches: - path: type: PathPrefix value: / --- apiVersion: gateway.networking.k8s.io/v1 kind: HTTPRoute metadata: name: qwen-backend-no-inference spec: parentRefs: - group: gateway.networking.k8s.io kind: Gateway name: qwen-inference-gateway sectionName: http rules: - backendRefs: - group: "" kind: Service name: qwen port: 8000 weight: 1 matches: - path: type: PathPrefix value: / --- apiVersion: gateway.envoyproxy.io/v1alpha1 kind: BackendTrafficPolicy metadata: name: backend-timeout spec: timeout: http: requestTimeout: 1h targetRef: group: gateway.networking.k8s.io kind: Gateway name: qwen-inference-gatewayDeploy the gateway.
kubectl apply -f inference-gateway.yamlThis step creates a namespace named
envoy-gateway-systemand a service namedenvoy-default-inference-gateway-645xxxxxin the cluster.Obtain the public IP address of the gateway.
export GATEWAY_HOST=$(kubectl get gateway/qwen-inference-gateway -o jsonpath='{.status.addresses[0].value}')Verify that the gateway is routing to the inference service via standard HTTP routing on port 8080.
curl -X POST ${GATEWAY_HOST}:8080/v1/chat/completions -H 'Content-Type: application/json' -d '{ "model": "/model/qwen", "max_completion_tokens": 100, "temperature": 0, "messages": [ { "role": "user", "content": "Write as if you were a critic: San Francisco" } ] }'Expected output:
{"id":"chatcmpl-aa6438e2-d65b-4211-afb8-ae8e76e7a692","object":"chat.completion","created":1747191180,"model":"/model/qwen","choices":[{"index":0,"message":{"role":"assistant","reasoning_content":null,"content":"San Francisco, a city that has long been a beacon of innovation, culture, and diversity, continues to captivate the world with its unique charm and character. As a critic, I find myself both enamored and occasionally perplexed by the city's multifaceted personality.\n\nSan Francisco's architecture is a testament to its rich history and progressive spirit. The iconic cable cars, Victorian houses, and the Golden Gate Bridge are not just tourist attractions but symbols of the city's enduring appeal. However, the","tool_calls":[]},"logprobs":null,"finish_reason":"length","stop_reason":null}],"usage":{"prompt_tokens":39,"total_tokens":139,"completion_tokens":100,"prompt_tokens_details":null},"prompt_logprobs":null}Verify that the gateway is routing to the inference service via the inference service extension on port 8081.
curl -X POST ${GATEWAY_HOST}:8081/v1/chat/completions -H 'Content-Type: application/json' -d '{ "model": "/model/qwen", "max_completion_tokens": 100, "temperature": 0, "messages": [ { "role": "user", "content": "Write as if you were a critic: Los Angeles" } ] }'Expected output:
{"id":"chatcmpl-cc4fcd0a-6a66-4684-8dc9-284d4eb77bb7","object":"chat.completion","created":1747191969,"model":"/model/qwen","choices":[{"index":0,"message":{"role":"assistant","reasoning_content":null,"content":"Los Angeles, the sprawling metropolis often referred to as \"L.A.,\" is a city that defies easy description. It is a place where dreams are made and broken, where the sun never sets, and where the line between reality and fantasy is as blurred as the smog that often hangs over its valleys. As a critic, I find myself both captivated and perplexed by this city that is as much a state of mind as it is a physical place.\n\nOn one hand, Los","tool_calls":[]},"logprobs":null,"finish_reason":"length","stop_reason":null}],"usage":{"prompt_tokens":39,"total_tokens":139,"completion_tokens":100,"prompt_tokens_details":null},"prompt_logprobs":null}
(Optional) Step 5: Configure LLM service observability metrics and dashboards
You must enable and use Managed Service for Prometheus in the cluster, which may incur additional fees.
You can add Prometheus metric collection annotations to the vLLM service pod to collect metrics by using the default service discovery mechanism of the Prometheus instance. This monitors the internal state of the vLLM service.
