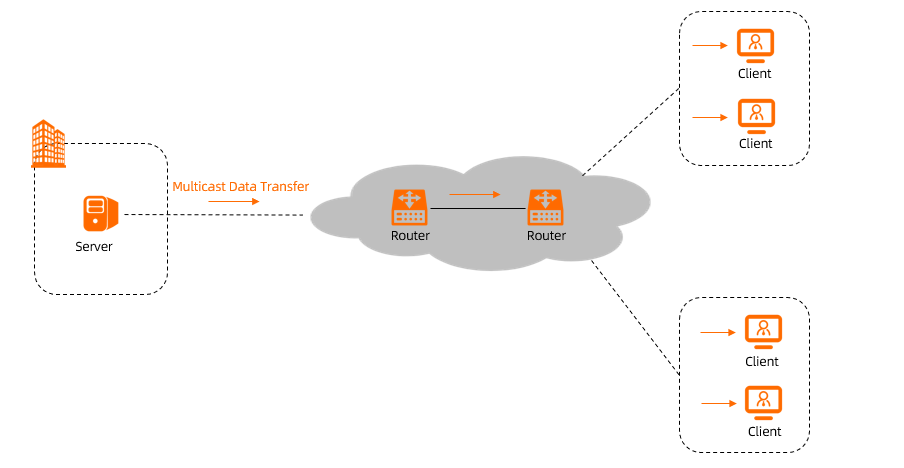
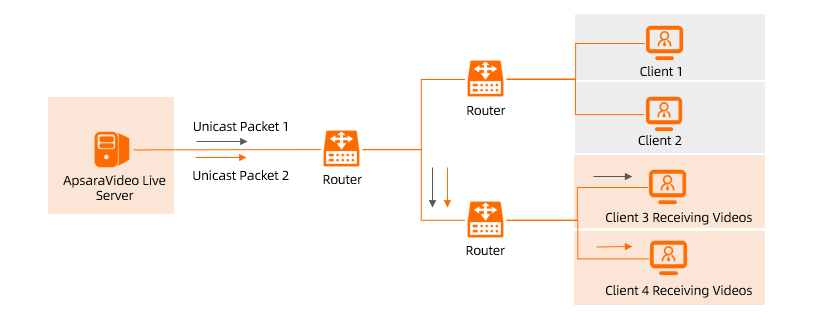
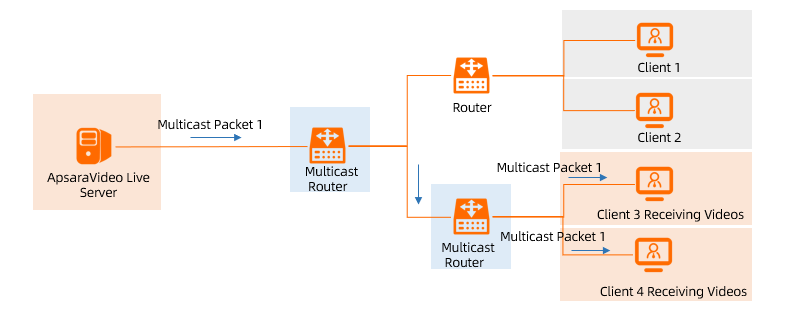
Enterprise Edition transit routers support multicast. After you connect an Enterprise Edition transit router to your network instances, you can create and manage multicast networks. The transit router also forwards multicast traffic between network instances.
Background information
Introduction to multicast features
This section describes the scenarios, advantages, and basic concepts of the multicast feature for Enterprise Edition transit routers.
Scenarios
After you enable the multicast feature for an Enterprise Edition transit router, you can create and manage multicast networks in the following scenarios:
Build a multicast network within a single virtual private cloud (VPC), as shown in Multicast Network 3 in the following figure.
Build a multicast network between different VPCs in the same region, as shown in Multicast Network 2 in the following figure.
Build a multicast network between different VPCs in different regions, as shown in Multicast Network 1 in the following figure.

