The Elastic Algorithm Service (EAS) module of Platform for AI (PAI) provides simplified deployment methods for different scenarios. You can configure parameters to deploy a Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG)-based large language model (LLM) chatbot. This significantly shortens the service deployment time. When you use the chatbot to perform model inference, the chatbot effectively retrieves relevant information from the knowledge base and combines the retrieved information with answers from LLM applications to provide accurate and informative answers. This significantly improves the quality of Q&A and overall performance. The chatbot is suitable for Q&A, summarization, and other natural language processing (NLP) tasks that rely on specific knowledge bases. This topic describes how to deploy a RAG-based LLM chatbot by building a vector database in an ApsaraDB RDS for PostgreSQL instance. This topic also describes how to perform model inference.
Background information
LLM applications have limits in generating accurate and real-time responses. Therefore, LLM applications are not suitable for scenarios that require precise information, such as the customer service or Q&A scenario. To resolve these issues, the RAG technique is used to enhance the performance of LLM applications. This significantly improves the quality of Q&A, summarization, and other NLP tasks that rely on specific knowledge bases.
RAG improves the answer accuracy and increases the amount of information about answers by combining LLM applications such as Tongyi Qianwen with information retrieval components. When a query is initiated, RAG uses an information retrieval component to find documents or information fragments related to the query in the knowledge base, and integrates these retrieved contents with the original query into an LLM application. The LLM application uses its induction and generation capabilities to generate factual answers based on the latest information. You do not need to retrain the LLM application.
The chatbot that is deployed in EAS integrates LLM applications with RAG to overcome the limits of LLM applications in terms of accuracy and timeliness. This chatbot provides accurate and informative answers in various Q&A scenarios and helps improve the overall performance and user experience of NLP tasks.
Prerequisites
A virtual private cloud (VPC), vSwitch, and security group are created. For more information, see Create and manage a VPC and Create a security group.
An Object Storage Service (OSS) bucket or File Storage NAS (NAS) file system is created to store fine-tuned model files. This prerequisite must be met if you use a fine-tuned model to deploy the chatbot. For more information, see Get started by using the OSS console or Create a file system.
NoteIf you use Faiss to build a vector database, you must prepare an OSS bucket.
Limits
The ApsaraDB RDS for PostgreSQL instance and EAS must reside in the same region.
Usage notes
This practice is subject to the maximum number of tokens of an LLM service and is designed to help you understand the basic retrieval feature of a RAG-based LLM chatbot.
The chatbot is limited by the server resource size of the LLM service and the default number of tokens. The conversation length supported by the chatbot is also limited.
If you do not need to perform multiple rounds of conversations, we recommended that you disable the with chat history feature of the chatbot. This effectively reduces the possibility of reaching the limit. For more information, see the How do I disable the with chat history feature of the RAG-based chatbot? section of this topic.
Step 1: Build a vector database in an RDS instance
RAG allows you to build a vector database in an RDS instance. When you build a vector database, you must save the required parameter configurations that are used to connect to the vector database in subsequent operations.
Create an RDS instance. For more information, see Create an instance.
We recommend that the RDS instance resides in the same region as the RAG-based LLM chatbot to enable communications over a VPC.
Create an account and a database for the RDS instance. For more information, see Create a database and an account.
When you create an account, select Privileged Account for Account Type.
When you create a database, select the created privileged account from the Authorized By drop-down list.
Configure the database connection.
Go to the Instances page. In the top navigation bar, select the region in which the RDS instance resides. Then, find the RDS instance and click the ID of the instance.
In the left-side navigation pane, click Database Connection.
On the Database Connection page, view the endpoints and port of the database.
Add pg_jieba to Running Parameter Value of the shared_preload_libraries parameter. For example, change Running Parameter Value to
'pg_stat_statements,auto_explain,pg_cron'. For more information, see Modify the parameters of an ApsaraDB RDS for PostgreSQL instance.NoteApsaraDB RDS for PostgreSQL uses the pg_jieba extension to segment Chinese text. You can use this extension for keyword-based retrieval and recall. For more information, see Use the pg_jieba extension.
