This topic provides an example of how to deploy a microservice application using Serverless Application Engine (SAE). This topic also describes how to enable public network access for the application and invoke methods between microservices.
Prerequisites
You have activated SAE and granted the required permissions. You have also created a VPC and a namespace. For more information, see Preparations.
Solution overview
Create applications: Deploy the Provider and Consumer applications to SAE. The Consumer application invokes services from the Provider application using the built-in service registration and discovery feature of SAE.
Access the application from the internet and verify the result: Configure a public endpoint for the Consumer application. Then, access the application from a browser to verify that the Consumer application can successfully invoke the Provider application.
Create Application
Deploy the Provider application to SAE
Log on to the SAE console. In the navigation pane on the left, choose . In the top menu bar, select a region. This topic uses the China (Hangzhou) region as an example. Click Create Application.
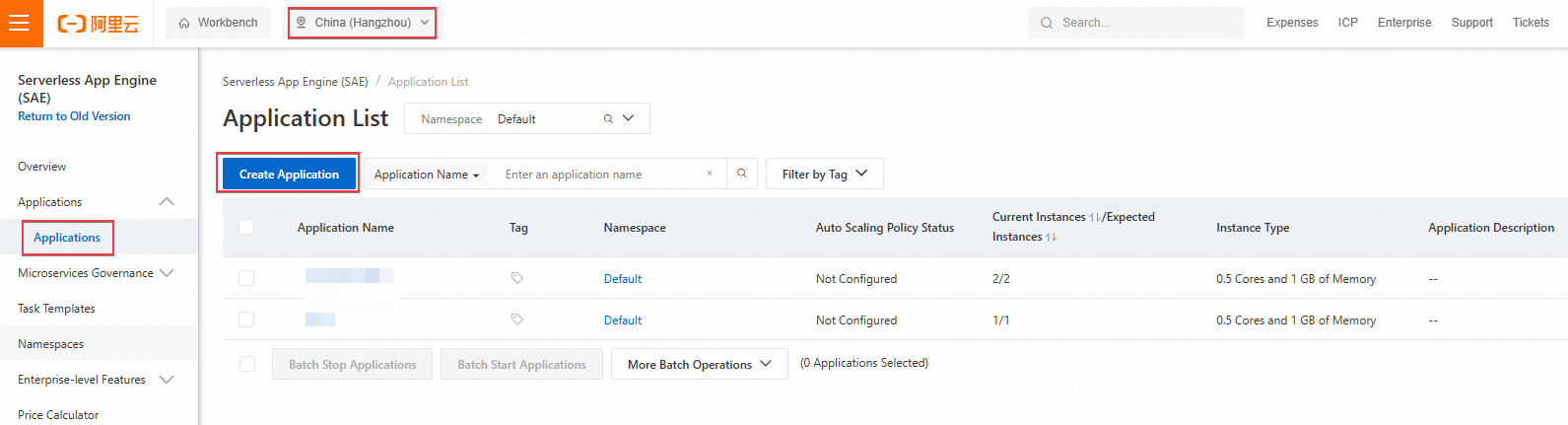
On the Create Application page, configure the parameters as described in the following table and leave the other parameters at their default values. Then, click Create Application Now. The application is created in about one minute.
This topic uses an official Demo Image to demonstrate the deployment process. You can skip the image building step. In a production environment, you must build an image from your business code, upload the image to an image repository, and then deploy the image to SAE.
Configuration Item
Example
Description
Application Name
microservice-provider
Customizable.
Deployment Method
Deploy Using Image
Click Set Image. Set Technology Stack to Java and Java Environment to Open JDK 8. On the Demo Image tab, set Image Version to microservice-java-provider-v1.0.
NoteThis topic provides a simplified example of the application creation process. After you configure the Basic Information for the application, you can click Next: Advanced Settings to configure advanced features, such as environment variables and logs. For more information, see Advanced Configuration.
Deploy the Consumer application to SAE
To deploy the Consumer application, repeat the preceding steps and modify the parameters as described in the following table.
