This topic describes the basic syntax and provides examples of regular expression functions.
Overview of regular expression functions
Simple Log Service supports the following regular expression functions. The regular expressions use the RE2 syntax.
Function | Syntax | Description | SQL support | SPL support |
regexp_extract_all(x, regular expression) | Extracts substrings that match a regular expression from a source string and returns an array of the substrings. | √ | × | |
regexp_extract_all(x, regular expression, n) | Extracts substrings that match a regular expression from a source string and returns an array of substrings that match a capturing group. | √ | × | |
regexp_extract(x, regular expression) | Extracts and returns the first substring that matches a regular expression from a source string. | √ | √ | |
regexp_extract(x, regular expression, n) | Extracts substrings that match a regular expression from a source string and returns the nth substring that matches a capturing group. | √ | √ | |
regexp_extract_bool(x, regular expression) | Extracts and returns a substring that matches a regular expression from a source string, and converts the substring to the BOOLEAN type. If the conversion fails, | √ | × | |
regexp_extract_bool(x, regular expression, n) | Extracts a substring that matches a regular expression from a source string, returns the substring that matches a capturing group, and converts the substring to the BOOLEAN type. If the conversion fails, | √ | × | |
regexp_extract_long(x, regular expression) | Extracts and returns a substring that matches a regular expression from a source string, and converts the substring to the BIGINT type. If the conversion fails, | √ | × | |
regexp_extract_long(x, regular expression, n) | Extracts a substring that matches a regular expression from a source string, returns the substring that matches a capturing group, and converts the substring to the BIGINT type. If the conversion fails, | √ | × | |
regexp_extract_double(x, regular expression) | Extracts and returns the first substring that matches a regular expression from a source string, and converts the substring to the DOUBLE type. If the conversion fails, | √ | × | |
regexp_extract_double(x, regular expression, n) | Extracts a substring that matches a regular expression from a source string, returns the substring that matches a capturing group, and converts the substring to the DOUBLE type. If the conversion fails, | √ | × | |
regexp_extract_map(x, regular expression, keys) | Specifies key information. The substrings that match capturing groups are used as values. | √ | × | |
regexp_extract_map(x, regular expression) | The regular expression contains two capturing groups that match a key and a value. | √ | × | |
regexp_like(x, regular expression) | Checks whether a source string matches a regular expression. | √ | √ | |
regexp_replace(x, regular expression) | Deletes substrings that match a regular expression from a source string and returns the remaining substrings. | √ | √ | |
regexp_replace(x, regular expression, replace string) | Replaces substrings that match a regular expression in a source string and returns the new string. | √ | √ | |
regexp_split(x, regular expression) | Splits a source string using a regular expression and returns an array of substrings. | √ | × |
When you use a regular expression function to extract a single quotation mark (') from a string, you must add another single quotation mark (') to the regular expression. For more information, see Example 3 of the regexp_extract function.
regexp_extract_all function
The regexp_extract_all function extracts substrings that match a regular expression from a source string.
Syntax
Extracts all substrings that match a regular expression from a source string and returns them in an array.
regexp_extract_all(x, regular expression)Extracts substrings that match a regular expression from a source string and returns an array of substrings that match a specific capturing group.
regexp_extract_all(x, regular expression, n)
Parameters
Parameter | Description |
x | The value is of the VARCHAR type. |
regular expression | A regular expression that contains capturing groups. For example, |
n | The nth capturing group. n is an integer that starts from 1. |
Return value type
Array type.
Examples
Example 1: Extract all digits from the value of the
server_protocolfield.Sample field
server_protocol:HTTP/2.0Query statement (Test)
*| SELECT regexp_extract_all(server_protocol, '\d+')Query and analysis results
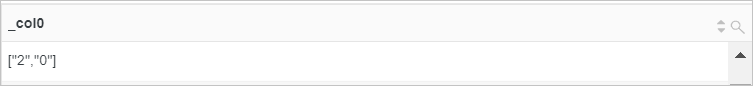
Example 2: Extract the Chrome part from the value of the
http_user_agentfield and calculate the number of requests that are initiated by the Chrome browser.Sample field
http_user_agent:Mozilla/5.0 (X11; Linux x86_64) AppleWebKit/535.1 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/14.0.803.0 Safari/535.1Query statement (Test)
*| SELECT regexp_extract_all(http_user_agent, '(Chrome)',1) AS Chrome, count(*) AS count GROUP BY ChromeQuery and analysis results
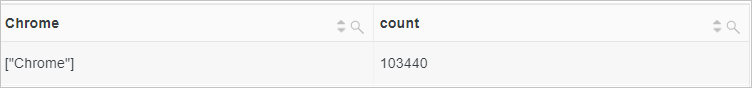
regexp_extract function
The regexp_extract function extracts substrings that match a regular expression from a source string.
Syntax
Extracts and returns the first substring that matches a regular expression from a source string.
regexp_extract(x, regular expression)Extracts substrings that match a regular expression from a source string and returns the substring that matches the nth capturing group.
regexp_extract(x, regular expression, n)
Parameters
Parameter | Description |
x | The value is of the VARCHAR type. |
regular expression | A regular expression that contains capturing groups. For example, |
n | The nth capturing group. n is an integer that starts from 1. |
Return value type
VARCHAR
Examples
SQL
Example 1: Extract the first digit from the value of the
server_protocolfield.Sample field
server_protocol:HTTP/2.0Query statement (Test)
*|SELECT regexp_extract(server_protocol, '\d+')Query and analysis results

