By Zhou Zhaofeng, nicknamed Muluo at Alibaba.
In today's world, data processing is indispensable to any application system. Data is the core that drives business innovation and intelligent development, and holding true to this, data processing technology is at the core of several innovations and is the key to sustaining a company's competitiveness. A complete technical architecture consists of an application system and a data system. The application system processes business logic, whereas the data system processes the remaining data. This article was written to inspire research and development engineers and data system architects in the field of big data and database systems.
It's clear that the technologies behind big data are continuously changing and evolving. And, with the development of related industries in recent years, including several business innovations, and the explosive growth of data along with the wide application of open-source technologies in big data and data analytics scenarios in past decades, the core components and technical architecture behind big data have come a long way. Among other things, the development of cloud computing has helped to decrease several of the obstacles involved with using big data technology. And, we expect that, in the near future, data will continue to drive new levels of business innovation. With big data technology being at the core of this, the technology surrounding big data will gradually become a lightweight and intelligent technological system that will be applied virtually everywhere. And, as such, it will become an increasingly necessary skill for research and development engineers from a variety of industries is understanding the world of cloud computing, where big data will live and continue to evolve now and in the future.
As big data as evolved, application systems and data systems have also become gradually more integrated with each other. Nowadays, data systems may run through the business interaction logic but are they are not hidden behind the application systems. In traditional application systems, there is a focus on interaction, whereas in modern application systems, familiarity with users comes during interaction itself. So, one thing we can learn from this transition is that the development of data systems drives the development of business systems, in a transition from business-oriented systems to large-scale, intelligent systems.
Today there still exists a need to solve certain technical difficulties for the business system to become large-scale and intelligent. The application of mature open-source technologies makes the construction of big data systems simple, and big data architectures become common. For example, the well-known Lambda architecture decreases technical difficulties to a certain extent. However, for subsequent maintenance of data systems, such as large-scale application, operations and maintenance control, and cost reduction of big data components, you need to master big data technologies, distributed technologies, and fault locating in complex environments, which can still be very difficult.
The core components of a data system include data pipeline, distributed storage, and distributed computing. Businesses generally use combinations of these components to build a data system architecture. Each component performs its specific duties, and upstream and downstream components exchange data with each other. For architects, it is highly challenging to choose and combine components.
Building off this general discussion, this article will discuss the data system used at Alibaba Group to provide inspiration to industry research and development engineers and architects. In this article, we will first introduce the several open-source components and the Alibaba Cloud products and services involved in each core component in our data system. Then, this article will analyzes the storage technology of structured data in the data system and introduce the design principle used by Alibaba Cloud Tablestore to meet the requirements for structured data storage in the data system.
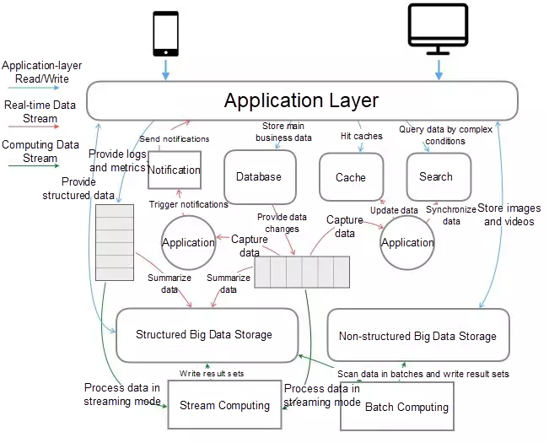
The above figure shows a typical technical architecture, including an application system and a data system. This architecture is not relevant to any specific business. Rather, it reflects the core components of a data application system and data stream relationships among components.
The application system implements the main business logic of applications and processes business data or application metadata. The data system summarizes and processes business data and other data and integrates it with business intelligence (BI), recommendation, or risk control systems.