Step 2: Deploy the RAG-based chatbot
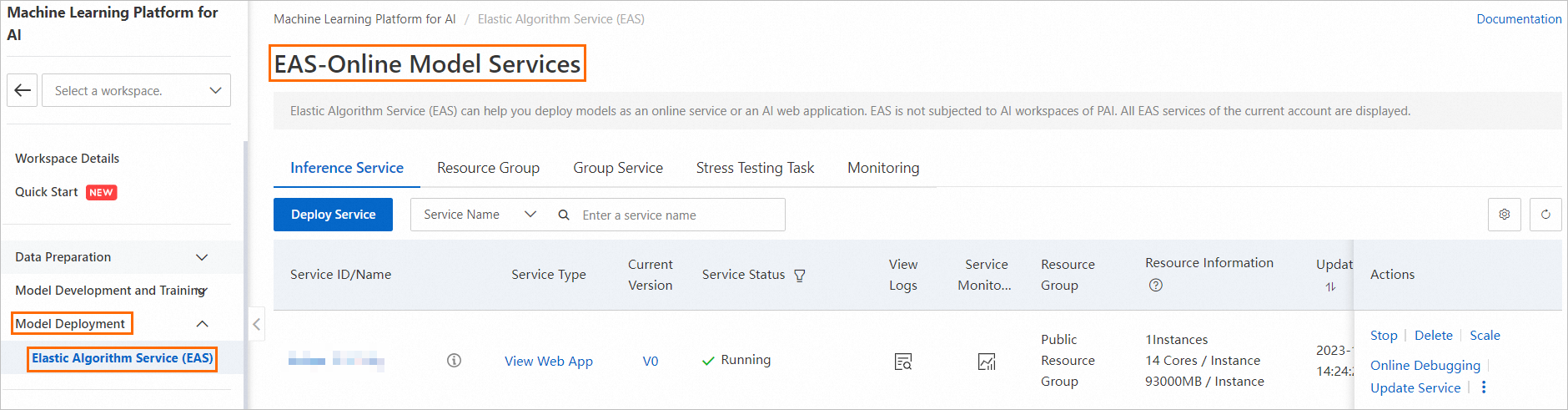
Go to the EAS page.
Log on to the Platform for AI (PAI) console.
In the left-side navigation pane, click Workspaces. On the Workspaces page, find the workspace to which you want to deploy the model and click its name to go to the Workspace Details page.
If no workspaces are available, you must create one. For more information, see Create a workspace.
In the left-side navigation pane, choose Model Deployment > Elastic Algorithm Service (EAS) to go to the Elastic Algorithm Service (EAS) page.
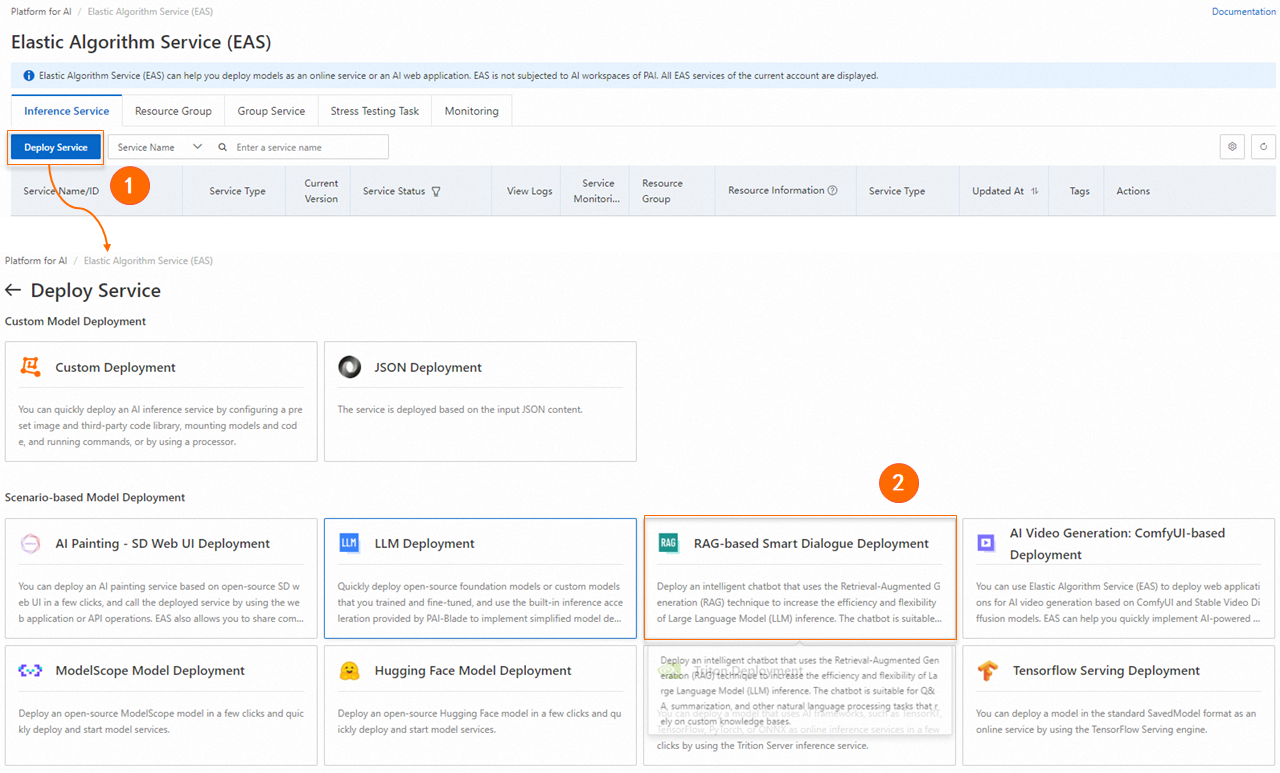
On the Elastic Algorithm Service (EAS) page, click Deploy Service. In the Scenario-based Model Deployment section, click RAG-based Smart Dialogue Deployment.
