In a production environment, the resources allocated to serverless pods are usually fixed. However, the resources that pods consume can fluctuate dynamically in different scenarios. To handle these fluctuations, Container Compute Service (ACS) provides an in-place scaling feature that lets you change pod specifications. This topic describes in-place scaling for ACS pods and provides best practices for using this feature to reduce resource costs and accelerate application startup.
Background information
In complex production environments, the computing power that services consume may fluctuate. This makes capacity planning for pods challenging. For example, some applications consume a large amount of CPU resources during startup, but their resource consumption remains low for long periods after startup. Stateful or game applications must meet fluctuating business demands during peak and off-peak hours while maintaining their state or persistent connections.
To handle these scenarios, serverless pods need more fine-grained and flexible resource specifications to match actual usage. If pods can dynamically change their specifications and scale on demand, capacity planning becomes much simpler, and costs are better aligned with actual resource consumption.
The in-place scaling feature for ACS pods lets you perform hot updates on container CPU resources with a low latency of about 10 seconds. When combined with the ack-advanced-vertical-pod-autoscaler (AVPA) component from ACS, this feature offers various automatic scaling capabilities to handle scenarios with changing resource requirements.
ACS supports in-place scaling of CPU resources for general-purpose and compute-optimized ACS pods with
ComputeQoS=default:The maximum resource specification that supports flexible upgrades and downgrades is
16vCpu16Gi.The supported scaling range lets you scale out the original CPU specification by up to 100% and scale in by up to 50%. For example, the scaling range for a
2vCpu4GiACS pod is from1vCpu4Gito4vCpu4Gi.The in-place scaling feature is also limited by ACS resource availability. If the configuration after scaling is outside the supported range, it is automatically adjusted to the nearest supported resource specification. For example, an ACS pod with
0.75vCpu1.5Giis automatically adjusted to1vCpu2Gi.
Scenarios
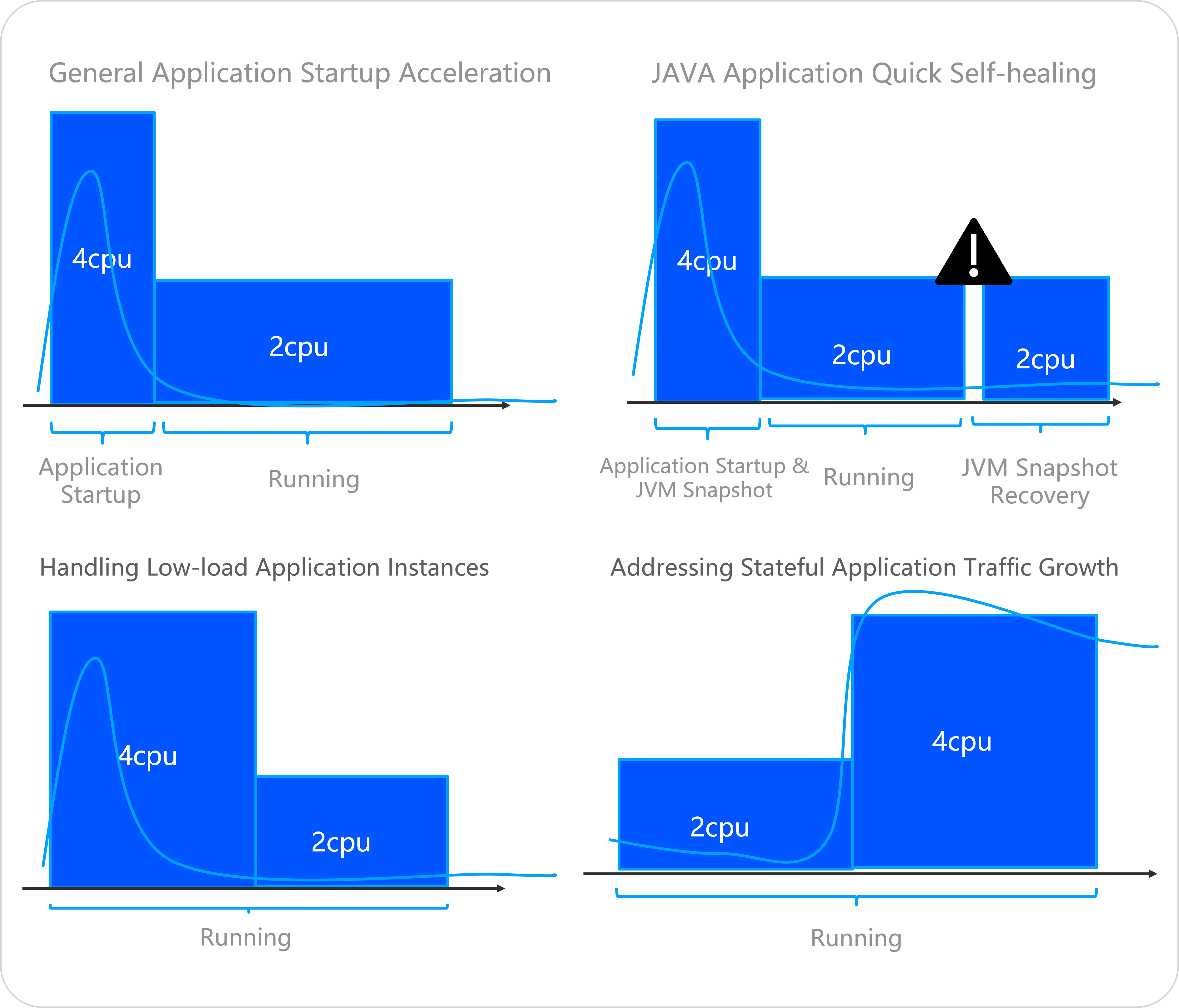
In-place scaling supports resizing a container without restarting it. You can use this feature in scenarios where computing power usage fluctuates, such as for application startup acceleration, in-place scaling of stateful applications, and handling local computing power hot spots in applications.
Specific scenarios include the following:
Startup acceleration for applications that require significant computing resources for compilation or preloading. You can allocate more CPU resources during startup and then scale down after startup is complete.
