In June 2025, we open-sourced the text-oriented Qwen3-Embedding and Qwen3-ReRanker model series, providing best-in-class performance across a variety of downstream tasks, including multilingual text retrieval, clustering, and classification, which have been widely adopted by developers in the community. Today, we are thrilled to announce the release of the Qwen3-VL-Embedding and Qwen3-VL-Reranker series, the newest models in the Qwen family. Built on the recently open-sourced and powerful Qwen3-VL foundation models, these models are specifically engineered for multimodal information retrieval and cross-modal understanding.
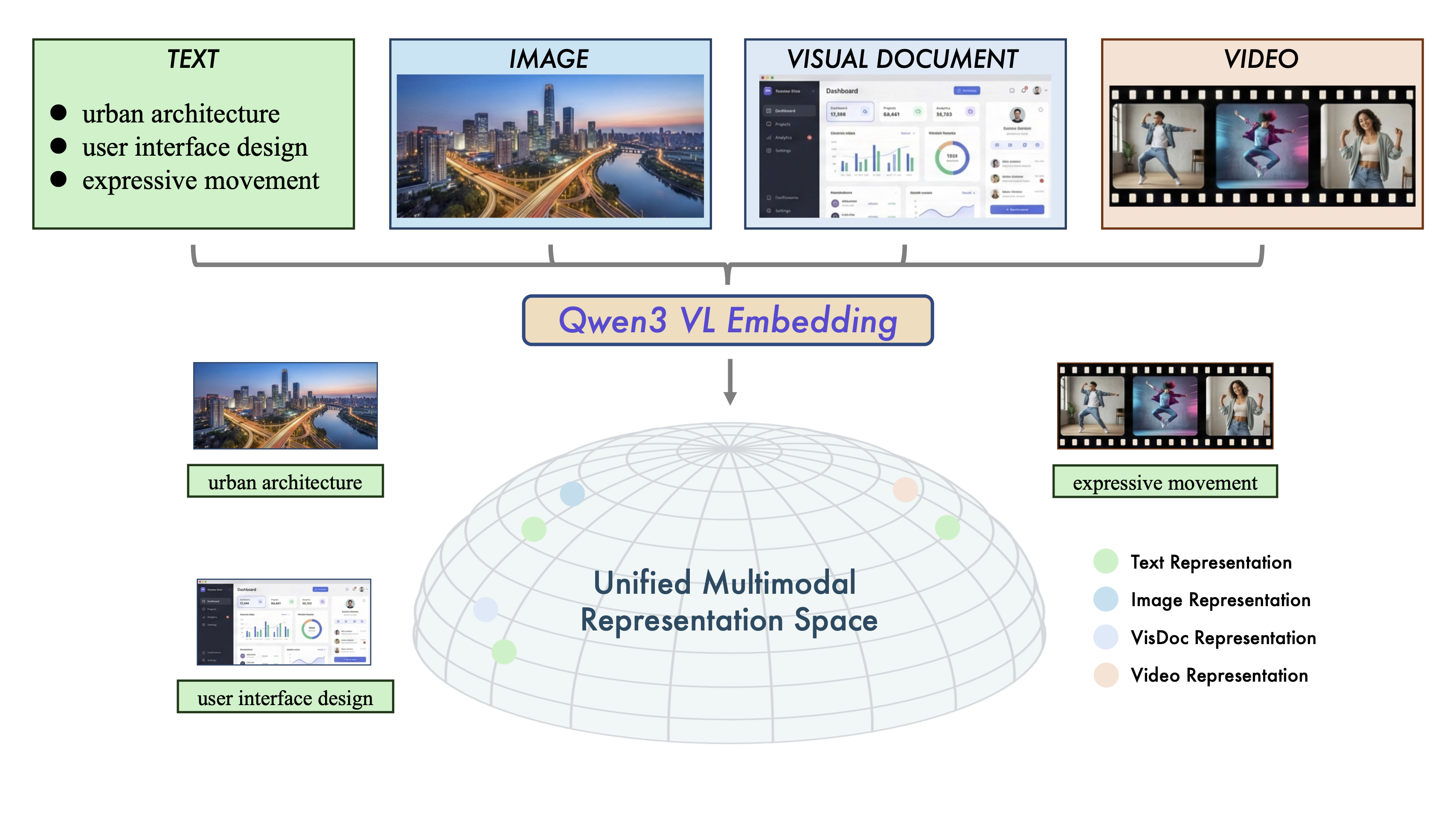
Figure 1: Illustration of the Unified Multimodal Representation Space. Qwen3-VL-Embedding model series represent multi-source data (Text, Image, Visual Document, and Video) into a common manifold.
