Common questions about vulnerability scanning, fixing, and post-fix verification in Security Center.
Vulnerability scanning
Why does the same server report multiple instances of the same vulnerability?
Security Center detects application vulnerabilities per running process instance. If a server runs two instances of the same process with the same vulnerability, for example, two Tomcat services on different ports, each instance is reported separately. If the vulnerable software is installed but not running, Security Center does not detect the vulnerability.
Why do scan results for vulnerabilities like Fastjson sometimes vary?
Detection depends on whether the vulnerable component (such as a JAR package) is loaded into a runtime state during the scan. In a dynamic loading model, Security Center detects the vulnerability only when business logic calls the vulnerable component. Scan results may differ depending on which components are active at the time of each scan.
To improve detection accuracy, run periodic or multiple scans.
After the agent goes offline, why does the console still show vulnerability records?
Security Center retains detected vulnerability records after the agent goes offline. However, these records automatically become stale, and you cannot fix, verify, or clear them. The staleness periods are:
| Vulnerability type | Becomes stale after | |-|-| | Linux software vulnerability, Windows system vulnerability | 3 days | | Web-CMS vulnerability | 7 days | | Application vulnerability | 30 days | | Urgent vulnerability | 90 days |
Security Center permanently deletes all data only if the service expires and is not renewed within 7 days.
Does vulnerability scanning or proof of concept (POC) validation for urgent vulnerabilities affect business systems?
Typically, no. POC validation sends only 1-2 harmless probe requests and does not perform any attack or destructive action. In rare cases, a minimal risk exists if the target application is exceptionally fragile when handling unexpected input.
Why does a vulnerability scan sometimes trigger an out-of-memory (OOM) error?
The Security Center agent has a default memory limit of 200 MB. If a scan exceeds this limit, the system's OOM mechanism terminates the detection process (ALiSecCheck) to conserve resources.
This behavior is normal and unrelated to a system-wide memory shortage. The memory limit is managed by a control group (cgroup) named aegisRtap0. Related OOM information appears in the dmesg logs. No user intervention is required.
What is the scope of a vulnerability scan?
Scanning covers both the system and application layers:
| Layer | Vulnerability types | |-|-| | System | Linux software vulnerability, Windows system vulnerability | | Application | Web-CMS vulnerability, application vulnerability, urgent vulnerability |
The Windows system vulnerability scan is limited to monthly security update patches.
How do I view the list of vulnerabilities that Security Center can detect?
Log on to the Security Center console.
In the left-side navigation pane, choose Risk Governance > Vulnerabilities.
In the overview section, find the Disclosed Vulnerabilities statistics card and click the total number to view all detectable vulnerabilities and their details.
Does Security Center support detection for vulnerabilities in services like Elasticsearch?
Yes. View detection results on the Application Vulnerability page in the console.
This feature requires the Subscription service (Enterprise Edition or Ultimate Edition) or the Pay-as-you-go service (Host Protection or Hosts and Container Protection). If your current edition does not support this feature, upgrade your edition first.
Vulnerability fixes
Why is the Fix button grayed out?
The most common cause is an edition limitation. The Basic Edition and Anti-virus Edition do not support one-click fix. Purchase the Vulnerability Fixing value-added service, or upgrade to Enterprise Edition or Ultimate Edition.
If your edition supports one-click fix, check for server-side issues:
Linux
| Issue | Solution | |-|-| | OS no longer maintained (Red Hat 5/6/7/8, CentOS 5, Ubuntu 12, Debian 8/9/10) | Manually upgrade the OS version. The vendor no longer provides patches. | | Insufficient disk space (less than 3 GB free) | Free up disk space or expand the disk. | | Package manager busy (apt or yum process running) | Wait for the process to finish, then retry. Alternatively, manually stop the process. | | Insufficient permissions | Make sure the file owner is root and permissions are set to 755. |
Windows
| Issue | Solution | |-|-| | Insufficient disk space (less than 500 MB free) | Free up disk space or expand the disk. | | Windows Update service disabled | Open the system service manager, enable the Windows Update Service, then retry. | | Windows Update service running (Wusa process active) | Wait for it to finish, or manually end the Wusa process, then retry. |
Why can't application vulnerabilities be fixed with one-click fix?