Vertical scaling of stateful applications, such as Redis, when the load increases.
Vertical scaling of online applications that experience local hot spots from large requests or persistent connection sessions.
After in-place scaling, the application pod is billed based on the new specification. During the scaling process or if scaling fails, billing continues based on the original specification.
In-place scaling can dynamically adjust the available CPU resources of a container. We recommend that you use these dynamic resources based on the characteristics of your application's programming language.
In-place scaling is not instantaneous. We recommend that you estimate the capacity buffer for your application before use. Do not use this feature to handle traffic and load bursts that occur within seconds.
Prerequisites
An ACS cluster of version 1.28 or later is created. For more information, see Create an ACS cluster.
Manually scale a pod
Step 1: Enable the in-place scaling feature gate
Log on to the ACS console. In the left navigation pane, click Clusters.
On the Clusters page, click the name of the target cluster. In the left navigation pane, click Add-ons.
In the Core Components area, on the Kube API Server card, click Configuration. Set featureGates to
InPlacePodVerticalScaling=trueto enable the in-place scaling feature. Note
NoteDuring the configuration, the status on the Kube API Server card changes to Executing. When the status changes back to Installed, the in-place resource scaling feature gate is enabled.
Step 2: Scale the ACS pod
On the Clusters page, click the name of the target cluster. In the left navigation pane, choose Workloads > Deployments.
Click Create from YAML and use the following sample YAML to create the Pod. The
scaling.alibabacloud.com/enable-inplace-resource-resize: 'true'annotation enables in-place scaling for the Pod.apiVersion: apps/v1 kind: Deployment metadata: labels: app: demo name: demo namespace: default spec: replicas: 1 selector: matchLabels: app: demo template: metadata: annotations: scaling.alibabacloud.com/enable-inplace-resource-resize: 'true' # Enable in-place scaling. labels: alibabacloud.com/compute-class: general-purpose alibabacloud.com/compute-qos: default app: demo spec: containers: - image: 'registry.cn-hangzhou.aliyuncs.com/acs-demo-ns/demo-java:java-with-metrics-v1' imagePullPolicy: IfNotPresent name: spring ports: - containerPort: 8080 protocol: TCP resources: limits: cpu: 1 memory: 4Gi requests: cpu: 1 memory: 4GiPod Annotations configuration item
Configuration item description
Value
scaling.alibabacloud.com/enable-inplace-resource-resize
Specify this annotation when you create the pod to enable in-place scaling for the current ACS pod.
