You can use Logtail to collect Linux systemd journal logs from binary files. This topic describes how to create a Logtail configuration to collect systemd journal logs in the Log Service console.
Prerequisites
Logtail V0.16.18 or later is installed on a Linux server. For more information, see Install Logtail on a Linux server.
Introduction
systemd is a system and service manager for Linux operating systems. systemd runs as an init process with PID 1. systemd replaces Upstart as the init system to boot and maintain services in user space. systemd manages the logs of all units in a centralized manner. The configuration file is /etc/systemd/journald.conf, and the logs include kernel and application logs.
The operating system on which systemd runs must support the journal log format.
Features
Specify the position for initial collection. Checkpoints are automatically stored for subsequent data collection. The process of systemd is not affected when applications are restarted.
Filter units.
Collect kernel logs.
Automatic parsing of log levels.
Run systemd as a container to collect journal logs from hosts. This feature is applicable when you collect logs from Docker and Kubernetes clusters.
Use cases
Monitor kernel events, and generate alerts when exceptions occur. The alerts are automatically generated.
Collect all system logs for long-term storage to release disk space.
Collect the output logs of the software unit for analysis or alerting.
Collect all journal logs. Perform faster log queries and keyword-based queries. These types of queries are more efficient than journalctl-based queries.
Procedure
Log on to the Simple Log Service console.
Click Import Data, then select Custom Data Plug-in.
Select the project and logstore. Then, click Next.
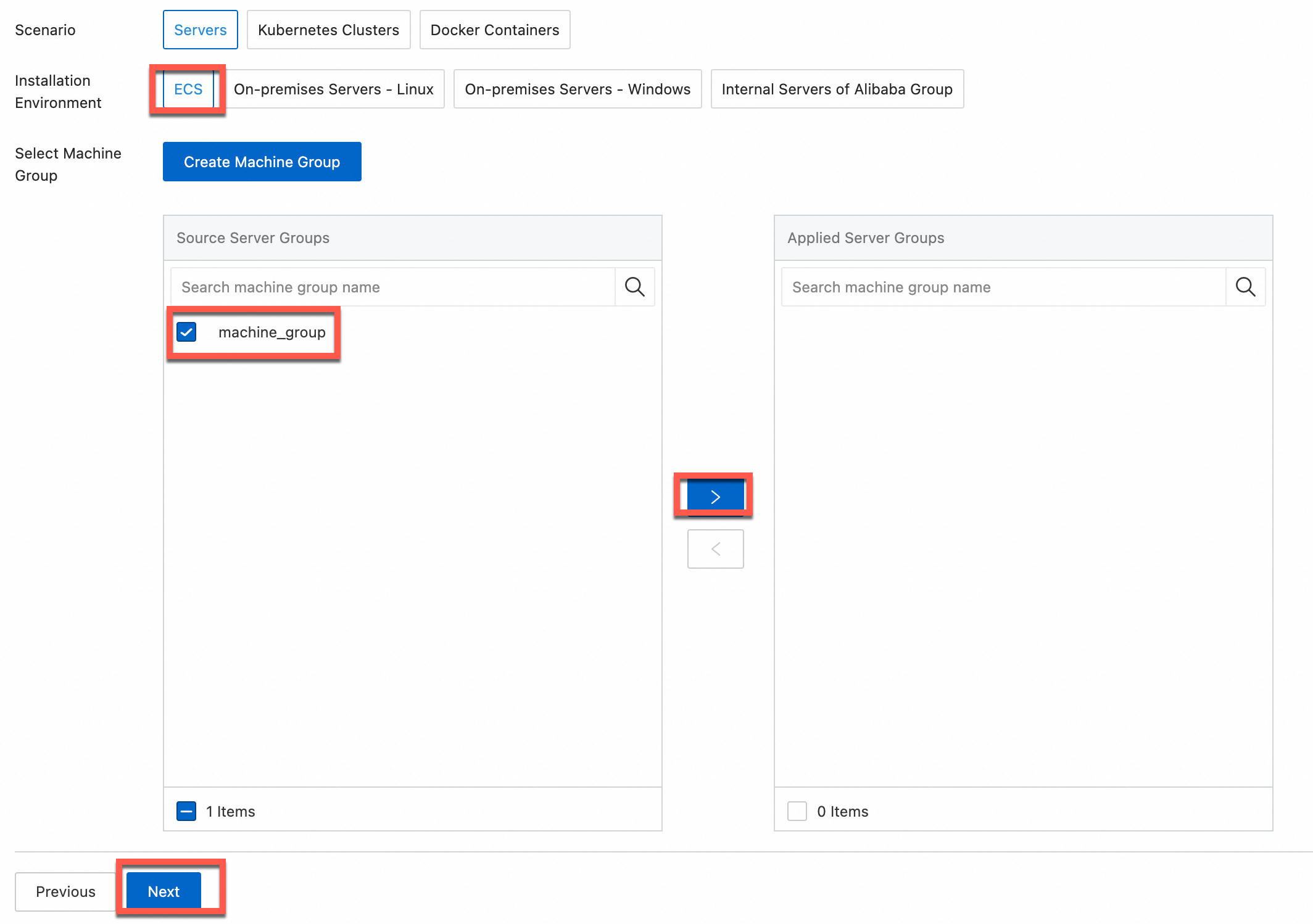
In the Machine Group Configurations step, configure a machine group.
