By Zheng Ji
With the rapid development of artificial intelligence, AI Agent is increasingly integrated into people's daily lives and work scenarios. In particular, since the release of the MCP protocol last November, the ability of AI Agent to interact with external data and tools has significantly improved, demonstrating greater autonomy and practicality. However, while enjoying the conveniences brought by MCP tools, users also face a series of practical challenges:
Complex Service Selection and Configuration: Currently, there are thousands of MCP servers on the market, and users need to select suitable servers based on specific tasks and manually configure them to the AI Agent. This process is not only cumbersome, but it may also significantly reduce usage efficiency and affect the overall experience.
Excessive Token Consumption: If too many MCP servers are configured for the AI Agent, it will require sending the complete descriptive information of all tools when interacting with the large model, leading to a surge in token consumption, increasing inference costs and reducing response speed.
Security and Trust Risks: For MCP servers provided by the open-source community that require local deployment, users often face security concerns: does this server have vulnerabilities? Is there a risk of data leakage? The lack of authoritative security assessment mechanisms makes it difficult for users to have sufficient trust while using it.
These issues somewhat restrict the popularization of the MCP ecosystem and the widespread application of AI Agent, necessitating systematic solutions to improve usability, efficiency, and security.
In response to the challenges faced by AI Agent during the use of the MCP protocol, the Nacos community has launched a powerful open-source product—Nacos MCP Router (hereinafter referred to as Router). Router is a standard MCP Server that follows the MCP protocol. Its core capability is to intelligently select the most suitable MCP Server from the MCP registry based on the semantic description and keywords of user tasks, providing these candidate tools to the large model for decision-making.
By introducing Router, users no longer need to manually configure different MCP Servers for different tasks, nor do they need to sift through a plethora of MCP services. The AI Agent only needs to integrate with this one MCP Server (the Router), greatly simplifying integration and management complexity.
More importantly, Router significantly optimizes token usage efficiency. In the initial phase, the AI Agent only needs to transmit Router's lightweight tool description to the large model, avoiding redundant transmission of all tool information. During execution, Router dynamically matches and only returns MCP tool descriptions relevant to the current task, thus greatly reducing context length, effectively alleviating token consumption problems caused by an excess of tool descriptions, lowering inference costs, and improving response speed.
Moreover, the security issues of MCP Servers are also becoming increasingly prominent. Currently, most open-source MCP Servers rely on local deployment and expose functionalities through standard input/output (stdio) protocols, posing potential security risks such as data leakage and process contamination. To address this, Router provides critical proxy and protocol conversion capabilities: supporting one-click conversion of stdio-based MCP Servers to more secure and controllable SSE or streamable HTTP protocols and achieving isolated operation of services through Docker container deployment. With this mechanism, users can deploy originally insecure stdio services in isolated container environments, effectively blocking sensitive data leakage paths, enhancing overall system security and maintainability.
As part of the Nacos MCP solution, the overall architecture diagram of Router is shown below:
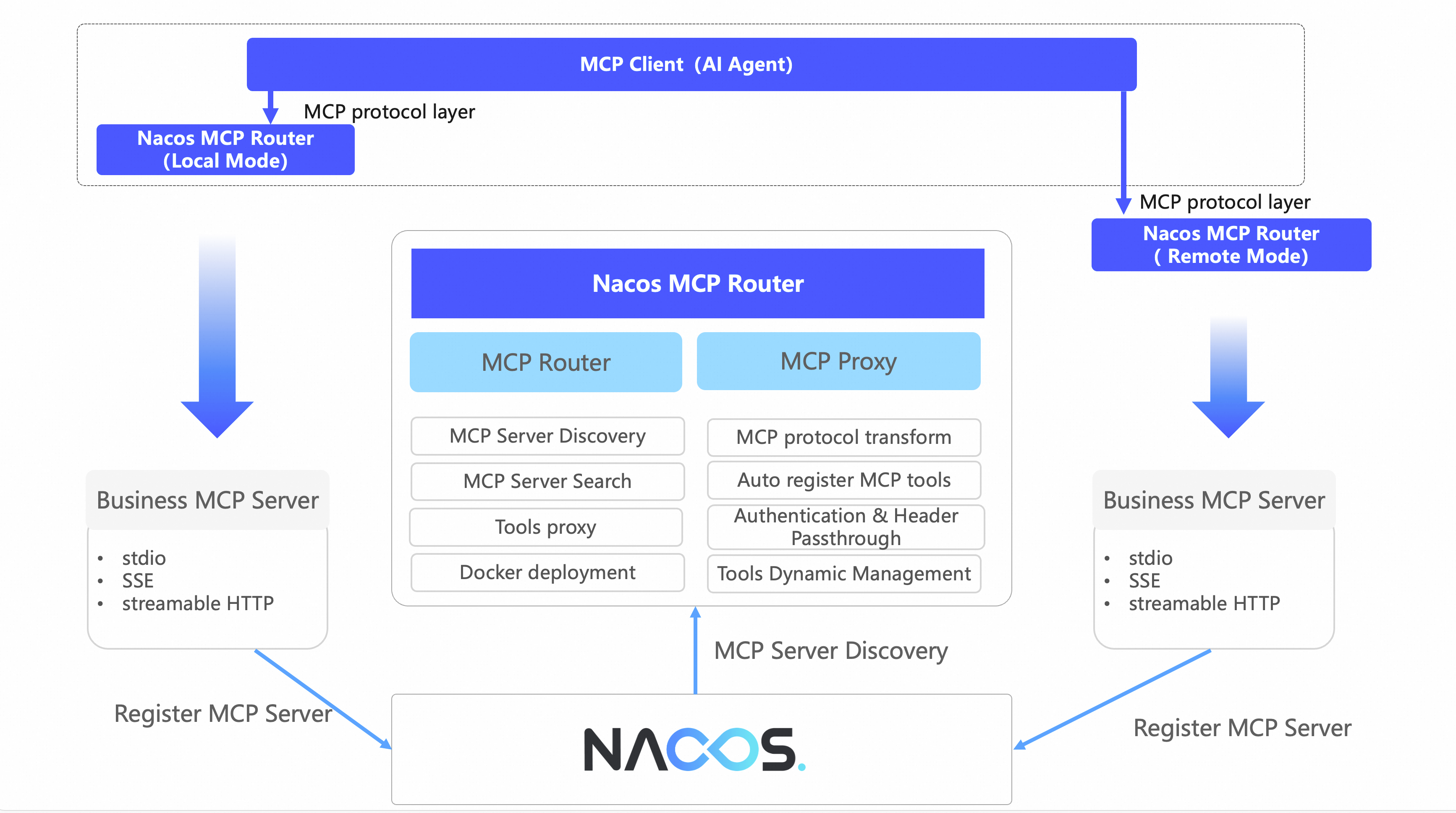
1. Router, as a standard MCP Server, communicates with the upper-layer MCP Client via the MCP protocol, supporting Local mode (stdio protocol) and Remote mode (SSE or streamable HTTP protocol).