true
After the pod is created, go to the Pods page and click Edit YAML to manually change the CPU resources from
1to2. Then, click Update.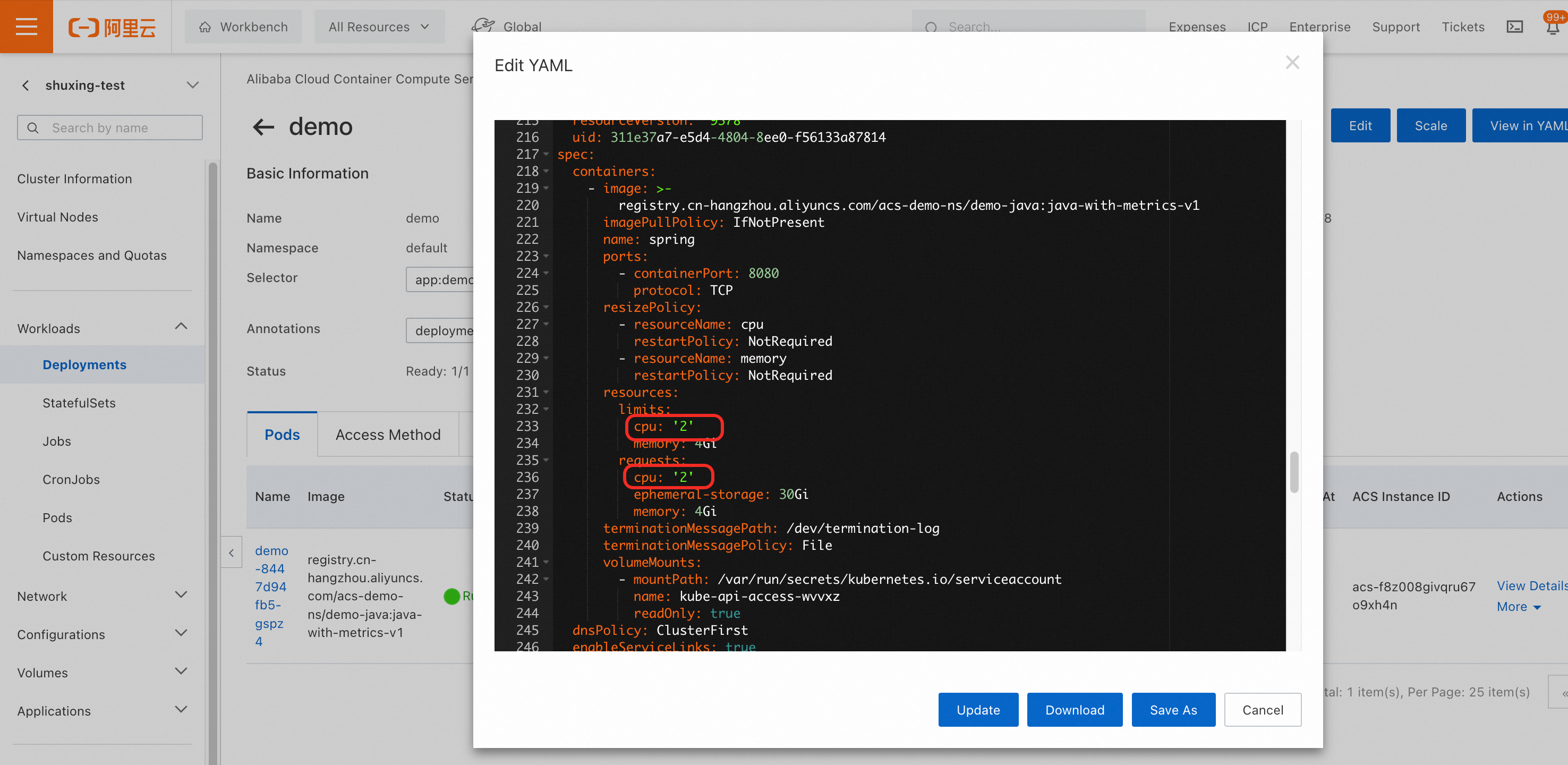
You can see that after the in-place scaling feature is enabled, the pod's specification is changed without a restart.
Use automatic in-place scaling to accelerate application startup
A typical Java application is a good example. During the startup phase, it consumes a large amount of resources for actions such as class loading and bytecode compilation. After the application enters a steady state, these resources are released. To accelerate application startup and reduce costs during normal operation, a serverless pod can use more resources during startup and then scale down after the service has started.
ACS provides a Java application startup acceleration feature. You can configure an ACS pod to start with more resources than its declared specification and then automatically scale down to the original specification after startup is complete. For more information about JVM parameter configuration, see Configure JVM parameters to accelerate the startup of Java applications.
Limits
Startup acceleration feature: The startup acceleration feature relies on the Ready state of pods to control scale-in actions. If a readiness probe is not configured, the container is considered ready as soon as it starts, and the automatic scale-in countdown is immediately triggered. We recommend that you configure a readiness probe on pods for which the startup acceleration feature is enabled.
