Tair DRAM-based instances are suitable for scenarios that involve highly concurrent read and write operations on hot data and require higher performance than what Redis Open-Source Edition instances can provide. Compared with Redis Open-Source Edition instances, DRAM-based instances offer more benefits, including enhanced multi-threading performance and integration of multiple extended data structures.
Benefits
Item | Description |
Compatibility | DRAM-based instances are fully compatible with native Redis, requiring no changes to business code. They offer compatibility with Redis 7.0, Redis 6.0, and Redis 5.0. |
Performance |
|
Synchronization mode | The semi-synchronous replication mode is additionally supported. In this mode, after an update initiated by the client is executed on the master node, the master node will replicate the logs to a replica node. A response is returned to the client only after the replica node confirms receipt of the logs. This ensures that no data is lost during high availability switchovers. |
Deployment architectures | DRAM-based instances support the standard, cluster, and read/write splitting architectures. |
Data Structure Module Integration | DRAM-based instances integrate multiple in-house Tair modules to expand the applicable scope of Tair. These modules include exString (including commands that enhance Redis string functionality), exHash, exZset, GIS, Bloom, Doc, TS, Cpc, Roaring, Search, and Vector. These modules remove your worries about storage structures and timeliness and allow you to focus on your application development. |
Enterprise-grade features | DRAM-based instances support several enterprise-grade features, such as data flashback, proxy query cache, and Global Distributed Cache. For more information, see Use data flashback to restore data by point in time, Use proxy query cache to address issues caused by hotkeys, and Global Distributed Cache. |
Data security |
|
Scenarios
Tair DRAM-based instances are suitable for scenarios such as live streaming, flash sales, and online education. The following section describes typical scenarios:
Scenario 1: During flash sales, the QPS on some cached hotkeys may exceed 200,000. Redis Open-Source Edition instances cannot meet this requirement.
Standard DRAM-based instances can efficiently handle requests during flash sales without performance issues.
Scenario 2: Redis Open-Source Edition cluster instances have limits on database transactions and Lua scripts.
DRAM-based instances provide high performance and eliminate the limits on the usage of commands in Redis Open-Source Edition cluster instances.
Scenario 3: You have created a self-managed Redis cluster that consists of one master node and multiple replica nodes. The number of replica nodes and O&M costs increase as your workloads increase.
DRAM-based instances that use the read/write splitting architecture can provide one data node and up to five read replicas to help you handle millions of QPS.
Scenario 4: You have created a self-managed Redis cluster to handle tens of millions of QPS. The number of data shards and O&M costs increase as your workloads increase.
DRAM-based cluster instances can downsize clusters by two thirds and significantly reduce O&M costs.
Comparison between threading models
Threading architecture | Description |
Figure 1. Redis single-threaded model | Redis Open-Source Edition and native Redis use a single-threaded model. The data processing flow is as follows: read requests, parse requests, process data, and send responses. In this situation, network I/O operations and request parsing consume most of available resources. |
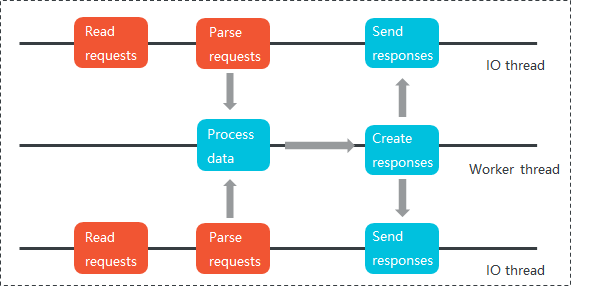
Figure 2. Tair multi-threading model | Tair DRAM-based instances separate tasks at different service stages and use multiple threads with clear division of labor to process tasks in parallel, thereby improving performance.