On the RAG-based LLM Chatbot Deployment page, configure the parameters. The following tables describe the key parameters in different sections.
Basic Information
Parameter
Description
Service Name
The name of the service.
Model Source
The source of the model. Valid values: Open Source Model and Custom Fine-tuned Model.
Model Type
The model type. You can select a model type based on your business requirements.
If you set Model Source to Custom Fine-tuned Model, you must configure the parameter quantity and precision for the model type.
Model Settings
If you set Model Source to Custom Fine-tuned Model, you must configure the path in which the fine-tuned model file is stored. Valid values:
NoteMake sure that the model file format is compatible with Hugging Face transformers.
Mount OSS: Select the OSS path in which the fine-tuned model file is stored.
Mount NAS: Select the NAS file system in which the fine-tuned model file is stored and the source path of the NAS file system.
Resource Configuration
Parameter
Description
Resource Configuration
If you set Model Source to Open Source Model, the system automatically selects an instance type based on the selected model type as the default value.
If you set Model Source to Custom Fine-tuned Model, you need to select an instance type that matches the model. For more information, see Deploy LLM applications in EAS.
Inference Acceleration
Inference acceleration can be enabled for the Qwen, Llama2, ChatGLM, or Baichuan2 model that is deployed on A10 or GU30 instances. The following inference acceleration methods are provided:
BladeLLM Inference Acceleration: The BladeLLM inference acceleration engine ensures high concurrency and low latency. You can use BladeLLM to accelerate LLM inference in a cost-effective manner.
Open-source vLLM Inference Acceleration
Vector Database Settings
Parameter
Description
Vector Database Type
The engine type of the vector database. Select RDS PostgreSQL.
Host Address
The internal endpoint or public endpoint of the RDS instance.
Internal endpoint: If the RAG application and the database reside in the same region, you can use the internal endpoint to connect the RAG application to your RDS instance.
Public endpoint: If the RAG application and the database reside in the different regions, you must apply for a public endpoint for your RDS instance. For more information, see Apply for or release a public endpoint.
Port
The port number. Default value: 5432.
Database
The name of the database that you create in the RDS instance.
Table Name
The name of a new or an existing table. If you enter the name of an existing table, the table schema must meet the requirements of the RAG-based LLM chatbot. For example, you can enter the name of the table that is automatically created when you deploy the RAG-based LLM chatbot by using EAS.
Account
The privileged account of the RDS instance
Password
The password of the privileged account.
VPC Configuration
Parameter
Description
VPC
If the host address is an internal endpoint, you must select the VPC of the RDS instance for the RAG-based LLM chatbot.
If the host address is a public endpoint, you must configure a VPC and vSwitch for the RAG-based LLM chatbot and create a NAT gateway and an elastic IP address (EIP) for the VPC. This enables the RAG-based LLM chatbot to be accessible over the Internet. You must add the EIP to the IP address whitelist of the RDS instance. For more information, see Use the SNAT feature of an Internet NAT gateway to access the Internet and Configure an IP address whitelist.
vSwitch
Security Group Name
The security group.
ImportantDo not use the security group named created_by_rds because this security group is used only for system access control.
Click Deploy.
If the value in the Service Status column changes to Running, the RAG-based chatbot is deployed.
Step 3: Perform model inference on the web UI
This section describes how to debug the RAG-based chatbot on the web UI. After you test the Q&A performance of the RAG-based chatbot on the web UI, you can call API operations provided by Platform for AI (PAI) to apply the RAG-based chatbot to your business system. For more information, see Step 4: Call API operations to perform model inference in this topic.
1. Configure the RAG-based chatbot
After you deploy the RAG-based chatbot, click View Web App in the Service Type column to enter the web UI.
Configure the machine learning model.
Embedding Model Name: Four models are available. By default, the optimal model is selected.
Embedding Dimension: After you configure the Embedding Model Name parameter, the system automatically configures this parameter.
Check whether the vector database is connected.
The system automatically recognizes and applies the vector database settings that are configured when you deploy the chatbot. The settings cannot be modified. Click Connect PostgreSQL to check whether the vector database on the RDS instance is connected.
2. Upload specified business data files
On the Upload tab, upload your business data files. You can upload files in the following formats: TXT, PDF, XLSX, XLS, CSV, DOCX, DOC, Markdown, and HTML.