Container restart scenario: If you expect automatic startup acceleration when a container restarts, not configuring a readiness probe may prevent automatic scale-up.
Resource configuration requirements: The startup acceleration feature relies on the pod's original resources to calculate the scale-up resources. Therefore, you must configure the original requests and limits values. Otherwise, the startup acceleration feature may not work.
Step 1: Enable the in-place scaling feature gate
Step 2: Install the ack-advanced-vertical-pod-autoscaler component
In the navigation pane on the left, choose . Search for and install the ack-advanced-vertical-pod-autoscaler component. For more information, see Use Helm to manage applications in ACS.
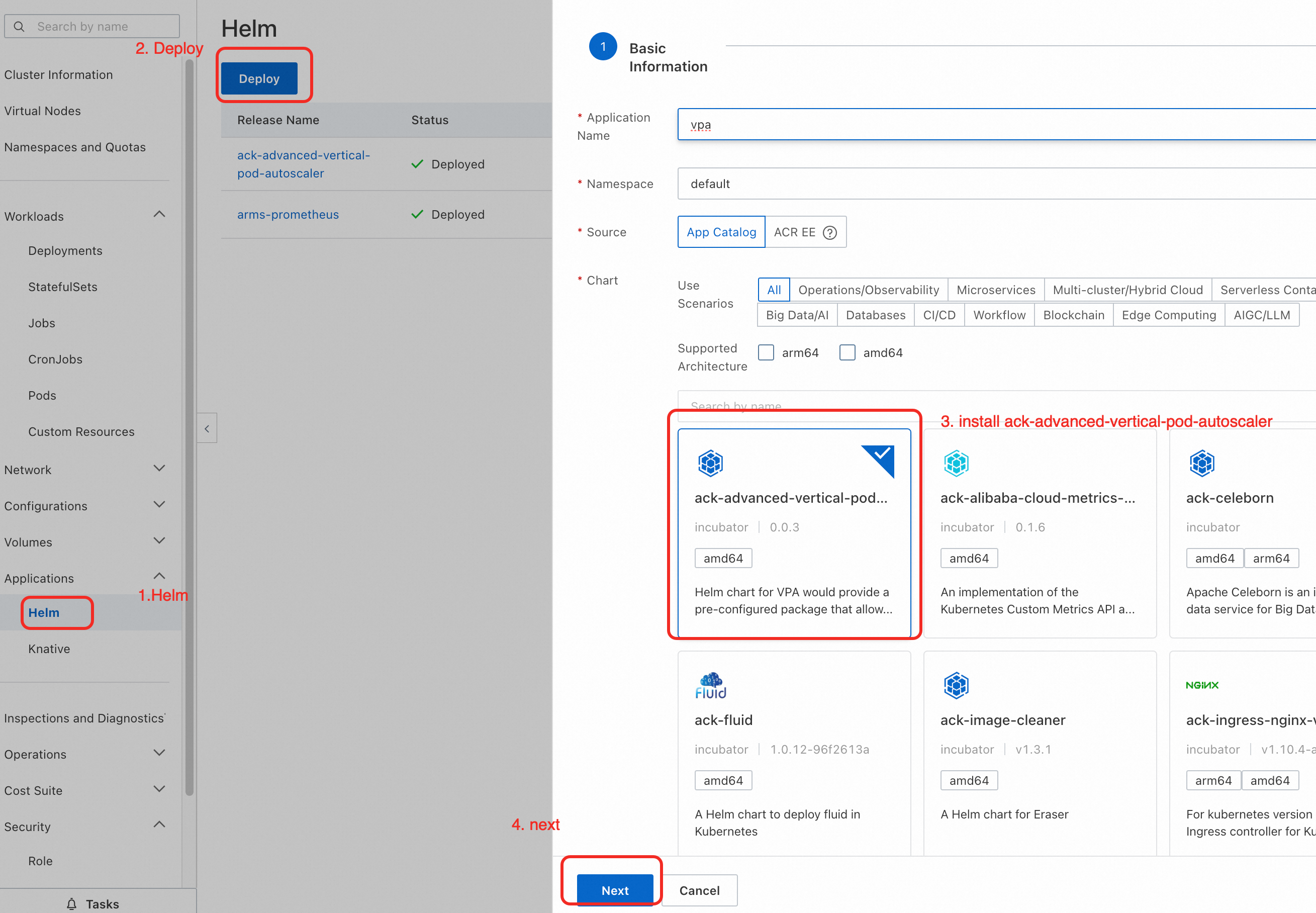
Step 3: Use in-place scaling to accelerate application startup
Create a Java workload and enable the startup acceleration feature. In the YAML file, in addition to
scaling.alibabacloud.com/enable-inplace-resource-resize: 'true', you also need to use thealibabacloud.com/startup-cpu-burst-factorandalibabacloud.com/startup-cpu-burst-duration-secondsannotations to configure the startup CPU burst factor and the startup CPU burst duration.apiVersion: apps/v1 kind: Deployment metadata: labels: app: spring-with-burst name: spring-with-burst namespace: default spec: replicas: 1 selector: matchLabels: app: spring-with-burst template: metadata: annotations: alibabacloud.com/startup-cpu-burst-factor: '2' #Set the startup scale-out factor to 2. The initial 2C starts with 4C and scales back to the initial state after the container is Ready. alibabacloud.com/startup-cpu-burst-duration-seconds: "30" #If not specified, it defaults to automatic scale-in 30 seconds after the pod is Ready. scaling.alibabacloud.com/enable-inplace-resource-resize: 'true' # Enable