Table: Model specifications for the Qwen3-VL-Embedding and Qwen3-VL-Reranker
| Model | Size | Layers | Sequence Length | Embedding Dimension | Quantization Support | MRL Support | Instruction Aware |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Qwen3-VL-Embedding-2B | 2B | 28 | 32K | 2048 | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Qwen3-VL-Embedding-8B | 8B | 36 | 32K | 4096 | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Qwen3-VL-Reranker-2B | 2B | 28 | 32K | - | - | - | Yes |
| Qwen3-VL-Reranker-8B | 8B | 36 | 32K | - | - | - | Yes |
Note: “Quantization Support” indicates the supported quantization formats for the embeddings. “MRL support” denotes whether the embedding model allows user-specified embedding dimension. “Instruction-aware” indicates whether the models support task-specific customization of the input instruction.
Similar to the Qwen3-Embedding and Qwen3-ReRanker model series, Qwen3-VL-Embedding employs a dual-tower architecture while Qwen3-VL-Rerank utilizes a single-tower architecture. We have designed a multi-stage training paradigm to fully leverage and unleash the powerful general multimodal semantic understanding capabilities of Qwen3-VL, providing high-quality semantic representations and a precise re-ranking mechanism for complex, large-scale multimodal retrieval tasks.
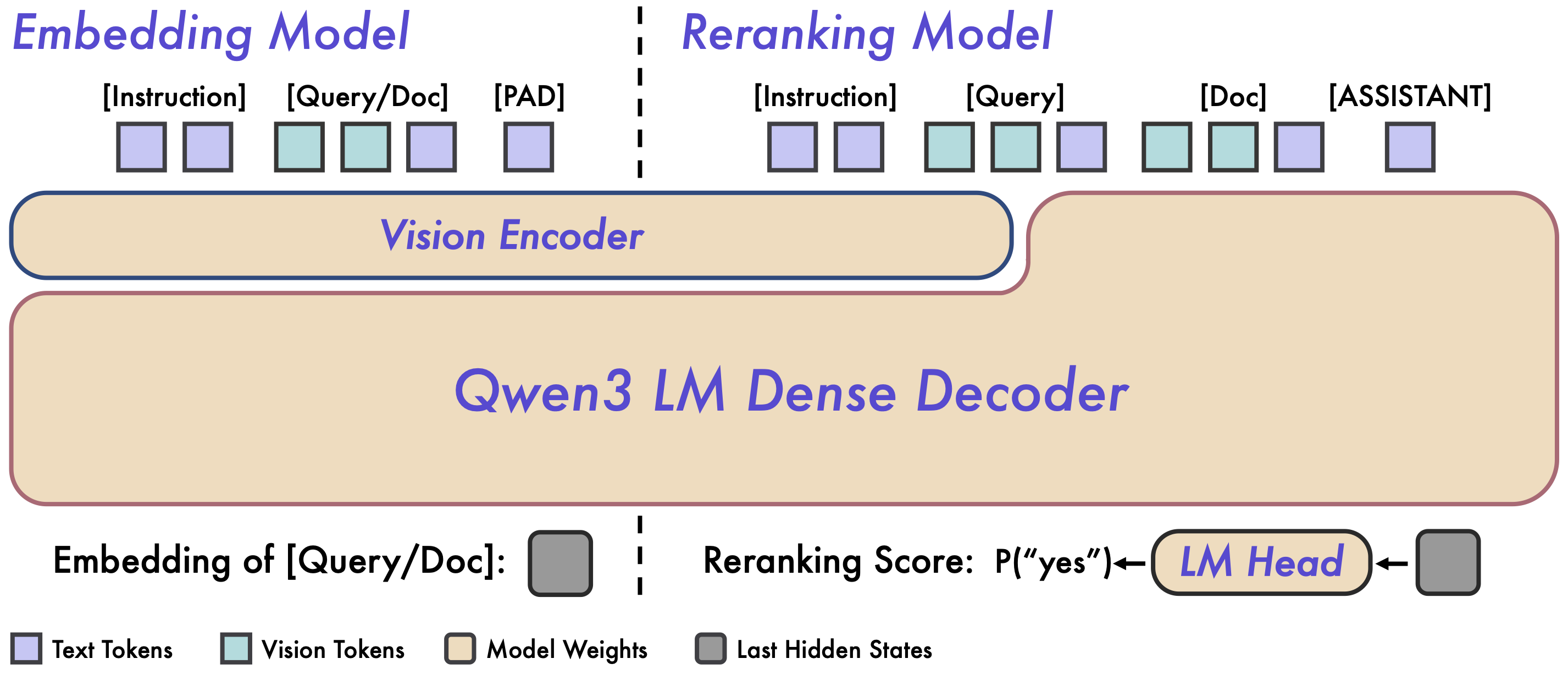
Figure 2: Overview of the Qwen3-VL-Embedding and Qwen3-VL-Reranker architecture.