Configure the Scenario and Installation Environment parameters as needed.
ImportantYou must configure the Scenario and Installation Environment parameters regardless of whether a machine group is available. The parameter settings affect subsequent configurations.
Ensure that a machine group is displayed in the Applied Server Groups section, and click Next.
Machine group available
Select a machine group from the Source Machine Group section.
No machine group available
Click Create Machine Group. In the Create Machine Group panel, configure the parameters. You can set the Machine Group Identifier parameter to IP Address or Custom Identifier. For more information, see Create a custom identifier-based machine group or Create an IP address-based machine group.
ImportantIf you apply a machine group immediately after you create the machine group, the heartbeat status of the machine group may be FAIL. This issue occurs because the machine group is not connected to Simple Log Service. To resolve this issue, you can click Automatic Retry. If the issue persists, see What do I do if no heartbeat connections are detected on Logtail?
In the Configure Data Source step, set the Configuration Name and Plug-in Configuration parameters, and then click Next.
inputs is required and is used to configure the data source settings for the Logtail configuration.
ImportantYou can specify only one type of data source in inputs.
processors is optional and is used to configure the data processing settings for the Logtail configuration to parse data. You can specify one or more processing methods.
If your logs cannot be parsed based only on the setting of inputs, you can configure processors in the Plug-in Configuration field to add plugins for data processing. For example, extract fields, extract log time, mask data, and filter logs. For more information, see Logtail plugins for data processing.
{ "inputs": [ { "detail": { "JournalPaths": [ "/var/log/journal" ], "Kernel": true, "ParsePriority": true, "ParseSyslogFacility": true }, "type": "service_journal" } ] }Parameter
Type
Required
Description
type
string
Yes
The type of the data source. Set the value to service_journal.
JournalPaths
String array
Yes
The path to journal logs. We recommend that you set this parameter to the default directory of the journal logs. Example: /var/log/journal.
SeekPosition
string
No
The method for initial collection. Valid values: head and tail. Default value: tail.
If you set this parameter to head, all data is collected.
If you set this parameter to tail, only the data that is generated after the Logtail configuration takes effect is collected.
Kernel
boolean
No
Specifies whether to collect kernel logs. Default value: true. This value indicates that kernel logs are collected.
Units
String array
No
The units whose logs are collected. By default, this parameter is empty, which indicates that the logs of all units are collected.
ParseSyslogFacility
boolean
No
Specifies whether to parse the facility field of system logs. Default value: false. If you do not add this parameter, the field is not parsed.
ParsePriority
boolean
No
Specifies whether to parse the Priority field. Default value: false. If you do not add this parameter, the field is not parsed.
If you set this parameter to true, the Priority field is parsed. The following list describes the mapping relationships for the field:
"0": "emergency" "1": "alert" "2": "critical" "3": "error" "4": "warning" "5": "notice" "6": "informational" "7": "debug"UseJournalEventTime
boolean
No
Specifies whether to use a field in journal logs as the log time. Default value: false. If you do not add this parameter, the collection time is used as the log time.
In real-time log collection, the difference between the log generation time and the log collection time is less than 3 seconds.
Create indexes and preview data. Then, click Next. By default, full-text indexing is enabled in Simple Log Service. You can also manually create field indexes for the collected logs or click Automatic Index Generation. Then, Simple Log Service generates field indexes. For more information, see Create indexes.
ImportantIf you want to query all fields in logs, we recommend that you use full-text indexes. If you want to query only specific fields, we recommend that you use field indexes. This helps reduce index traffic. If you want to analyze fields, you must create field indexes. You must include a SELECT statement in your query statement for analysis.
Click Query Log. Then, you are redirected to the query and analysis page of your Logstore.
