Web Application Firewall (WAF) protects domain names that are deployed in a hybrid cloud. This topic describes how to add a domain name from a hybrid cloud environment to WAF.
Background information
The Hybrid Cloud WAF solution provides unified Web Application Protection for multicloud, cross-cloud, and hybrid cloud environments. These environments can include public clouds, private clouds, and on-premises data centers. This solution helps you build an elastic and efficient security system that integrates on-premises and cloud resources. After you add a domain name to WAF, traffic to the protected domain name can be forwarded to origin servers over the Internet or an internal network.
Prerequisites
A WAF instance is purchased, and the number of domain names that are added to the WAF instance is less than the upper limit.
NoteThe maximum number of domain names that can be added to a WAF instance varies based on the specifications of the instance and the number of extra domain names that you purchase. For more information, see Extra domain package.
If you use a WAF instance in the Chinese mainland to protect a domain name, you must complete an Internet Content Provider (ICP) filing for the domain name before you add the domain name to the instance. If you add the domain name to a WAF instance before you complete an ICP filing, WAF may report an error and prompt you to complete the ICP filing.
You have deployed an on-premises WAF protection node cluster, and the nodes in the cluster can connect to the Internet. For more information, see Deploy a Hybrid Cloud WAF protection cluster.
Limits
If you use Hybrid Cloud WAF protection nodes to protect internal services, clients cannot use IP addresses in the 172.16.0.0/16 CIDR block to access these services.
Add a hybrid cloud website
Log on to the WAF console. In the top navigation bar, select the resource group and the region in which the WAF instance is deployed. The region can be Chinese Mainland or Outside Chinese Mainland.
In the left-side navigation pane, choose .
On the Domain Names tab, click Website Access.
NoteBy default, the Access Mode parameter is set to CNAME Record on the Add Domain Name page.
Enter the website information and click Next.
Configuration item
Description
Domain Name
Enter the domain name that you want to protect. You can enter an exact-match domain name, such as www.aliyundoc.com, or a wildcard domain name, such as *.aliyundoc.com. You can enter only one domain name.
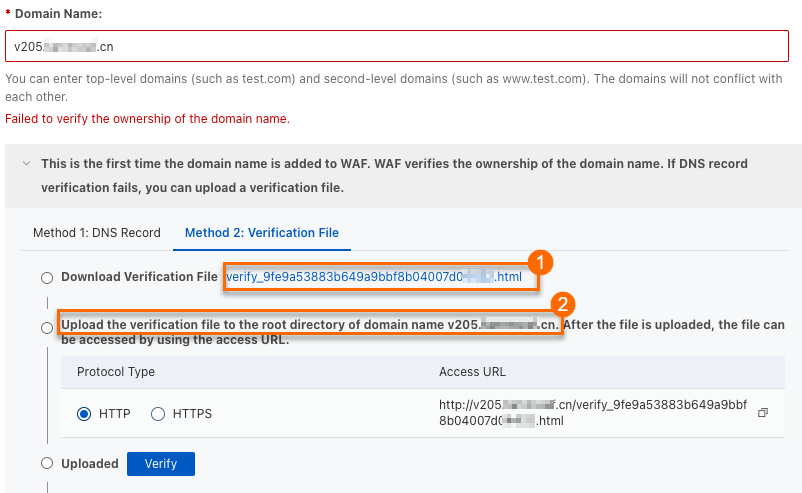
If this is the first time you add the domain name, you must verify its ownership before you can add it.
NoteA wildcard domain name can match subdomains at the same level and at different levels. For example,
*.aliyundoc.comcan match multi-level domain names such aswww.aliyundoc.com,example.aliyundoc.com, andwww.example.aliyundoc.com.A second-level wildcard domain name can match the corresponding second-level primary domain name. For example,
*.aliyundoc.comcan matchaliyundoc.com.A third-level wildcard domain name cannot match the corresponding third-level primary domain name. For example,
*.example.aliyundoc.comcannot matchexample.aliyundoc.com.If a protected object contains both an exact-match domain name and a wildcard domain name that can match the exact-match domain name, the protection rules and forwarding configurations of the exact-match domain name take precedence.
Protection Resource
Select the type of resource that you want WAF to protect. In this case, select Hybrid Cloud Cluster.
Protocol Type
Select the protocol that the website uses. Valid values:
HTTP
HTTPS
ImportantIf the website supports HTTPS encryption, select HTTPS. After you add the domain name, upload the certificate and private key file for the domain name. For more information, see Upload an HTTPS certificate.
After you select HTTPS, you can enable the following features:
HTTP2 (This option is available only after you select HTTPS.)
If your website supports HTTP 2.0, enable this setting. The port for HTTP 2.0 is the same as the port for HTTPS. After you enable this setting, you only need to set the HTTPS port. For more information, see Does adding a service that uses HTTP 2.0 to WAF affect the origin server?.
NoteOnly WAF instances of the Enterprise, Ultimate, and Exclusive editions support HTTP2.
Node Settings
Select a Protection Node Group Name.
If one of your websites is deployed on multiple protection nodes, you can click Add Protection Node to the right of Node Settings to add multiple protection nodes to WAF at the same time.