... annotations: prometheus.io/path: /metrics # The HTTP path where you want to expose the metrics. prometheus.io/port: "8000" # The exposed port for metrics, which is the listening port of the vLLM server. prometheus.io/scrape: "true" # Specifies whether to scrape the metrics of the current pod. ...The following table displays some monitoring metrics provided by the vLLM service:
Metric
Description
vllm:gpu_cache_usage_perc
The percentage of GPU cache usage by vLLM. When vLLM starts, it preemptively occupies as much GPU video memory as possible for KV Cache. For vLLM servers, the lower the utilization, the more space the GPU has to allocate resources to new requests.
vllm:request_queue_time_seconds_sum
The time spent queuing in the waiting state. After LLM inference requests arrive at the vLLM server, they may not be processed immediately and need to wait for the vLLM scheduler to schedule prefill and decode.
vllm:num_requests_running
vllm:num_requests_waiting
vllm:num_requests_swapped
The number of requests running inference, waiting, and swapped to memory. This can be used to assess the current request pressure on the vLLM service.
vllm:avg_generation_throughput_toks_per_s
vllm:avg_prompt_throughput_toks_per_s
The number of tokens consumed per second during the prefill stage and generated during the decode stage.
vllm:time_to_first_token_seconds_bucket
The latency level from when a request is sent to the vLLM service until the first token is responded to. This metric typically represents the time required for the client to receive the first response after outputting the request content and is an important metric affecting the LLM user experience.
Based on these metrics, you can set specific alert rules to enable real-time monitoring and anomaly detection of the LLM service performance.
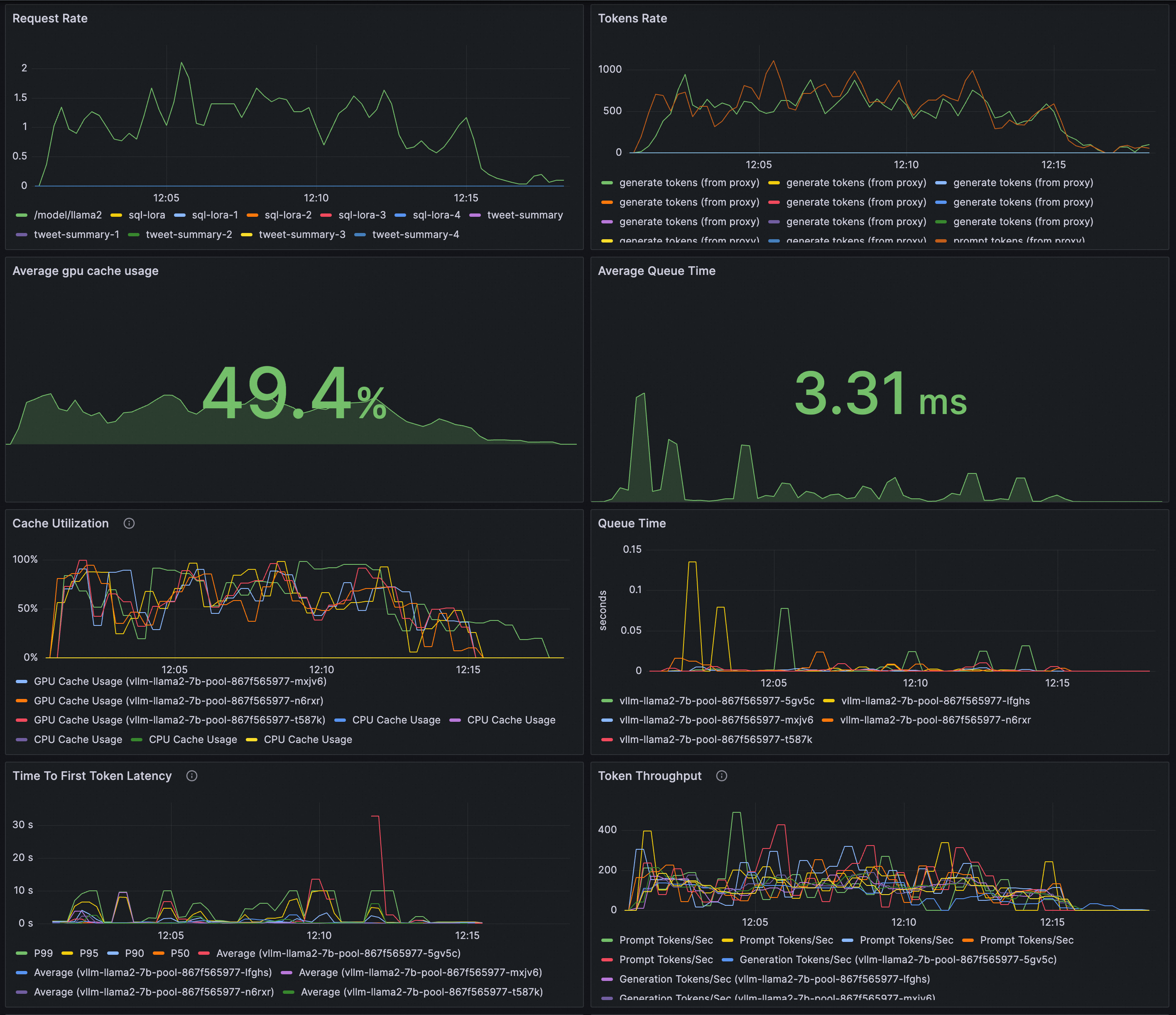
Configure a Grafana dashboard for real-time monitoring of the LLM inference service. You can use the Grafana dashboard to observe the LLM inference service deployed based on vLLM:
Monitor the request rate and total token throughput for the LLM service.