System vulnerabilities (Linux software vulnerabilities and Windows system vulnerabilities) are in the operating system or its components. Their remediation paths are standardized, so one-click fix works.
Application vulnerabilities exist in self-deployed applications such as website code or third-party software. Their remediation depends on your business logic and code implementation, so they must be handled manually.
Why are there so many vulnerabilities on my server?
Older software versions accumulate vulnerabilities over time as new attack methods emerge. Regular scanning and patching is an ongoing security task. To focus on the highest-priority risks, turn on the Show Only Exploitable Vulnerabilities toggle.
What should I do if I get a "Permission acquisition failed" error when fixing a vulnerability?
The file required for the fix is not owned by root.
In Security Center, view the vulnerability details to identify the specific file and its path.
Log on to the server and change the file owner to
root.Return to the Security Center console and retry the fix.
In what order are vulnerabilities fixed in a batch?
Linux software vulnerabilities and Web-CMS vulnerabilities are fixed in the order they appear in the console list.
Windows system vulnerabilities that require prerequisite patches are fixed first. The remaining vulnerabilities are then fixed in the order they appear in the console list.
Why is restarting ineffective after fixing an Ubuntu kernel vulnerability?
This happens when the GRUB boot order was manually modified before the fix. The system fix script cannot automatically set the newly installed kernel as the default boot item.
Solution 1: Automatically configure the new kernel
This solution abandons the original custom GRUB configuration and lets the system apply the default settings for the new kernel.
Before running the fix, log on to your Ubuntu server.
Run the following command:
export DEBIAN_FRONTEND=noninteractiveReturn to the Security Center console and run the one-click fix.
Restart the server as prompted. The system automatically enables the latest kernel.
Solution 2: Manually modify the boot order
Use this solution to keep the original GRUB configuration.
In the Security Center console, run the one-click fix and restart the server as prompted.
Log on to your Ubuntu server.
Modify the GRUB boot order to set the newly installed kernel as the default boot item. This typically involves modifying
/etc/default/gruband runningupdate-grub. For details, see Modify the kernel boot order for ECS Linux CentOS.Restart the server again.
Do I need to restart the system after fixing a vulnerability?
Windows: A restart is always required.
Linux software vulnerability: A restart is required if a kernel vulnerability was fixed, or if the vulnerability has a Restart Required tag on the Linux Software Vulnerability tab under Risk Governance > Vulnerabilities in the Security Center console.
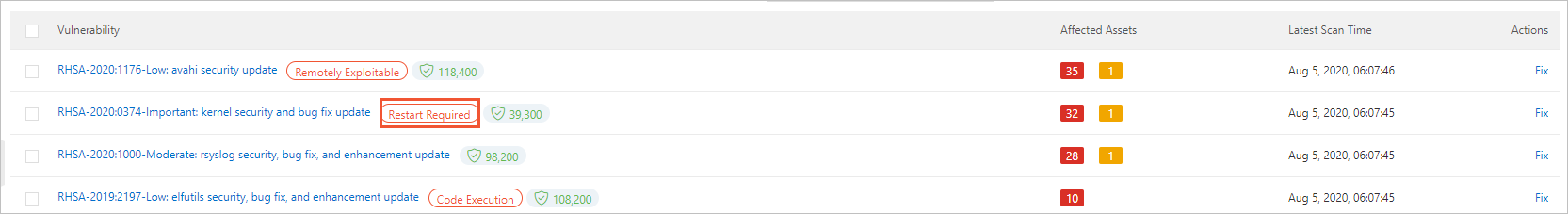
Why does a vulnerability rollback fail?
Two common causes:
Agent offline: The rollback operation depends on the Security Center agent being online. If the agent is offline, the command cannot be delivered. Troubleshoot and resolve the agent connectivity issue first.