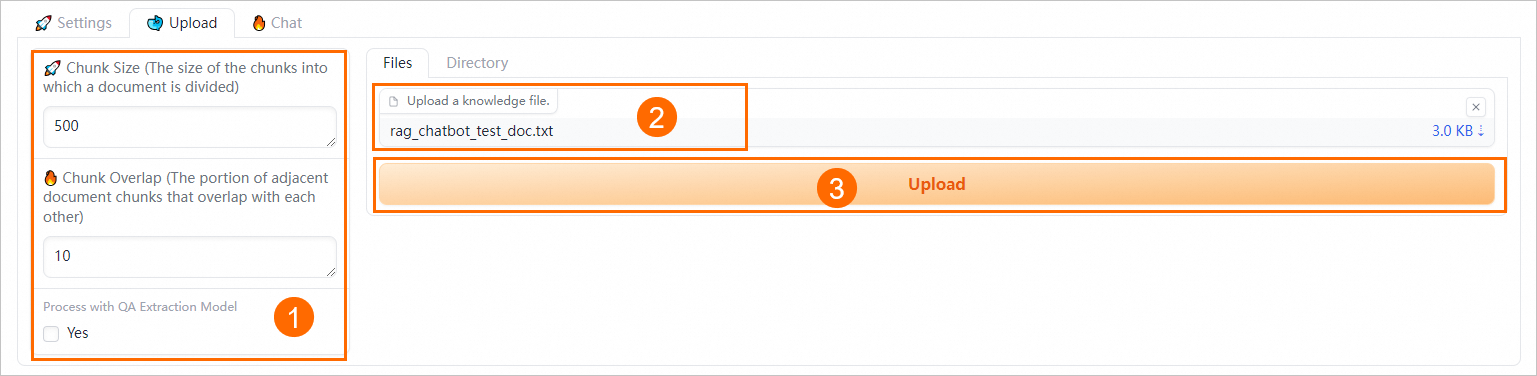
Configure semantic-based chunking parameters.
Configure the following parameters to control the granularity of document chunking and enable automatic Q&A extraction.
Parameter
Description
Chunk Size
The size of each chunk. Unit: bytes. Default value: 500.
Chunk Overlap
The portion of overlap between adjacent chunks. Default value: 10.
Process with QA Extraction Model
Specifies whether to extract Q&A information. If you select Yes, the system automatically extracts questions and corresponding answers in pairs after business data files are uploaded. This way, more accurate answers are returned in data queries.
On the Files tab, upload one or more business data files. You can also upload a directory that contains the business data files on the Directory tab. For example, you can upload the rag_chatbot_test_doc.txt file.
The system performs data cleansing and semantic-based chunking on the business data files before uploading the business data files. Data cleansing includes text extraction and hyperlink replacement.
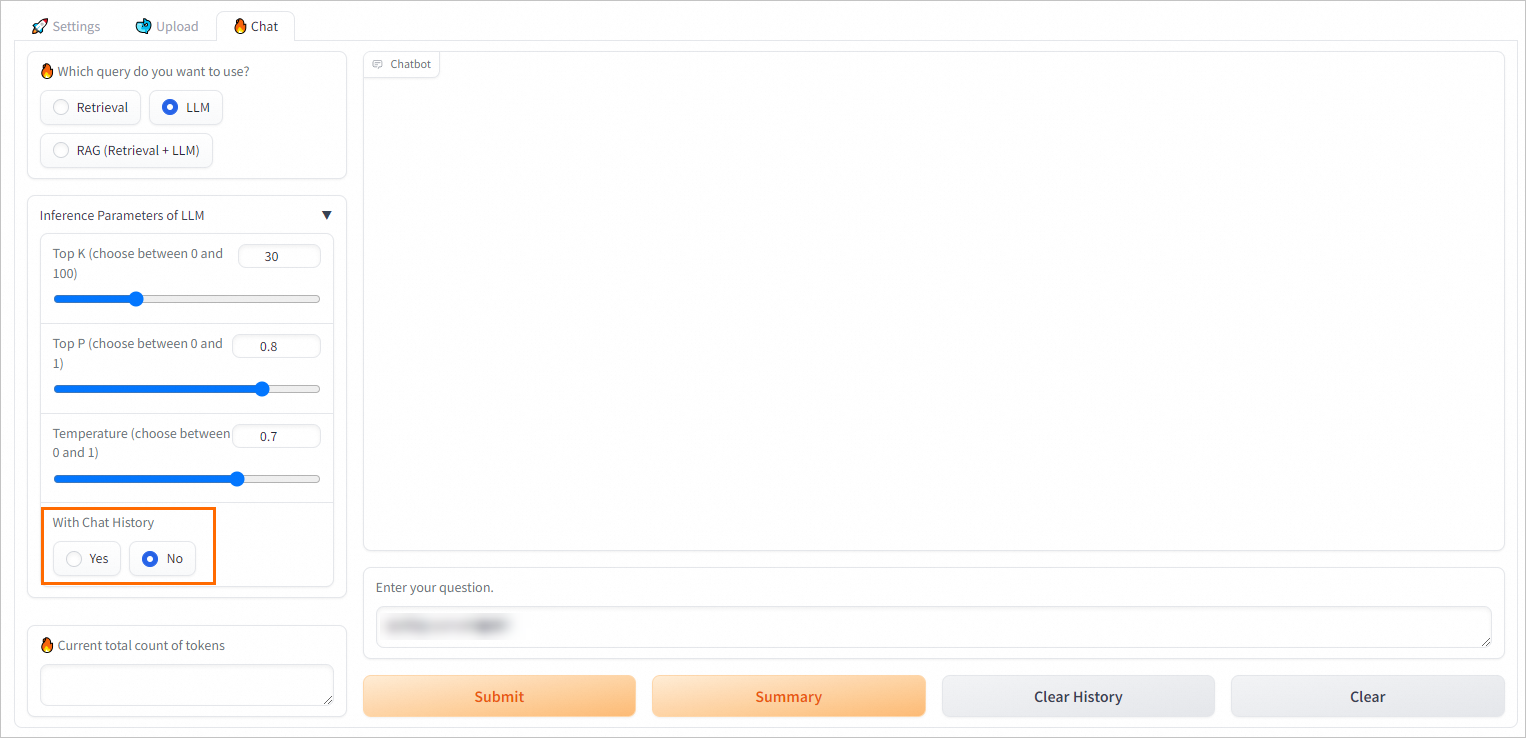
3. Configure model inference parameters
On the Chat tab, configure Q&A policies.