in-place scaling. labels: alibabacloud.com/compute-class: general-purpose alibabacloud.com/compute-qos: default app: spring-with-burst spec: containers: - image: 'registry.cn-hangzhou.aliyuncs.com/acs-demo-ns/demo-java:java-with-metrics-v1' imagePullPolicy: IfNotPresent name: spring ports: - containerPort: 8080 protocol: TCP resources: limits: cpu: 1 memory: 4Gi requests: cpu: 1 memory: 4Gi readinessProbe: tcpSocket: port: 8080 initialDelaySeconds: 20 periodSeconds: 10Pod annotation
Description
Value
scaling.alibabacloud.com/enable-inplace-resource-resize
Enables in-place scaling for the ACS pod.
true
alibabacloud.com/startup-cpu-burst-factor
Specifies that the ACS pod starts with a multiple of its original CPU specification.
2
NoteThe in-place scaling feature can scale up a pod to only twice its original specification. For example, if the original specification is
2 vCPUs, the pod starts with4 vCPUs.alibabacloud.com/startup-cpu-burst-duration-seconds
Specifies the number of seconds to wait after startup is complete before the ACS pod is scaled in.
30 or greater
NoteThe default value is 30 seconds. The pod is scaled in 30 seconds after it enters the Ready state. If the pod never becomes Ready, it remains in the scaled-up state.
alibabacloud.com/startup-cpu-burst-disable-restart
Optional. Disables automatic scale-up when the container restarts.
true
NoteIf you do not add this annotation, automatic scale-up is enabled when the container restarts.
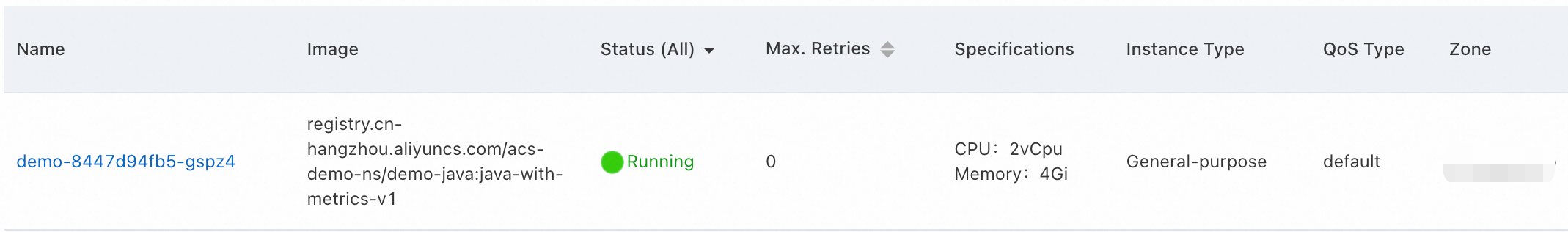
Step 4: Observe the pod creation and service startup process
After the application is created, go to its details page. You can see that the pod is created with 2 vCPUs and 4 GiB of memory. After the pod starts and the CPU burst duration ends, the pod is automatically scaled down to 1 vCPU and 4 GiB of memory.
View pod events.
