This topic explains the process of achieving environment isolation using Alibaba Cloud Serverless App Engine (SAE) and ApsaraMQ for RocketMQ, facilitating traffic shaping in asynchronous scenarios without altering business code.
Background information
Supported versions of Message Queue for Apache RocketMQ: 4.2.0 and later.
Both pull and push modes are supported.
You need to set
enablePropertyFilter=trueon the server and then restart it.
Preparations
Deploy SAE demo application
- Download the demo package.
- Deploy backbone applications. Deploy the following backbone applications: Application A, Application B, and Application C. For more information, see Host Spring Cloud applications to SAE.
- Deploy the following canary release applications: Application A-gray, Application B-gray, and Application C-gray. Add
-Dalicloud.service.tag=grayto the startup command to distinguish the canary release applications with the backbone applications.
-Dnacos.use.endpoint.parsing.rule=false -Dnacos.use.cloud.namespace.parsing=false. Deploy RocketMQ
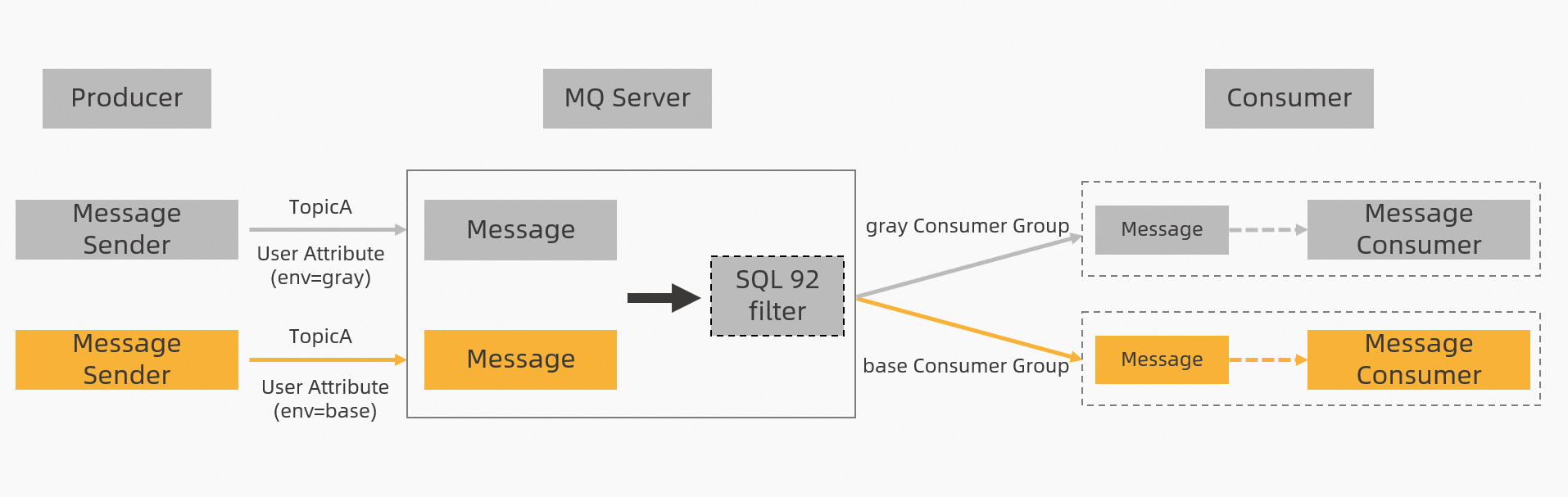
Canary release is effective for messages only if the RocketMQ-based canary release feature is enabled for both message producers and consumers. At present, it supports only RocketMQ message types, encompassing both the open-source version (Apache RocketMQ) and the Alibaba Cloud commercial version (ApsaraMQ for RocketMQ).
For Apache RocketMQ, ensure both RocketMQ Server and RocketMQ Client are version 4.5.0 or later. For more information, see Apache RocketMQ.
When utilizing Alibaba Cloud ApsaraMQ for RocketMQ, the Platinum Edition is required, and the Ons Client version must be 1.8.0.Final or newer. For more information, see the quick start overview.
After enabling the RocketMQ-based canary release feature, SAE modifies the message consumer groups. For instance, if the original consumer group is
group1with the environment taggray, it will be changed togroup1_grayafter the feature is activated. If you are using Alibaba Cloud ApsaraMQ for RocketMQ, please ensure the group is created beforehand.By default, the SQL92 filtering method is used. To utilize this method with Apache RocketMQ, you must activate the SQL92 filtering feature on the server by setting
enablePropertyFilter=trueinbroker.conf.
