This topic lists common Web Application Firewall (WAF) 3.0 issues that you may encounter during onboarding.
Overview
Pre-onboarding capabilities and configuration
What is the difference between an origin IP address and a back-to-origin IP address in WAF?
Can I use both cloud native integration and CNAME record mode for the same domain in WAF 3.0?
How can I configure WAF to protect a single domain with multiple origin server IPs?
What is the correct way to integrate WAF 3.0 with CDN or Anti-DDoS Proxy?
Does WAF support a cross-account architecture that uses CDN, Anti-DDoS Proxy, and WAF?
How does WAF use a custom header to obtain and record the client's source IP address?
The same domain name resolves to multiple cloud product instances. How should I onboard them?
Multiple domain names resolve to the same cloud product instance. How should I onboard them?
What domain name suffixes are supported for CNAME onboarding?
Does protecting an HTTP 2.0 service with WAF affect the origin server?
Does WAF support onboarding for websites that use NTLM protocol authentication?
Is the WAF QPS limit for the entire WAF instance or for a single configured domain name?
Issues during onboarding
Post-onboarding issues
What is the difference between an origin IP address and a back-to-origin IP address in WAF?
These two terms define the source and destination of traffic after it has been processed by WAF.
Origin IP: This is the public IP address of your actual server that hosts your services (such as an ECS instance, SLB, or OSS bucket). It is the final destination for legitimate traffic that WAF forwards.
Back-to-origin IP: This is an IP address from a range owned by WAF. When WAF forwards a request to your origin server, it uses a back-to-origin IP as the source. You should configure your origin server's firewall or security group to allow traffic only from these WAF IP ranges.
Can the same domain name use the cloud native mode and the CNAME record mode at the same time?
No, this is not supported. Using both modes for the same domain will cause routing conflicts and disable WAF protection.
Each domain can only be onboarded using one method at a time. To switch a domain from CNAME record mode to cloud native mode, you must first delete its CNAME configuration from WAF and then add the domain again using the cloud native mode.
How can I configure WAF to protect a single domain with multiple origin server IPs?
Yes, you can configure a single domain name in WAF to forward traffic to multiple origin servers for load balancing and high availability. WAF allows you to add up to 20 origin IP addresses for a single domain.
Does WAF perform health checks on origin servers?
Yes, health checks are enabled by default.
WAF continuously monitors the status of all configured origin IP addresses. If an origin IP becomes unresponsive, WAF will temporarily stop sending traffic to it and distribute the requests among the remaining healthy IPs. After a brief silence period, WAF will attempt to send traffic to the unresponsive IP again to check if it has recovered.
How does an exclusive IP in WAF help mitigate DDoS attacks?
An exclusive IP address isolates your WAF-protected services from those of other customers. This prevents a large-scale DDoS attack on another customer's domain from impacting the performance or availability of your domains (an issue sometimes called the "noisy neighbor" effect). For more information, see Value of exclusive IP addresses.
What is the correct way to integrate WAF 3.0 with CDN or Anti-DDoS Proxy?
Yes, WAF is fully compatible with these services. To integrate them correctly, you must ensure the traffic flows in the following order: Client -> CDN/Anti-DDoS Proxy-> WAF -> Origin Server.
To achieve this:
Add your domain to WAF and obtain the WAF CNAME address.
In your CDN or Anti-DDoS Proxy configuration, set the origin address to the CNAME provided by WAF.
For more information, see Improve website security by deploying Anti-DDoS Proxy and WAF and Deploy WAF and CDN to protect a domain name for which CDN is enabled.
Does WAF support a cross-account architecture that uses CDN, Anti-DDoS Proxy, and WAF?
Yes, this cross-account architecture is fully supported. You can use CDN, Anti-DDoS Proxy, and WAF services from different Alibaba Cloud accounts to build a comprehensive security architecture.
When using WAF for HTTPS traffic, how are my SSL certificate and private key secured, and is my traffic logged?
Certificate security
To inspect HTTPS traffic for attacks, WAF requires your SSL certificate and private key. These are stored and managed in a dedicated Key Server built on Alibaba Cloud Key Management Service (KMS), which is designed to protect the security, integrity, and availability of your cryptographic keys in compliance with regulatory standards. For more information, see What is KMS?.