Monitor the internal state of the inference workload.
Ensure that the Prometheus instance, which serves as the data source for Grafana, has collected the monitoring metrics for vLLM. To create an observable dashboard for the LLM inference service, you can import the following content into Grafana:
Preview:
For ACK clusters, use vllm benchmark to perform stress testing on the inference service and compare the load balancing capabilities of standard HTTP routing and inference extension routing.
Deploy the stress testing workload.
kubectl apply -f- <<EOF apiVersion: apps/v1 kind: Deployment metadata: labels: app: vllm-benchmark name: vllm-benchmark namespace: default spec: progressDeadlineSeconds: 600 replicas: 1 revisionHistoryLimit: 10 selector: matchLabels: app: vllm-benchmark strategy: rollingUpdate: maxSurge: 25% maxUnavailable: 25% type: RollingUpdate template: metadata: creationTimestamp: null labels: app: vllm-benchmark spec: containers: - command: - sh - -c - sleep inf image: registry-cn-hangzhou.ack.aliyuncs.com/dev/llm-benchmark:random-and-qa imagePullPolicy: IfNotPresent name: vllm-benchmark resources: {} terminationMessagePath: /dev/termination-log terminationMessagePolicy: File dnsPolicy: ClusterFirst restartPolicy: Always schedulerName: default-scheduler securityContext: {} terminationGracePeriodSeconds: 30 EOFStart the stress test.
Obtain the Gateway internal IP address.
export GW_IP=$(kubectl get svc -n envoy-gateway-system -l gateway.envoyproxy.io/owning-gateway-namespace=default,gateway.envoyproxy.io/owning-gateway-name=qwen-inference-gateway -o jsonpath='{.items[0].spec.clusterIP}')Perform the stress test.
Standard HTTP routing
kubectl exec -it deploy/vllm-benchmark -- env GW_IP=${GW_IP} python3 /root/vllm/benchmarks/benchmark_serving.py \ --backend vllm \ --model /models/DeepSeek-R1-Distill-Qwen-7B \ --served-model-name /model/qwen \ --trust-remote-code \ --dataset-name random \ --random-prefix-len 10 \ --random-input-len 1550 \ --random-output-len 1800 \ --random-range-ratio 0.2 \ --num-prompts 3000 \ --max-concurrency 200 \ --host $GW_IP \ --port 8080 \ --endpoint /v1/completions \ --save-result \ 2>&1 | tee benchmark_serving.txtInference service routing
kubectl exec -it deploy/vllm-benchmark -- env GW_IP=${GW_IP} python3 /root/vllm/benchmarks/benchmark_serving.py \ --backend vllm \ --model /models/DeepSeek-R1-Distill-Qwen-7B \ --served-model-name /model/qwen \ --trust-remote-code \ --dataset-name random \ --random-prefix-len 10 \ --random-input-len 1550 \ --random-output-len 1800 \ --random-range-ratio 0.2 \ --num-prompts 3000 \ --max-concurrency 200 \ --host $GW_IP \ --port 8081 \ --endpoint /v1/completions \ --save-result \ 2>&1 | tee benchmark_serving.txt
After the tests, you can compare the routing capabilities of standard HTTP routing and inference service extension through the dashboard.