Backup snapshot invalid: Rollback relies on the backup snapshot created before the fix. If the snapshot has expired or been manually deleted, the rollback cannot proceed.
Why does creating a snapshot fail when fixing a vulnerability?
RAM user without permission: If the RAM user performing the operation does not have permission to create snapshots, snapshot creation fails. Use an Alibaba Cloud account for the operation. For more information, see Overview of RAM users.
Non-Alibaba Cloud server: Snapshot creation for vulnerability fixes is supported only on Alibaba Cloud servers.
Post-fix verification
A vulnerability has been fixed, but Security Center still reports it. What should I do?
Some vulnerabilities, particularly Linux kernel vulnerabilities, require a server restart after the fix. On the vulnerability details page, click Restart. After the restart completes, click Verify. If the status shows Repaired, the vulnerability is successfully fixed.
The host has not installed a specific patch, but the Windows vulnerability shows as fixed. Why?
This is expected behavior due to the Windows cumulative update mechanism. Windows security updates use a cumulative model: each monthly security patch includes all security fixes from previous months. When Security Center detects that the latest cumulative update is installed, it marks all older vulnerabilities covered by that update as fixed.
To confirm whether a specific older vulnerability is covered, visit the official Microsoft patch website and search for the latest installed patch by its KB number. Check its package details to verify coverage.
After fixing a vulnerability, why does it still show "Not fixed"?
Three possible causes:
Verification delay: After a manual fix, click Verify to trigger an instant scan. The status update takes a few minutes.
Console cache: Force-refresh the page or wait a few minutes.
Incomplete fix: The fix may not have fully succeeded, or there may be multiple vulnerability paths with only one fixed. Recheck the fix steps.
Can Security Center automatically verify vulnerabilities in "Fixed and Pending Restart" state?
No. Restart the server from the Security Center console or manually, then click Verify to confirm whether the fix succeeded.
If you do not actively verify, Security Center checks during subsequent periodic scans. After the vulnerability is not detected in the first scan, the system retains the vulnerability record for 3 days. If the vulnerability is not detected for 3 consecutive days, the system clears the record.
Why is there no response when I manually verify after fixing a vulnerability?
Two possible causes:
Scan level not configured: Security Center only scans and updates vulnerability severity levels selected in Vulnerability Settings. If the target vulnerability's severity level is not selected, the system does not update its status. Verify that the scan levels in Vulnerability Settings cover the target vulnerability.
Agent offline: The Verify function relies on real-time communication between the console and the agent on the server. If the agent is offline, the console cannot deliver the verification command. Troubleshoot the connectivity issue first, then retry verification.
Fixing specific vulnerability types
Security Center still reports a kernel vulnerability after an upgrade. What should I do?
Confirm the kernel is upgraded. Run the following commands to check the running kernel version and verify it meets the requirements in the vulnerability details: Confirm the system starts using the new kernel:
uname -av cat /proc/versioncat /etc/grub.confRemove old kernel packages. List all installed kernel packages and identify old versions: Uninstall the old kernel package: Alternatively, use the distribution-recommended method. For CentOS/Red Hat:
ImportantBefore removing old kernel packages, create a snapshot or image for the current instance in the Elastic Compute Service console.
rpm -qa | grep kernelrpm -e kernel-<old_version_number>yum remove kernel-<old_version_number>Ignore the alert (optional). If the running kernel has already fixed the vulnerability, ignore the alert:
Log on to the Log on to the Security Center console.
In the navigation pane on the left, choose . In the upper-left corner of the console, select the region where your asset is deployed: Chinese Mainland or Outside Chinese Mainland.
On the Linux Software Vulnerability tab, find the vulnerability and click its name.
In the Actions column, click the
 icon and select Ignore.
icon and select Ignore.
How do I manually update an Ubuntu kernel?
Updating the kernel is a high-risk operation. Follow the instructions in Suggestions on how to fix server software vulnerabilities before proceeding.