2. Router has two main working modes: intelligent routing mode and proxy mode.
3. Router takes the Nacos MCP Registry as the data source to obtain the list of MCP Servers. Users can consume MCP Servers through Router after configuring them in Nacos or relying on SDKs for automatic registration.
In intelligent routing mode, Router is a standard MCP Server, providing three MCP tools:
● search_mcp_server: intelligently filters MCP Servers based on task descriptions and keywords;
● add_mcp_server: initializes the specified MCP Server; if it is the stdio protocol, it executes installation and initialization logic; if it is the SSE or streamable HTTP protocol, it executes connection establishment and initialization logic;
● use_mcp_tool: uses a particular tool of the target MCP Server; Router will proxy the tool request to the target MCP Server.
The architectural diagram is as follows:
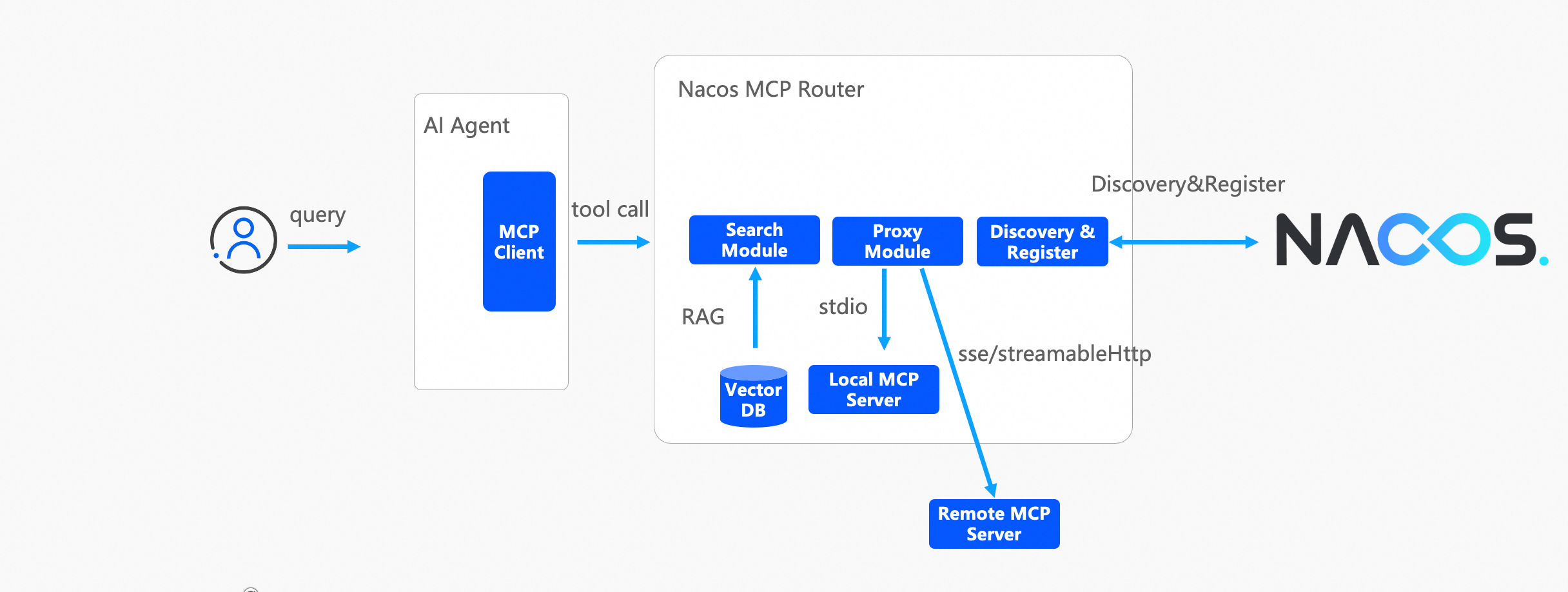
The workflow in intelligent routing mode is as follows:
