This topic describes the core concepts, configuration methods, access control policies, and common scenarios for SourceIdentity. It also provides troubleshooting guidance.
What is SourceIdentity
SourceIdentity is a source identity that you set for the current session when you call an OpenAPI operation to assume a RAM role and obtain a temporary Security Token Service (STS) token.
The main purposes of using SourceIdentity are:
Trace identities in complex scenarios such as role chaining
A role chain is a scenario where a RAM identity or a user who logs on through role-based SSO assumes a role, obtains a role session, and then calls an API operation to assume another role. For example, User A → Role B → Role C. The RAM roles in a role chain can belong to the same Alibaba Cloud account or different accounts.
In a role assumption scenario, you can set
RoleSessionNameto audit the source identity. However, in a role chain scenario,RoleSessionNamemight be modified during multiple role assumptions. This makes it difficult to accurately obtain the identity of the original operator.After
SourceIdentityis set at the beginning of a role chain, its value persists in the role session and cannot be changed. This ensures that the identity of the original operator can be traced in logs, even after multiple role assumptions.For more information about the application of
SourceIdentityin a role chain, see Role chain example.Implement fine-grained access control for high-privilege roles
Administrators can configure fine-grained authorization based on the value or existence of
SourceIdentity. This is useful when a shared role, which is a role used by multiple identities, is used to perform operations.For example, an administrator can use condition keys in an access policy to require that a source identity must set a specific
SourceIdentityvalue when assuming a role. This restricts role assumption for a high-privilege role or access to core resources to specific source identities.
Methods to set SourceIdentity
You can set SourceIdentity when you call STS to assume a role using one of the following three API operations.
Use the AssumeRole operation
When you call the AssumeRole API operation, you can use the SourceIdentity parameter to specify the source identity. For example, you can set the value to Alice. This applies to standard role assumption scenarios where a RAM user or RAM role assumes another role.
After a successful call, SourceIdentity is returned as a top-level field in the response. The following example shows a sample response:
{
"RequestId": "6894B13B-6D71-4EF5-88FA-F3278173****",
"AssumedRoleUser": {
"AssumedRoleId": "34458433936495****:alice",
"Arn": "acs:ram::123456789012****:role/alice"
},
"Credentials": {
"SecurityToken": "********",
"Expiration": "2015-04-09T11:52:19Z",
"AccessKeySecret": "wyLTSmsyPGP1ohvvw8xYgB29dlGI8KMiH2pK****",
"AccessKeyId": "STS.L4aBSCSJVMuKg5U1****"
},
"SourceIdentity": "Alice"
}For more information about how to call this operation, see AssumeRole - Obtain temporary identity credentials for a RAM role.
Use the AssumeRoleWithSAML operation
In a SAML role-based SSO scenario, the value of SourceIdentity is provided by the identity provider (IdP) in the SAML assertion.
You can configure a SAML attribute in the IdP and map it to a user identity, such as a username. The attribute name must be https://www.aliyun.com/SAML-Role/Attributes/SourceIdentity.
After the configuration is complete, the SAML response issued by the IdP contains the following SAML assertion. This example assumes that the user's User Principal Name (UPN) prefix is mapped to the SourceIdentity value:
<Attribute Name="https://www.aliyun.com/SAML-Role/Attributes/SourceIdentity">
<AttributeValue>upn_prefix</AttributeValue>
</Attribute>The response for a successful call is the same as the response for the AssumeRole operation. For more information about how to call this operation, see AssumeRoleWithSAML - Obtain temporary identity credentials for a RAM role during SAML role-based SSO.
Use the AssumeRoleWithOIDC operation
In an OpenID Connect (OIDC) role-based SSO scenario, the value of SourceIdentity is provided by the IdP as a claim in the ID token, also known as an OIDC token.
You can configure a custom ID token claim in the IdP and map it to a user identity, such as a username. The claim name must be https://www.aliyun.com/source_identity. For example:
After the configuration is complete, the ID token issued by the IdP contains the following claim. This example assumes that the user's UPN prefix is mapped to the SourceIdentity value:
{
"https://www.aliyun.com/source_identity": "upn_prefix"
}The response for a successful call is the same as the response for the AssumeRole operation. For more information about how to call this operation, see AssumeRoleWithOIDC - Obtain temporary identity credentials for a RAM role during OIDC role-based SSO.
Format requirements
The value must be 2 to 64 characters in length.
The value can contain letters, digits, and the following special characters:
=,,,.,@,-, and_.The value cannot use prefixes reserved by Alibaba Cloud, such as
acs:,aliyun:, oralibabacloud:.