Configuration Item | Example | Description |
Application Name | microservice-consumer | Customizable. |
Deployment Method | Deploy Using Image | Click Set Image. Set Technology Stack to Java and Java Environment to Open JDK 8. On the Demo Image tab, set Image Version to microservice-java-consumer-v1.0. |
Access the application from the internet and verify the result
Configure a public endpoint
On the Application List page, click the name of the Consumer application that you created. In this example, the application is named
microservice-consumer.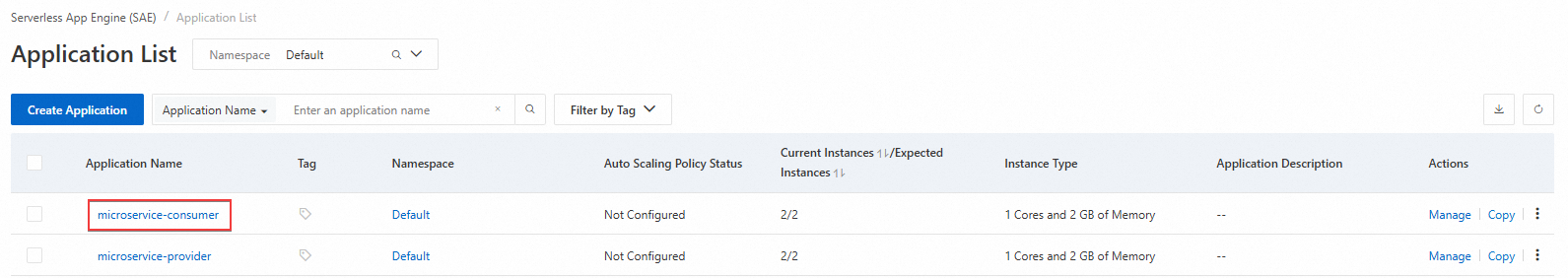
On the Basic Information page, on the Application Information tab, click Add Internet-facing CLB in the Application Access Settings section.

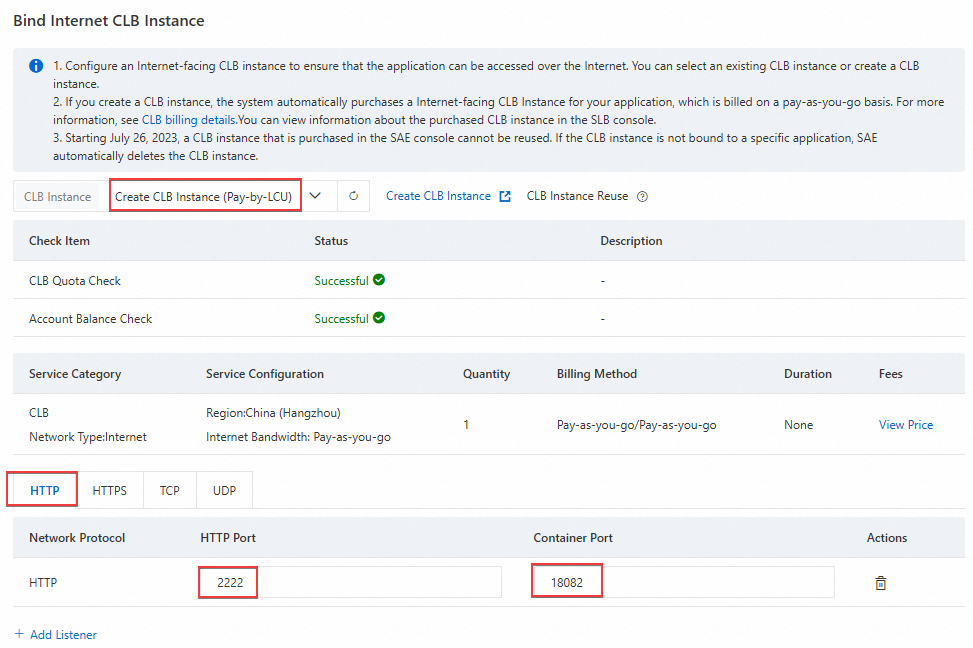
In the Add Internet-facing CLB panel that appears, configure the parameters as described in the following table. Then, click OK.
If the page prompts you to activate a service, follow the on-screen instructions.
Configuration Item
Example
Description
CLB Instance
Create CLB Instance (Pay-As-You-Go)
You can create one of the following two types of CLB instances:
Create CLB Instance (Subscription)
Create CLB Instance (Pay-As-You-Go)
Protocol Type
HTTP
The available protocol types are HTTP, HTTPS, TCP, and UDP. This topic uses HTTP as an example. For information about how to configure other protocols, see Bind a CLB instance to an application and generate a public or internal endpoint.
Protocol Port
2222
Custom. The port number must be between 1 and 65535.
Container Port
18082
In this example, the container port is 18082. In a production environment, set this parameter as needed.
Test the access
Copy the public endpoint that you added for the Consumer application and access the endpoint from a browser. The URL format is
Public endpoint/consumer-echo/hello. A successful access verifies that the application is deployed and accessible from the Internet.