The proxy mode is relatively simpler. The initial intention of proxy mode is to convert stdio protocol MCP Servers to SSE or streamable HTTP protocol MCP Servers at the click of a button, while also providing users with an isolated MCP operating environment via container technology.
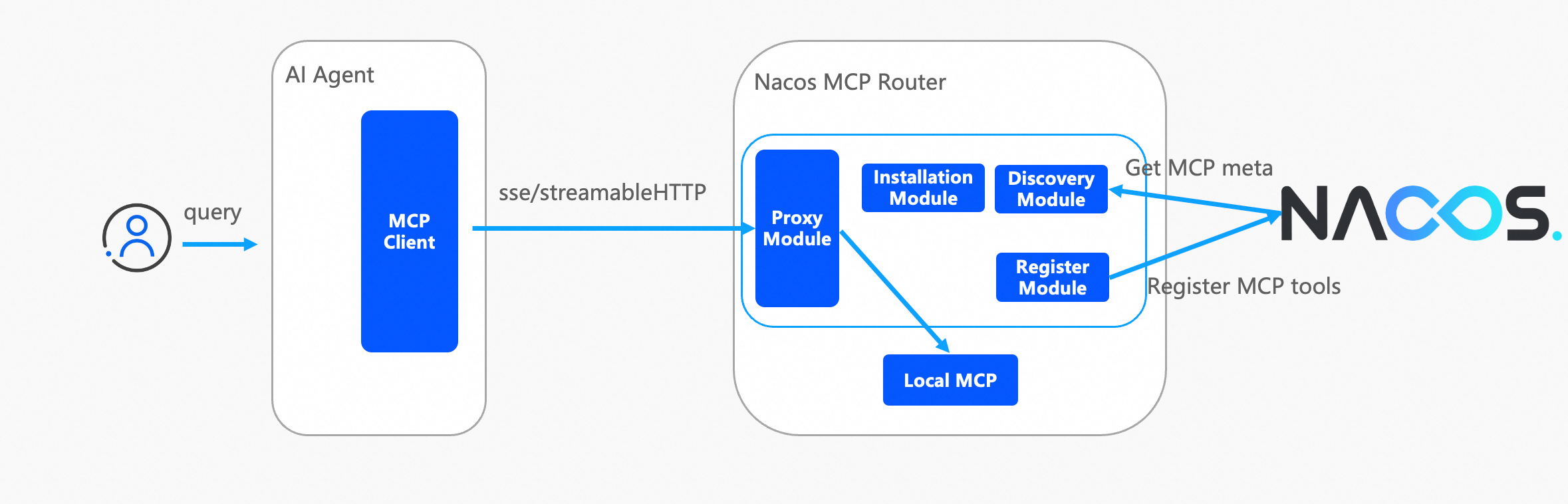
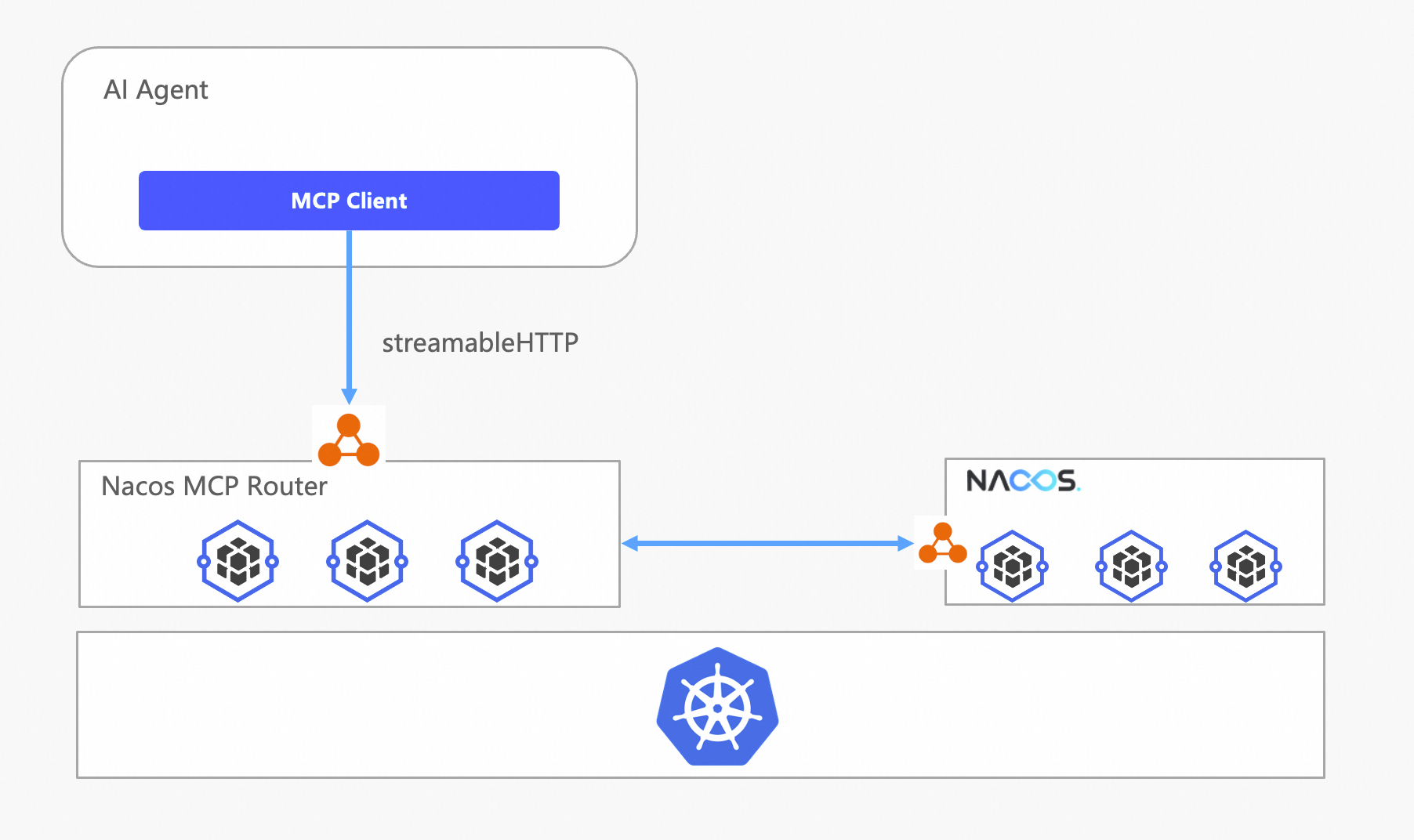
● Both Nacos and Router are containerized deployments, isolating computing resources
● Nacos and Router are deployed in multiple copies to enhance stability
● Router uses SLB to provide load balancing capabilities and expose services externally
● It is recommended to use streamable HTTP protocol to provide stateless MCP Server
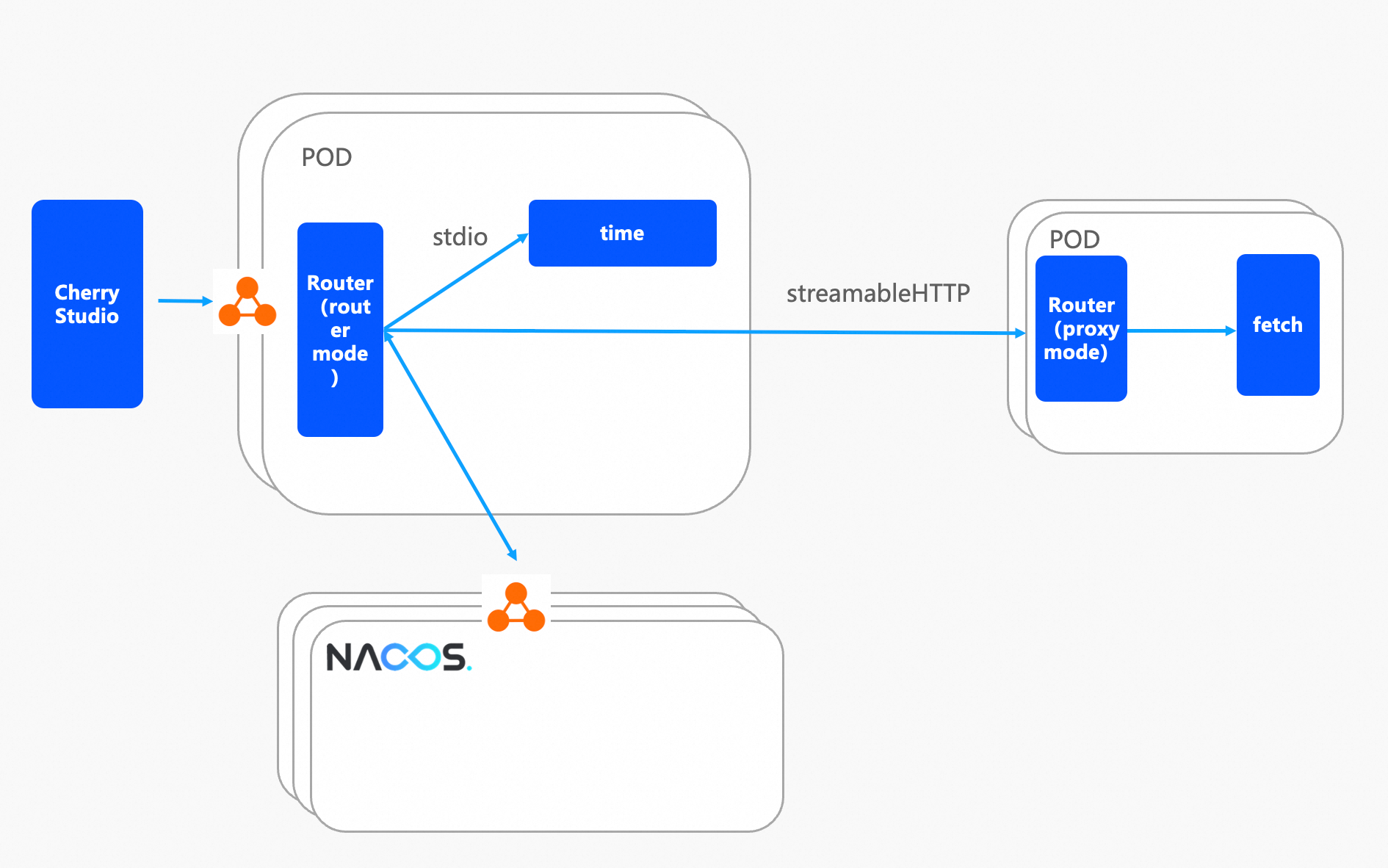
To reduce complexity, this deployment is based on Alibaba Cloud's container platform ACS, as the Serverless delivery model of ACS helps users avoid the complexity of managing underlying K8s resources.
Creating Nacos and Nacos MCP Router Clusters
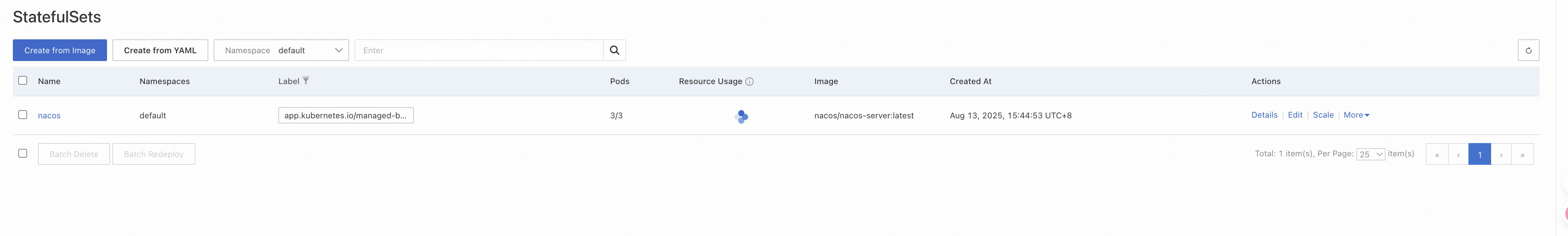