Traffic logging
WAF uses your uploaded SSL certificate and key to decrypt HTTPS traffic for real-time inspection only. We only record parts of request content that contain attack signatures (payloads) for purposes such as displaying attack reports and data statistics. We do not record the full content of requests or responses without your authorization.
Alibaba Cloud WAF has obtained multiple international authoritative certifications, such as ISO 9001, ISO 20000, ISO 22301, ISO 27001, ISO 27017, ISO 27018, ISO 27701, ISO 29151, BS 10012, CSA STAR, Classified Protection Compliance Level 3, SOC 1/2/3, C5, HK Finance, OSPAR, and PCI DSS. As a standard Alibaba Cloud product, it has the same level of security and compliance qualifications as the Alibaba Cloud platform. For more information, see Alibaba Cloud Trust Center.
My website is protected by WAF, but why can't I find it in the domain name list?
Your website's ICP filing may have expired, which causes the domain name to no longer meet the onboarding requirements. WAF automatically purges such domain names from the protected list. You must complete the ICP filing for the domain name and then add the website to WAF again. For more information about Alibaba Cloud ICP filing, see ICP filing process.
Before you protect your website with a WAF instance in the Chinese mainland, you must ensure that the domain name has a valid ICP filing. To comply with relevant laws and regulations, WAF instances in the Chinese mainland periodically purge domain names with expired ICP filings.
How does WAF use a custom header to get and record the client's source IP address?
Obtain the client's source IP address from a custom header: If other Layer 7 proxy services, such as Anti-DDoS Pro and Anti-DDoS Premium or CDN, are deployed in front of WAF, you can use a custom header to store the client IP address. This method improves security by preventing attackers from forging the X-Forwarded-For (XFF) header to bypass WAF detection rules. To do this, place the client's source IP address in a custom header field, such as X-Client-IP or X-Real-IP, and configure WAF to read from that header field. WAF then retrieves the value of the specified header field as the client's source IP address. If you specify multiple header fields, WAF attempts to read the client IP address from the headers in the order they are specified.
Record the client IP address in a custom header: When you add a website for WAF protection, you can enable traffic marking. This feature causes WAF to write the client IP address into a custom header field of the client request. The backend server can then obtain the client IP address from the specified header field in the back-to-origin request that is forwarded by WAF. This is useful for scenarios where the backend server needs to obtain the client IP address from a specific custom header for business analysis.
The same domain name resolves to multiple cloud product instances. How should I onboard them?
If you use cloud native mode, you must onboard all these cloud product instances, for example, the service ports of an SLB instance, at the same time. This allows WAF to redirect traffic for all of them.
If you use CNAME mode, after you add the domain name, all cloud product instances are protected by the WAF default mitigation policy.
Multiple domain names resolve to the same cloud product instance. How should I onboard them?
When you use cloud native mode, all domain names on an onboarded cloud product instance are protected by the WAF default mitigation policy. However, if you want to configure different protection rules for individual domain names, you must add them as protected objects. For more information, see Manually add a protected object.
If you use CNAME mode, you must add the domain names one by one.
What domain name suffixes are supported for CNAME onboarding?
WAF 3.0 supports most domain name suffixes, including Chinese domain name suffixes. For a list of supported Chinese suffixes, see iana.org.
WAF 3.0 supports more domain name suffixes than WAF 2.0. If you find that a domain name is not supported for onboarding in WAF 2.0, we recommend that you upgrade to WAF 3.0.
Does WAF support HTTPS mutual authentication?
No, CNAME and transparent proxy modes do not support HTTPS mutual authentication. However, the service-based onboarding solution for WAF 3.0 supports it. Currently, cloud products that support service-based onboarding include ALB, MSE, FC, and SAE. You can configure this type of onboarding in the cloud native mode section of the WAF console.
Does WAF support WebSocket, HTTP 2.0, or SPDY protocols?
WAF supports the WebSocket protocol. The Enterprise Edition and higher subscription plans, along with the pay-as-you-go plan, support listening for the HTTP 2.0 protocol. The SPDY protocol is not supported.
