When the anti-ransomware service backs up data, it starts the hbrclient and ids processes to read object files, which consumes server memory. The hbrclient process remains active during the backup task. After the task is complete, the hbrclient process is typically stopped. Data is cached on your server as backup files. If these backup files become large, they consume a significant amount of memory and cause backup tasks to fail. This topic describes how to troubleshoot this issue and provides several solutions, such as modifying related configurations.
Problem description
The status of a backup job is Failed, and an out-of-memory (OOM) error is reported.
Cause
A backup job may consume excessive server memory if you back up too many files, back up oversized files, or if the program runs abnormally.
Solutions
The anti-ransomware feature and Cloud Backup share the same client. Therefore, configuration changes made to the anti-ransomware client also affect Cloud Backup. Before you make adjustments, fully assess the impact on the Cloud Backup service.
Exclude network mount paths
Do not add network mount paths, such as Object Storage Service (OSS) or NAS addresses mounted to an Elastic Compute Service (ECS) server, to the protected folder for anti-ransomware. This operation may cause unexpected API call fees because of frequent data access. The following three solutions are available:
Use the Cloud Backup service: For more information, see Quick Start - OSS backup and Quick Start - On-premises NAS backup.
Upgrade the client: Upgrade the anti-ransomware client to the latest version. The system automatically adds the mount path to the exclusion list.
Split the protected folder. You can split the protected folder path in the mitigation policy into multiple paths. In the same mitigation policy, backups for the multiple protected folders are executed sequentially. Because the amount of data in each split folder is smaller than in the original folder, each backup job consumes fewer resources.
For example, if your protected folder in the mitigation policy is
/user/bin, you can split the protected folder path as needed, as shown in the following figure. For more information, see Modify a mitigation policy.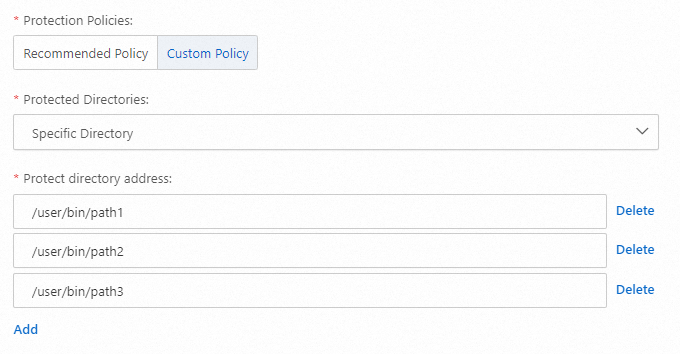
Limit the network bandwidth for backups
You can limit the backup throughput as needed to reduce disk, memory, and CPU usage. In the Edit Policies panel, modify the Maximum Backup Network Bandwidth setting. For more information, see Modify a mitigation policy.

If you set Network Bandwidth Throttling for Backup to 0, the bandwidth is not limited.
Upgrade resource configurations
Backing up a large amount of data requires more memory. If your server has insufficient memory for your backup needs, upgrade the server's memory configuration. For more information about resource requirements, see Resource requirements for backups.
If you use an ECS instance, see Change instance types to upgrade its configuration.
After you split the protected folder path, Security Center executes the backup plan based on the new folders. This does not affect the restoration of previously backed up data.
Adjust the CPU usage limit
If your resource configuration is sufficient for the backup data size, you can increase the CPU usage limit for backups. This allocates more computing resources to backup jobs, improves concurrency, and reduces the waiting time for resources. This helps prevent long waits during the backup process and increases the overall backup speed.
Before you adjust the CPU usage limit, fully assess the system performance and current load to ensure that the system can handle the increased load.
The anti-ransomware feature and Cloud Backup share the same client. Therefore, configuration changes made to the anti-ransomware client also affect Cloud Backup. Before you make adjustments, fully assess the impact on the Cloud Backup service.
For example, if your system has eight CPU cores, you can increase the default CPU allocation from one core to two. Go to the installation directory of the anti-ransomware agent (the default is the ../client directory), and add cpu_max_procs = 2 to the hbr.config configuration file.
The following table lists the default installation directory for each version of the anti-ransomware agent.
Agent version | Operating system of the server | Installation directory of the anti-ransomware agent |
1.X.X | Windows | C:\Program Files (x86)\Alibaba\Aegis\hbr\client |
Linux | /usr/local/aegis/hbr/client | |
2.X.X | Windows | C:\Program Files (x86)\Alibaba\Aegis\hbrclient\client |
Linux | /usr/local/aegis/hbrclient/client |
If the hbr.config file does not exist, create an hbr.config file and add only the cpu_max_procs = 2 configuration. The configuration takes effect the next time a backup job starts.
If the preceding methods do not resolve the issue, submit a ticket for online technical support and provide the following information:
Total memory of the device
Available memory
Memory used by the backup process during backup
Total number of backup files
Backup data size
Backup client version
Disk I/O and network throughput
Screenshots of CPU and memory information from Cloud Monitor before and during the backup. For more information about how to view this information, see Cloud service monitoring.