The Nacos MCP Router now supports one-click deployment via Helm, including the Nacos cluster that Router depends on, and can automatically create SLB to expose services. First, ensure that Helm and kubectl are correctly installed and configured. For convenience, we deploy Nacos and Router on Alibaba Cloud ACS, and the deployment script is as follows:
git clone https://github.com/nacos-group/nacos-mcp-router.git
cd nacos-mcp-router/helm
bash randomize_values.sh
helm install nacos-mcp-router . -n nacos-mcp --create-namespaceAfter executing the command successfully, wait for the cluster initialization to complete. After deployment, it appears as shown below, including 3 nodes of Nacos, MySQL, and Router.
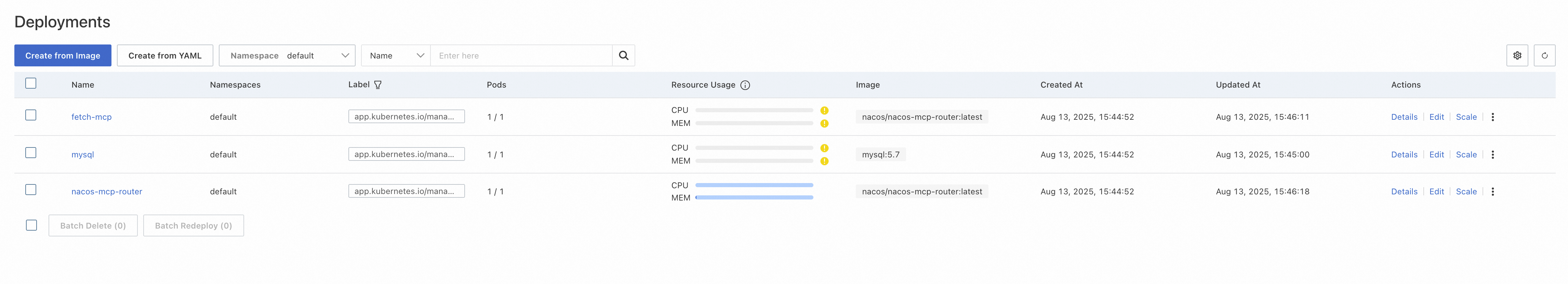
1. Log in to the Nacos console: After the cluster deployment is complete, we need to register the relevant MCP Servers in Nacos. Find the external SLB of Nacos in the ACS console to access the Nacos console and register the MCP Server.
