ApsaraDB for MongoDB automatically creates replica set instances. You can manage the primary node and secondary nodes of a replica set instance. Replica set instances provide advanced features such as disaster recovery and failover. When you use replica set instances, these advanced features are enabled by default.
Architecture
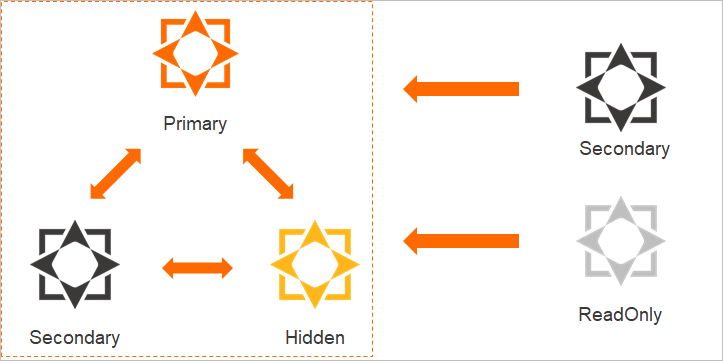
ApsaraDB for MongoDB uses a multi-node architecture to ensure high availability. A replica set instance consists of a primary node, one or more secondary nodes, a hidden node, and one or more optional read-only nodes. The primary and secondary nodes term covers primary, secondary, and hidden nodes. The following table describes these nodes.
Node | Feature | Description |
Primary node | A primary node processes read and write requests. | Each replica set instance can have only one primary node. |
Secondary node | A secondary node uses oplogs to synchronize data from the primary node. If the primary node fails, a secondary node can be elected as the new primary node to ensure high availability. |
|
Hidden node | A hidden node uses oplogs to synchronize data from the primary node. If a secondary or read-only node fails, the hidden node can be elected as a new secondary or read-only node to ensure high availability. |
|
Read-only node | A read-only node uses oplogs to synchronize data from the primary or secondary node that has the lowest latency. Read-only nodes can be used to relieve read pressure on the primary and secondary nodes in business scenarios where a large number of read requests exist. If a replica set instance has two or more read-only nodes, you can use a read-only connection string URI to connect to these nodes to balance read loads. Note For more information, see Read-only nodes. |
|
Scale out a replica set instance
ApsaraDB for MongoDB allows you to add more nodes to an instance. You can increase the number of secondary nodes or read-only nodes based on your business needs. For more information, see Change the configurations of a replica set instance.
Each replica set instance contains only one hidden node. More secondary and read-only nodes can be added to a replica set instance, whereas the number of hidden nodes cannot be increased.
For example, assume that you run websites that provide online reading services or run systems that provide order queries. These websites and systems process a large number of read operations and a small number of write operations. In addition, the number of operations on these websites or systems may surge due to impromptu events. In these scenarios, you can add or remove secondary or read-only nodes to adjust the read capability of your replica set instance.