The Embedding model receives single-modal or mixed-modal input and maps it into a high-dimensional semantic vector. Specifically, we extract the hidden state vector corresponding to the [EOS] token from the base model’s last layer to serve as the final semantic representation of the input. This method ensures efficient, independent encoding necessary for large-scale retrieval. The Reranking model receives an input pair (Query, Document) and performs joint encoding. It utilizes the Cross-Attention mechanism within the base model to achieve deeper, finer-grained inter-modal interaction and information fusion between the Query and the Document. The model ultimately expresses the relevance score of the input pair by predicting the generation probability of two special tokens (yes and no).
| Qwen3-VL-Embedding | Qwen3-VL-Reranker | |
| Core Function | Semantic Representation, Embedding Generation | Relevance Scoring, Re-ranking |
| Input | Single modality or mixed modalities (Text, Image, Video, Screenshots) | (Query, Document) pair, where Query and Document can be single- or mixed-modal inputs |
| Mechanism | Independent Encoding, Efficient Retrieval (Dual-Tower) | Deep Inter-Modal Interaction, Precise Alignment (Single-Tower/Cross-Attention) |
| Objective | Semantic Clustering within Vector Space | Output Relevance Score |
We primarily evaluated the Qwen3-VL-Embedding model on MMEB-v2 and MMTEB benchmarks. The Qwen3-VL-Embedding-8B model achieves state-of-the-art results on MMEB-V2, surpassing all previous open-source models and proprietary model services. When breaking down performance across different retrieval modalities, our model consistently achieves SOTA results on image, visual document, and video retrieval subtasks. Meanwhile, on the text-only multilingual MMTEB benchmark, the Qwen3-VL-Embedding model shows a performance gap compared to the text-only Qwen3-Embedding model of comparable size. However, when compared to other similarly sized models on the evaluation leaderboard, it still demonstrates highly competitive performance.