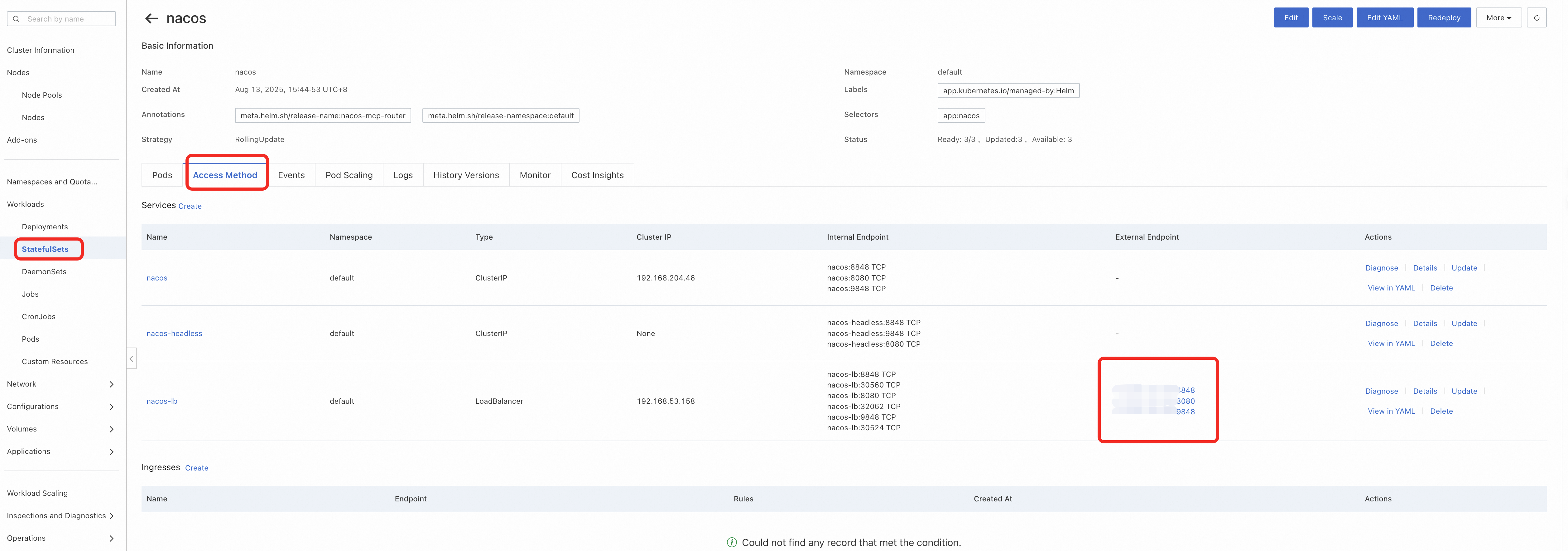
2. Initialize the console password: The first time logging into the Nacos console requires initializing the password, here, the password should be initialized to the value of NACOS_PASSWORD in the values.yaml file

3. Register Local MCP Server
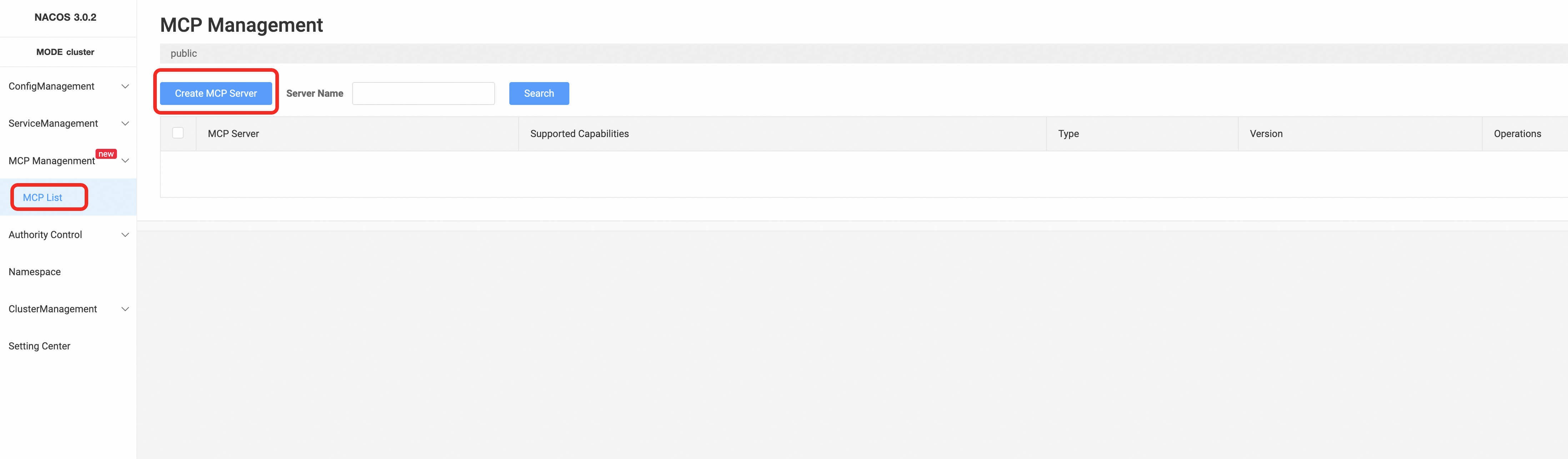
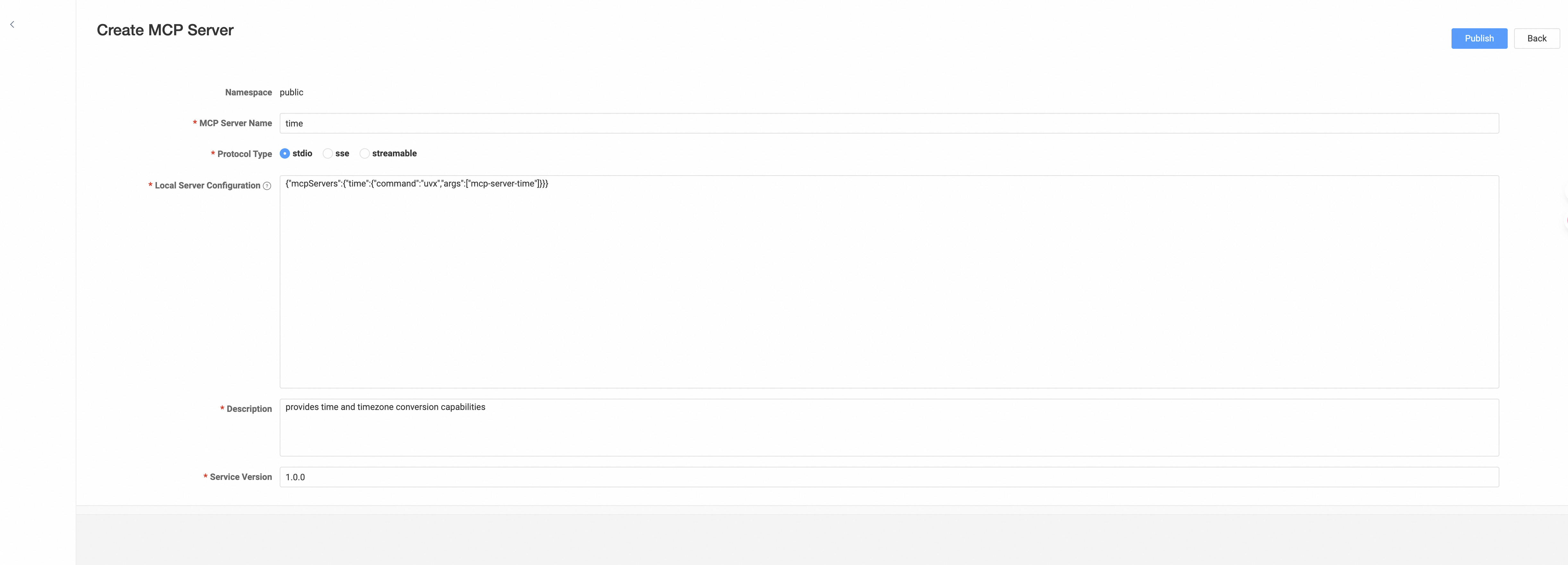
As mentioned earlier, Router supports MCP protocol conversion. This section describes deploying Router in proxy mode and proxying stdio protocol MCP Servers while exposing streamable HTTP protocol, taking MCP Server fetch as an example:
● Deploy fetch
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: fetch-mcp
spec:
replicas: 1
selector:
matchLabels:
app: fetch-mcp
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: fetch-mcp
spec:
containers:
