This topic describes how to use the Foreign Data Wrapper (FDW) extension for PostgreSQL. This allows an ApsaraDB RDS for PostgreSQL instance to access an external database over the Internet.
Background information
An ApsaraDB RDS for PostgreSQL instance can access other types of external databases, such as MySQL, SQL Server, PostgreSQL, and Redis, using the FDW feature. Because RDS for PostgreSQL instances are deployed in a Virtual Private Cloud (VPC), you must configure an Internet NAT gateway and associate an Elastic IP Address (EIP) to access database services over the Internet.
This topic explains how to enable an RDS for PostgreSQL instance to access the Internet by configuring an Internet NAT gateway and an EIP. You can configure a Source Network Address Translation (SNAT) entry to allow the RDS for PostgreSQL instance to access the Internet. This method also ensures the network security of the instance. External networks cannot access the instance through the NAT gateway.
For more information about NAT Gateway and SNAT, see Use the SNAT feature of an Internet NAT gateway to access the Internet.
Prerequisites
A target database is available and accessible over the Internet. Examples include MySQL, SQL Server, PostgreSQL, or Redis databases with public IP addresses.
An RDS for PostgreSQL instance is created. For more information, see Quickly create an RDS for PostgreSQL instance.
ImportantThe RDS for PostgreSQL instance requires specific extensions to access the target database over the Internet. Ensure that your RDS for PostgreSQL instance supports the required extensions. For more information about the extensions supported by different RDS for PostgreSQL versions, see List of extensions supported by RDS for PostgreSQL.
MySQL: mysql_fdw
SQL Server: tds_fdw
PostgreSQL: postgres_fdw
Redis: redis_fdw
Accounts are created for both the target database and the RDS for PostgreSQL instance.
To create an account for the target database, see the official documentation for the database engine.
To create an account for the RDS for PostgreSQL instance, see Create an account.
A database that contains data is created in the target database.
Procedure
Configure an Internet NAT gateway
Create a NAT Gateway.
Log on to the NAT Gateway console.
On the Internet NAT Gateway page, click Create Internet NAT Gateway.
(Optional) If you are using NAT Gateway for the first time, on the Internet NAT Gateway page, in the Service-linked Role Creation section, click Create Service-linked Role. After the role is created, you can create a NAT Gateway.
On the Create Internet NAT Gateway page, set the following parameters and click Buy Now.
NoteThe following table lists only the key parameters. For more information about all parameters, see Use the SNAT feature of an Internet NAT gateway to access the Internet.
Configuration
Description
Region
Select the region where you want to create the Internet NAT gateway. The region must be the same as the region of the RDS for PostgreSQL instance.
Network And Zone
Select the VPC and vSwitch for the Internet NAT gateway instance. They must be the same as the VPC and vSwitch of the RDS for PostgreSQL instance.
You can go to the Database Connection page in the RDS console to view the VPC of the target RDS for PostgreSQL instance.
Network Type
In this topic, Internet NAT Gateway is selected.
EIP
In this topic, Configure Later is selected.
On the Confirm page, confirm the Internet NAT gateway configuration and click Activate Now.
After you create the instance, you can view it on the Internet NAT Gateway page.
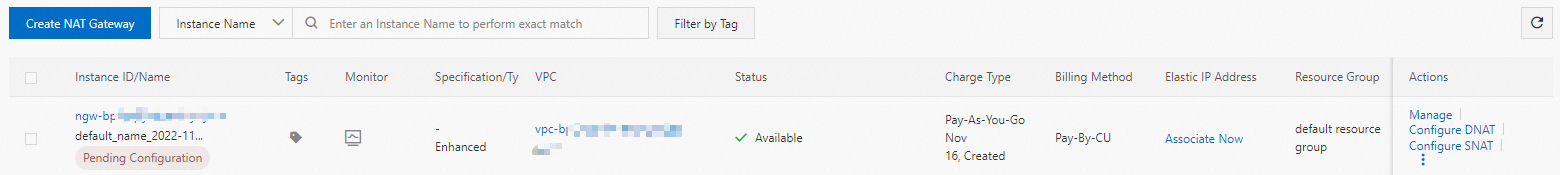
Associate an EIP with the Internet NAT gateway.