Example 2: Extract the file part from the value of the
request_urifield and calculate the number of access requests for each file.Sample field
request_uri:/request/path-3/file-5Query statement (Test)
* | SELECT regexp_extract(request_uri, '.*\/(file.*)', 1) AS file, count(*) AS count GROUP BY fileQuery and analysis results
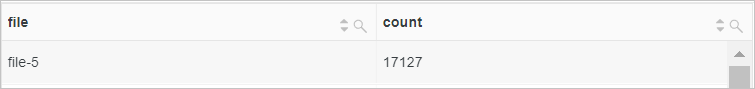
Example 3: Extract the single quotation mark (') and the digits from the value of the
messagefield.Sample field
message:error'1232Query statement
* | SELECT regexp_extract(message, '''\d+')NoteWhen you use a regular expression function to extract a single quotation mark (') from a string, you must add another single quotation mark (') to the regular expression.
Query and analysis results

SPL
Example 1: Extract the first digit from the value of the server_protocol field.
Sample field
server_protocol:HTTP/2.0Query statement
* | extend a = regexp_extract(server_protocol, '\d+')Query and analysis results
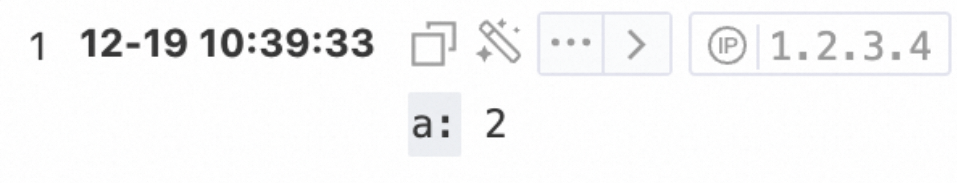
Example 2: Extract the file part from the value of the
request_urifield.Sample field
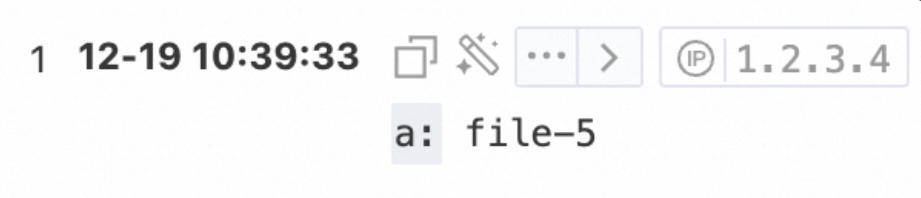
request_uri:/request/path-3/file-5Query statement
* | extend a = regexp_extract(request_uri, '.*\/(file.*)',1)Query and analysis results
Example 3: Extract the single quotation mark (') and the digits from the value of the
messagefield.Sample field
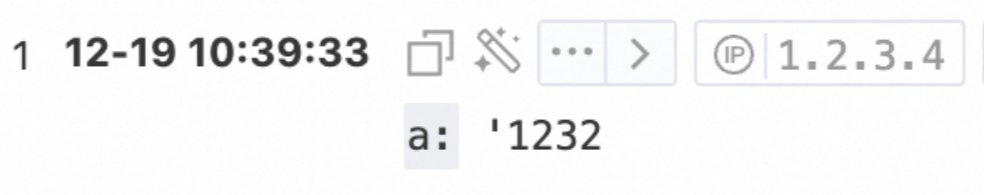
message:error'1232Query statement
* | extend a = regexp_extract(message, '''\d+') Note
When you use a regular expression function to extract a single quotation mark (') from a string, you must add another single quotation mark (') to the regular expression.
Query and analysis results
regexp_extract_bool function
The regexp_extract_bool function extracts a substring that matches a regular expression from a source string and converts the substring to the BOOLEAN type. If the conversion fails, null is returned. The conversion is successful only if the substring is "true" or "false". These values are case-insensitive.
Syntax
Extracts a substring that matches a regular expression from a source string and converts it to the BOOLEAN type. If the conversion fails,
nullis returned.regexp_extract_bool(x, regular expression)Extracts a substring that matches a regular expression from a source string, returns the substring that matches a specified capturing group, and converts it to the BOOLEAN type. If the conversion fails,
nullis returned.regexp_extract_bool(x, regular expression, n)
Parameters
Parameter | Description |
x | The value is of the VARCHAR type. |
regular expression | A regular expression that contains capturing groups. For example, |
n | The nth capturing group. n is an integer that starts from 1. |
Return value type
BOOLEAN
Examples
Extract the boolean value from a field value.
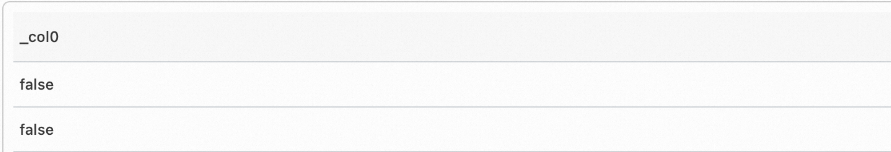
Sample field
falseQuery statement (Test)
*| select regexp_extract_bool('false', '[a-zA-Z]+')Query and analysis results
regexp_extract_long function
The regexp_extract_long function extracts a substring that matches a regular expression from a source string and converts the substring to the BIGINT type. If the conversion fails, null is returned.
Syntax
