This topic describes how to create an API data source.
Prerequisites
You have created an API interface.
Limits
The API data source feature is not supported in the international site (alibabacloud.com).
Only the Professional Edition supports creating API data sources.
When the connection method of the API data source is direct connection mode, the data volume returned by each request must meet the following conditions: no more than 10 MB, no more than 100 columns, and no more than 1,000 rows.
Feature Entry
You can access the API data source creation page through either of the following methods.
Go to the data source creation page from the data source creation entry, and select API data source.

You can also Add API Data Source on the API data source management interface.

Procedure
Creating a new API data source mainly involves three steps: establishing API connection, parsing request results, and data synchronization settings.
Step 1: Establish API Connection
In this step, you need to configure the basic authentication information, connection method, and parameter settings for the API connection. The specific instructions are as follows.
Configure the information for each item under Basic Authentication.

Parameter name
Description
Connection Name
The custom name of the API interface displayed in the Quick BI data source list.
The name can consist of Chinese characters, numbers, letters, underscores (_), or hyphens (-).
Interface Address
Enter the request address of the API interface.
Request Type
Select the request type of the API interface. Two types are supported: GET and POST. The default is GET.
GET: Typically used to request resources on the server. It is a data retrieval behavior and cannot modify data on the server.
POST: Typically used to transmit data to the server, such as submitting forms. It can modify data on the server.
Select the Connection method. You can choose either Extract or Direct connection.

Extract: Supports manual or periodic scheduled data updates. It is suitable for scenarios with low real-time data requirements.
Direct connection: Supports direct connection to the API for real-time data updates. It is suitable for small data volume scenarios with high real-time requirements.
The direct connection method supports enabling Short-term cache, with cache time options of 5 minutes, 10 minutes, or 30 minutes. After enabling, it can avoid repeated requests within a certain period, protecting the source API service's access performance and saving API service call costs.
NoteIn direct connection mode, the data volume returned by each request must meet the following conditions: no more than 10 MB, no more than 100 columns, and no more than 1,000 rows.

(Optional) Configure the data that needs to be passed as parameters in Parameter settings. You can decide whether to configure this based on your needs.
Parameter name
Description
Common Parameters
Parameters after the request address are common parameters, in the format
url?key1=value1&key2=value2.You can click Add Parameter to pass parameters through common parameters. For example, for API interfaces with large data volumes, you can request through pagination by providing a dynamic parameter
${PageIndex}. For detailed information about parameters, see Parameter Introduction.
For detailed information about parameters, see Parameter Introduction.Header Parameters
Parameters stored in the Header are header parameters.
Typically, constant values are passed through the Header. You can manually add (①), delete (②), and modify (③) Header parameters.

For detailed information about parameters, see Parameter Introduction.
Request Body
When the Request type in Basic Authentication is POST, you can maintain request body information in the parameter settings.
The request body is typically used to carry data that the user needs to send to the server. You need to write its specific content and format according to the field content of the current API.
Quick BI supports two request body formats: JSON and x-www-form-urlencoded.

JSON: Processes complex data structures, suitable for scenarios where data includes nested objects or arrays.
x-www-form-urlencoded: Processes simple key-value pair data, suitable for simple form submission scenarios.
Authorization Verification
You can choose no authorization verification, or select Basic Authentication or Digest Authentication.
For specific information, see HTTP authentication 01 basic authentication and digest authentication.
Pre-request
If you need to perform some preparation work or verification steps before requesting the API, for example, if you need to obtain a Token through an authentication interface to successfully call the current API, you can set a pre-request for the current API.
After setting, the system will execute the added "pre-requests" in sequence before calling the main API. At the same time, it supports storing the response results of this request as dynamic parameters, which can be referenced in the main API's header parameters, common parameters, request body, or other pre-requests to achieve dynamic parameter acquisition.
For examples of using pre-requests, see Operation Example.
NoteA maximum of 3 pre-requests are supported.

Click Test connection, and after success, proceed to the Next step.

Step 2: Parse Request Results
In the Data structure area under the Parse request results section, all fields returned by the current API request will be displayed. You can select fields as needed and modify their field types.
In extract mode, only selected parameters will be synchronized to the Quick BI system.
When selecting fields, they must be at the same level, otherwise parsing will fail.
You can view the values of selected fields in the Data preview area.