The system architecture contains the following common core components:
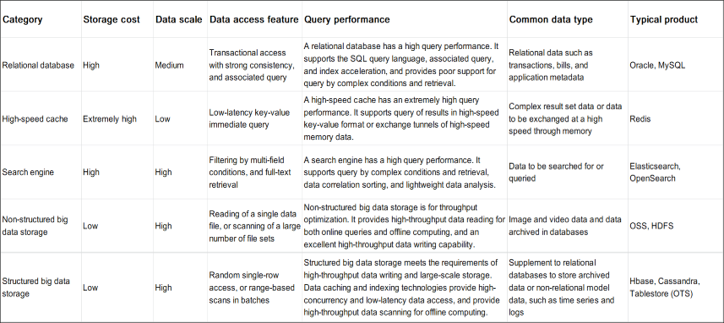
Further analysis of data storage components shows that various data storage components are designed to meet the data storage requirements of different scenarios, and provide different data models and different optimization preferences for online and offline. The following table lists comparisons in detail:
The data system architecture contains multiple storage components. Some of the data in these storage components are directly written from applications, and some are replicated from other storage components. For example, data in the business relational database is usually from businesses, whereas data in the high-speed cache and search engine is usually synchronized and replicated from business databases.
Storage components for different purposes have upstream and downstream data links of different types. You can classify these components into primary storage and secondary storage. The two storage types are designed for different objectives:
At this point, it's critical to address a few significant questions: Why are primary and secondary storage available? And, is it possible to store, read, and write data in a unified manner to meet the demands of all scenarios?
Currently, data cannot be stored, read, and written in a unified manner. The storage engine supports multiple technologies, including row store or columnar store, B+Tree or log-structured merge-tree (LSM-tree), storage of immutable data, frequently updated data, or time-based partition data, and designing for high-speed random query or high-throughput scanning. Moreover, database products are divided into the catagories of TP and AP. Although in the direction of Hybrid Transaction/Analytical Processing (HTAP), the underlying storage is still divided into row store and columnar store.
An example of the primary storage and secondary storage dichotomy in the actual architecture is the relationship between the primary table and a secondary index table in a relational database, which may be regarded as a primary-secondary relationship.
Data in the index table varies from the primary table, which features strong consistency and is optimized for query by combinations of specific conditions. The relationship between the relational database and the high-speed cache and search engine is also a primary-secondary relationship, providing high-speed querying and retrieval with eventual data consistency.
The relationship between an online database and the data warehouse is also a primary-secondary relationship. Data in the online database is replicated to the data warehouse in a centralized manner for efficient BI analysis. The architecture design of primary-secondary storage components that complement each other is called a derived data system. In the system, the greatest technical challenge is to synchronize and replicate data between the primary and secondary components.
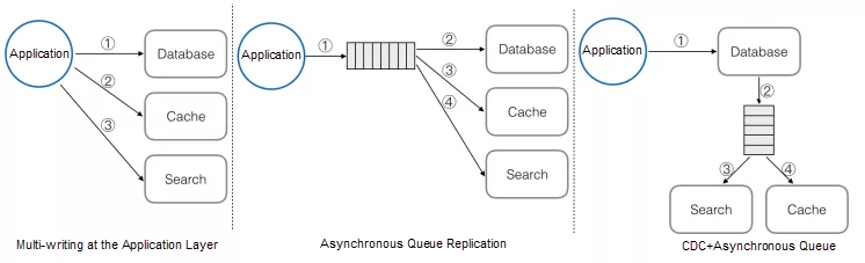
The common data replication modes shown in the preceding figure are described as follows:
The data derivation system is an important technical architecture design principle. The CDC technology is the key means to better drive the data stream. The storage components with CDC technology effectively support the data derivation system, making the entire data system architecture more flexible and reducing the complexity of data consistency design for a rapid iteration design.
However, most storage components do not support CDC technology, such as HBase. Alibaba Cloud Tablestore supports this sophisticated CDC technology, and the application of CDC technology promoted innovations made in terms of our architecture, which will be described in detail in the following sections.
