ApsaraDB RDS for PostgreSQL provides the pldebugger extension that you can use to debug stored procedures.
Background information
ApsaraDB RDS for PostgreSQL supports multiple stored procedure languages, such as plpgsql, plpython, plperl, and pltcl. You can use these stored procedure languages to create functions or stored procedures.
Prerequisites
Your ApsaraDB RDS for PostgreSQL instance must meet the following requirements:
Major engine version
Minor engine version
PostgreSQL 14, 15, 16, and 17
20250630 or later
PostgreSQL 10, 11, 12, and 13
20230830 or later
ImportantTo standardize extension management and enhance the security protection of ApsaraDB RDS for PostgreSQL, RDS plans to optimize some extensions that have security risks in subsequent kernel iterations. Therefore, you can no longer create this extension on instances that run a minor engine version earlier than 20230830. For more information, see Limits on creating extensions.
If you have already created this extension on an instance that runs a minor engine version earlier than 20230830, its functionality is not affected.
If you want to create or re-create this extension, you must upgrade the minor engine version of your instance to the latest version.
You have created a privileged account for your ApsaraDB RDS for PostgreSQL instance. For more information, see Create an account.
Make sure that you use pgAdmin 4 v4.19 or later. To download pgAdmin 4, see pgAdmin 4.
Install and uninstall the extension
Set instance parameters. Add plugin_debugger to the Value of the shared_preload_libraries parameter. For example, change the Value to
'pg_stat_statements,auto_explain,plugin_debugger'.Use a privileged account to connect to the database where you want to install the extension and execute the following SQL statements to create or delete the extension.
Create the extension
CREATE EXTENSION pldbgapi;Delete the extension
DROP EXTENSION pldbgapi;
Debugging example
Use a pgAdmin client to connect to the ApsaraDB RDS for PostgreSQL database. For more information, see Connect to an ApsaraDB RDS for PostgreSQL instance.
Create a test database and a stored procedure.
The following SQL statements are an example:
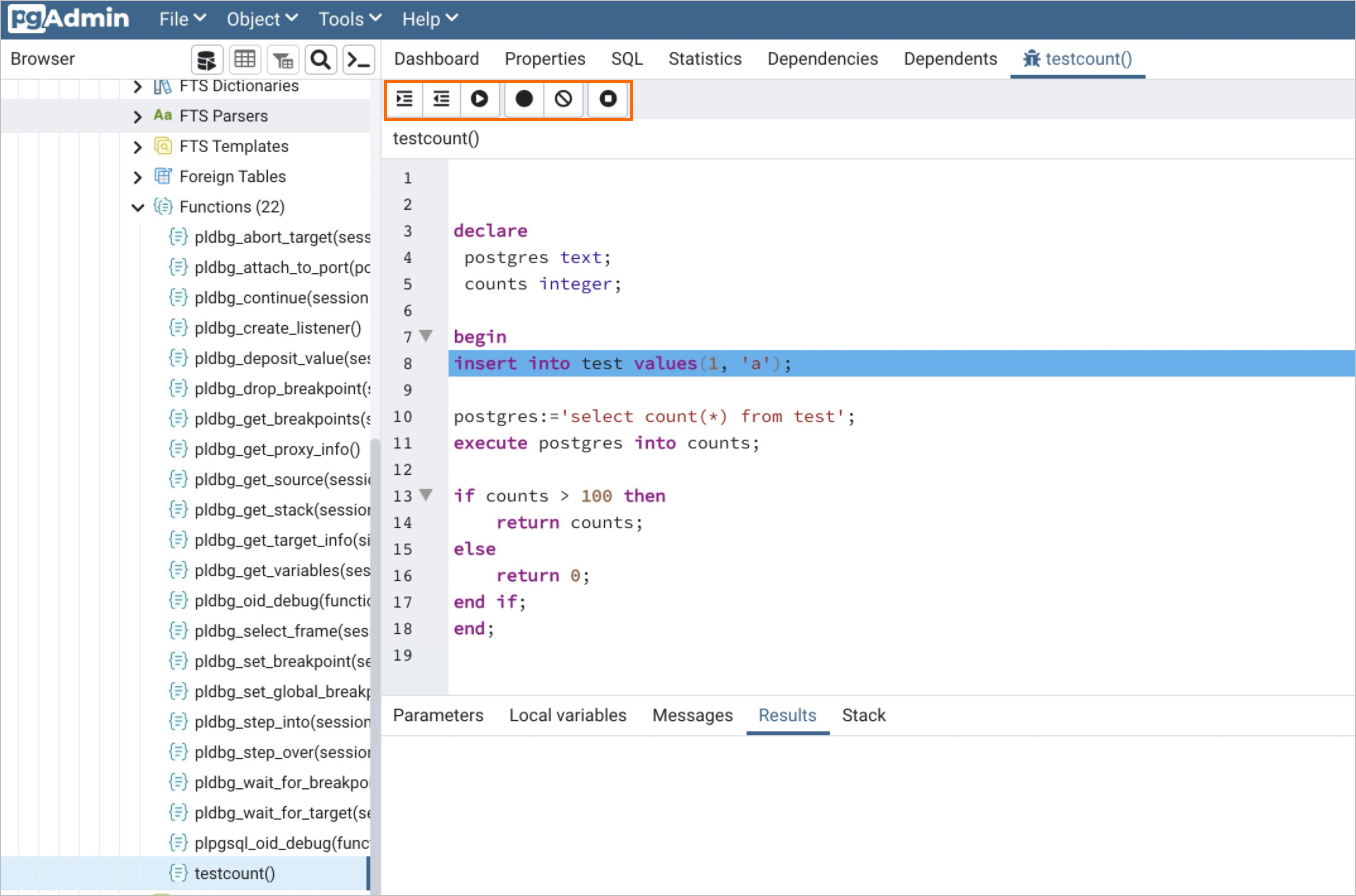
CREATE TABLE test( id int, name VARCHAR(50)); CREATE OR REPLACE FUNCTION public.testcount() RETURNS integer AS $$ DECLARE postgres text; counts integer; BEGIN INSERT INTO test VALUES(1, 'a'); postgres:='SELECT COUNT(*) FROM test'; EXECUTE postgres INTO counts; IF counts > 100 THEN RETURN counts; ELSE RETURN 0; END IF; END; $$ language plpgsql;Right-click the function that you want to debug.
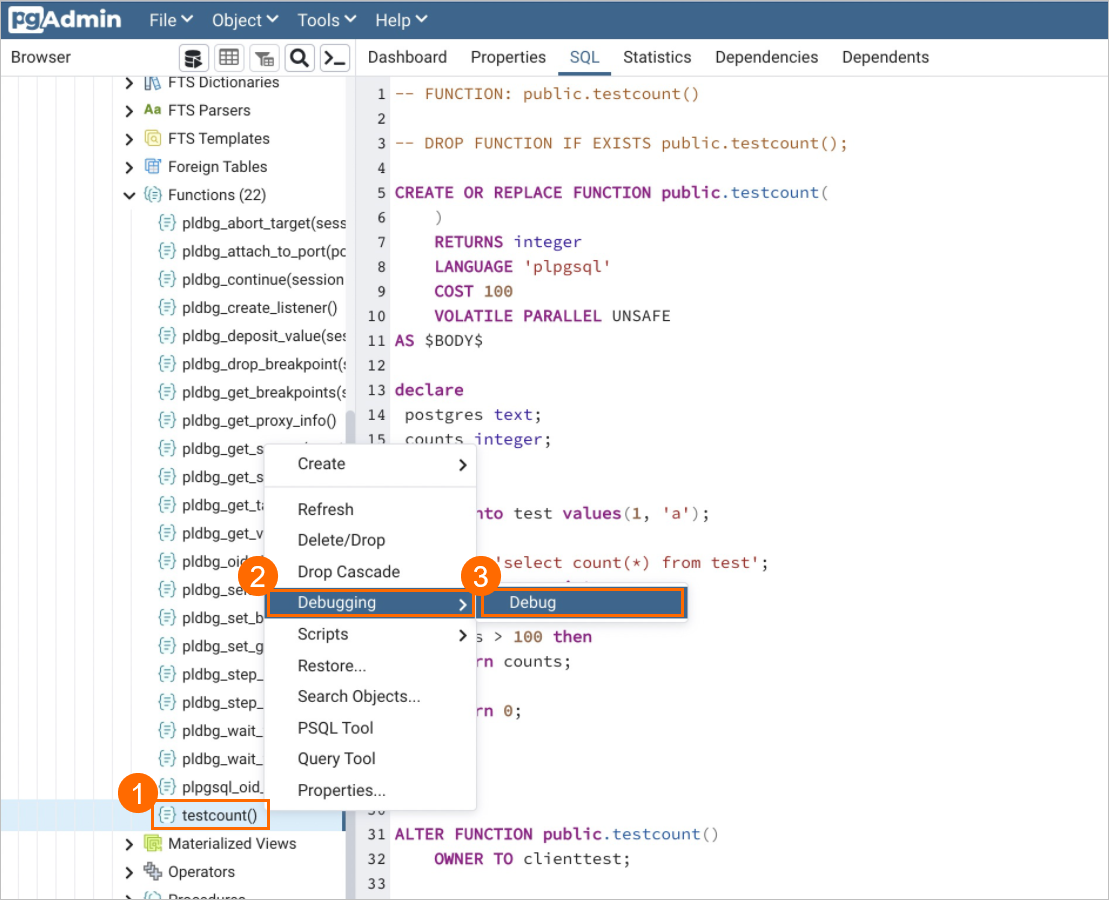
In the function debugging pane on the right side of the pgAdmin interface, you can debug the objective function step by step. The available operations include Step Into, Step Over, Continue, Add Breakpoint, and Stop. At the bottom, you can view information about local variables, debugging results, and the function stack.