Permission settings and condition control
You can use a combination of identity-based access policies and role trust policies to precisely control the use of SourceIdentity.
Permission operation
Name | Type | Scope | Function |
| Permission operation |
| Grants the permission to set |
Permission operation configuration example
To allow an identity, such as a RAM user or RAM role, to set SourceIdentity when calling AssumeRole, you must grant the sts:SetSourceIdentity permission in both the identity-based access policy of the principal and the role trust policy of the target role. Add sts:SetSourceIdentity to the Action block.
Example of an identity-based access policy (granted to the principal):
{ "Version": "1", "Statement": [ { "Effect": "Allow", "Action": [ "sts:AssumeRole", "sts:SetSourceIdentity" ], "Resource": "acs:ram::ACCOUNT_ID:role/TARGET_ROLE" } ] }Example of a role trust policy (configured for the assumed role):
{ "Statement": [ { "Action": [ "sts:AssumeRole", "sts:SetSourceIdentity" ], "Effect": "Allow", "Principal": { "RAM": [ "acs:ram::ACCOUNT_ID:root" ] } } ], "Version": "1" }
Permission operation configuration example for a role-based SSO scenario
When you assume a role by calling the AssumeRoleWithSAML or AssumeRoleWithOIDC operation, you only need to grant the sts:SetSourceIdentity permission in the role trust policy of the target role. The following example shows a policy for SAML role-based SSO:
{
"Statement": [
{
"Action": [
"sts:AssumeRole",
"sts:SetSourceIdentity"
],
"Condition": {
"StringEquals": {
"saml:recipient": [
"https://signin.aliyun.com/saml-role/sso"
]
}
},
"Effect": "Allow",
"Principal": {
"Federated": [
"acs:ram::ACCOUNT_ID:saml-provider/PROVIDER_NAME"
]
}
}
],
"Version": "1"
}If you configure the SourceIdentity attribute in the IdP, the trust policies of all roles associated with that IdP must include the sts:SetSourceIdentity operation. Otherwise, users cannot log on through SSO because of insufficient permissions.
Condition keys
Name | Type | Scope | Function |
| Condition key |
| Associates one or more |
| Condition key (global) |
| Associates one or more |
Currently, the acs:SourceIdentity condition key is effective only during policy evaluation for STS.
The difference between the sts:SourceIdentity and acs:SourceIdentity condition keys is as follows:
sts:SourceIdentitymatches theSourceIdentityattribute in the role assumption request.acs:SourceIdentitymatches theSourceIdentityattribute that exists in the role session, including the STS token, after the role is successfully assumed.
If you are assuming a role for the first time, you must configure the sts:SourceIdentity condition key in the policy, including the identity-based access policy and the role trust policy. Because no valid role session has been generated yet, using the acs:SourceIdentity condition key will cause the role assumption to fail.
Condition control example
Using the sts:SourceIdentity condition key in the Condition block of a policy, you can require that a specific SourceIdentity value must be passed when a role is assumed. You can configure conditions in one or both of the following types of policies:
Set conditions in an identity-based access policy: Restrict the identity to setting a specific
SourceIdentityvalue when it assumes a specific role.Set conditions in a role trust policy: Restrict any identity to setting a specific
SourceIdentityvalue when assuming the role.
Note that you must also add the sts:SetSourceIdentity permission to the Action block of the policy. Otherwise, the condition control feature will not work.
After a RAM user logs on to the console, the user cannot use the Switch Identity feature to assume a role that requires SourceIdentity to be set. This is because the console does not support entering this parameter.
Assume there is a high-privilege RAM role for the production environment named prod-role. An administrator needs to implement the following controls:
Only the RAM users Alice and Bob can assume
prod-role.When assuming
prod-role,SourceIdentitymust be set, and its value must match the username of the principal. For example, when Alice assumes the role, the value can be set toaliceoralice@exampledomain.com.
Step 1: Configure the role trust policy for prod-role
This policy ensures that only Alice and Bob can assume this role, and the request must contain a SourceIdentity value that starts with alice or bob.
{
"Statement": [
{
"Action": [
"sts:AssumeRole",
"sts:SetSourceIdentity"
],
"Condition": {
"StringLike": {
"sts:SourceIdentity": [
"alice*",
"bob*"
]
}
},
"Effect": "Allow",
"Principal": {
"RAM": [
"acs:ram::ACCOUNT_ID:user/alice",
"acs:ram::ACCOUNT_ID:user/bob"
]
}
}
],
"Version": "1"
}Step 2: Configure identity-based access policies for Alice and Bob
The following policies grant Alice and Bob the permission to assume prod-role and require them to set a SourceIdentity value that matches their respective usernames in the request.