To prevent attackers from using HTTP 2.0 cleartext smuggling to bypass WAF, you can create a custom rule to block requests where the header name is Upgrade and the value is h2c. For more information, see Create a custom rule to defend against specific requests.
Does protecting an HTTP 2.0 service with WAF affect the origin server?
Yes. Protecting an HTTP 2.0 service with WAF means that WAF can process HTTP 2.0 requests from clients. However, WAF currently supports forwarding back-to-origin requests only over HTTP 1.0/1.1. HTTP 2.0 is not yet supported between WAF and the origin server. Therefore, if you protect an HTTP 2.0 service with WAF, the HTTP 2.0 features of the origin server are affected. For example, the HTTP 2.0 multiplexing feature of the origin server may become ineffective, which causes an increase in the origin server's service bandwidth.
Does WAF support onboarding for websites that use NTLM protocol authentication?
No. If a website uses NTLM protocol authentication, access requests forwarded by WAF may fail the origin server's NTLM authentication. The client repeatedly sees authentication prompts. We recommend that you use other methods for website authentication.
Is the WAF QPS limit for the entire WAF instance or the upper limit for a single configured domain name?
The WAF queries per second (QPS) limit applies to the entire WAF instance.
For example, if you have configured three domain names for protection on a WAF instance, the total QPS for these three domain names cannot exceed the specified limit. If the QPS exceeds the limit of your purchased WAF instance, the instance may enter a sandbox. If the actual QPS exceeds the specification or the instance enters a sandbox, the product is no longer guaranteed to follow the Service-Level Agreement (SLA).