Step 1: Enable the RocketMQ-based canary release feature for applications
In the demo, the spring-cloud-c and spring-cloud-a applications are the producer and consumer of messages, respectively. By adding the startup parameter -Dprofiler.micro.service.mq.gray.enable=true, you can enable RocketMQ message grayscale for them on SAE.
To enable or disable the RocketMQ-based canary release feature, redeploy the application on the SAE console.
Step 2: ingest traffic and perform verification
The diagram below illustrates the demo's structure. Application calls include Spring Cloud service calls and Dubbo service calls, which are widely used microservices frameworks. Application C produces RocketMQ messages for Application A, which, upon consumption, initiates new calls. The diagram demonstrates the basic and standard usage of Spring Cloud, Dubbo, and RocketMQ.
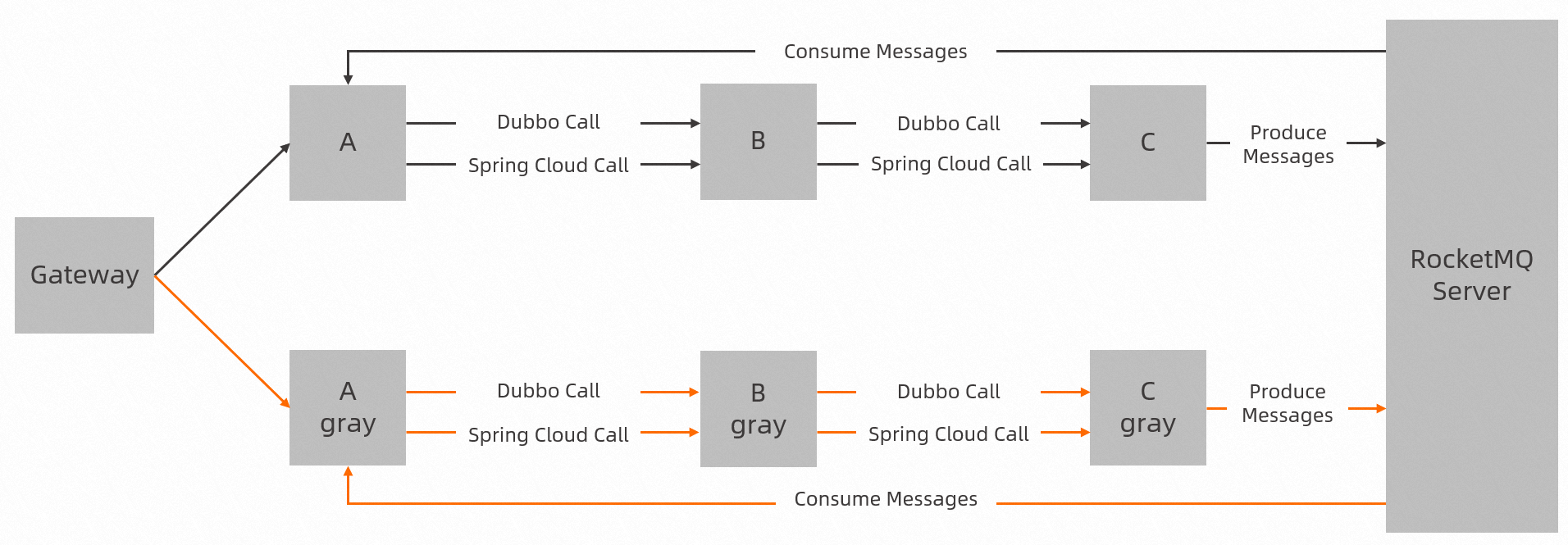
The demo's call chain is as follows: the spring-cloud-zuul application, upon receiving a request for /A/dubbo, forwards it to spring-cloud-a. Spring-cloud-a then uses the Dubbo protocol to access spring-cloud-b, which in turn accesses spring-cloud-c. After processing the request, spring-cloud-c produces a message and returns its environment tag and IP address. Spring-cloud-a consumes the message and simultaneously calls spring-cloud-b using the Spring Cloud protocol. Spring-cloud-b then calls spring-cloud-c in the same manner, with results displayed in the logs.
# When accessing /A/dubbo
# the return value is A[10.25.xx.xx] -> B[10.25.xx.xx] -> C[10.25.xx.xx].
# At the same time, spring-cloud-a receives the message and returns the following log:
c.a.mse.demo.service.MqConsumer: topic:TEST_MQ,producer:C[10.25.xx.xx],invoke result:A[10.25.xx.xx] -> B[10.25.xx.xx] -> C[10.25.xx.xx]You can log on to the SAE console to view the logs for the spring-cloud-a application and confirm its configuration. The baseline environment is capable of processing messages produced by both the canary release and baseline environments. Calls made within the Spring Cloud from either the canary release or baseline environment are directed to the corresponding downstream environment.