Each DRAM-based instance reads and parses requests in I/O threads, places the parsed requests as commands in a queue, and then sends these commands to worker threads. Then, the worker threads run the commands to process the requests and send the responses to I/O threads using a different queue. Tair DRAM-based instances support up to four I/O threads running concurrently. Unlocked queues and pipelines are used to transmit data between I/O threads and worker threads to improve multi-threading performance. Note
|
Unlike Redis 6.0 multi-threading (which improves performance by up to 2 times but consumes high CPU resources), the Real Multi-IO of DRAM-based instances can thoroughly accelerate I/O and command execution, providing greater resistance to connection impacts and linearly increasing throughput capacity.
Performance comparison
Redis Open-Source Edition instances use the same single-threading model as native Redis databases. In the single-threading model, each data node supports 80,000 to 100,000 QPS. Tair DRAM-based instances use a multi-threaded model, which allows the I/O, worker, and auxiliary threads to process requests in parallel. Each data node of a DRAM-based instance delivers performance that is approximately three times that delivered by each data node of a Redis Open-Source Edition instance. The following table describes the comparison between Redis Open-Source Edition instances and Tair DRAM-based instances of different architectures and their use cases.
Architecture | Redis Open-Source Edition instances | Tair DRAM-based instances |
Standard architecture | These instances are not suitable if the QPS that is required on a single node exceeds 100,000. | These instances are suitable if the QPS that is required on a single node exceeds 100,000. |
Cluster architecture | A cluster instance consists of multiple data nodes. Each data node provides performance that is similar to that of a standard instance. If a data node stores hot data and receives a large number of concurrent requests for the hot data, the read and write operations on other data that is stored on the data node may be affected. As a result, the performance of the data node deteriorates. | These instances provide high performance to read and write hot data at reduced maintenance costs. |
Read/write splitting architecture | These instances provide high read performance and are suitable for scenarios in which the number of read operations is greater than the number of write operations. However, these instances cannot support a large number of concurrent write operations. | These instances provide high read performance and can support a large number of concurrent write operations. These instances are suitable for scenarios in which a large number of write operations need to be processed but the number of read operations is greater than the number of write operations. |
Integration of multiple Redis modules
Similar to open source Redis, Redis Open-Source Edition supports a variety of data structures such as String, List, Hash, Set, Sorted Set, and Stream. These data structures are sufficient to support common development workloads but not sophisticated workloads. To manage sophisticated workloads, you must modify your application data or run Lua scripts.
DRAM-based instances integrate multiple in-house Tair modules to expand the applicable scope of Tair. These modules include exString (including commands that enhance Redis string functionality), exHash, exZset, GIS, Bloom, Doc, TS, Cpc, Roaring, Search, and Vector. These modules simplify business development in complex scenarios and allow you to focus on your business innovation.
DRAM-based instances that are compatible with Redis 7.0 or 6.0 support all the preceding data structures.
DRAM-based instances that are compatible with Redis 5.0 support all the preceding data structures other than TairVector.
Enterprise-grade features
Enterprise-grade feature | Description |
After you enable the data flashback feature for a Tair instance, Tair retains append-only file (AOF) backup data for up to seven days. During the retention period, you can specify a point in time that is accurate to the second to create an instance and restore the backup data at the specified point in time to the new instance. | |
After you enable the proxy query cache feature, the configured proxy nodes cache requests and responses for hotkeys. If the same requests are received from a client within a specific validity period, Tair retrieves the responses to the requests from the cache and returns the responses to the client. During this process, Tair does not need to interact with backend data shards. For more information, see Use proxy query cache to address issues caused by hotkeys. | |
Global Distributed Cache for Tair is an active geo-redundancy database system that is developed based on Redis Open-Source Edition. Global Distributed Cache supports business scenarios in which multiple sites in different regions provide services at the same time. It helps enterprises replicate the active geo-redundancy architecture of Alibaba. | |
Two-way data synchronization using DTS | Data Transmission Service (DTS) supports two-way data synchronization between Tair instances. This synchronization solution is suitable for scenarios such as active geo-redundancy and geo-disaster recovery. For more information, see Configure two-way data synchronization between Tair instances. |
FAQ
Q: What do I do if a client does not support the commands that are provided by new modules?
A: You can define the commands from the new data module in your application code before you use the commands in your client. You can also use a client that provides built-in support for these commands. For more information, see Clients.