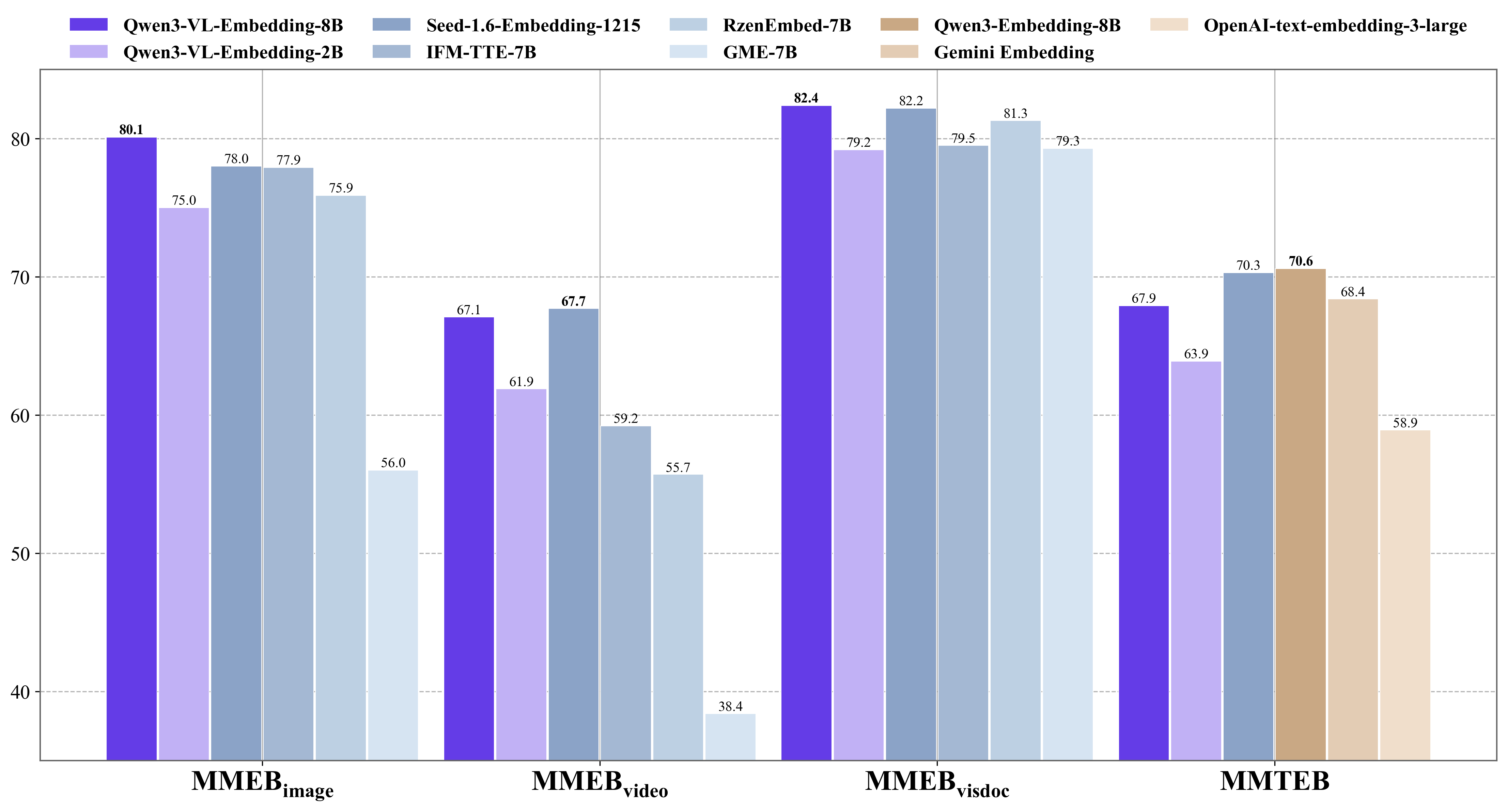
Figure 3: Evaluation results on MMEB-v2 and MMTEB benchmarks.
We utilize retrieval task datasets from various subtasks of MMEB-v2 and MMTEB retrieval benchmarks. For visual document retrieval, we employ JinaVDR and ViDoRe v3 datasets. Our results demonstrate that all Qwen3-VL-Reranker models consistently outperform the base embedding model and baseline rerankers, with the 8B variant achieving the best performance across most tasks.
| Model | Size | MMEB-v2(Retrieval) - Avg | MMEB-v2(Retrieval) - Image | MMEB-v2(Retrieval) - Video | MMEB-v2(Retrieval) - VisDoc | MMTEB(Retrieval) | JinaVDR | ViDoRe(v3) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Qwen3-VL-Embedding-2B | 2B | 73.4 | 74.8 | 53.6 | 79.2 | 68.1 | 71.0 | 52.9 |
| jina-reranker-m0 | 2B | - | 68.2 | - | 85.2 | - | 82.2 | 57.8 |
| Qwen3-VL-Reranker-2B | 2B | 75.1 | 73.8 | 52.1 | 83.4 | 70.0 | 80.9 | 60.8 |
| Qwen3-VL-Reranker-8B | 8B | 79.2 | 80.7 | 55.8 | 86.3 | 74.9 | 83.6 | 66.7 |
Embedding and reranking models are typically used together in retrieval systems. The embedding model performs initial recall to retrieve a substantial set of candidates, while the reranking model sorts these candidates based on newly computed relevance scores to present the most accurate results for the user query. This two-stage retrieval process leverages the complementary strengths of both models: the efficiency and scalability of the embedding model for broad candidate retrieval, and the precision and fine-grained scoring capability of the reranking model for final ranking. This approach achieves superior retrieval performance compared to using either model alone. Below are basic usage examples.