On the Events tab, select Pod to view details about the scale-down. In this example, the event message
Starting to resize resource down for container: spring cpu: 2 -> 1, memory: 4Gi -> 4Giis displayed.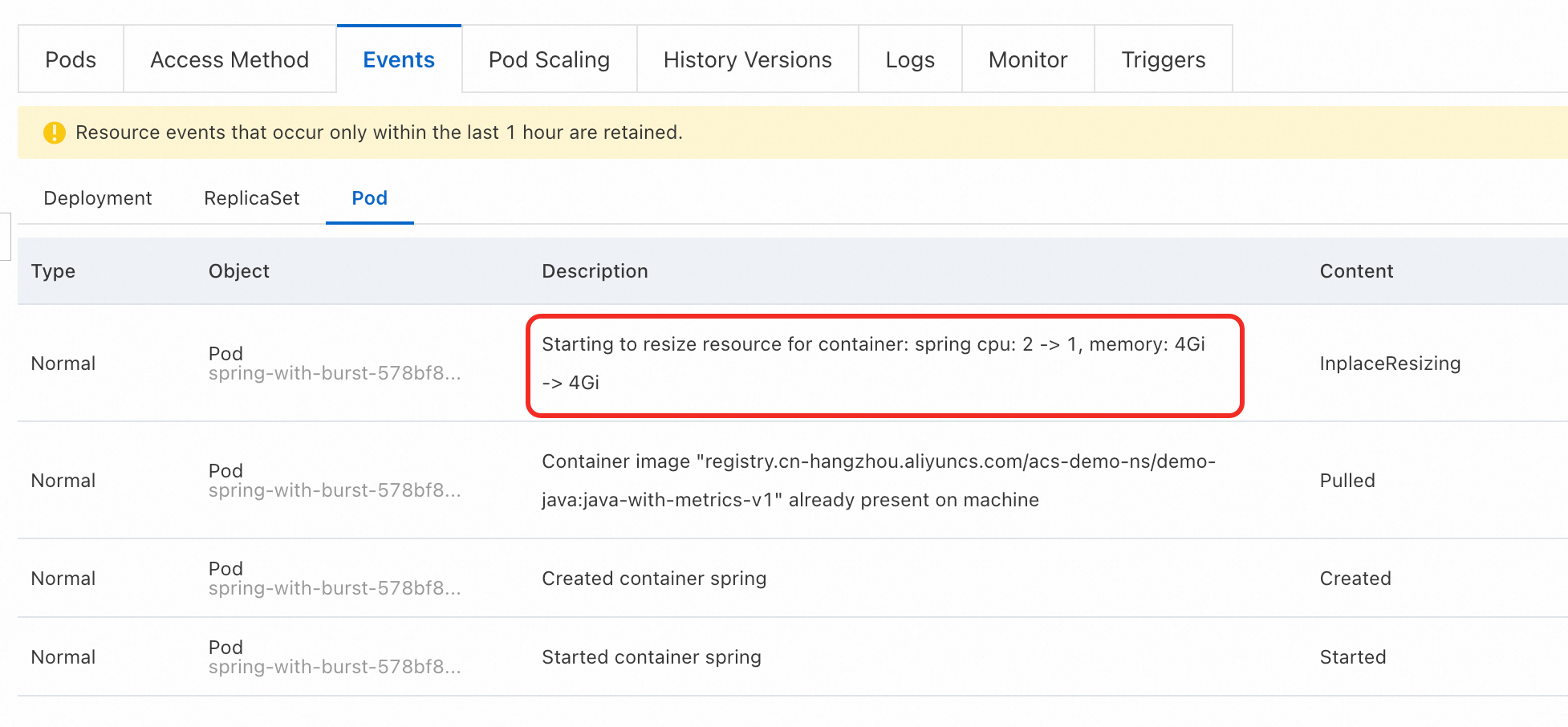
In addition to checking events to monitor the scaling progress, you can also check the status.resize field of a pod. A non-empty value indicates that the pod is being scaled.
View pod monitoring data.