- name: fetch-mcp
image: "nacos/nacos-mcp-router:latest"
env:
- name: TRANSPORT_TYPE
value: streamable_http
- name: MODE
value: "proxy"
- name: PROXIED_MCP_NAME
value: "fetch"
- name: PROXIED_MCP_SERVER_CONFIG
value: '{"mcpServers":{"fetch":{"command":"uvx","args":["mcp-server-fetch"]}}}'
- name: AUTO_REGISTER_TOOLS
value: "false"
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: fetch-mcp
spec:
type: ClusterIP
selector:
app: fetch-mcp
ports:
- name: http
port: 8000
targetPort: 8000Deploy using kubectl:
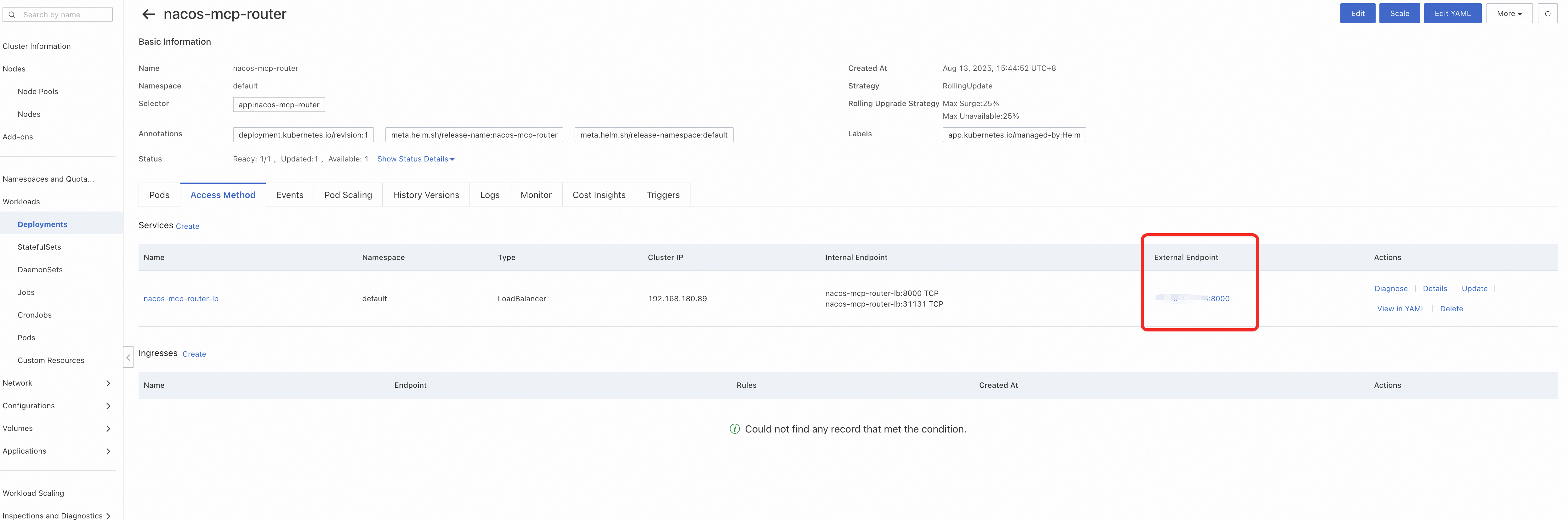
kubectl apply -f nacos-mcp-router-proxy-deployment.yaml -n nacos-mcp● After deployment, you can see the access information of fetch-mcp:
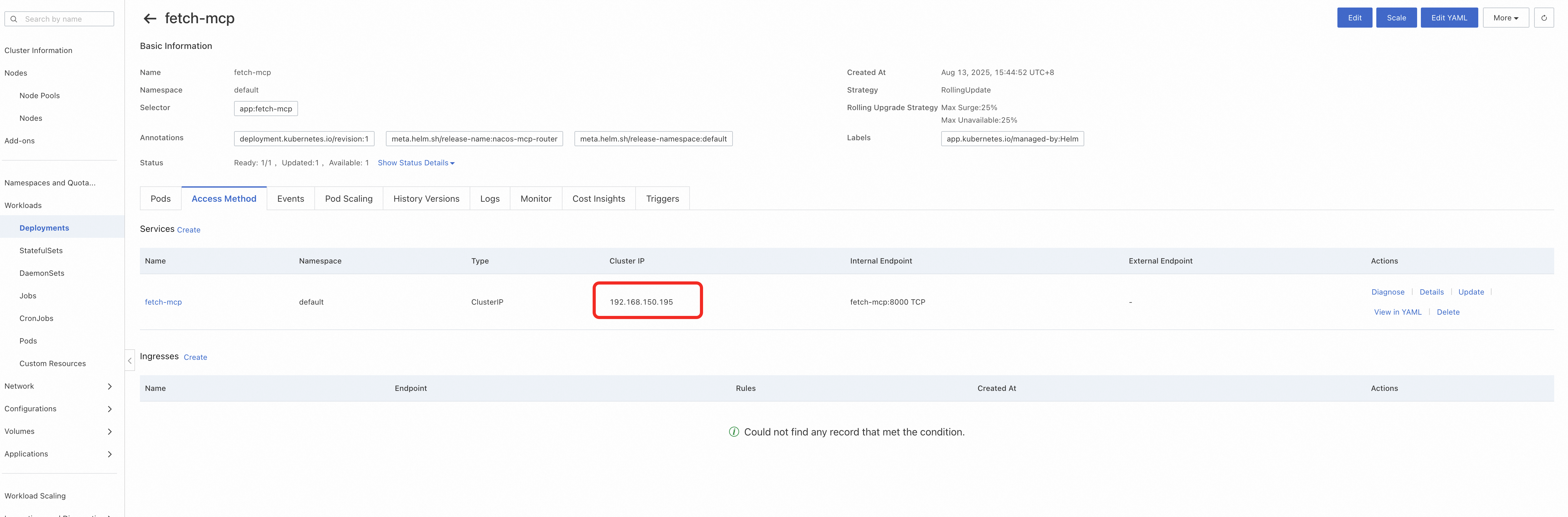
● In the Nacos console, simply register fetch as a streamable protocol MCP Server.