from scripts.qwen3_vl_embedding import Qwen3VLEmbedder
import numpy as np
import torch
# Define a list of query texts
queries = [
{"text": "A woman playing with her dog on a beach at sunset."},
{"text": "Pet owner training dog outdoors near water."},
{"text": "Woman surfing on waves during a sunny day."},
{"text": "City skyline view from a high-rise building at night."}
]
# Define a list of document texts and images
documents = [
{"text": "A woman shares a joyful moment with her golden retriever on a sun-drenched beach at sunset, as the dog offers its paw in a heartwarming display of companionship and trust."},
{"image": "https://qianwen-res.oss-cn-beijing.aliyuncs.com/Qwen-VL/assets/demo.jpeg"},
{"text": "A woman shares a joyful moment with her golden retriever on a sun-drenched beach at sunset, as the dog offers its paw in a heartwarming display of companionship and trust.", "image": "https://qianwen-res.oss-cn-beijing.aliyuncs.com/Qwen-VL/assets/demo.jpeg"}
]
# Specify the model path
model_name_or_path = "Qwen/Qwen3-VL-Embedding-2B"
# Initialize the Qwen3VLEmbedder model
model = Qwen3VLEmbedder(model_name_or_path=model_name_or_path)
# We recommend enabling flash_attention_2 for better acceleration and memory saving,
# model = Qwen3VLEmbedder(model_name_or_path=model_name_or_path, dtype=torch.float16, attn_implementation="flash_attention_2")
# Combine queries and documents into a single input list
inputs = queries + documents
embeddings = model.process(inputs)
# Compute similarity scores between query embeddings and document embeddings
similarity_scores = (embeddings[:4] @ embeddings[4:].T)
# Print out the similarity scores in a list format
print(similarity_scores.tolist())
# [[0.83203125, 0.74609375, 0.73046875], [0.5390625, 0.373046875, 0.48046875], [0.404296875, 0.326171875, 0.357421875], [0.1298828125, 0.06884765625, 0.10595703125]]from scripts.qwen3_vl_reranker import Qwen3VLReranker
import numpy as np
import torch
# Specify the model path
model_name_or_path = "Qwen/Qwen3-VL-Reranker-2B"
# Initialize the Qwen3VLEmbedder model
model = Qwen3VLReranker(model_name_or_path=model_name_or_path)
# We recommend enabling flash_attention_2 for better acceleration and memory saving,
# model = Qwen3VLReranker(model_name_or_path=model_name_or_path, dtype=torch.float16, attn_implementation="flash_attention_2")
# Combine queries and documents into a single input list
inputs = {
"instruction": "Retrieval relevant image or text with user's query",
"query": {"text": "A woman playing with her dog on a beach at sunset."},
"documents": [
{"text": "A woman shares a joyful moment with her golden retriever on a sun-drenched beach at sunset, as the dog offers its paw in a heartwarming display of companionship and trust."},
{"image": "https://qianwen-res.oss-cn-beijing.aliyuncs.com/Qwen-VL/assets/demo.jpeg"},
{"text": "A woman shares a joyful moment with her golden retriever on a sun-drenched beach at sunset, as the dog offers its paw in a heartwarming display of companionship and trust.", "image": "https://qianwen-res.oss-cn-beijing.aliyuncs.com/Qwen-VL/assets/demo.jpeg"}
],
"fps": 1.0
}
scores = model.process(inputs)
print(scores)
# [0.8408790826797485, 0.6197134852409363, 0.7778129577636719]For more usage examples, please visit our GitHub repository.
The Qwen3-VL-Embedding and Qwen3-VL-Reranker model series represent our initial exploration into unified multimodal representation and retrieval. Compared to text-only embedding and reranking models, multimodal approaches, particularly unified multimodal embedding and reranking systems, still present vast opportunities for exploration in terms of model maturity, usability and application scenario expansion. The open-sourcing of Qwen3-VL-Embedding and Qwen3-VL-Reranker marks a new starting point. We look forward to collaborating with the community to explore and build more general-purpose unified multimodal retrieval capabilities.
If you find Qwen3-VL-Embedding and Qwen3-VL-Reranker helpful in your research, please consider citing us 📝 :)
@article{qwen3vlembedding,
title={Qwen3-VL-Embedding and Qwen3-VL-Reranker: A Unified Framework for State-of-the-Art Multimodal Retrieval and Ranking},
author={Li, Mingxin and Zhang, Yanzhao and Long, Dingkun and Chen, Keqin and Song, Sibo and Bai, Shuai and Yang, Zhibo and Xie, Pengjun and Yang, An and Liu, Dayiheng and Zhou, Jingren and Lin, Junyang},
journal={arXiv},
year={2026}
}Security by Ant Digital Technologies — AI-driven End-to-End Protection for Digital Identity

1,319 posts | 463 followers
FollowPM - C2C_Yuan - May 31, 2024
Alibaba Cloud Big Data and AI - December 29, 2025
Alibaba Cloud Community - September 27, 2025
Alibaba Cloud Indonesia - November 7, 2025
Alibaba Cloud Community - November 26, 2024
Alibaba Cloud Community - September 6, 2024

1,319 posts | 463 followers
Follow AI Acceleration Solution
AI Acceleration Solution
Accelerate AI-driven business and AI model training and inference with Alibaba Cloud GPU technology
Learn More Offline Visual Intelligence Software Packages
Offline Visual Intelligence Software Packages
Offline SDKs for visual production, such as image segmentation, video segmentation, and character recognition, based on deep learning technologies developed by Alibaba Cloud.
Learn More Tongyi Qianwen (Qwen)
Tongyi Qianwen (Qwen)
Top-performance foundation models from Alibaba Cloud
Learn More Network Intelligence Service
Network Intelligence Service
Self-service network O&M service that features network status visualization and intelligent diagnostics capabilities
Learn MoreMore Posts by Alibaba Cloud Community