Extracts a substring that matches a regular expression from a source string and converts it to the BIGINT type. If the conversion fails,
nullis returned.regexp_extract_long(x, regular expression)Extracts a substring that matches a regular expression from a source string, returns the substring that matches a specified capturing group, and converts it to the BIGINT type. If the conversion fails,
nullis returned.regexp_extract_long(x, regular expression, n)
Parameters
Parameter | Description |
x | The value is of the VARCHAR type. |
regular expression | A regular expression that contains capturing groups. For example, |
n | The nth capturing group. n is an integer that starts from 1. |
Return value type
BIGINT
Examples
Extract the number from the
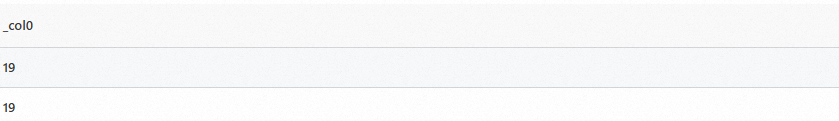
timefield.Sample field
time:19/Dec/2024:06:16:06Query statement (Test)
*|SELECT regexp_extract_long(time, '(\d{2})/', 1)Query and analysis results
regexp_extract_double function
The regexp_extract_double function extracts a substring that matches a regular expression from a source string and converts the substring to the DOUBLE type. If the conversion fails, null is returned.
Syntax
Extracts a substring that matches a regular expression from a source string and converts it to the DOUBLE type. If the conversion fails,
nullis returned.regexp_extract_double(x, regular expression)Extracts a substring that matches a regular expression from a source string, returns the substring that matches a specified capturing group, and converts it to the DOUBLE type. If the conversion fails,
nullis returned.regexp_extract_double(x, regular expression, n)
Parameters
Parameter | Description |
x | The value is of the VARCHAR type. |
regular expression | A regular expression that contains capturing groups. For example, |
n | The nth capturing group. n is an integer that starts from 1. |
Return value type
Double data type.
Examples
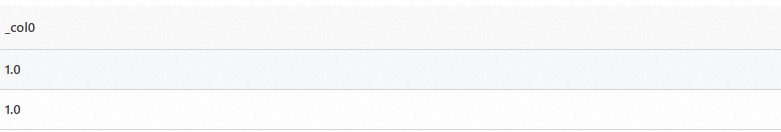
Extract the number from the
server_protocolfield.Sample field
server_protocol:HTTP/1.1Query statement (Test)
*|SELECT regexp_extract_double(server_protocol, '\d+')Query and analysis results
regexp_extract_map function
The regexp_extract_map function extracts substrings that match all capturing groups in a regular expression from a source string.
Syntax
Specifies key information. The substrings that match the capturing groups are used as values.
regexp_extract_map(x, regular expression, keys)The regular expression contains two capturing groups that match a key and a value.
regexp_extract_map(x, regular expression)Parameters
Parameter | Description |
x | The value is of the VARCHAR type. |
regular expression | A regular expression that contains capturing groups. For example, |
keys | The names of the keys for the captured substrings. The value is of the ARRAY(VARCHAR) type. The number of elements must be the same as the number of capturing groups in the regular expression parameter. |
Return value type
MAP(VARCHAR, VARCHAR)
Examples
Example 1: Extract the protocol name and version from the server_protocol field.
Sample field
server_protocol: 'HTTP/2.0'Query statement
select regexp_extract_map(server_protocol, '(\w+)/([\d\.]+)', array['name', 'version']) as protocolQuery and analysis results