Advantages
Low cost
The multicast feature for Enterprise Edition transit routers is a cloud-native service from Alibaba Cloud. This feature lets you quickly build multicast networks without purchasing physical devices or third-party software certificates. You can enable the multicast feature as needed and pay for only the resources that you use.
High reliability
Enterprise Edition transit routers support multi-zone disaster recovery. This design prevents a single point of failure and ensures high availability for your multicast network.
Easy maintenance
Enterprise Edition transit routers provide a unified, visual management interface. This simplifies management compared to using the command line. You can manage multicast sources and members without needing to configure multicast routes.
Terms
The following table describes the basic concepts of the multicast feature for Enterprise Edition transit routers.
Term | Description |
Multicast domain | A multicast domain defines the scope of a multicast network within a region. Only resources inside the multicast domain can send or receive multicast traffic. Resources outside the domain cannot. You can create multiple multicast domains for an Enterprise Edition transit router. Multicast domains in the same region are isolated from each other. However, multicast groups that have the same multicast IP address can communicate across different regions. |
Multicast group | In a multicast domain, a multicast group is a set of resources that send and receive the same multicast messages. Each group is identified by a multicast IP address.
|
Multicast source | A multicast source is a resource in a multicast group that sends multicast traffic. |
Multicast member | A multicast member is a resource in a multicast group that receives multicast traffic. |
Networking modes
You can build a multicast network in static mode or using the Internet Group Management Protocol (IGMP).
Static mode: After you create a multicast domain, you can manually create multicast sources and members to build the multicast network.
IGMP mode: After you create a multicast domain, hosts can dynamically join a multicast group using IGMP. This simplifies the deployment and management of the multicast network.
IGMP is a protocol in the TCP/IP protocol suite that manages IPv4 multicast group membership. When a host joins a multicast group using IGMP, the host becomes both a multicast source and a multicast member of the group on the transit router. For more information about how IGMP works on a transit router, see IGMP for transit routers.
For more information about how to create a multicast network, see Create and manage a multicast network.
Billing
When you use the multicast feature of an Enterprise Edition transit router, you are charged connection fees, data processing fees, and inter-region connection fees that vary based on your network scenario. For more information about how connection fees and inter-region connection fees are billed, see Cloud Enterprise Network billing.
The following section describes how data processing fees are calculated for multicast.
Billing rules
Data processing fees are charged on a pay-as-you-go basis. The billing cycle is one hour. If your usage in a billing cycle is less than one hour, you are charged for a full hour.
Data processing fee for multicast = Multicast traffic × Unit price per GBUSD 0.02/GB
Multicast traffic consists of the following two parts:
The total multicast traffic sent from each multicast source to the Enterprise Edition transit router.
The total multicast traffic sent from the Enterprise Edition transit router to each multicast member.