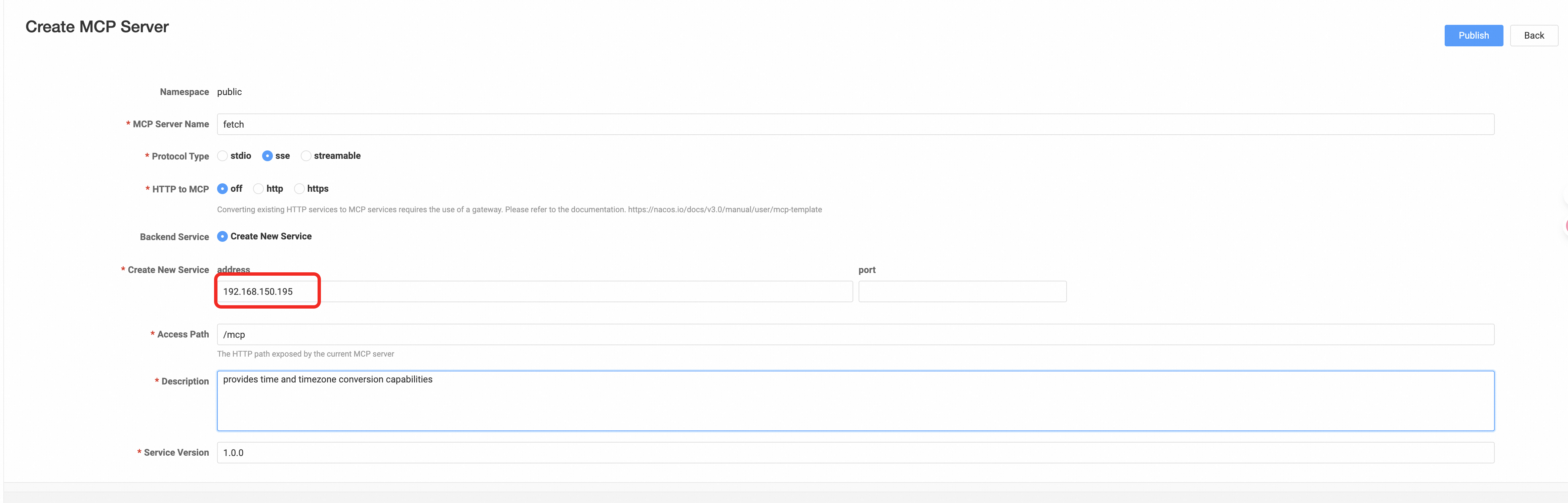
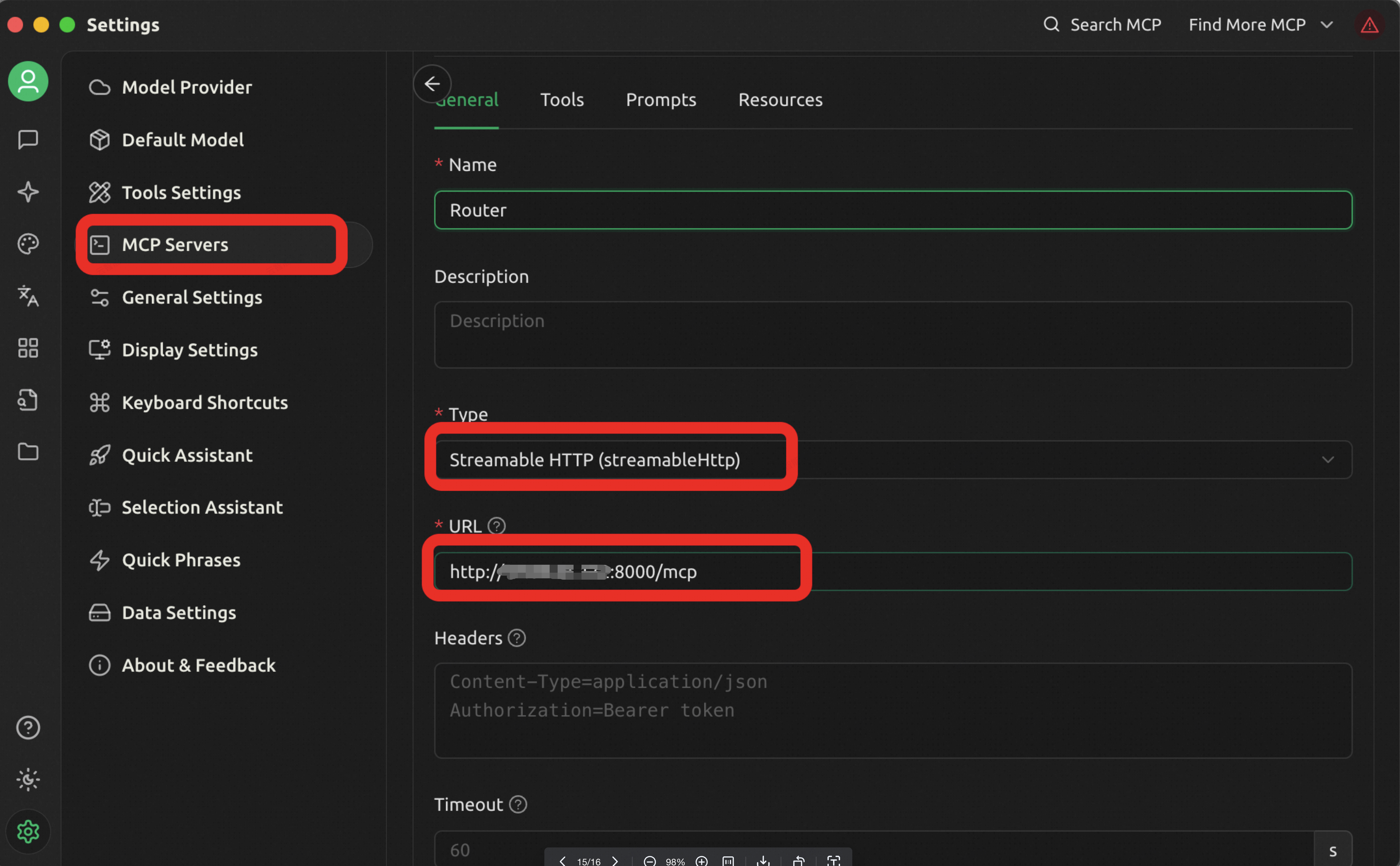
● Configure the cherry studio MCP server, select streamable protocol, the address is the public address of the Router
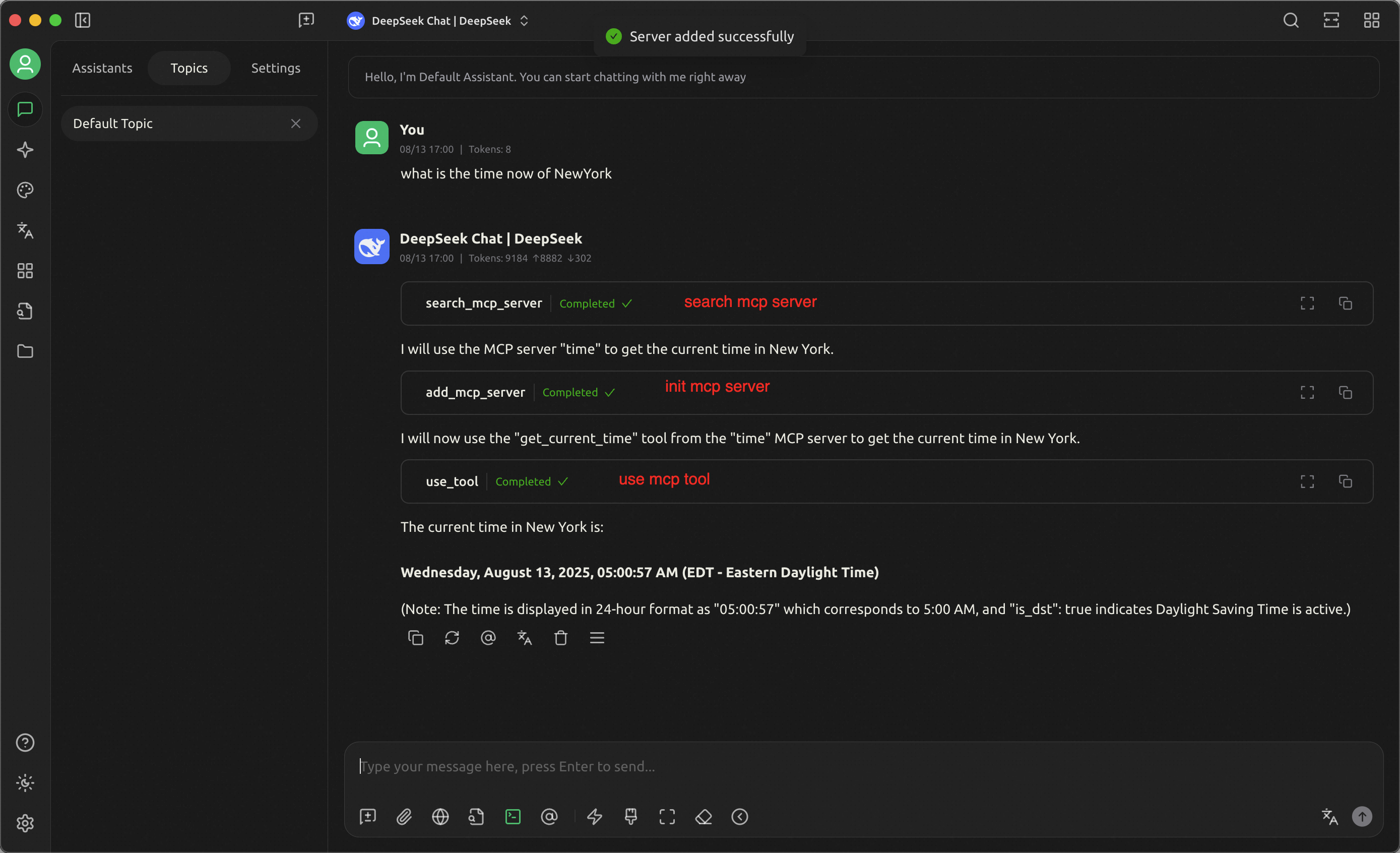
● Use Router to automatically discover MCP
There are many things the Nacos MCP Router aims to achieve in the future, with recent focuses on security, stability, and intelligence:
● Security: Unified authentication management for MCP
● Stability: Rate limiting for tool calls, observability
● Intelligence: Virtual MCP construction, MCP tool filtering, optimization of retrieval accuracy
Everyone is welcome to participate in co-building, starred at: https://github.com/nacos-group/nacos-mcp-router
Leap in Log Collection Efficiency: Comprehensive Upgrade from iLogtail to LoongCollector
Cracking Five Challenges in Heterogeneous Log Cleaning: Fully Boosting O&M Data Observability

664 posts | 55 followers
FollowAlibaba Cloud Native Community - May 29, 2025
Alibaba Cloud Native Community - June 13, 2025
Alibaba Cloud Native Community - June 10, 2025
Alibaba Cloud Native Community - September 3, 2025
Alibaba Cloud Native Community - April 15, 2025
Alibaba Cloud Native Community - September 29, 2025

664 posts | 55 followers
Follow Best Practices
Best Practices
Follow our step-by-step best practices guides to build your own business case.
Learn More Cloud-Native Applications Management Solution
Cloud-Native Applications Management Solution
Accelerate and secure the development, deployment, and management of containerized applications cost-effectively.
Learn More AI Acceleration Solution
AI Acceleration Solution
Accelerate AI-driven business and AI model training and inference with Alibaba Cloud GPU technology
Learn More Offline Visual Intelligence Software Packages
Offline Visual Intelligence Software Packages
Offline SDKs for visual production, such as image segmentation, video segmentation, and character recognition, based on deep learning technologies developed by Alibaba Cloud.
Learn MoreMore Posts by Alibaba Cloud Native Community