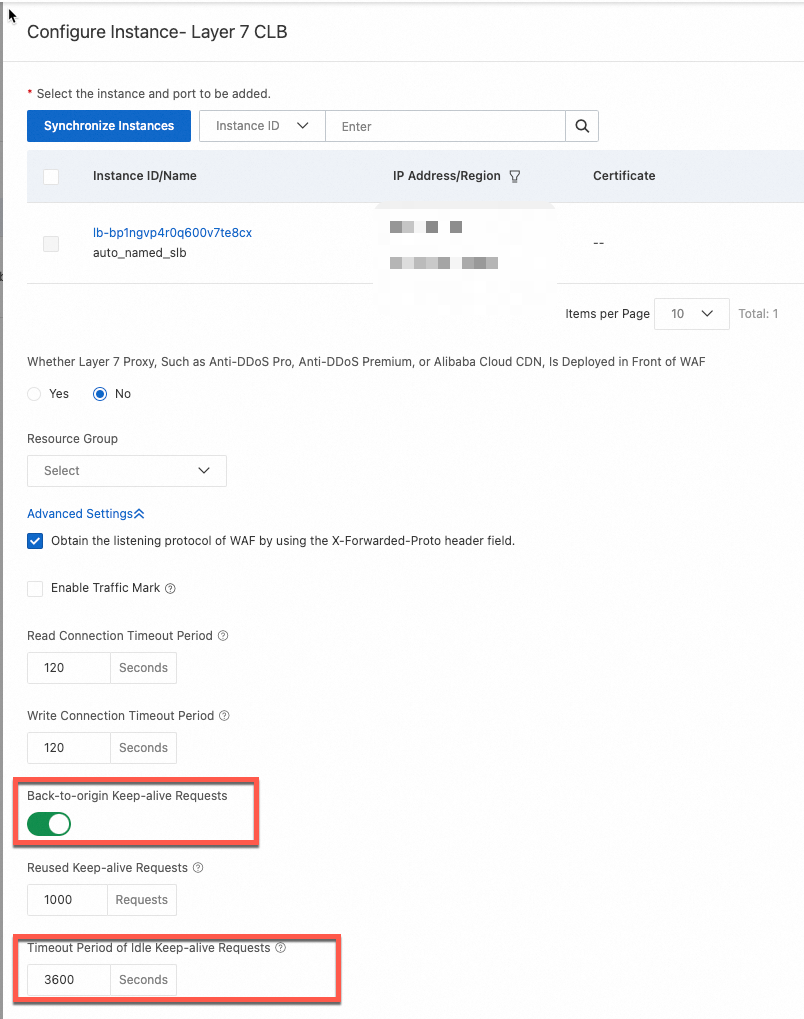
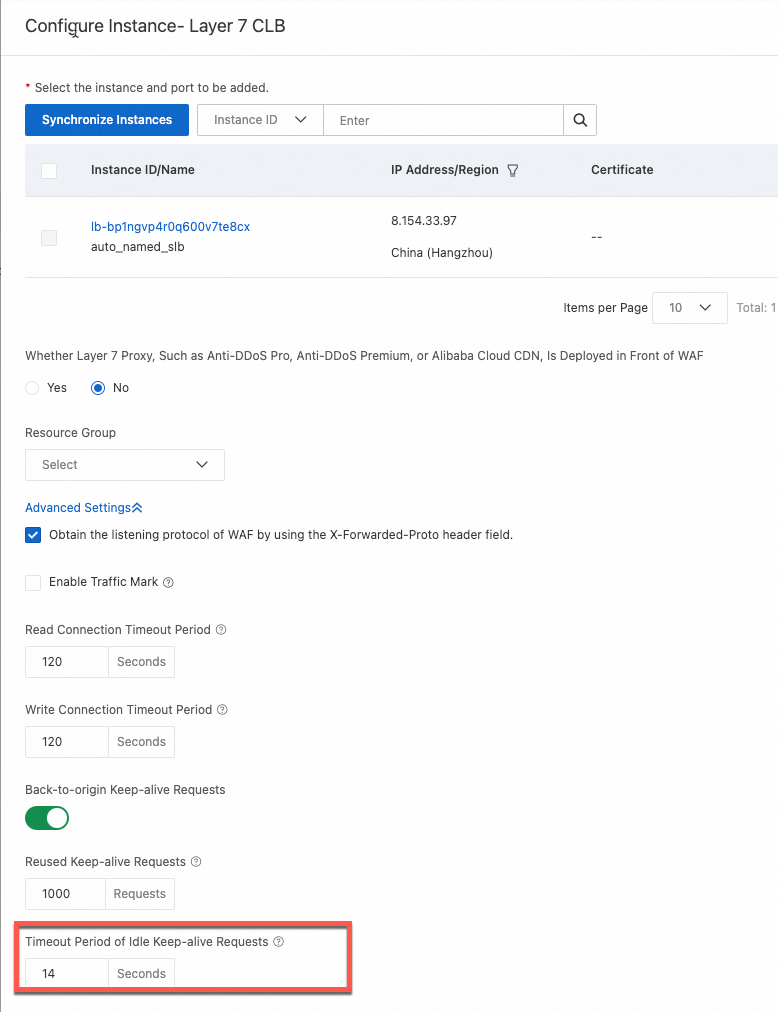
How do I view the WAF back-to-origin IP ranges and the CNAME provided by WAF?
You can find the WAF back-to-origin IP ranges and the CNAME address provided by WAF for each onboarded domain name in the location shown in the following figure on the onboarding list page.
Troubleshooting when the SLB, NLB, or ECS instance to be onboarded cannot be found on the configuration page
Possible causes | Related operations |
The SLB, NLB, or ECS instance to be onboarded does not meet the conditions. | Check the instance against the onboarding conditions. For more information about the conditions, see SLB instance onboarding conditions, NLB instance onboarding conditions, and ECS instance onboarding conditions. |
No corresponding listener is added to the SLB instance to be onboarded. |
|
WAF failed to synchronize with SLB, NLB, or ECS instances | For the specific steps to synchronize assets, see Manually sync assets. |
When adding an HTTPS traffic redirection port, a message indicates that the SLB certificate is incomplete. What should I do?
Problem description
When you add an HTTPS traffic redirection port, WAF validates the source of the certificate configured for that port. After you add the port, the following message appears: The SLB certificate for port XXX is incomplete. Go to the SLB console and reselect a certificate from Certificate Management Service.
Possible causes
The configured certificate was not purchased from Alibaba Cloud Certificate Management Service (Original SSL Certificate) and has not been uploaded to Alibaba Cloud Certificate Management Service (Original SSL Certificate).