Example 2: Extract all key-value pairs from the content field.
Sample field
content: 'verb="GET" URI="/healthz" latency="45.911µs" userAgent="kube-probe/1.30+"'Query statement
select regexp_extract_map(content, '(\w+)="([^"]*)"') as argsOutput data

regexp_like function
The regexp_like function checks whether a source string matches a regular expression.
Syntax
regexp_like(x, regular expression)Parameters
Parameter | Description |
x | The value is of the VARCHAR type. |
regular expression | A regular expression. |
Return value type
BOOLEAN
Examples
SQL
Check whether the value of the server_protocol field contains digits.
Sample field
server_protocol:HTTP/2.0Query statement (Test)
*| select regexp_like(server_protocol, '\d+')Query and analysis results
SPL
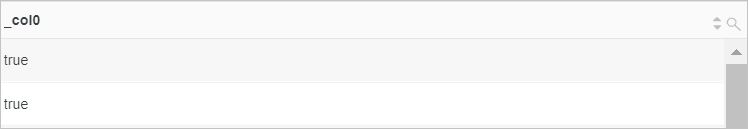
Check whether the value of the server_protocol field contains digits.
Sample field
server_protocol:HTTP/2.0Query statement
* |extend a = regexp_like(server_protocol, '\d+')Query and analysis results

regexp_replace function
Deletes or replaces substrings that match a regular expression in a source string.
Syntax
Deletes substrings that match a regular expression from a source string and returns the remaining substrings.
regexp_replace(x, regular expression)Replaces substrings that match a regular expression in a source string and returns the new string.
regexp_replace(x, regular expression, replace string)
Parameters
Parameter | Description |
x | The value is of the VARCHAR type. |
regular expression | A regular expression. |
replace string | The substring that is used for replacement. |
Return value type
VARCHAR
Examples
SQL
Example 1: Replace the region names that start with
cnin the value of theregionfield with China and calculate the number of requests from China.Examples
region:cn-shanghaiQuery statement (Test)
* | select regexp_replace(region, 'cn.*','China') AS region, count(*) AS count GROUP BY regionQuery and analysis results

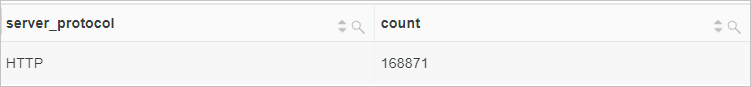
Example 2: Delete the version number from the value of the
server_protocolfield and calculate the number of requests for each communication protocol.Sample field
server_protocol:HTTP/2.0Query statement (Test)
*| select regexp_replace(server_protocol, '.\d+') AS server_protocol, count(*) AS count GROUP BY server_protocolQuery and analysis results
SPL
Example 1: Replace the region names that start with cn in the value of the
regionfield with China.Sample field
region:cn-shanghaiQuery statement
* | extend a = regexp_replace(region, 'cn.*','China')Query and analysis results

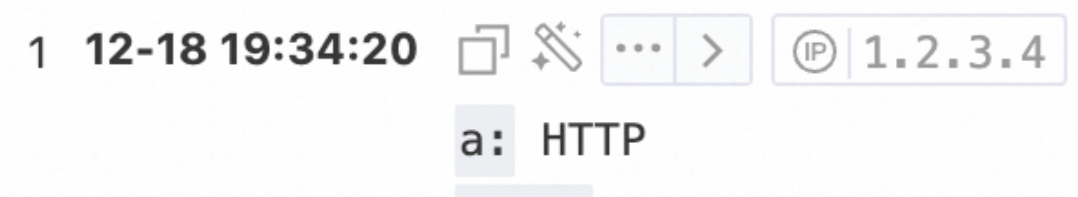
Example 2: Delete the version number from the value of the
server_protocolfield.Sample field
server_protocol:HTTP/2.0Query statement (Test)
* | extend a = regexp_replace(server_protocol, '.\d+')Query and analysis results
regexp_split function
The regexp_split function splits a source string and returns an array of substrings.
Syntax
regexp_split(x, regular expression)Parameters
Parameter | Description |
x | The value is of the VARCHAR type. |
regular expression | A regular expression. |
Return value type
The data type is an array.
Examples
Use forward slashes (/) to split the value of the request_uri field.
Sample field
request_uri:/request/path-0/file-7Query statement (Test)
* | SELECT regexp_split(request_uri,'/')Query and analysis results