A good product uses a data derivation architecture to continuously expand its capabilities, making the derivation process transparent and solving data synchronization, consistency, and resource ratio problems. In reality, most of the technical architectures use the derived architectures of product combinations and need to manage data synchronization and replication, such as the combinations of MySQL with Elasticsearch and Hbase with Solr.
The biggest problems with these combinations are:
When an architect designs a specific architecture, one of the biggest challenges he or she will have to face is the selection and combination of computing and storage components. Computing engines of the same type have a slight difference. Generally, mature and ecological computing engines are preferred, such as the batch computing engine, Spark and the stream computing engine, or Flink.
And, the selection of storage components is also challenging. Storage components include databases (SQL and NoSQL databases, with NoSQL databases divided into multiple types according to various data models), object storage, file storage, and high-speed cache. The main reason for the complexity of storage options on the market is that architects must comprehensively consider various factors such as data layering, cost reduction, and online and offline query optimization preferences.
In addition, the current technology is developing in a diversified way. No storage product meets the requirements of data writing, storage, query, and analysis in all scenarios. Consider the following observations, for example.
The final trend of data storage architecture is as follows:
The structured big data storage, a critical component in the data system, assumes a major role in connecting online and offline data. As a structured data summary storage in the data mid-end, it summarizes data in online databases for offline data analysis and stores offline data analysis result sets to support online query or data derivation. Based on the positioning, the key requirements for structured big data storage are summarized as follows.
The first requirement is the most basic, and the second and third ones are the bonus items.
Currently, HBase and Cassandra are well-known structured big data storage products in the open-source field. Cassandra is the top product of the wide column model under the NoSQL category and is widely used outside China. However, let's focus on HBase as it is more popular than Cassandra in China.
HBase is a wide column model database based on the HDFS storage and computing separation architecture. HBase has excellent scalability and supports large-scale data storage, with the following advantages:
However, HBase has several major defects that we cannot ignore:
Most senior players in China perform secondary development based on HBase. They work on various solutions to make up for the weak query capability of HBase, and develop their own index solutions, for example, self-developed secondary index solutions, full-text retrieval solutions with connection to Solr, and bitmap index solutions for datasets with small discrimination, based on their business query features. In general, HBase is an excellent open-source product, with many excellent design ideas worth learning.
Tablestore is a structured big data storage product developed by Alibaba Cloud. For more information, visit the official website and read the corresponding guide. The design principle of Tablestore takes into account the requirements for structured big data storage in the data system, and designs and implements some distinctive features based on the design principle of the data derivation system.
The design principle of the Tablestore absorbs the design ideas of excellent open-source products and has developed some special features based on actual business needs. The technical principle of Tablestore is summarized as follows:
1. Diversified Indexes
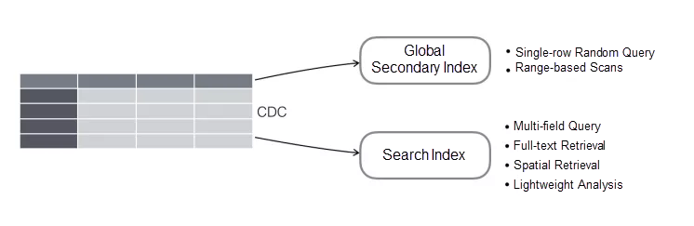
Alibaba Cloud Tablestore provides a variety of index types, including the global secondary index and search index. Similar to secondary indexes of traditional relational databases, global secondary indexes optimize condition-based queries that meet the leftmost matching principle and provide low-cost storage and efficient random queries and range-based scans. The search index feature provides more query capabilities, including query by combinations of conditions in any columns, full-text retrieval, and spatial query. The search index feature also supports lightweight data analysis and provides basic statistical aggregate functions.
2. Tunnel Service
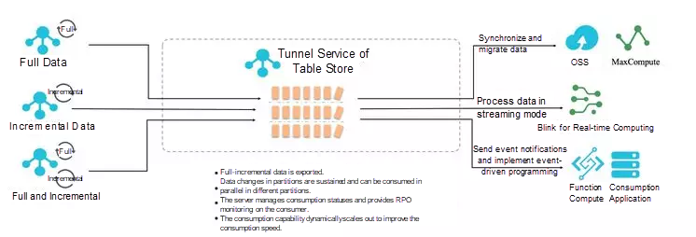
Tunnel Service is the CDC technology of Tablestore and is the core function supporting the data derivation system. Use Tunnel Service for data synchronization, event-driven programming, real-time subscription of incremental data in tables, and stream computing between heterogeneous storage components. Currently, you can seamlessly connect Tablestore to Blink in the cloud, and it is the only structured big data storage that is directly used as a stream source of Blink.
The big data processing architecture, a part of the data system architecture, has been developed over many years and contains some basic design ideas for core architectures, such as the most far-reaching Lambda architecture. Lambda architecture is a relatively basic architecture with some defects, based on which new architectures such as Kappa and Kappa+ are gradually introduced to solve some problems in Lambda architecture. Tablestore combines with the computing engine based on the CDC technology and designs a new Lambda Plus architecture based on Lambda architecture. The following figure shows the Lambda Plus architecture.
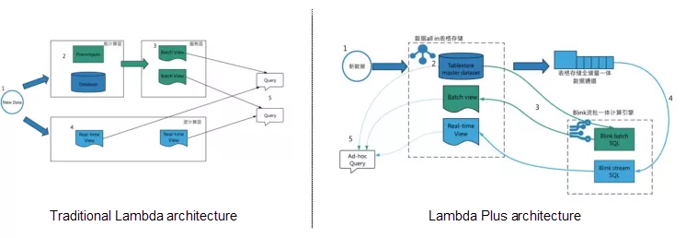
The core ideas of Lambda architecture are as follows:
Based on the Tunnel Service of Tablestore, Tablestore is completely integrated with Blink as the stream source, dim, and sink of Blink. Let's take a quick look at the essentials of the Lambda Plus architecture.
This article has described the core components of the data system architecture, the selection of storage components, and the design principle of the data derivation system. The data derivation system helps to effectively sort out the data stream relationships between storage components, based on which the article raises several key requirements for the structured big data storage component. Alibaba Cloud Tablestore is designed based on this principle and has launched some special features. In the future, we will continue to follow this principle to develop more capabilities to facilitate analysis for structured big data in Tablestore. Tablestore will be more integrated with the open-source computing ecosystem and connected to more mainstream computing engines.
A Big Data-Based Public Opinion Analysis System: Architecture Anatomy
How We Developed DingTalk: Implementing the Message System Architecture

57 posts | 12 followers
FollowAlibaba Cloud Storage - February 27, 2020
淘系技术 - April 14, 2020
Alibaba Developer - May 8, 2019
ApsaraDB - July 3, 2019
Alibaba Cloud Community - August 29, 2022
Alibaba Clouder - May 20, 2020

57 posts | 12 followers
Follow ApsaraDB for HBase
ApsaraDB for HBase
ApsaraDB for HBase is a NoSQL database engine that is highly optimized and 100% compatible with the community edition of HBase.
Learn More MaxCompute
MaxCompute
Conduct large-scale data warehousing with MaxCompute
Learn More Data Lake Storage Solution
Data Lake Storage Solution
Build a Data Lake with Alibaba Cloud Object Storage Service (OSS) with 99.9999999999% (12 9s) availability, 99.995% SLA, and high scalability
Learn More OSS(Object Storage Service)
OSS(Object Storage Service)
An encrypted and secure cloud storage service which stores, processes and accesses massive amounts of data from anywhere in the world
Learn MoreMore Posts by Alibaba Cloud Storage