Alice's identity-based access policy
{ "Version": "1", "Statement": [ { "Effect": "Allow", "Action": [ "sts:AssumeRole", "sts:SetSourceIdentity" ], "Resource": "acs:ram::ACCOUNT_ID:role/prod-role", "Condition": { "StringLike": { "sts:SourceIdentity": [ "alice*" ] } } } ] }Bob's identity-based access policy
{ "Version": "1", "Statement": [ { "Effect": "Allow", "Action": [ "sts:AssumeRole", "sts:SetSourceIdentity" ], "Resource": "acs:ram::ACCOUNT_ID:role/prod-role", "Condition": { "StringLike": { "sts:SourceIdentity": [ "bob*" ] } } } ] }
Condition control example for a role-based SSO scenario
Assume that the dev-role role can only be assumed through SAML role-based SSO and is limited to users with the employee IDs employeeid-alice and employeeid-bob. The IdP adds the user's employee ID to the SAML assertion as the SourceIdentity value.
The trust policy for dev-role is configured as follows:
{
"Statement": [
{
"Action": [
"sts:AssumeRole",
"sts:SetSourceIdentity"
],
"Condition": {
"StringEquals": {
"saml:recipient": [
"https://signin.aliyun.com/saml-role/sso"
],
"sts:SourceIdentity": [
"employeeid-alice",
"employeeid-bob"
]
}
},
"Effect": "Allow",
"Principal": {
"Federated": [
"acs:ram::ACCOUNT_ID:saml-provider/PROVIDER_NAME"
]
}
}
],
"Version": "1"
}Recommendations for using condition control
Test before going live: Do not directly enable mandatory policies for
SourceIdentityin a production environment. This includes identity-based access policies and role trust policies that have thests:SourceIdentitycondition key configured. First, use a test role and policy to perform a full verification. After you confirm that the configuration is correct, you can gradually apply the policies to the production environment.Communicate in advance: Before you enable a mandatory policy, inform the relevant users about how to use
SourceIdentityand what values are allowed. This helps prevent disruptions to normal business operations.
Role chain example
Scenario description
A Continuous Integration/Continuous Deployment (CI/CD) automation tool, such as Jenkins, runs using the RAM role automation-role. This role can be assumed by developers, such as Alice and Bob.
A developer, such as Alice, uses the tool to deploy an application to an OSS bucket in the production environment. The deployment operation requires assuming a higher-privilege role, deploy-role, which has write permissions on the OSS bucket.
Alice, Bob, and automation-role belong to Alibaba Cloud account A. deploy-role belongs to Alibaba Cloud account B.
Business requirements and workflow
automation-role can successfully assume deploy-role only when the original caller is Alice. Call requests from other users, such as Bob, should be rejected.
The workflow is as follows:
Alice calls the
AssumeRoleoperation to assumeautomation-roleand setsSourceIdentitytoalicein the request.After
automation-roleobtains an STS token, it calls theAssumeRoleoperation again to assumedeploy-role. TheSourceIdentityvalue is automatically passed.The trust policy of
deploy-rolechecks whether the incomingSourceIdentityisalice. If the verification is successful, the role assumption is allowed.
Policy configuration steps
Step 1: Modify the trust policy of deploy-role
This policy trusts only role assumption requests from the automation-role role in account A and requires that the SourceIdentity value must be alice.
{
"Statement": [
{
"Action": [
"sts:AssumeRole",
"sts:SetSourceIdentity"
],
"Condition": {
"StringEquals": {
"acs:SourceIdentity": [
"alice"
]
}
},
"Effect": "Allow",
"Principal": {
"RAM": [
"acs:ram::ACCOUNT_A_ID:role/automation-role"
]
}
}
],
"Version": "1"
}In the preceding role trust policy, the condition key acs:SourceIdentity is used instead of sts:SourceIdentity. This ensures that the deploy-role role accepts access requests only from the automation-role role and only when the SourceIdentity in the role session is set to alice.
Step 2: Modify the access policy and trust policy of automation-role
Access policy: Allows the
automation-rolerole to assume thedeploy-rolerole in account B.{ "Version": "1", "Statement": [ { "Effect": "Allow", "Action": [ "sts:AssumeRole", "sts:SetSourceIdentity" ], "Resource": "acs:ram::ACCOUNT_B_ID:role/deploy-role" } ] }Trust policy: Allows Alice and Bob to assume
automation-role.{ "Statement": [ { "Action": [ "sts:AssumeRole", "sts:SetSourceIdentity" ], "Effect": "Allow", "Principal": { "RAM": [ "acs:ram::ACCOUNT_A_ID:user/alice", "acs:ram::ACCOUNT_A_ID:user/bob" ] } } ], "Version": "1" }
Step 3: Modify the identity-based access policies for Alice and Bob
Allow them to assume the automation-role role and require them to set a SourceIdentity value that exactly matches their username.