Configure Q&A policies for retrieval-based queries
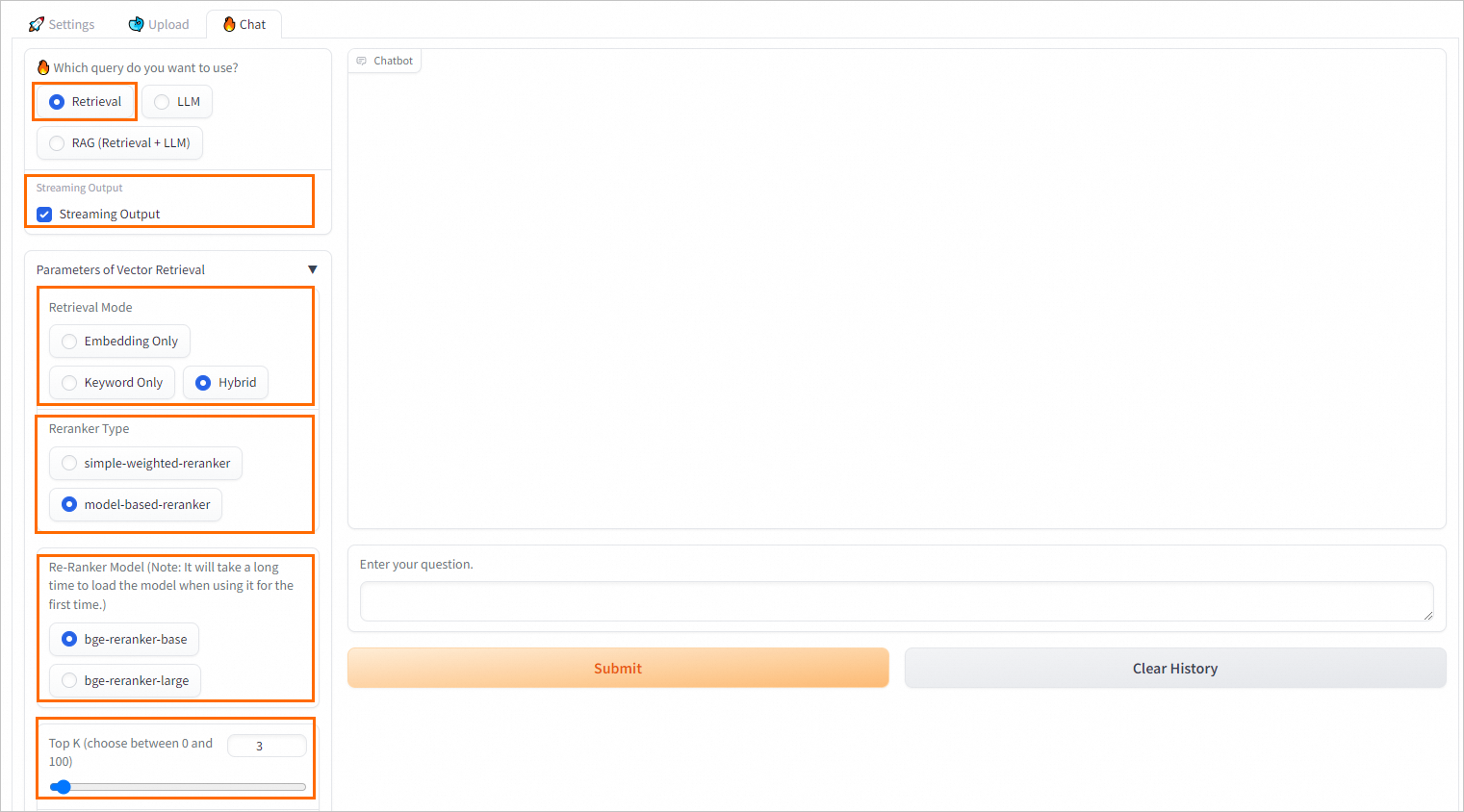
Parameter | Description |
Streaming Output | Specifies whether to return results in streaming mode. If you select Streaming Output, the results are returned in streaming mode. |
Retrieval Model | The retrieval method. Valid values:
Note In most complex scenarios, vector database-based retrieval delivers better performance. However, in some vertical fields in which corpora are scarce or in scenarios in which accurate matching is required, vector database-based retrieval may not achieve the same effectiveness as the traditional retrieval based on sparse and dense vectors. Retrieval based on sparse and dense vectors calculates the keyword overlap between user queries and knowledge files and is simpler and more efficient. ApsaraDB RDS for PostgreSQL uses the pg_jieba extension to segment Chinese text. You can use this extension for keyword-based retrieval and recall. For more information, see Use the pg_jieba extension. |