On the NAT Gateway console, find the Internet NAT gateway instance that you created and click its instance ID to go to the Basic Information page.
On the Associated EIP tab, click Associate EIP.
In the Associate EIP dialog box, select Purchase and Associate EIP.
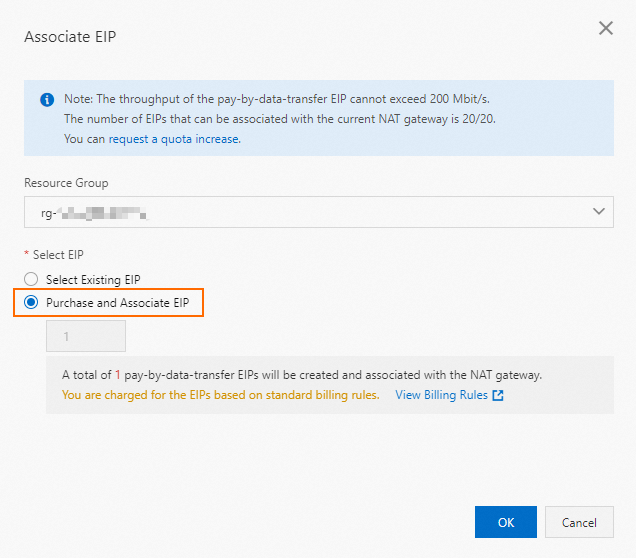
Click OK.
After an EIP is associated, it is listed in the Associated EIP section.
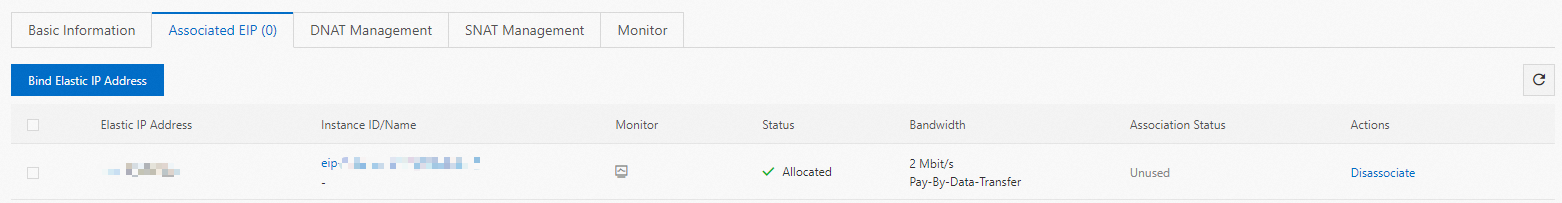
Create an SNAT entry.
On the NAT Gateway console, find the Internet NAT gateway instance that you created and click its instance ID to go to the Basic Information page.
On the SNAT tab, click Create SNAT Entry.
On the Create SNAT Entry page, configure the following parameters and click OK.
Configuration
Description
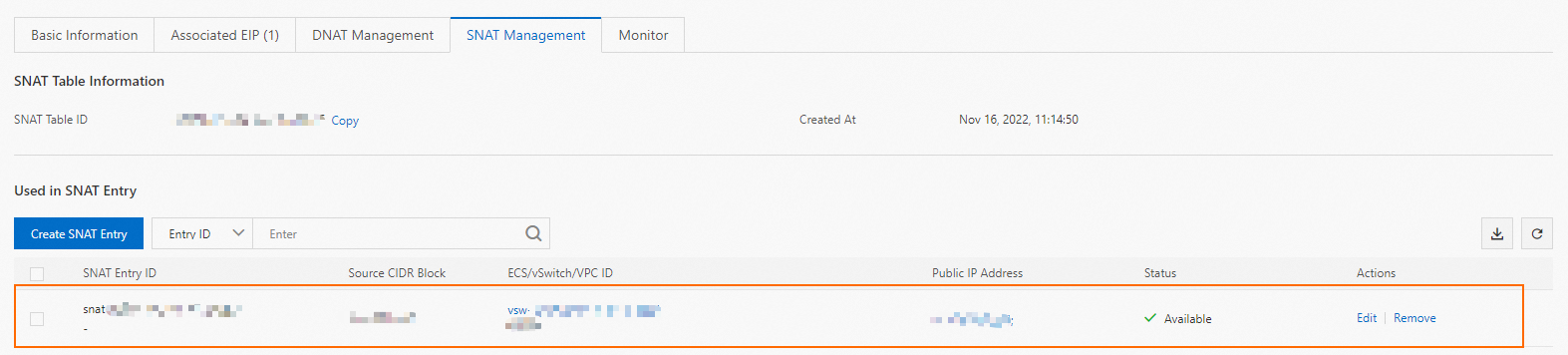
SNAT Entry
Select the granularity for the SNAT entry. This topic uses VSwitch Granularity as an example. This specifies that the RDS for PostgreSQL instance in the vSwitch uses the configured public IP address to access the Internet.
Select vSwitch
From the drop-down list, select the vSwitch of the RDS for PostgreSQL instance.
Select EIP
Select the public IP address that provides Internet access. This topic uses a single IP address as an example. From the drop-down list, select the associated EIP.
After the entry is created, you can view it in the SNAT Entry List.
Configure the target database
Add the EIP that is associated with the Internet NAT gateway to the whitelist of the target database.
MySQL: See Privileges Provided by MySQL
PostgreSQL: See The pg_hba.conf File
SQL Server: See Configure the Windows Firewall to Allow SQL Server Access
Redis: Use a firewall to restrict IP access to a specific port. For example, if you use iptables on CentOS, run the following command:
iptables -A INPUT -s <EIP_associated_with_the_Internet_NAT_gateway> -p tcp --dport <Redis_port_number> -j ACCEPT
Configure the RDS for PostgreSQL instance
Connect to the RDS for PostgreSQL instance. For more information, see Connect to a PostgreSQL instance.
Create the extension.
NoteThis topic uses a MySQL database that is accessible over the Internet as an example. In this example, the mysql_fdw extension is created.
CREATE EXTENSION mysql_fdw;Create a server definition for the target database.
CREATE SERVER <server_name> FOREIGN DATA WRAPPER mysql_fdw OPTIONS ( host '<public_IP_of_the_target_database>', port '<port_of_the_target_database>' );The following example shows the command for a MySQL service that is accessible over the Internet:
CREATE SERVER mysql_server80 FOREIGN DATA WRAPPER mysql_fdw OPTIONS ( host 'XX.XX.XX.XX', port '3306' );Create a user mapping. This maps the MySQL server definition to a user in the RDS for PostgreSQL instance. This allows the user in the RDS for PostgreSQL instance to access data in the target MySQL database.
CREATE USER MAPPING FOR <RDS_for_PostgreSQL_username> SERVER <created_server_name> OPTIONS ( username '<username_for_the_target_database>', password '<password_for_the_target_database>' );The following is an example command:
CREATE USER MAPPING FOR pg_client SERVER mysql_server80 OPTIONS ( username 'testuser', password 'U123456!' );Create a foreign table.
CREATE FOREIGN TABLE <foreign_table_name> ( id int, name varchar(10) ) SERVER <created_server_name> OPTIONS ( dbname '<database_name_of_the_target_database>', table_name '<table_name_of_the_target_database>' );The following is an example command:
CREATE FOREIGN TABLE mysql_fdw_test ( id int, name varchar(10) ) SERVER mysql_server80 OPTIONS ( dbname 'testdb', table_name 'test' );Test the connection.
After you complete these configurations, you can access the tables in the external database from your RDS for PostgreSQL instance.
For example, if you created a foreign table named
mysql_fdw_test, you can query the foreign table directly in the RDS for PostgreSQL instance to retrieve data from the target database.SELECT * FROM mysql_fdw_test;