Origin Server Address
Specify the addresses of the origin server of the website. You can specify addresses in IP address format or Domain Name (such As CNAME) format. After the website is added, WAF forwards filtered access requests to the server address that you specify. The following items describe the settings:
IP address format: Enter the public IP address of the origin server. The IP address must be reachable over the Internet.
You can enter multiple IP addresses. Press the Enter key after you enter each IP address. You can add a maximum of 20 origin IP addresses.
NoteIf you specify multiple IP addresses, WAF automatically performs health checks and load balancing among these addresses.
WAF instances outside the Chinese mainland support only IPv4 addresses. WAF instances in the Chinese mainland support the following configuration methods:
Configure both IPv4 and IPv6 addresses
If you enable Follow IPv4/IPv6 For Origin Fetch Protocol, requests from IPv6 addresses are forwarded to IPv6 origin servers, and requests from IPv4 addresses are forwarded to IPv4 origin servers. If you do not enable Follow IPv4/IPv6 For Origin Fetch Protocol, no distinction is made, and hybrid origin fetch is performed. This means that both IPv4 and IPv6 requests may be forwarded to IPv4 or IPv6 origin servers.
ImportantWhen you use origin fetch over IPv6, you must make sure that the IPv6 Status of the domain name in the Website Config list is enabled. For more information, see Enable IPv6 protection.
Configure only IPv4 addresses
Both IPv4 and IPv6 requests are forwarded over IPv4. This means that WAF forwards requests to the IPv4 origin server address that you specify.
Configure only IPv6 addresses
Both IPv4 and IPv6 requests are forwarded over IPv6. This means that WAF forwards requests to the IPv6 origin server address that you specify.
Domain Name (such As CNAME) format: Enter the origin URL of the server, such as the CNAME of an OSS bucket.
If you use the domain name format, origin fetch over IPv4 is supported. This means that WAF forwards client requests to the IPv4 address to which the origin URL is resolved.
ImportantThe origin URL of the server must be different from the domain name of the website that you want to protect.
If the address of your origin server is an OSS domain name, you must go to the OSS console to attach a custom domain name to the OSS domain name after you add the website. For more information, see Attach a custom domain name.
Destination Server Port
Add the forwarding service ports that the website uses.
NoteThis feature can be configured only by Alibaba Cloud technical support.
The ports must be within the range of enabled ports for the hybrid cloud cluster. By default, ports 80, 8080, 443, and 8443 are enabled for a hybrid cloud cluster. When you create a hybrid cloud cluster, you can specify a custom range of ports to enable. For more information, see Configure basic information for a hybrid cloud cluster.
WAF uses the ports that you add here to receive and forward service traffic for the website. The service traffic of the website domain name is forwarded only through the added service ports. WAF does not forward any access requests on other ports to the origin server. Therefore, enabling these ports does not pose any security threats to the origin server.
ImportantThe Protocol Type and Destination Server Port that you set for the website must be the same as the protocol and port that the origin server uses to provide web services. Port mapping is not supported. For example, if the origin server uses port 80 and the HTTP protocol to provide web services, you must configure the same port and protocol for the domain name. If you set other ports, requests cannot be forwarded.
Default ports:
If you set Protocol Type to HTTP, the server port is set to HTTP 80 by default.
If you set Protocol Type to HTTPS, the server port is set to HTTPS 443 by default.
NoteThe port for HTTP 2.0 is the same as the port for HTTPS.
Custom ports: Click Custom and specify custom ports for the HTTP or HTTPS protocol. Separate multiple ports with commas (,).
Click View Port Range to query all available ports.
Load Balancing Algorithm
If you specify multiple addresses of origin servers, select a load balancing algorithm for the origin servers. Valid values:
IP hash (default): Requests from the same client are forwarded to the same origin server. This algorithm is suitable for scenarios in which session consistency needs to be maintained. However, this may cause uneven load balancing.
Polling: Client requests are sequentially forwarded to origin servers from the origin server list. This algorithm is suitable for scenarios in which multiple origin servers are used and a high requirement for even load balancing on origin servers is imposed.
Least time: The intelligent DNS resolution feature and the upgraded least-time back-to-origin algorithm ensure the shortest latency for the entire link from when service traffic is connected to a protection node to when the traffic is forwarded to an origin server.
NoteYou can select Least time only after you enable intelligent load balancing. For more information, see Intelligent load balancing.
After the settings take effect, WAF distributes origin fetch requests to multiple origin server addresses based on the specified load balancing algorithm to implement load balancing.
Is a Layer 7 proxy such as Anti-DDoS Proxy or CDN deployed in front of WAF?
Enable Traffic Mark
Resource Group
Select the resource group to which the domain name belongs from the resource group list.
NoteYou can use the Resource Management service to create resource groups to manage cloud resources by business department, project, or other dimensions. For more information, see Create a resource group.
Bind the host of your computer to the Server Load Balancer (SLB) instance that is deployed in front of the on-premises WAF instance, and then test whether traffic passes through WAF as expected.
NoteCurrently, this operation can be performed only by Alibaba Cloud technical support.
Change the DNS record of the domain name to the IP address of the on-premises SLB instance.
Click the Complete. Return to Domain Name List button.
The domain name is now protected by Hybrid Cloud WAF.