The certificate for the HTTPS port listener of the SLB instance was uploaded through the SLB console. However, this upload method does not automatically synchronize the certificate information to Certificate Management Service (Original SSL Certificate). Because WAF only retrieves certificate information from Certificate Management Service, WAF cannot obtain the complete certificate content, which causes the 'certificate is incomplete' message to appear.
The certificate that you previously uploaded was manually deleted, and your certificate is no longer in Certificate Management Service (Original SSL Certificate).
Solutions
Upload your certificate to Certificate Management Service (Original SSL Certificate). For more information, see Upload SSL Certificate.
Create a certificate in the SLB console and select Alibaba Cloud Certificates as the certificate source. For more information, see Select an Alibaba Cloud-issued certificate.
In the SLB console, select the uploaded server certificate. For more information, see Step 2: Configure an SSL certificate.
For the origin IP address in WAF, should I enter the public IP address or private IP address of an ECS instance?
You should enter the public IP address. WAF uses the Internet for origin fetch and does not support private IP addresses.
The public IP address of the origin server is exposed. What if an attacker bypasses WAF by directly attacking the origin's public IP address?
You can use one of the following methods: Method 1: In CNAME record mode, configure the origin server to allow traffic only from the WAF back-to-origin IP ranges. This ensures that only WAF can communicate with the origin server. For more information, see Allow WAF back-to-origin IP addresses.
Method 2: Use cloud native mode.
Multiple scenarios for receiving a 502 status code after onboarding WAF
Problem description
After you onboard WAF, accessing the backend service returns a 502 status code. The logs show requests with a 502 status code.
Causes and solutions
Scenario 1: 502 error in CNAME mode
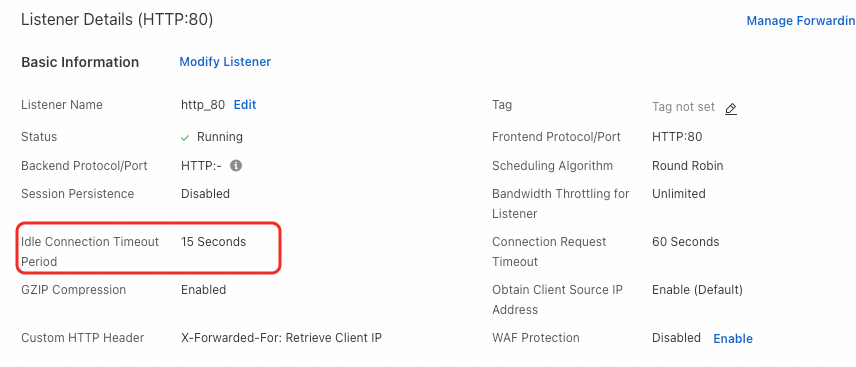
Scenario 2: Intermittent 5xx errors with a Layer 7 SLB in cloud native mode
Scenario 3: Intermittent 502 errors due to a long URI
Scenario 4: Intermittent 502 errors when WAF sends back-to-origin requests to multiple Layer 4 SLBs
File upload fails after onboarding WAF
This issue may occur because the file upload exceeds the size limit. WAF supports a maximum file upload size of 2 GB. If the request body exceeds 2 GB, WAF returns a 413 status code. You can check the returned status code to determine if the file transfer size limit was reached.
How do I update a certificate that is about to expire?
The update method varies depending on the onboarding mode:
For CNAME mode, see Update the certificate bound to a domain name.
For cloud native mode with an ECS instance, see Update the certificate bound to an ECS traffic redirection port.
For cloud native mode with an SLB instance, see Update the certificate bound to an SLB traffic redirection port.
For cloud native mode with an NLB instance, see Update the certificate bound to an NLB traffic redirection port.
For cloud native mode with an ALB instance, you do not need to update it in the WAF console. Simply deploy the certificate to the ALB instance in the Certificate Management Service (Original SSL Certificate) console. For more information, see Deploy an SSL certificate to an Alibaba Cloud service.
After onboarding through cloud native mode, can the origin server get the real client IP address?
Yes, it can. WAF directly provides the real client IP address to the cloud product instance.