Billing example
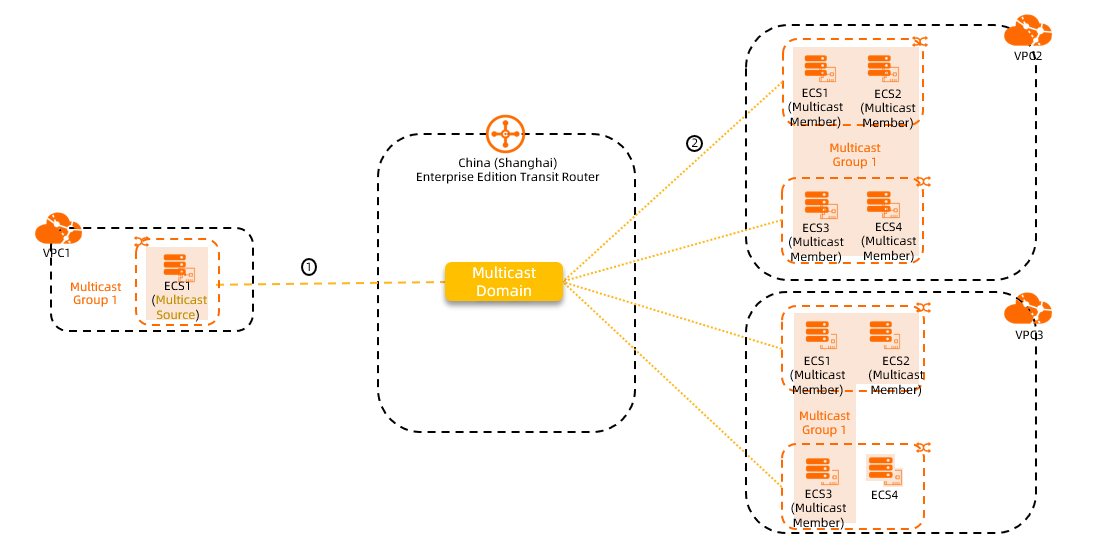
The following example, based on the preceding figure, describes how data processing fees are calculated for multicast. In the figure, the Elastic Computing Service (ECS) instances in VPC1, VPC2, and VPC3 have joined Multicast Group 1. ECS1 in VPC1 is the multicast source, and the ECS instances in VPC2 and VPC3 are the multicast members. When the Enterprise Edition transit router forwards multicast traffic, you are charged for the following two traffic components:
Billable part | Description |
① | The total multicast traffic sent from the multicast source to the Enterprise Edition transit router. |
② | The total multicast traffic sent from the Enterprise Edition transit router to ECS1, ECS2, ECS3, and ECS4 in VPC2, and to ECS1, ECS2, and ECS3 in VPC3. |
Assume that the multicast traffic is 2 GB for part ① and 8 GB for part ②. Then:
Data processing fee = (2 + 8) GB × USD 0.02/GB = USD 0.20
Limits
The multicast feature is available for Enterprise Edition transit routers only in the following regions: China (Hangzhou), China (Shanghai), China (Beijing), China (Ulanqab), China (Shenzhen), China (Chengdu), China (Hohhot), China (Hong Kong), Japan (Tokyo), Singapore, Germany (Frankfurt), UK (London), US (Virginia), US (Silicon Valley), and SAU (Riyadh - Partner Region).
Enterprise Edition transit routers support multicast only for traffic between VPCs.
Elastic network interfaces (ENIs) created by an Enterprise Edition transit router in a VPC cannot be added to a multicast network.
An ENI can be a multicast source and a multicast member in the same multicast group.
Only the primary private IP address of an ENI can be used for multicast communication. Other IP addresses of the ENI do not support multicast.
The following table describes the quota limits on multicast resources.
Resource
Default quota
Request a quota increase
Maximum number of multicast domains that can be created for each transit router
20
Not adjustable
Maximum number of multicast domains that can be associated with each VPC
NoteThe total number of multicast domains associated with all vSwitch instances in a VPC cannot exceed the quota.
20
Maximum number of multicast sources and members for each transit router
2,000
You can use one of the following methods to increase the quota:
Request a quota increase on the Quotas page in the CEN console. For more information, see Manage CEN quotas.
Request a quota increase in the Quota Center console. For more information, see Submit an application to increase a quota.
You can request to increase the quota to 3,000. To request a higher quota, contact your account manager. The maximum quota is 10,000.
Maximum number of multicast members in a multicast group of a transit router
100
Not adjustable
Maximum number of multicast sources in a multicast group of a transit router
100
Maximum number of vSwitches that can be associated with a multicast domain of a transit router
10
Maximum number of inter-region multicast members that can be associated with a multicast group of a transit router
15
Number of multicast groups supported by each multicast domain
20 (Deprecated)
Maximum bandwidth of each multicast group
NoteThe bandwidth refers to the sum of the bandwidth that the multicast sources use to transmit packets to the multicast group and the bandwidth that the multicast group uses to transmit packets to the multicast members.
10 Gbps
You cannot disable the multicast feature after it is enabled. Enabling this feature does not affect your other services.