When you deploy a Spring Cloud application or a Dubbo application that is developed in your on-premises environment to Serverless App Engine (SAE), you can use the built-in service registry of SAE or a Microservices Engine (MSE) Nacos registry to register and discover services. This topic describes how to configure Nacos service registration and discovery feature for Spring Cloud or Dubbo application in the SAE console.
Prerequisites
A virtual private cloud (VPC) is created and available. For more information, see Create and manage a VPC.
The access port of your Nacos registry, such as port 8848, is added to your security group before you run your application. For more information, see Add a security group rule.
A Nacos engine is created and a namespace is created for the instance.
Recommendations
If you have a large number of microservices applications, you can use one of the following types of service registries that are listed in descending order by recommendation level:
MSE Nacos registry
Self-managed service registry
SAE built-in service registry
For more information, see Release notes for the MSE Nacos engine and Open source Nacos.
Limits
For more information on the limits of using a MSE Nacos registry, see Application of MSE Nacos SDKs and unrecommended versions of Nacos SDKs.
Feature entry
The procedure depends on the scenario:
Create an application
Log on to the SAE console. In the left-side navigation pane, choose . On the page that appears, select a region in the top navigation bar and a namespace from the Namespace drop-down list, and then click Create Application.
On the Basic Information page, configure the parameters and click Next: Advanced Settings.
Modify a running application
After you redeploy an application, the application is restarted. To prevent unpredictable errors such as business interruptions, we recommend that you deploy applications during off-peak hours.
Log on to the SAE console. In the left-side navigation pane, choose . On the page that appears, select a region in the top navigation bar and a namespace from the Namespace drop-down list, and click the target application name.
On the Basic Information page, click Deploy Application.
Modify a stopped application
Log on to the SAE console. In the left-side navigation pane, choose . On the page that appears, select a region in the top navigation bar and a namespace from the Namespace drop-down list, and click the target application name.
On the Basic Information page, click Modify Configuration.
Configure the service registration and discovery feature
Expand the Service Registration and Discovery section. Select Nacos-based Registry Service and Discovery as MSE Nacos Professional Edition, then select a created MSE Nacos Instance and the corresponding Namespace.

Verify the result
In this example, the consumer application is used to verify the result. On the Instances tab of the Basic Information page, click Webshell in the Actions column of the instance. In the Webshell window, run the following commands to check whether the application is deployed. For more information, see Use the webshell feature to check the health status of applications.
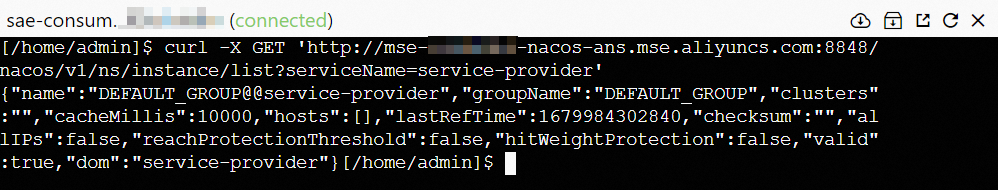
Verify whether the service is registered.
curl -X GET 'http://192.168.XX.XX:8848/nacos/v1/ns/instance/list?serviceName=service-provider'service-provider: the service name.192.168.XX.XX:8848: the IP address and port number of the server on which Nacos is installed. Replace192.168.XX.XXwith the internal endpoint of the MSE Nacos registry. Log on to the MSE console, and click the desired instance on the Instances tab. On the Basic Information page of the instance, obtain the internal endpoint of the registry.
If the following output is returned, the service is registered.
Verify whether the access URL of the microservices application is normal.
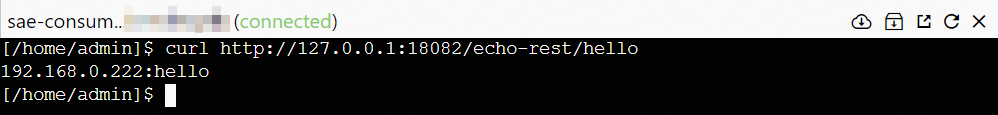
Run one of the following commands based on your business requirements. 127.0.0.1:18082 indicates the IP address and access port of the server on which the provider application and the consumer application run.
curl http://127.0.0.1:18082/echo-rest/{custom variable}curl http://127.0.0.1:18082/echo-feign/{custom variable}
The following output indicates that the consumer application called the provider application and the access URL to the microservices application is normal.