Reranker Type | Most vector databases compromise data accuracy to provide high computing efficiency. As a result, the top K results that are returned from the vector database may not be the most relevant. In this case, you can use the simple-weighted-reranker or model-based-reranker model to perform a higher-precision re-rank operation on the top K results that are returned from the vector database to obtain more relevant and accurate knowledge files. Note If you use a model for the first time, you may need to wait for a period of time before the model is loaded. |
Top K | The number of the most relevant results that are returned from the vector database. |
Similarity Score Threshold | The similarity threshold. A larger value indicates a higher similarity. |
Configure Q&A policies for RAG-based queries (retrieval + LLM)
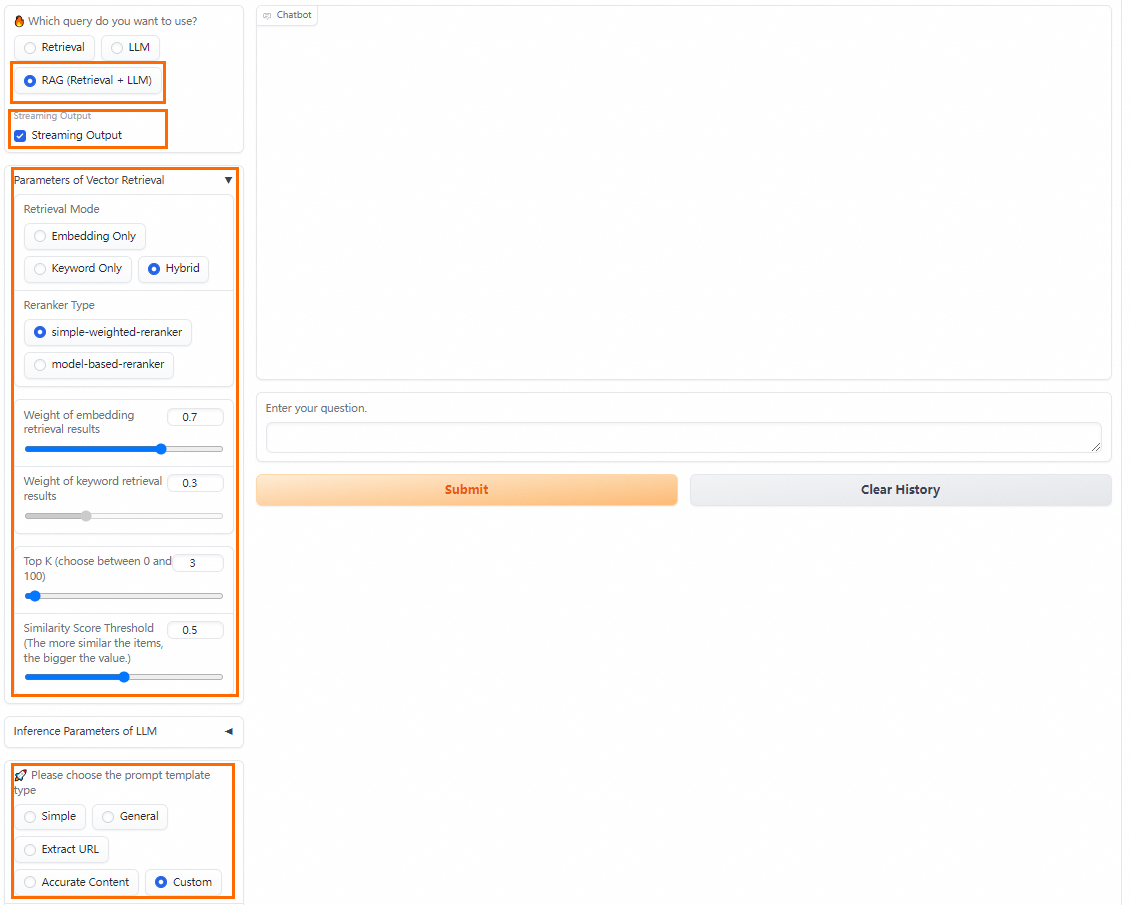
PAI provides various prompt policies. You can select a predefined prompt template or specify a custom prompt template for better inference results.
You can configure the following parameters in RAG (retrieval + LLM) query mode: Streaming Output, Retrieval Mode, and Reranker Type. For more information, see RAG-based LLM chatbot.