(Optional) On the Application List page, click the name of the Provider application that you created. In this example, the application is named
microservice-provider. In the navigation pane on the left, choose . Repeat the previous step and refresh the page. Observe that the total number of requests for the Provider application increases each time you access the Consumer application. This indicates that the method invocation between the microservices is successful.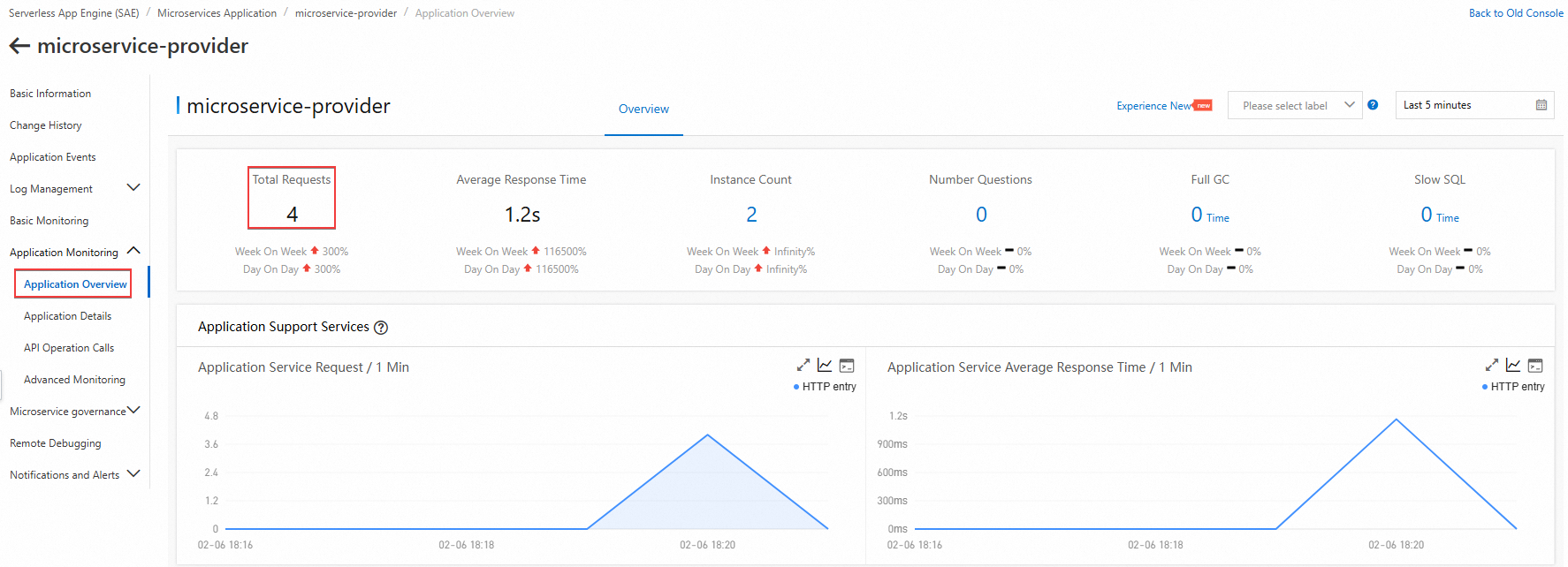
Clean up resources
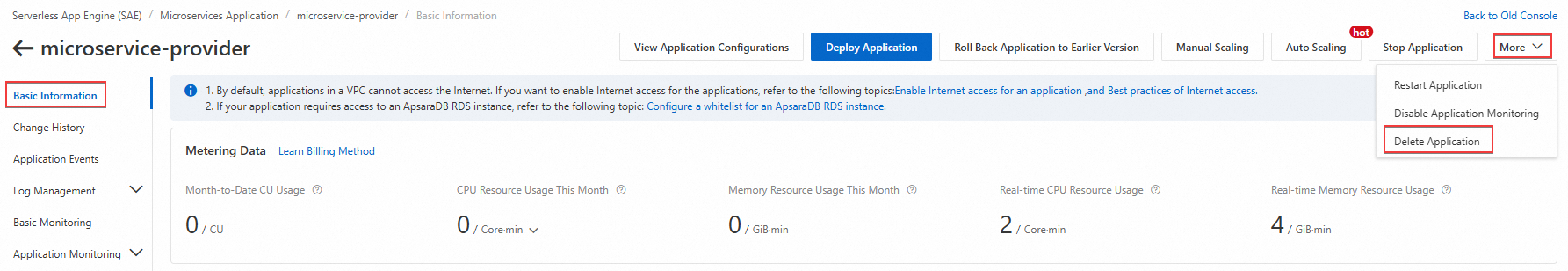
After you complete this tutorial, delete the resources if you no longer need them. Otherwise, you will continue to be charged for them.
Log on to the SAE console. In the navigation pane on the left, choose . Switch to the region where the resources are located. This tutorial uses the China (Hangzhou) region as an example. On the Application List page, click the name of the application that you created to go to its details page. Then, choose and follow the on-screen instructions.
References
Demo images usually do not meet actual business requirements. In a production environment, you must deploy microservice applications using methods such as a Docker image repository or a code package and configure advanced features. For more information, see the following topics.