Alice's identity-based access policy
{ "Version": "1", "Statement": [ { "Effect": "Allow", "Action": [ "sts:AssumeRole", "sts:SetSourceIdentity" ], "Resource": "acs:ram::ACCOUNT_A_ID:role/automation-role", "Condition": { "StringEquals": { "sts:SourceIdentity": [ "alice" ] } } } ] }Bob's identity-based access policy
{ "Version": "1", "Statement": [ { "Effect": "Allow", "Action": [ "sts:AssumeRole", "sts:SetSourceIdentity" ], "Resource": "acs:ram::ACCOUNT_A_ID:role/automation-role", "Condition": { "StringEquals": { "sts:SourceIdentity": [ "bob" ] } } } ] }
View SourceIdentity in ActionTrail
You can find the SourceIdentity field in the audit logs of ActionTrail for identity traceability.
In
AssumeRole*event logs:SourceIdentityappears in theresponseElementsandrequestParametersfields.{ "eventId": "9BCD28D0-7FDB-5BF2-9302-CDA6CCC5****", "eventVersion": 1, "responseElements": { "SourceIdentity": "alice", "RequestId": "9BCD28D0-7FDB-5BF2-9302-CDA6CCC5****", ... }, ... "requestParameters": { "SourceIdentity": "alice", "X-Acs-Request-Id": "9BCD28D0-7FDB-5BF2-9302-CDA6CCC5****", ... }, "serviceName": "Sts", "eventName": "AssumeRole", ... }
In event logs for accessing cloud resources:
SourceIdentityappears in theuserIdentity.sessionContextfield.{ "eventId": "46B5B0A1-19F7-5A56-BE2C-0BCFE5F8****", "userIdentity": { "sessionContext": { "sourceIdentity": "alice", ... }, "type": "assumed-role", ... }, "serviceName": "Ecs", "eventName": "DescribeInstances", ... }
Common troubleshooting
The most common issue when configuring SourceIdentity is insufficient permissions. The following sections describe two typical error scenarios and their troubleshooting methods.
Scenario 1: Issues caused by an identity-based access policy
Error message:
{
"RequestId": "AC9DDEC1-3E1F-50B8-A2D1-BAA155FD****",
"Code": "NoPermission",
"Message": "You are not authorized to do this action. You should be authorized by RAM.",
"AccessDeniedDetail": {
"PolicyType": "AccountLevelIdentityBasedPolicy",
"AuthAction": "sts:SetSourceIdentity",
...
}
}Cause analysis:
"PolicyType": "AccountLevelIdentityBasedPolicy"indicates that the error is caused by the caller's identity-based access policy."AuthAction": "sts:SetSourceIdentity"indicates that the permission for thests:SetSourceIdentityoperation is missing.
Solution: Contact an administrator to check the caller's identity-based access policy and ensure the following:
The policy includes
"Action": "sts:SetSourceIdentity".The
Resourcescope of the policy includes the target role that you are trying to assume.If the policy contains a
Conditionblock, confirm that theSourceIdentityvalue in the request meets the conditions.
Scenario 2: Issues caused by a role trust policy
Error message:
{
"RequestId": "ECC91EE1-0EB0-5E79-B3F5-E54FD8B9****",
"Code": "NoPermission",
"Message": "You are not authorized to do this action. You should be authorized by RAM.",
"AccessDeniedDetail": {
"PolicyType": "AssumeRolePolicy",
"AuthAction": "sts:SetSourceIdentity",
...
}
}Cause analysis:
"PolicyType": "AssumeRolePolicy"indicates that the error is caused by the target role's role trust policy."AuthAction": "sts:SetSourceIdentity"indicates that the target role does not trust thests:SetSourceIdentityoperation.
Solution: Contact an administrator to check the target role's role trust policy and ensure the following:
The policy includes
"Action": "sts:SetSourceIdentity".If the policy contains a
Conditionblock, confirm that theSourceIdentityvalue in the request meets the conditions.
General troubleshooting recommendations
Narrow the scope: If you encounter a permission issue when setting
SourceIdentity, first try to remove theSourceIdentityparameter and assume the role again. If the operation succeeds, the issue is likely related to the permission configuration forSourceIdentity.Analyze the error: Carefully read the
AccessDeniedDetailsection of the error message, especially thePolicyTypefield. This can help you quickly determine whether the issue is caused by an identity-based access policy or a role trust policy.Use a diagnostic tool: If you only have the
RequestId, use the OpenAPI Troubleshoot tool. Enter theRequestId, and the system returns detailed diagnostic information to help you locate the permission issue. For example: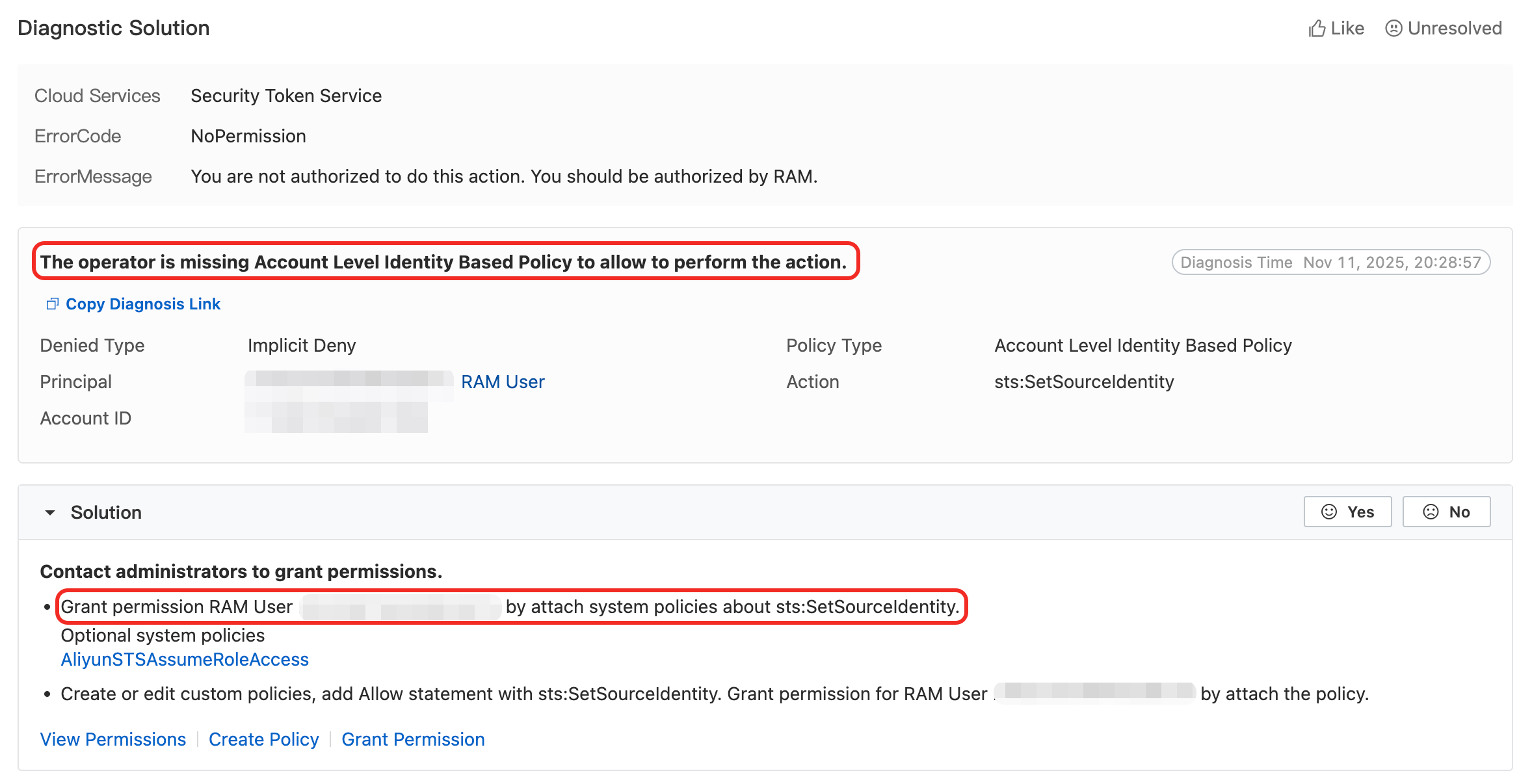
Compare the policy and the request: After you locate the specific policy, carefully check the settings for
ResourceandCondition. Ensure that they match the parameters in the API request, such as the target role'sARNand theSourceIdentityvalue.
For more information about how to troubleshoot permission issues, see How to troubleshoot access errors due to insufficient permissions.