4. Perform model inference
Retrieval
The chatbot returns the top K relevant results from the vector database.
LLM
The chatbot uses only the LLM application to generate an answer.
RAG (retrieval + LLM)
The chatbot enters the results returned from the vector database and the query into the selected prompt template and sends the template to the LLM application to provide an answer.
Step 4: Call API operations to perform model inference
Obtain the invocation information of the RAG-based chatbot.
Click the name of the RAG-based chatbot to go to the Service Details page.
In the Basic Information section, click View Endpoint Information.
On the Public Endpoint tab of the Invocation Method dialogue box, obtain the service endpoint and token.
Connect to the vector database through the WebUI and upload knowledge base files.
You can also upload knowledge base to the vector base based on the structure of a generated table, which conforms to the PAI-RAG format.
Call the service through APIs.
PAI allows you to call the RAG-based chatbot by using the following API operations in different query modes:
service/query/retrievalin retrieval mode,service/query/llmin LLM mode, andservice/queryin RAG mode. Sample code:cURL command
Initiate a single-round conversation request
Method 1: Call the
service/query/retrievaloperation.curl -X 'POST' '<service_url>service/query/retrieval' -H 'Authorization: <service_token>' -H 'accept: application/json' -H 'Content-Type: application/json' -d '{"question": "What is PAI?"}' # Replace <service_url> and <service_token> with the service endpoint and service token that you obtained in Step 1.Method 2: Call the
/service/query/llmoperation.curl -X 'POST' '<service_url>service/query/llm' -H 'Authorization: <service_token>' -H 'accept: application/json' -H 'Content-Type: application/json' -d '{"question": "What is PAI?"}' # Replace <service_url> and <service_token> with the service endpoint and service token that you obtained in Step 1.You can add other adjustable inference parameters such as
{"question":"What is PAI?", "temperature": 0.9}.Method 3: Call the
service/queryoperation.curl -X 'POST' '<service_url>service/query' -H 'Authorization: <service_token>' -H 'accept: application/json' -H 'Content-Type: application/json' -d '{"question": "What is PAI?"}' # Replace <service_url> and <service_token> with the service endpoint and service token that you obtained in Step 1.You can add other adjustable inference parameters such as
{"question":"What is PAI?", "temperature": 0.9}.
Initiate a multi-round conversational search request
You can initiate a multi-round conversational search request only in RAG and LLM query modes. The following sample code shows an example on how to initiate a multi-round conversational search request in RAG query mode:
# Send the request. curl -X 'POST' '<service_url>service/query' -H 'Authorization: <service_token>' -H 'accept: application/json' -H 'Content-Type: application/json' -d '{"question": "What is PAI?"}' # Provide the session ID returned for the request. This ID uniquely identifies a conversation in the conversation history. After the session ID is provided, the corresponding conversation is stored and is automatically included in subsequent requests to call an LLM. curl -X 'POST' '<service_url>service/query' -H 'Authorization: <service_token>' -H 'accept: application/json' -H 'Content-Type: application/json' -d '{"question": "What are the benefits of PAI?","session_id": "ed7a80e2e20442eab****"}' # Provide the chat_history parameter, which contains the conversation history between you and the chatbot. The parameter value is a list in which each element indicates a single round of conversation in the {"user":"Inputs","bot":"Outputs"} format. Multiple conversations are sorted in chronological order. curl -X 'POST' '<service_url>service/query' -H 'Authorization: <service_token>' -H 'accept: application/json' -H 'Content-Type: application/json' -d '{"question":"What are the features of PAI?", "chat_history": [{"user":"What is PAI", "bot":"PAI is an AI platform provided by Alibaba Cloud..."}]}' # If you provide both the session_id and chat_history parameters, the conversation history is appended to the conversation that corresponds to the specified session ID. curl -X 'POST' '<service_url>service/query' -H 'Authorization: <service_token>' -H 'accept: application/json' -H 'Content-Type: application/json' -d '{"question":"What are the features of PAI?", "chat_history": [{"user":"What is PAI", "bot":"PAI is an AI platform provided by Alibaba Cloud..."}], "session_id": "1702ffxxad3xxx6fxxx97daf7c"}'
Python
The following sample code shows an example on how to initiate a single-round conversational search request:
