Service Catalog is developed based on Infrastructure as Code (IaC) capabilities that are provided by Alibaba Cloud. Service Catalog helps enterprises configure products that meet specific requirements and define product launch constraints. This way, enterprises can select products based on their business requirements in a convenient manner when they migrate their workloads to the cloud. This improves the delivery efficiency of IT services.
How Service Catalog works
The following list describes how Service Catalog works:
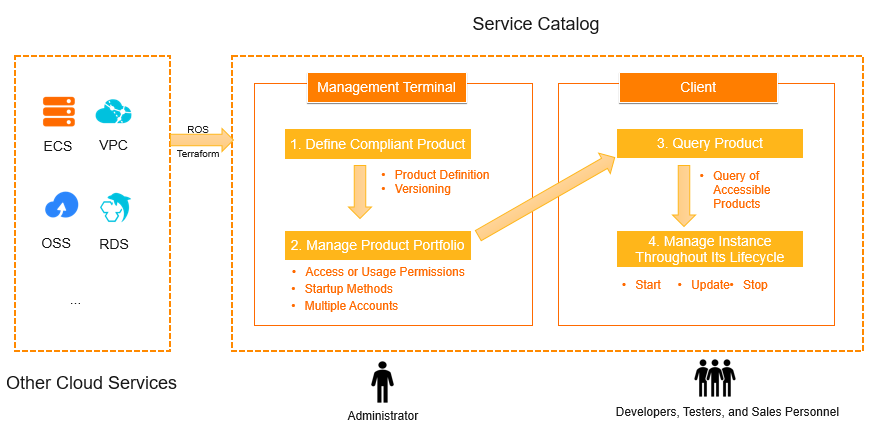
The administrator creates a product based on a Terraform template and adds the product to a product portfolio for centralized management.
The administrator grants product launch and access permissions to an end user.
The end user launches and accesses a product. After the product is launched, a product instance is created in the Service Catalog console and a stack is created in the Resource Orchestration Service (ROS) console. The stack resides in the region where the product instance is deployed.
The end user manages cloud resources that are required by the product in the Service Catalog console based on business requirements.
Features
The administrator can manage products and product portfolios.
The administrator can define compliant products based on Terraform and manage multiple versions of products.
The administrator can create product portfolios and add existing products to the product portfolios. The administrator can also grant the product access and launch permissions to end users. Then, the end users can manage products.
The administrator can manage all product instances. If an end user transfers to another position and no longer needs to manage a product instance, the administrator can manage the product instance to prevent service interruption.
End users can launch products and manage product instances.
End users can query the list of products and launch products based on their business requirements.
End users can manage product instances throughout the lifecycles of the product instances. For example, end users can query, update, and stop product instances.
Benefits
Ensures security and compliance of resource usage.
Service Catalog allows enterprises to define compliance requirements for the types, specifications, naming conventions, and resource orchestration of 104 cloud services by using Terraform. For more information, see Services that work with Service Catalog.
Accelerates resource delivery.
End users can access compliant cloud resources based on their business requirements to accelerate resource delivery.
Simplifies lifecycle management.
Service Catalog allows enterprises to orchestrate resources in groups. Then, end users can query, update, or stop the cloud resources that belong to a resource group at a time.
Facilitates centralized management.
Service Catalog allows enterprises to configure compliance settings for products in a centralized manner and share the settings among multiple enterprise cloud accounts for efficient management.
Scenarios
The administrator wants to design a compliant enterprise product.
The administrator can design a product that meets the security and compliance requirements of the enterprise by using Service Catalog. For example, the administrator can specify the specifications that can be selected to create an Elastic Compute Service (ECS) instance. This reduces security risks and ensures controllable costs.
An end user wants to build cloud infrastructure in an efficient manner.
A product can consist of a single server or can be a website that consists of databases, middleware, and servers. We recommend that the administrator grants only required launch and access permissions to an end user. This allows the end user to query and launch products in an efficient manner and reduces the needs for the end user to switch between different cloud service consoles to manage resources.
The administrator wants to grant permissions based on the principle of least privilege.
The administrator can grant the permissions only on a specific product to an end user (enterprise employee). This prevents management risks that are caused by excessive permissions.