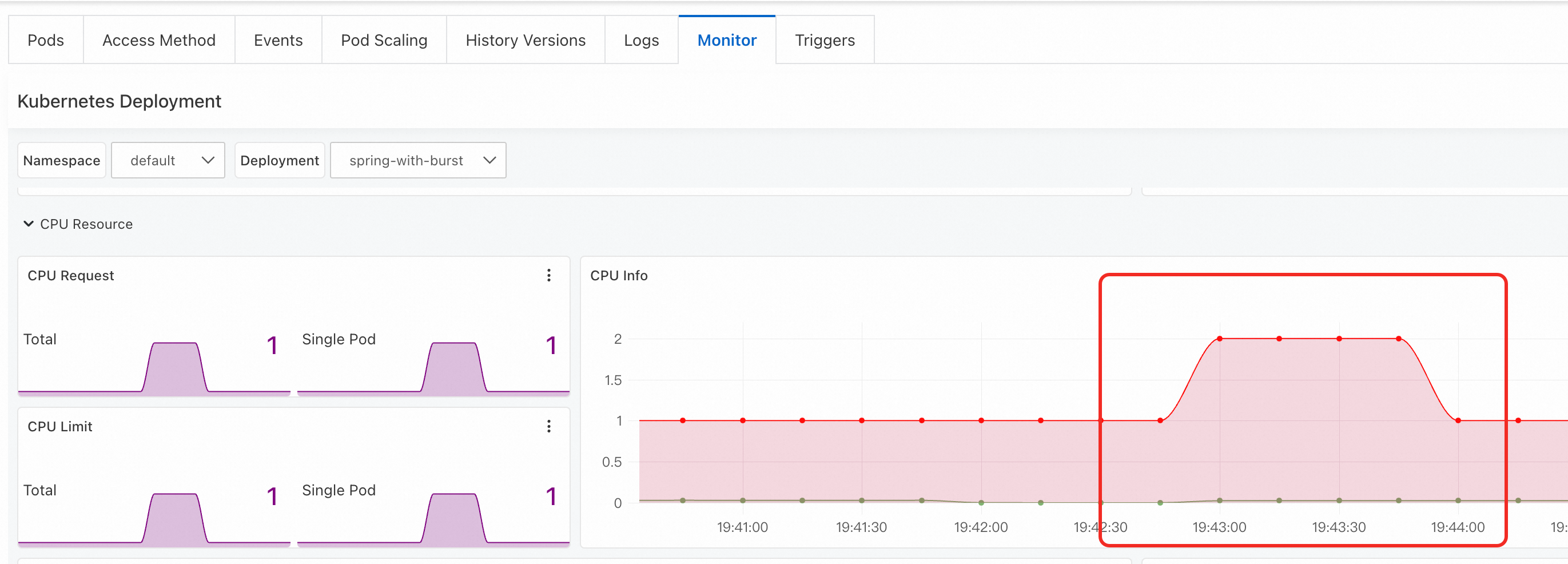
On the Monitor tab, in the CPU Info section, you can observe the change in CPU usage.
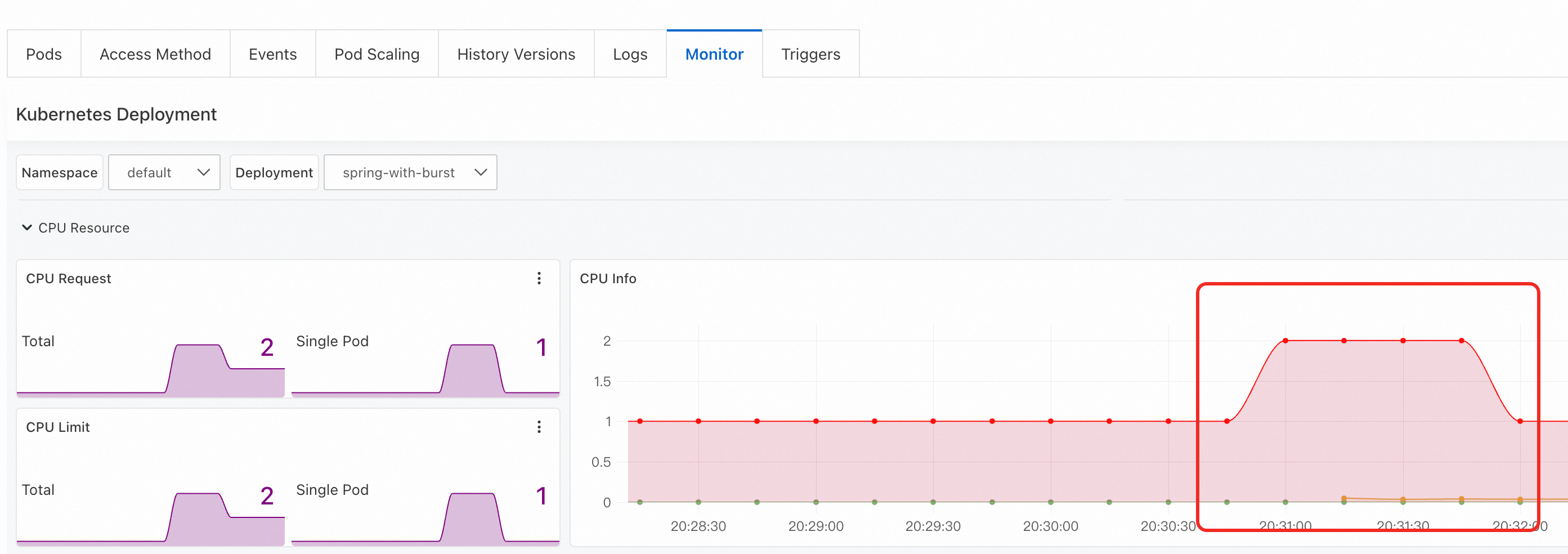
Step 5: Observe the service startup process after the pod container restarts
ack-advanced-vertical-pod-autoscaler 0.0.2 and later versions enable in-place scaling for a pod by default after the pod restarts. You can add the alibabacloud.com/startup-cpu-burst-disable-restart annotation to a pod to explicitly disable this feature.Send a kill signal to Process 1 in the container to simulate a container crash and check whether the corresponding service is accelerated. Replace {POD_NAME} with the actual pod name before you run the command.