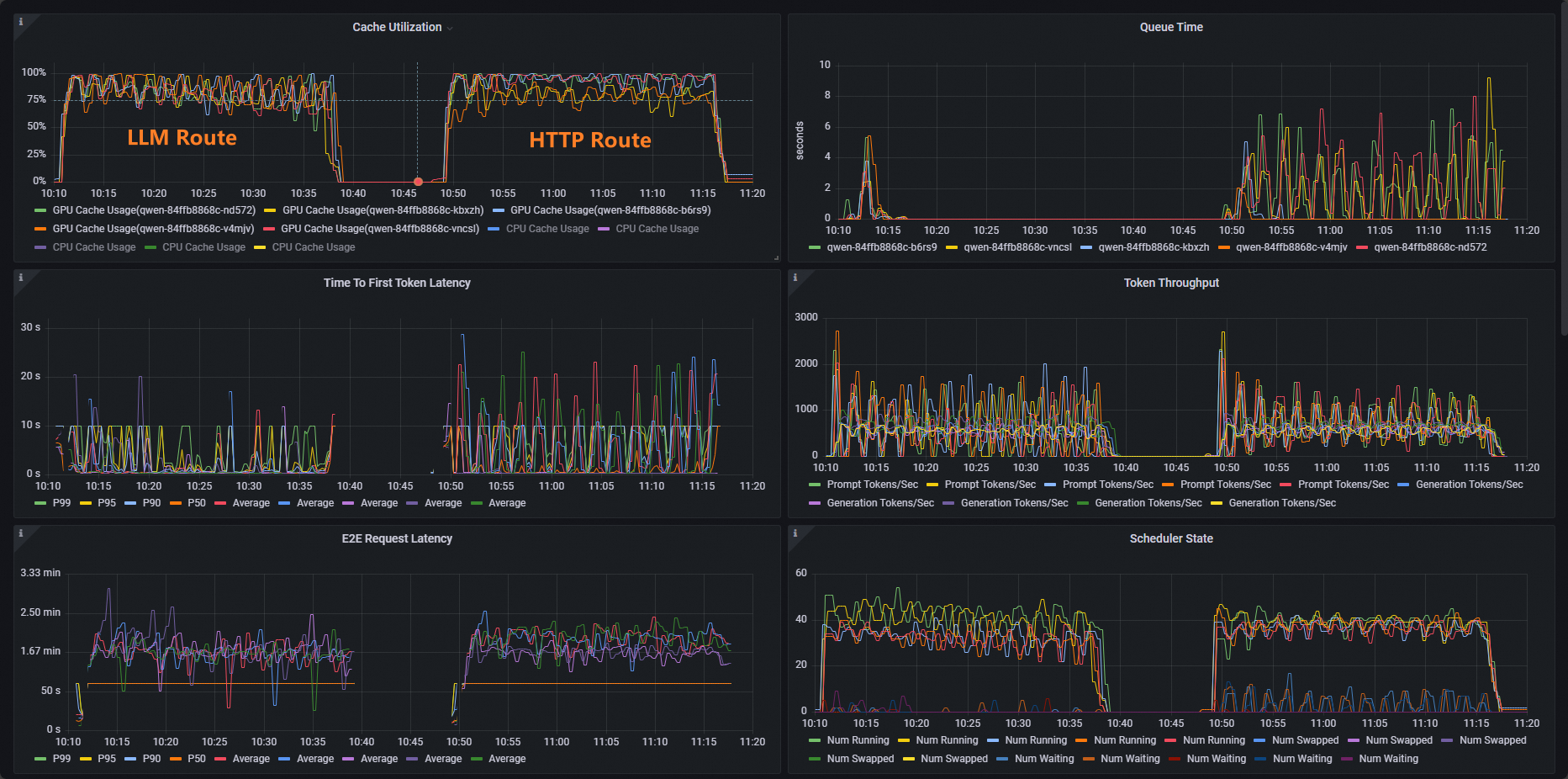
As you can see, the cache utilization distribution of workloads using HTTP Route is uneven, while the cache utilization distribution of workloads using LLM Route is normal.
What to do next
Gateway with Inference Extension provides various load balancing policies to meet the requirements in different inference scenarios. To configure a load balancing policy for pods in an InferencePool, add the inference.networking.x-k8s.io/routing-strategy annotation to the configurations of the InferencePool.
The following sample YAML template uses the app: vllm-app selector to select the inference service pod and uses the default load balancing policy that works based on the metrics of the inference server.
apiVersion: inference.networking.x-k8s.io/v1alpha2
kind: InferencePool
metadata:
name: vllm-app-pool
annotations:
inference.networking.x-k8s.io/routing-strategy: "DEFAULT"
spec:
targetPortNumber: 8000
selector:
app: vllm-app
extensionRef:
name: inference-gateway-ext-procThe following table describes the load balancing policies provided by ACK Gateway with Inference Extension.
Policy | Description |
DEFAULT | The default load balancing policy that works based on the metrics of the inference service. This policy evaluates the status of the inference server based on multi-dimensional metrics and performs load balancing based on the evaluated status. The metrics include the request queue length and GPU cache utilization. |
PREFIX_CACHE | The request prefix-matching load balancing policy. This policy attempts to send requests with the same prefix to pods on the same inference server. This policy is suitable for scenarios where a large number of requests with the same prefix are received and the inference server has the auto prefix caching feature enabled. The following list describes the typical scenarios:
|