You must wait approximately 1 minute for the indexes to take effect. Then, you can view the collected logs on the Raw Logs tab. For more information about how to query and analyze logs, see Guide to log query and analysis.
Examples
Example 1
Collect journal logs from the default directory
/var/log/journal. Logtail configuration:{ "inputs": [ { "detail": { "JournalPaths": [ "/var/log/journal" ] }, "type": "service_journal" } ] }Sample log:
MESSAGE: rejected connection from "192.168.0.250:43936" (error "EOF", ServerName "") PACKAGE: embed PRIORITY: 6 SYSLOG_IDENTIFIER: etcd _BOOT_ID: fe919cd1268f4721bd87b5c18afe59c3 _CAP_EFFECTIVE: 0 _CMDLINE: /usr/bin/etcd --election-timeout=3000 --heartbeat-interval=500 --snapshot-count=50000 --data-dir=data.etcd --name 192.168.0.251-name-3 --client-cert-auth --trusted-ca-file=/var/lib/etcd/cert/ca.pem --cert-file=/var/lib/etcd/cert/etcd-server.pem --key-file=/var/lib/etcd/cert/etcd-server-key.pem --peer-client-cert-auth --peer-trusted-ca-file=/var/lib/etcd/cert/peer-ca.pem --peer-cert-file=/var/lib/etcd/cert/192.168.0.251-name-3.pem --peer-key-file=/var/lib/etcd/cert/192.168.0.251-name-3-key.pem --initial-advertise-peer-urls https://192.168.0.251:2380 --listen-peer-urls https://192.168.0.251:2380 --advertise-client-urls https://192.168.0.251:2379 --listen-client-urls https://192.168.0.251:2379 --initial-cluster 192.168.0.249-name-1=https://192.168.0.249:2380,192.168.0.250-name-2=https://192.168.0.250:2380,192.168.0.251-name-3=https://192.168.0.251:2380 --initial-cluster-state new --initial-cluster-token abac64c8-baab-4ae6-8412-4253d3cfb0cf _COMM: etcd _EXE: /opt/etcd-v3.3.8/etcd _GID: 995 _HOSTNAME: iZbp1f7y2ikfe4l8nx95amZ _MACHINE_ID: f0f31005fb5a436d88e3c6cbf54e25aa _PID: 10926 _SOURCE_REALTIME_TIMESTAMP: 1546854068863857 _SYSTEMD_CGROUP: /system.slice/etcd.service _SYSTEMD_SLICE: system.slice _SYSTEMD_UNIT: etcd.service _TRANSPORT: journal _UID: 997 __source__: 172.16.1.4 __tag__:__hostname__: logtail-ds-8kqb9 __topic__: _monotonic_timestamp_: 1467135144311 _realtime_timestamp_: 1546854068864309Example 2
NoteLimitations on collecting host journal logs from a container:
A container running systemd version 247 or earlier cannot collect journal logs from a host running systemd version 249 or later.
A container running systemd version 249 or later can read both old and new log formats.
Collect system logs from hosts in Kubernetes clusters in DaemonSet mode. Use Logtail plug-ins to filter log fields for important fields. Logtail configuration:
{ "inputs": [ { "detail": { "JournalPaths": [ "/logtail_host/var/log/journal" ], "ParsePriority": true, "ParseSyslogFacility": true }, "type": "service_journal" } ], "processors": [ { "detail": { "Exclude": { "UNIT": "^libcontainer.*test" } }, "type": "processor_filter_regex" }, { "detail": { "Include": [ "MESSAGE", "PRIORITY", "_EXE", "_PID", "_SYSTEMD_UNIT", "_realtime_timestamp_", "_HOSTNAME", "UNIT", "SYSLOG_FACILITY", "SYSLOG_IDENTIFIER" ] }, "type": "processor_pick_key" } ] }Sample log:
MESSAGE: rejected connection from "192.168.0.251:48914" (error "EOF", ServerName "") PRIORITY: informational SYSLOG_IDENTIFIER: etcd _EXE: /opt/etcd-v3.3.8/etcd _HOSTNAME: iZbp1i0czq3zgvxlx7u8ueZ _PID: 10590 _SYSTEMD_UNIT: etcd.service __source__: 172.16.0.141 __tag__:__hostname__: logtail-ds-dp48x __topic__: _realtime_timestamp_: 1547975837008708
Troubleshooting
If no data is displayed on the preview page or query page after logs are collected by using Logtail, you can troubleshoot the errors based on the instructions that are provided in What do I do if errors occur when I use Logtail to collect logs?