kubectl exec -it {POD_NAME} -- kill 1When the container restarts, the pod specification is changed to 2vCpu4G. After the new container is running and a preset delay elapses, the pod specification is automatically downgraded to 1vCpu4Gi.
View pod events.
On the Events tab, select Pod to view details about the upgrade and downgrade. In this example, the event messages are
Starting to resize resource for container: spring cpu: 1 -> 2, memory: 4Gi -> 4GiandStarting to resize resource for container: spring cpu: 2 -> 1, memory: 4Gi -> 4Gi.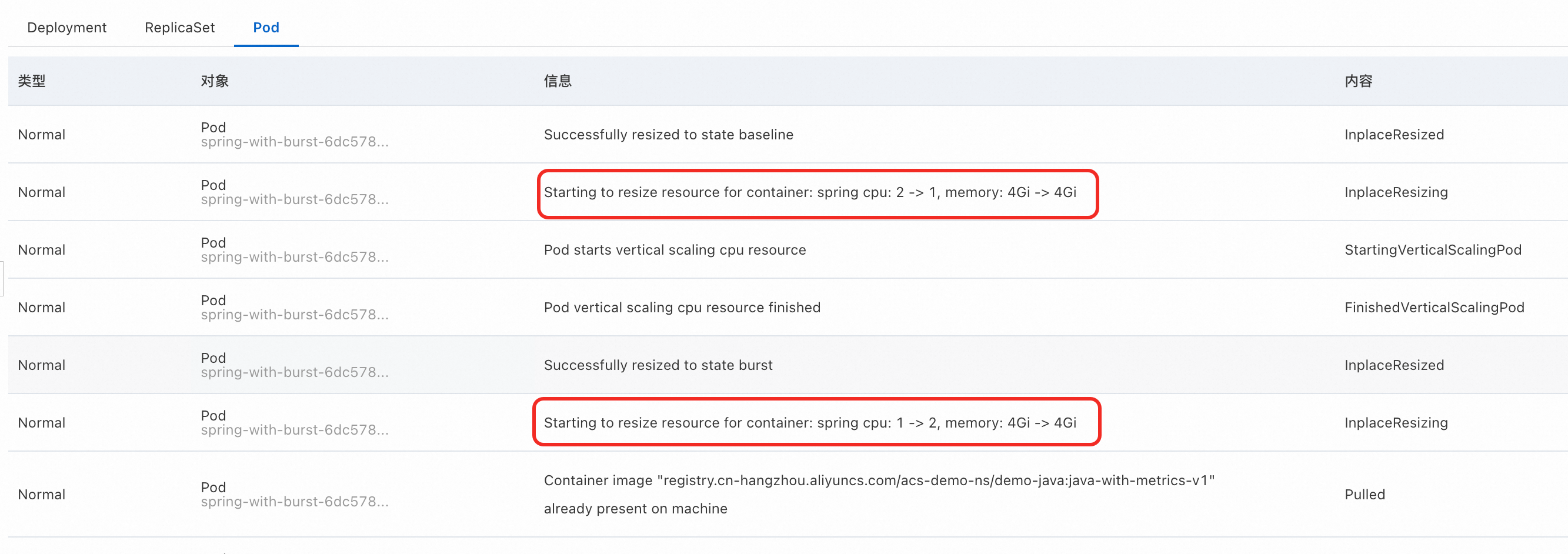
View pod monitoring data.
On the Monitor tab, you can see in the CPU Info section that the CPU usage changes over time.