In a cloud-native instance deployed across multiple zones, when the number of nodes in the primary zone is greater than or equal to 2 (with a total of at least 3 nodes), the high availability (HA) system performs a failover first within the primary zone if the master node fails. This feature helps prevent latency spikes during a master node failover to the secondary zone.
The current cloud-native standard and cluster architectures automatically enable this feature, requiring no manual intervention from you. This topic uses the cluster architecture as an example for explanation.
Background information
In multi-zone deployment, the master and replica nodes of each shard in a cluster instance are deployed across different zones within the same region. The zones are physically separated areas with independent power and network connections to ensure high disaster recovery.
When the master node of a shard fails, the instance automatically triggers a failover to minimize the impact. In most cases, the client is also deployed in the primary zone. If no instance failover occurs, the client and the master node of the cluster instance remain in the same zone. In this case, access latency is minimized, which results in the most healthy connection. The following figure shows the architecture of a three-shard cluster instance.

When the master node of a shard fails and triggers a failover, the HA system switches workloads from the master node to a replica node in the secondary zone. In this case, the client accesses the instance across zones (data centers), which can significantly increase access latency.
Cross-zone latency is much higher than latency within the same zone. For information about the average cross-zone latency, go to the Cloud Network Performance page.

Tair (Redis OSS-compatible) is an in-memory database that provides high performance and low latency. High network latency can directly affect the overall response time of service requests. To optimize performance, stability, and disaster recovery, we recommend that you add a replica node to the primary zone of the cluster instance.
If the master node fails and triggers a failover, the instance preferentially performs a switchover in the same zone. After the switchover, the master node remains in the primary zone, which does not increase access latency.
If a zone-level failure occurs in the primary zone, the instance performs a cross-zone switchover for disaster recovery.
Solution overview
Tair (Redis OSS-compatible) allows you to specify two to five nodes for a shard of a cluster instance.
When the number of nodes is 2, one node is deployed in the primary zone and the other is deployed in the secondary zone.
When the number of nodes is 3, two nodes are deployed in the primary zone and one node is deployed in the secondary zone.
When the number of nodes is 4 or 5, you can deploy the remaining nodes in the primary or secondary zone.
The following figure shows the architecture of a cluster instance with three shards and three nodes (two nodes in the primary zone and one node in the secondary zone).

If the master node of a shard fails and triggers a failover, the HA system preferentially switches workloads from the master node to a replica node in the primary zone. In this case, the client continues to access the instance within the same zone to prevent increase in access latency, as shown in the following figure.

How-to guide
If you have not created an instance, you must create a cloud-native instance that is deployed across multiple zones. For more information, see Step 1: Create an instance.
The following figure shows a configuration in which the number of nodes in the primary zone is greater than or equal to 2.
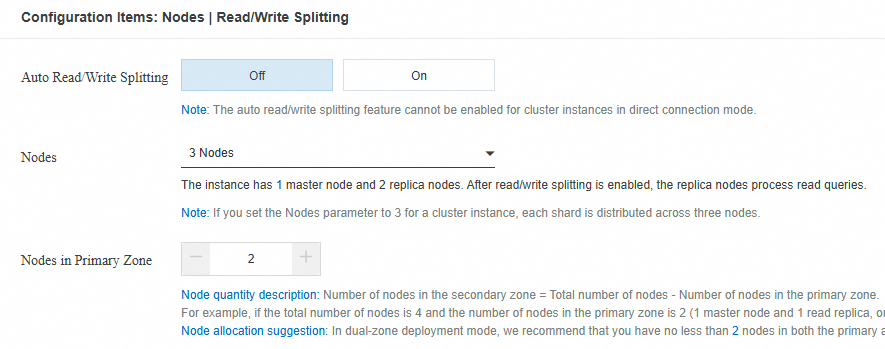
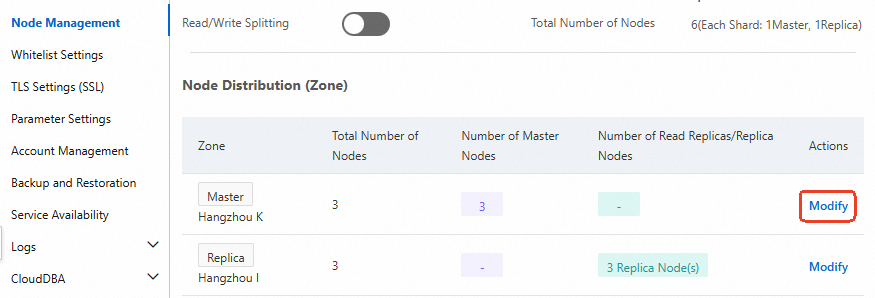
If you have created a cloud-native cluster instance that is deployed across multiple zones, you can go to the Node Management page of the instance details page and click Modify to increase the number of nodes in the primary zone to at least 2.
If you have created a classic instance, you can create an instance that meets the preceding conditions and use Data Transmission Service (DTS) to synchronize data to the new instance. For more information, see Configure one-way data synchronization between instances.