You can migrate data from ApsaraDB RDS for MySQL or PolarDB for MySQL to ApsaraDB for ClickHouse to perform real-time analysis. This topic describes how to import data from ApsaraDB RDS for MySQL to ApsaraDB for ClickHouse. This example helps you learn how to migrate data with ease.
Prerequisites
A destination ApsaraDB for ClickHouse cluster is created.
NoteIf no ApsaraDB for ClickHouse cluster is created, create a cluster first. For more information, see Create an ApsaraDB for ClickHouse cluster.
A privileged database account is created for the destination cluster. For more information, see Create an account.
The ApsaraDB RDS for MySQL instance and the destination ApsaraDB for ClickHouse cluster reside in the same region and use the same virtual private cloud (VPC). The IP address of the ApsaraDB for ClickHouse cluster is added to the whitelist of the ApsaraDB RDS for MySQL instance. The IP address of the ApsaraDB RDS for MySQL instance is also added to the whitelist of the ApsaraDB for ClickHouse cluster. Otherwise, resolve the network issue first. For more information, see the What do I do if a connection fails to be established between the destination cluster and the data source? section of the FAQ topic.
For more information about how to configure a whitelist for an ApsaraDB for ClickHouse cluster, see Configure a whitelist.
For more information about how to configure a whitelist for an ApsaraDB RDS for MySQL instance, see Configure an IP address whitelist.
NoteYou can execute the
SELECT * FROM system.clusters;statement to query the IP address of the ApsaraDB for ClickHouse cluster.
Step 1: Create a table in the ApsaraDB RDS for MySQL instance and write data to the table
This step involves the operations for creating a database, creating a table, and writing data. If the ApsaraDB RDS for MySQL instance already has relevant data, skip this step.
Connect to the ApsaraDB RDS for MySQL instance by using Data Management (DMS). For more information, see Use DMS to log on to an ApsaraDB RDS for MySQL instance.
Execute the CREATE DATABASE statement to create a database named testdb.
CREATE DATABASE testdb;Execute the CREATE TABLE statement to create the
mysql_test_tabletable in thetestdbdatabase.CREATE TABLE testdb.mysql_test_table ( v1 Int NOT NULL, v2 Int DEFAULT NULL, v3 Float DEFAULT NULL ) ENGINE=InnoDB;Write data to the
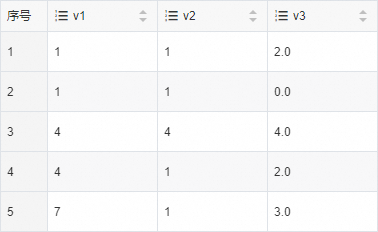
mysql_test_tabletable.INSERT INTO testdb.mysql_test_table VALUES (4,4,4.0),(1,1,2.0),(1,1,0.0),(4,1,2.0),(7,1,3.0);
Step 2: Create a table in ApsaraDB for ClickHouse
Connect to the ApsaraDB for ClickHouse cluster by using DMS. For more information, see Use DMS to connect to an ApsaraDB for ClickHouse cluster.
Execute the CREATE TABLE statement to create a table. In the following example, the
clickhouse_test_tabletable is created in thedefaultdatabase.CREATE TABLE default.clickhouse_test_table ON CLUSTER default ( v1 Int32, v2 Nullable(Int32), v3 Nullable(Float32) ) ENGINE = MergeTree ORDER BY v1;NoteThe data types of a table in ApsaraDB for ClickHouse must be mapped to the data types of a table in ApsaraDB RDS for MySQL. For more information about the mappings, see the Data type mappings section of this topic.
If NOT NULL is not specified for a column in the statement that you use to create a table in the ApsaraDB RDS for MySQL instance, the value of the column can be NULL. The corresponding column in the statement that you use to create a table in ApsaraDB for ClickHouse is identified as Nullable.
(Optional) Create a distributed table named
clickhouse_test_table_distributed.NoteIf your ApsaraDB for ClickHouse cluster is a multi-node cluster, we recommend that you create a distributed table. Distributed tables use the storage and computing resources of each server in the ApsaraDB for ClickHouse cluster to implement the efficient execution of data write and query operations. Distributed tables not only support excellent horizontal scalability but also ensure high performance and high availability.
CREATE TABLE clickhouse_test_table_distributed ON CLUSTER default AS clickhouse_test_table ENGINE = Distributed(default, default, clickhouse_test_table, rand());
Step 3: Read data from the ApsaraDB RDS for MySQL instance and write data to the ApsaraDB for ClickHouse cluster
Connect to the ApsaraDB for ClickHouse cluster by using DMS and execute the migration statement. For more information, see Use DMS to connect to an ApsaraDB for ClickHouse cluster.
Syntax:
INSERT INTO <Name of the table in ApsaraDB for ClickHouse> select * from mysql('<Endpoint of the ApsaraDB RDS for MySQL instance>:<Port>', '<ApsaraDB RDS for MySQL database name>','<Name of the table in the ApsaraDB RDS for MySQL instance>', '<Database account of ApsaraDB RDS for MySQL>', '<Password of the database account of ApsaraDB RDS for MySQL>')For more information about how to obtain the endpoint and port of the ApsaraDB RDS for MySQL instance, see View and manage instance endpoints and ports.
Example:
INSERT INTO clickhouse_test_table_distributed SELECT * FROM mysql('rm-bp16t9h3999xb****.mysql.rds.aliyuncs.com:3306','testdb','mysql_test_table','test','123456Aa');Step 4: Query the data imported to the ApsaraDB for ClickHouse cluster
Query the data imported to the ApsaraDB for ClickHouse cluster. Enter the following query statement and click Execute(F8) to check whether the data is imported:
SELECT * FROM clickhouse_test_table_distributed;NoteIf you import data to a local table, replace the name of the distributed table
clickhouse_test_table_distributedin the query statement with the name of the local tableclickhouse_test_table, and execute the query statement.The following query result is returned:
Data type mappings
Data type in ApsaraDB RDS for MySQL or PolarDB for MySQL | Data type in ApsaraDB for ClickHouse |
Unsigned tinyint | UInt8 |
Tinyint | Int8 |
Unsigned smallint | UInt16 |
Smallint | Int16 |
Unsigned int and Unsigned mediumint | UInt32 |
Int and Mediumint | Int32 |
Unsigned bigint | UInt64 |
Bigint | Int64 |
Float | Float32 |
Double | Float64 |
Date | Date |
Datetime and Timestamp | DateTime |
Binary | FixedString |
Others | String |