Step 3: Data Synchronization Settings
In the Data synchronization settings section, set the update cycle for the API data source.
Click the Update cycle selection box, and in the dropdown list, select the update cycle for the API data source. You can choose manual update or scheduled update.
NoteThe update cycle only needs to be configured when the connection method in the connection settings is extract.

Select Manual update, and data synchronization will only occur when manually triggered.
Select Scheduled update and configure the update frequency (daily or hourly), and data synchronization will occur at the scheduled time each day.
Click Finish to create the API data source. After success, you can see the data source you created in the API data source management interface.
You can edit the API data source by clicking the
 icon to the right of the API data source.Note
icon to the right of the API data source.NoteThe connection method cannot be edited.

Parameter Introduction
Quick BI supports customizing parameters in the form of key-value pairs in common parameters and header parameters according to actual API call requirements, to help with the successful integration of API data sources. The introduction to parameters is as follows.
Fixed parameters: Parameters with fixed values are fixed parameters, in the format
KeyA = ValueA, for example:user=myname.Variable parameters: Parameters with dynamically changing values are variable parameters, in the format
KeyA = ${ValueA}, for example:mydate=${bizdate}.Quick BI has built-in rich variable parameters, including system variables, system functions and other dynamic parameters, which provide accurate and standardized parameter writing methods while allowing you to quickly apply variable parameters. For specific information about built-in variable parameters, see Built-in Variable Parameters below.
Built-in Variable Parameters
You can click the  icon to the right of the parameter value input box to select built-in parameters from the variable panel that appears.
icon to the right of the parameter value input box to select built-in parameters from the variable panel that appears.
System Variables
Currently, the system variables provided by Quick BI include date-type variables and pagination-type variables. Their effective range includes: interface address, common parameters, header parameters, request body, and pre-request.
Date-type variables
Date-type system variables consist of two parts: basic date parameters and time interval offset:
Date dynamic parameters: Provide offsets based on the business date.
{yyyyMMdd}is the business date, which is the day before the current data update date, i.e., T-1.
Hour parameter offset: Provides offset based on hours.
HHrepresents hoursmmrepresents minutesssrepresents secondsHour offset:
delta/24
For example, the expression for 1 hour before the specified business time is:
${HH-1/24}.Minute parameter offset: Provides offset based on minutes.
HHrepresents hoursmmrepresents minutesssrepresents secondsMinute offset:
delta/24/60
For example, 1 minute before the business date:
${HHmmss-1/24/60}.Seconds are not currently supported.
System variable
Variable description
Current date
Actual value
${yyyyMMdd}
The day before the current data update date, i.e., T-1.
2022-01-10
20220109
${yyyy-MM-dd}
The day before the current data update date, i.e., T-1.
2022-01-10
2022-01-09
${yyyy-MM}
Extract the year and month part of the current update date.
2022-01-10
2022-01
${yyyy}
Extract the year part of the current update date.
2022-01-10
2022
${yyyy/MM/dd HH:mm:ss}
Extract the current update date and convert it to yyyy/MM/dd HH:mm:ss format.
2022-01-10
2022/01/09 00:00:00
${HH}
Extract the hour part of the current update date.
2022-01-10
00
${timestamp}
Extract the timestamp of the current request, in seconds
1725936000
2024-11-11 00:00:00
Pagination-type variables
In extract mode, API data sources support Pagination Requests.
NoteBy default, a maximum of 1,000 records per page and a maximum of 100 pages are supported.
When a single page returns more than 1,000 records, the current synchronization task will report an error and exit.
Both GET and POST requests are supported. Request examples are as follows.

System variable
Variable description
Example
${PageIndex}
Indicates that the marked parameter is the starting page number for pagination, defaulting to 1.
${PageIndex} starts retrieving data from page 1 by default.
${PageIndex:num}
Indicates that the marked parameter is the starting page number for pagination, with the starting page number specified as num.
${PageIndex:2} will start retrieving data from page 2.
System Functions
System functions effective range: interface address, common parameters, header parameters, request body, pre-request.
System function | Function description | Example |
BI_MD5(String data) | Returns the result after MD5 encryption | b10a8db164e0754105b7a99be72e3fe5 |
Dynamic parameters
The Dynamic parameters tab only displays dynamic parameters that have been created in Pre-request. