This topic describes how to create script jobs by writing Shell, Python, or PHP scripts.
Overview
The following figure shows how script jobs work.
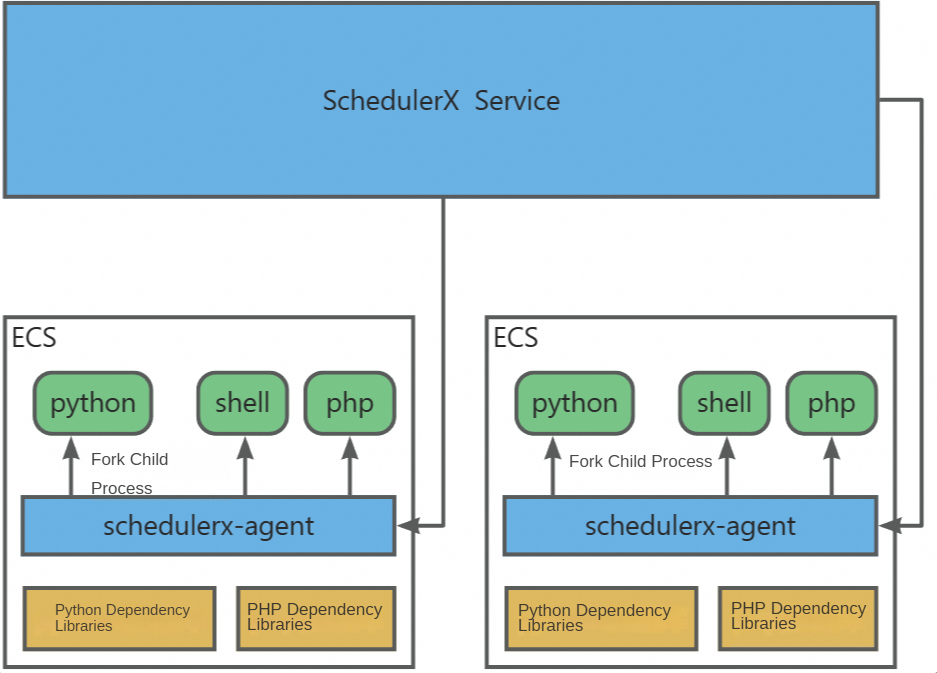
To use script jobs, you must deploy the
SchedulerX agenton the desired device in advance. The agent communicates with the server, receives script execution commands, and returns execution results.You must deploy the dependencies required for script execution on the desired device in advance. The dependencies include Python dependency libraries and dependent files.
Each time a script is executed, the
SchedulerX agentperforms aforkoperation on a child process to execute the script. This child process does not occupy the memory of theSchedulerX agent, but occupies the memory of the deployment machine. The specific memory consumption depends on the script content. If many script jobs run simultaneously, the device may run out of memory. If you need to execute a script that requires excessive memory resources, we recommend that you use Kubernetes jobs to execute scripts based on pods.
Prerequisites
The SchedulerX agent is deployed in advance to execute scripts.
Create a script job
Log on to the MSE console, go to the SchedulerX Version page, and then click Tasks in the left-side navigation pane to create a job on the Tasks page. In the Create task panel, select ScriptTask from the Task type drop-down list.