The following example updates kernel 3.1* to kernel 4.4 on Ubuntu 14.04.
Confirm the current kernel version is 3.1*:
uname -av
Check whether the latest kernel update package is available:
apt list | grep linux-image-4.4.0-94-generic apt list | grep linux-image-extra-4.4.0-94-genericIf no related update is available, run
apt-get updateto retrieve the latest package list.Install the kernel update:
apt-get update && apt-get install linux-image-4.4.0-94-generic apt-get update && apt-get install linux-image-extra-4.4.0-94-genericRestart the server to apply the new kernel.
After the server restarts, verify the kernel update:
uname -avdpkg -l | grep linux-image

What should I do if a vulnerability shows no available updates?
No official patch available
When the update command returns a message such as already installed and latest version or No Packages marked for Update, the official update source has not released a patch. This may affect packages such as Gnutls, Libnl, and MariaDB. Wait for the official software source to release an update.
OS version reached end of life (EOL)
If the software package is the latest version supported by the current system but still does not meet the fix requirements, the OS version may be past its EOL (for example, CentOS 6.x). Two options:
Upgrade the OS to a version within its official support period.
After assessing the risk and confirming it is manageable, ignore the vulnerability in the Security Center console.
Other questions
How do I handle a timeout when connecting to the Alibaba Cloud Yum source?
If the connection times out, an error similar to the following appears:
[Errno 12] Timeout on http://mirrors.aliyun.com/centos/6/os/x86_64/repodata/repomd.xml: (28, 'connect() timed out!')Check whether DNS resolution is working. Run
ping mirrors.aliyun.comornslookup mirrors.aliyun.com.If network access is normal, wait a moment and retry. The timeout may be caused by temporary network fluctuations or high traffic on the mirror source.
How do I clear Windows vulnerability patch packages from the client directory?
After a one-click fix, the Security Center agent automatically downloads, installs, and removes the patch package. No manual action is needed.
If the patch package is not removed within 3 days after the fix, manually clear it:
Log on to the Log on to the Security Center console.
In the navigation pane on the left, choose . In the upper-left corner of the console, select the region where your asset is deployed: Chinese Mainland or Outside Chinese Mainland.
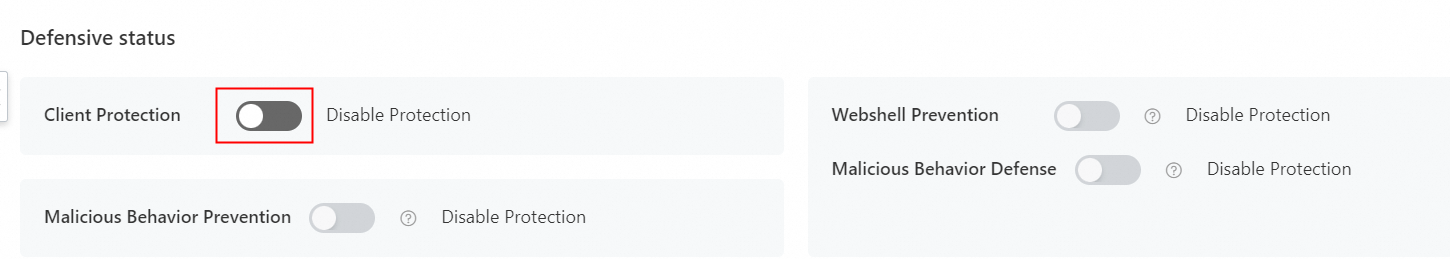
If client self-protection is enabled, go to the server details page in Asset Center and turn off the Client Protection toggle.
Client self-protection blocks requests to delete or download process files from the agent directory on Windows servers. If you have not enabled client self-protection, skip this step.
Log on to the Windows server with administrator permissions and delete the patch package from the following directory:
ImportantThe default patch package path is
C:\Program Files (x86)\Alibaba\Aegis\globalcfg\hotfix.(Optional) On the server details page, turn on Client Protection.