import requests EAS_URL = 'http://xxxx.****.cn-beijing.pai-eas.aliyuncs.com' headers = { 'accept': 'application/json', 'Content-Type': 'application/json', 'Authorization': 'MDA5NmJkNzkyMGM1Zj****YzM4M2YwMDUzZTdiZmI5YzljYjZmNA==', } def test_post_api_query_llm(): url = EAS_URL + '/service/query/llm' data = { "question":"What is PAI?" } response = requests.post(url, headers=headers, json=data) if response.status_code != 200: raise ValueError(f'Error post to {url}, code: {response.status_code}') ans = dict(response.json()) print(f"======= Question =======\n {data['question']}") print(f"======= Answer =======\n {ans['answer']} \n\n") def test_post_api_query_retrieval(): url = EAS_URL + '/service/query/retrieval' data = { "question":"What is PAI?" } response = requests.post(url, headers=headers, json=data) if response.status_code != 200: raise ValueError(f'Error post to {url}, code: {response.status_code}') ans = dict(response.json()) print(f"======= Question =======\n {data['question']}") print(f"======= Answer =======\n {ans['docs']}\n\n") def test_post_api_query_rag(): url = EAS_URL + '/service/query' data = { "question":"What is PAI?" } response = requests.post(url, headers=headers, json=data) if response.status_code != 200: raise ValueError(f'Error post to {url}, code: {response.status_code}') ans = dict(response.json()) print(f"======= Question =======\n {data['question']}") print(f"======= Answer =======\n {ans['answer']}") print(f"======= Retrieved Docs =======\n {ans['docs']}\n\n") # LLM test_post_api_query_llm() # Retrieval test_post_api_query_retrieval() # RAG (Retrieval + LLM) test_post_api_query_rag()Set the EAS_URL parameter to the endpoint of the RAG-based chatbot. Make sure to remove the forward slash (
/) at the end of the endpoint. Set the Authorization parameter to the token of the RAG-based chatbot.Initiate a multi-round conversational search request
You can initiate a multi-round conversational search request only in RAG (Retrieval + LLM) and LLM query modes. Sample code:
import requests EAS_URL = 'http://xxxx.****.cn-beijing.pai-eas.aliyuncs.com' headers = { 'accept': 'application/json', 'Content-Type': 'application/json', 'Authorization': 'MDA5NmJkN****jNlMDgzYzM4M2YwMDUzZTdiZmI5YzljYjZmNA==', } def test_post_api_query_llm_with_chat_history(): url = EAS_URL + '/service/query/llm' # Round 1 query data = { "question":"What is PAI?" } response = requests.post(url, headers=headers, json=data) if response.status_code != 200: raise ValueError(f'Error post to {url}, code: {response.status_code}') ans = dict(response.json()) print(f"=======Round 1: Question =======\n {data['question']}") print(f"=======Round 1: Answer =======\n {ans['answer']} session_id: {ans['session_id']} \n") # Round 2 query data_2 = { "question": "What are the benefits of PAI?", "session_id": ans['session_id'] } response_2 = requests.post(url, headers=headers, json=data_2) if response.status_code != 200: raise ValueError(f'Error post to {url}, code: {response.status_code}') ans_2 = dict(response_2.json()) print(f"=======Round 2: Question =======\n {data_2['question']}") print(f"=======Round 2: Answer =======\n {ans_2['answer']} session_id: {ans_2['session_id']} \n\n") def test_post_api_query_rag_with_chat_history(): url = EAS_URL + '/service/query' # Round 1 query data = { "question":"What is PAI?" } response = requests.post(url, headers=headers, json=data) if response.status_code != 200: raise ValueError(f'Error post to {url}, code: {response.status_code}') ans = dict(response.json()) print(f"=======Round 1: Question =======\n {data['question']}") print(f"=======Round 1: Answer =======\n {ans['answer']} session_id: {ans['session_id']}") print(f"=======Round 1: Retrieved Docs =======\n {ans['docs']}\n") # Round 2 query data = { "question":"What are the features of PAI?", "session_id": ans['session_id'] } response = requests.post(url, headers=headers, json=data) if response.status_code != 200: raise ValueError(f'Error post to {url}, code: {response.status_code}') ans = dict(response.json()) print(f"=======Round 2: Question =======\n {data['question']}") print(f"=======Round 2: Answer =======\n {ans['answer']} session_id: {ans['session_id']}") print(f"=======Round 2: Retrieved Docs =======\n {ans['docs']}") # LLM test_post_api_query_llm_with_chat_history() # RAG (Retrieval + LLM) test_post_api_query_rag_with_chat_history()Set the EAS_URL parameter to the endpoint of the RAG-based chatbot. Make sure to remove the forward slash (
/) at the end of the endpoint. Set the Authorization parameter to the token of the RAG-based chatbot.
Other features
After you connect to a database that is used as a vector database on the RDS instance, you can view the imported knowledge base content. For more information about how to connect to a database, see Connect to an ApsaraDB RDS for PostgreSQL instance.
References
You can also use EAS to deploy the following items:
You can deploy an LLM application that can be called by using the web UI or API operations. After the LLM application is deployed, use the LangChain framework to integrate enterprise knowledge bases into the LLM application and implement intelligent Q&A and automation features. For more information, see Quickly deploy LLMs in EAS.
You can deploy an AI video generation model service by using ComfyUI and Stable Video Diffusion models. This helps you complete tasks such as short video generation and animation on social media platforms. For more information, see Use ComfyUI to deploy an AI video generation model service.
FAQ
How do I disable the with chat history feature of the RAG-based chatbot?
On the web UI page of the RAG-based chatbot, do not select Chat history.