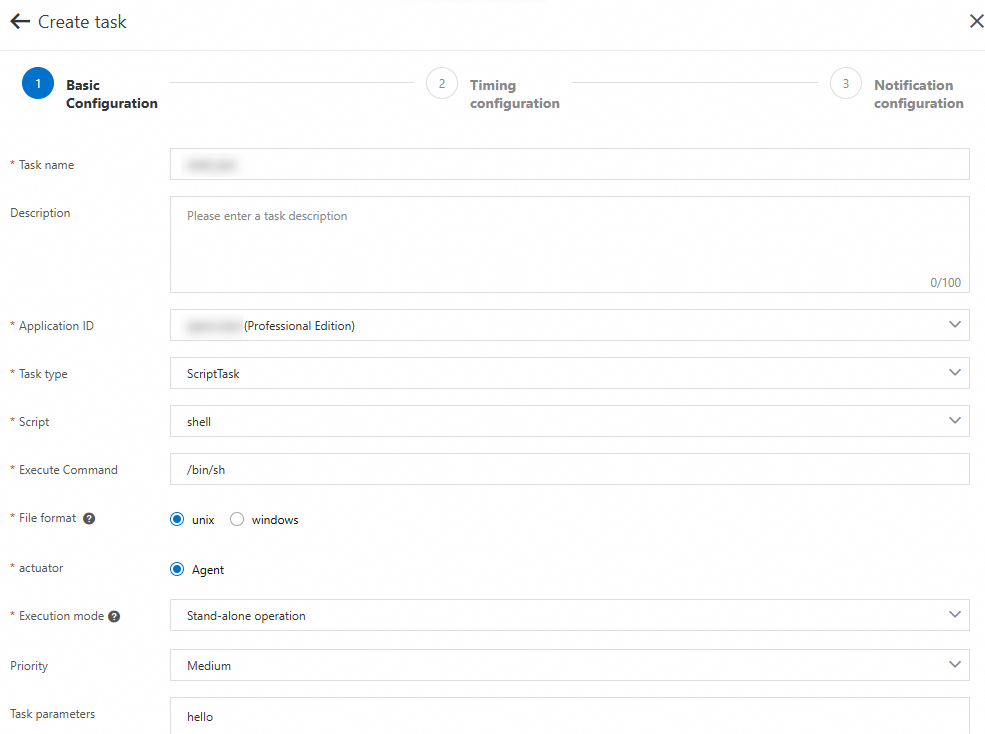
Step 1: Select a script language
Select shell, python, or php from the Script drop-down list. The Script parameter specifies the language used by the script.
Step 2: Select an execution command
Specify the Execute Command parameter based on the script language.
Shell script: The default parameter value is
/bin/sh.Python script: The default parameter value is
python. You can change the parameter value topython2orpython3.PHP script: The default parameter value is
php.
Step 3: Select a file format
Different line feed characters are used for the Unix and Windows operating systems.
If you need to execute scripts on a
Windowsoperating system, selectwindowsfor the File format parameter.If you need to execute scripts on a
Linux, Unix, or macOSoperating system, selectunixfor the File format parameter.
If the script is sourced from on a Windows operating system but needs to run on a Linux operating system, select unix for the File format parameter.
Step 4: Select an execution mode
Prerequisite: The SchedulerX agent is deployed in advance to execute scripts. For more information, see Use the SchedulerX agent to connect an application to SchedulerX (Script or HTTP jobs).
Select an execution mode from the Execution mode drop-down list.
Stand-alone operation: If you deploy multiple SchedulerX agents, a random agent is selected to execute scripts each time.
Broadcast run: If you deploy multiple SchedulerX agents, all the agents work at the same time to execute scripts in broadcast mode. This execution mode is suitable for scenarios in which O&M operations are performed on destination objects in batches.
Shard run: For more information, see Create a Python sharding job.
Write scripts
After a script job is created, a script template is generated by default based on the script language. You can click EditScript to modify the script content.
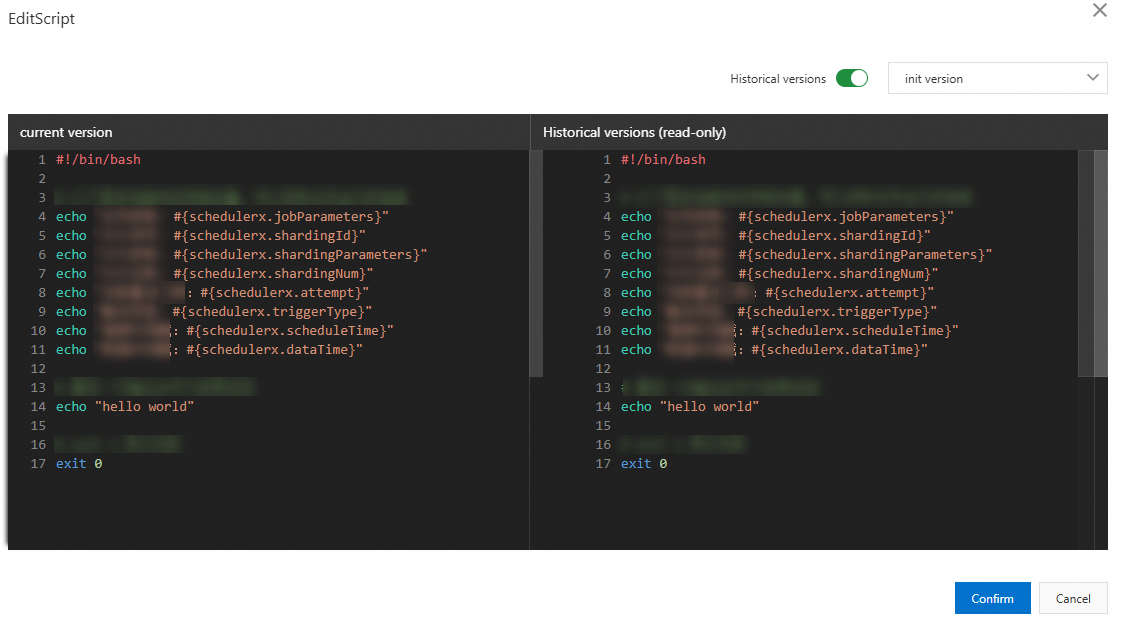
Script version history
You can use the script version history feature for Professional Edition applications. In the EditScript panel, turn on the Historical versions switch to go to the version comparison page.
The left-side pane shows the current version, and the right-side pane shows a historical version.
Click the version drop-down list to view historical version information, including the version number and creation time.
Modify the script content, click Confirm, and then enter a new version name.
Demo
Distributed processing by using broadcast jobs
Connect to two
SchedulerX agents.Create a script job whose Script is set to shell and Execution mode is set to Broadcast run. The following figure shows the script content.
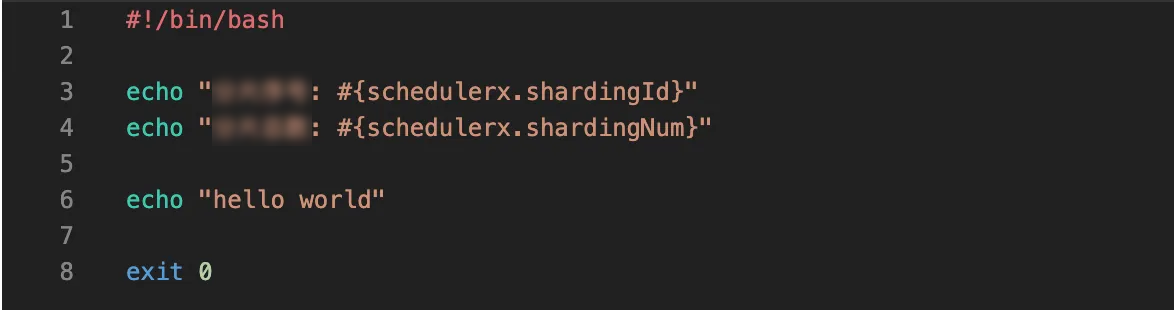
Click Run once in the Operation column of the desired job.
On the Instances page, click Log in the Operation column of the desired job instance to view the script content executed by each machine.
The following figure shows the operational log of
172.16.13.125. The log information shows that the shard ID is 1, and the total number of shards is 2.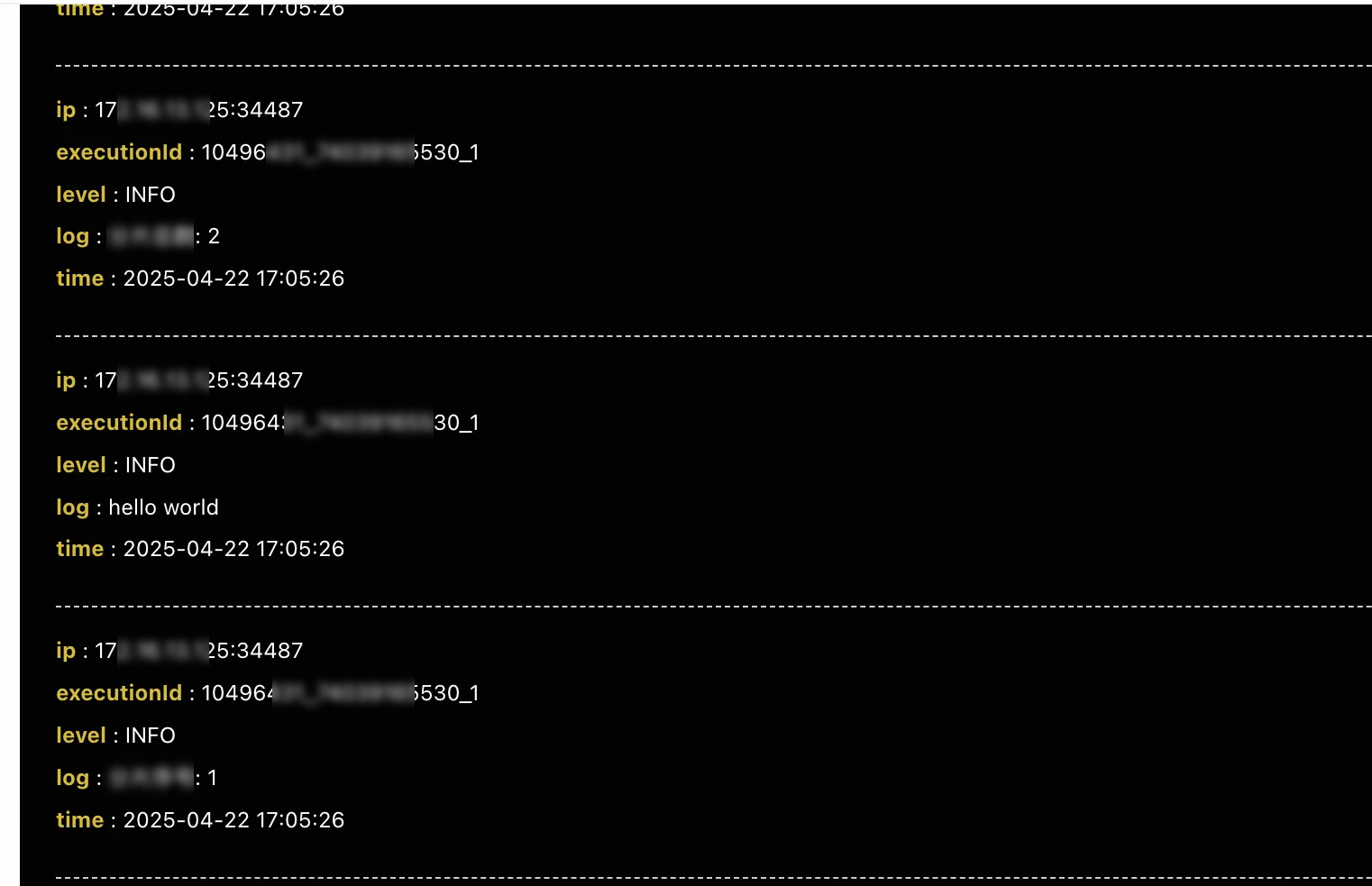
The following figure shows the operational log of
172.16.13.120. The log information shows that the shard ID is 0, and the total number of shards is 2.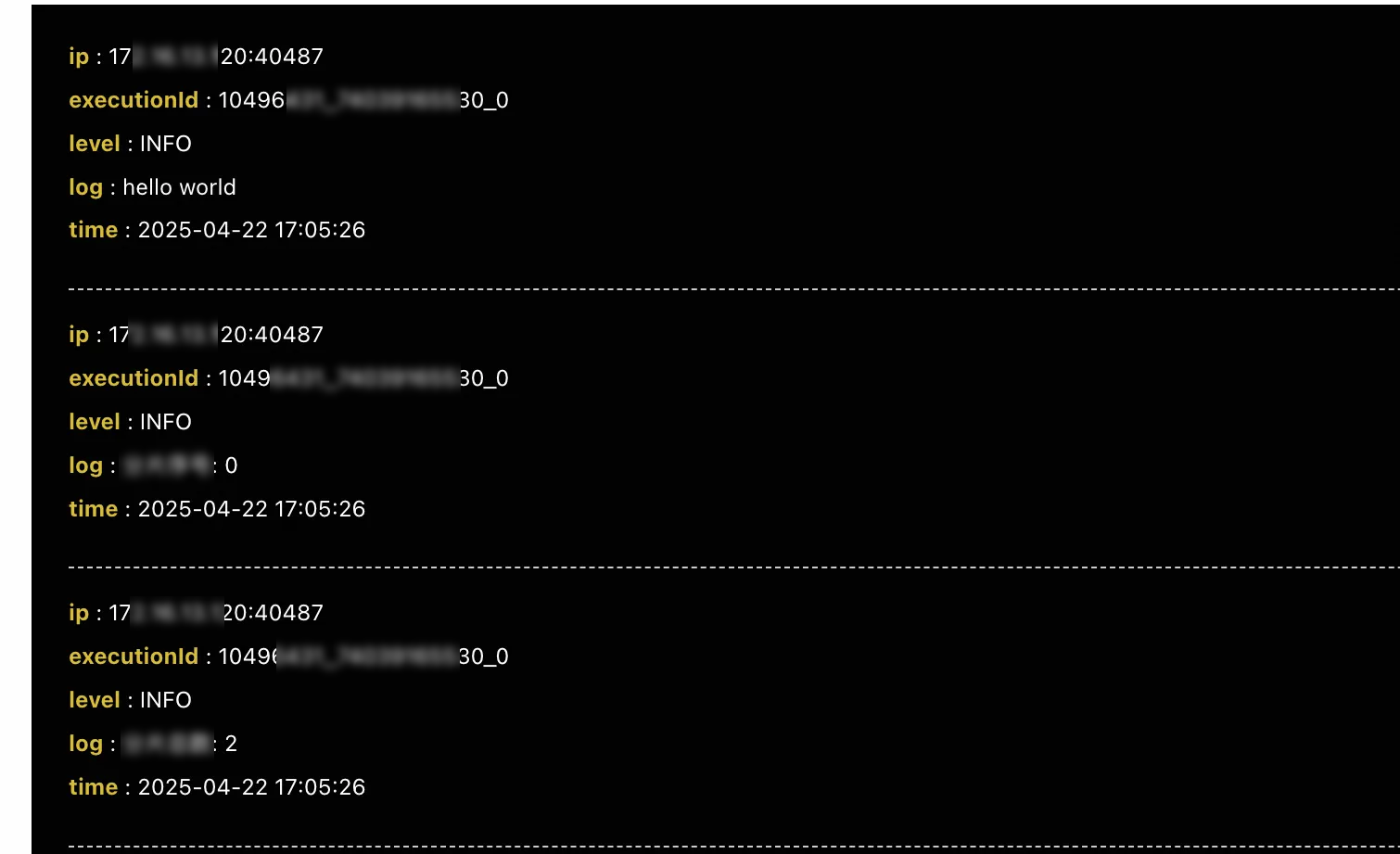
Distributed processing by using sharding jobs
Create a script job whose Script is set to shell and Execution mode is set to Shard run. The following figure shows other job configurations.
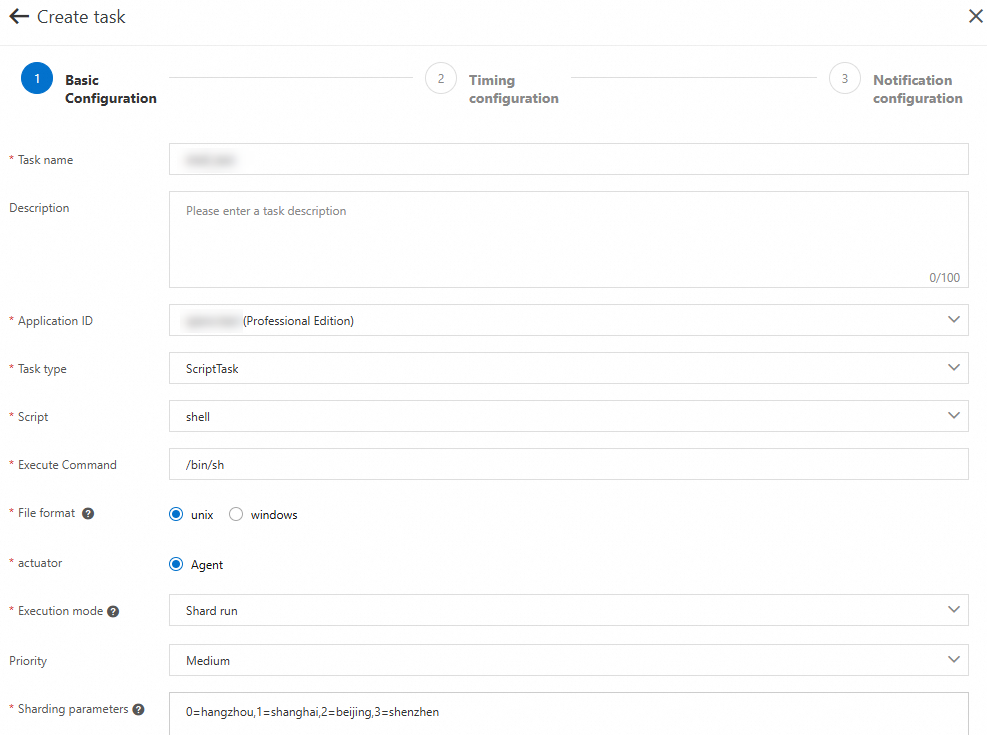
After you create a job, click Edit Script for the desired job. The following figure shows the script content.
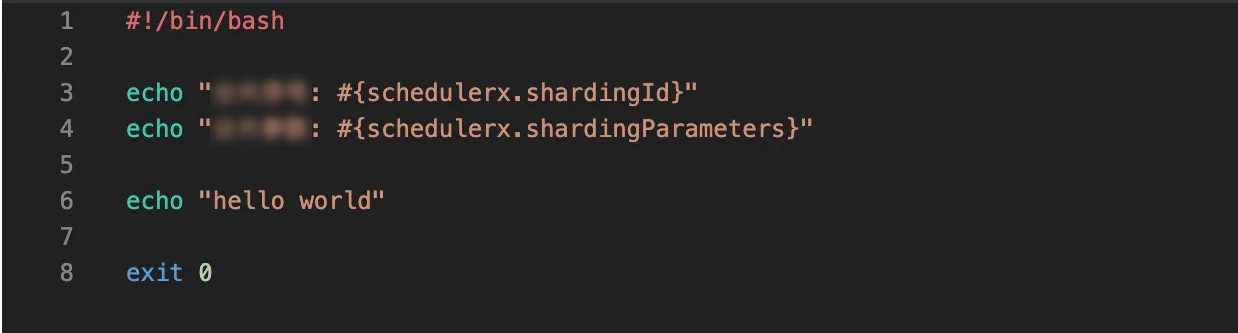
Click Run once in the Operation column of the desired job.
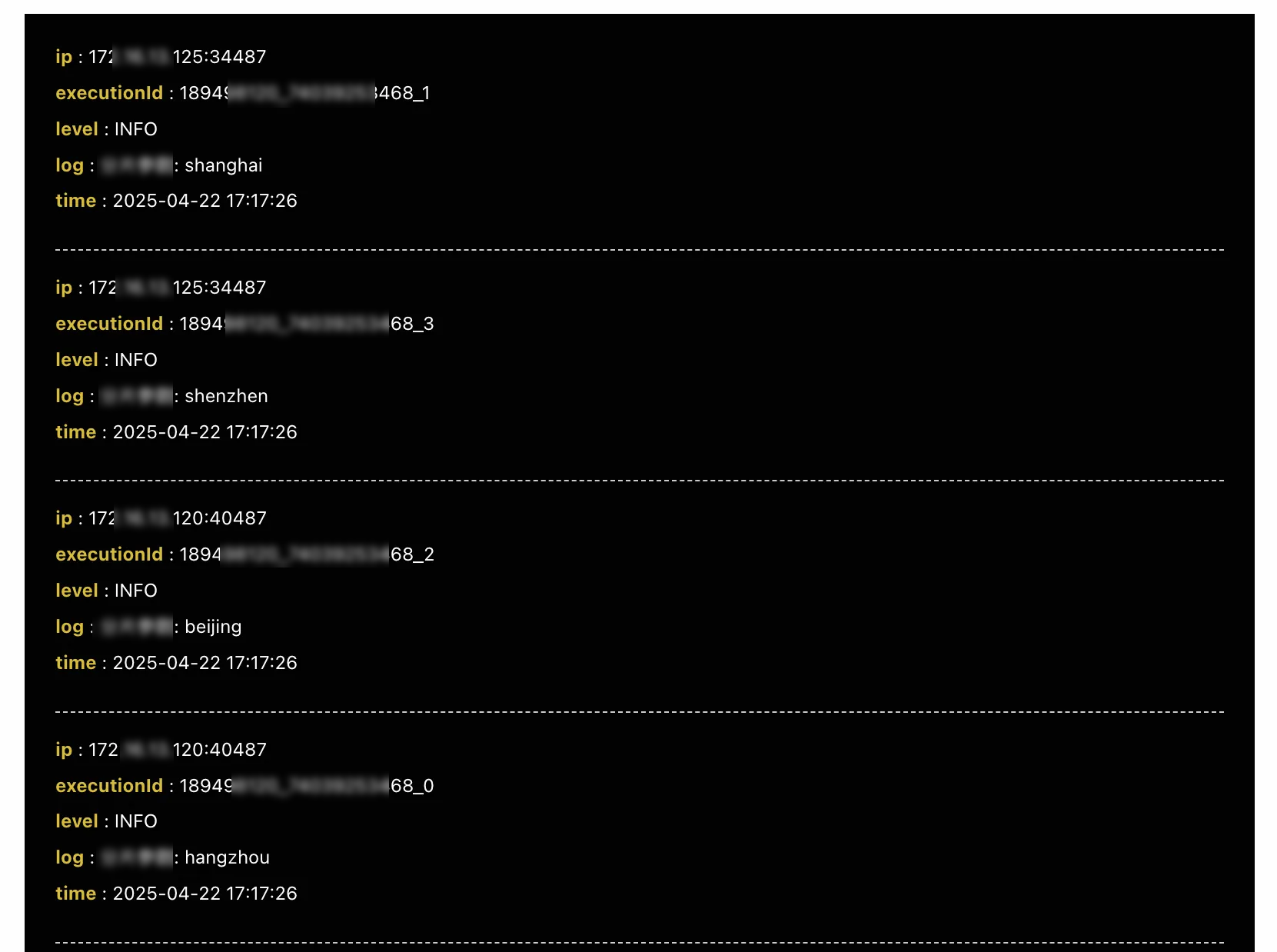
On the Instances page, click Log in the Operation column of the desired job instance to view the shard parameters of each machine.
The log information shows that
172.16.13.120is executed twice and the shard parameters involved arehangzhouandbeijing, respectively.The log information shows that
172.16.13.125is executed twice and the shard parameters involved areshenzhenandshanghai, respectively.
References
For information about system built-in parameters, see System variables of scripts.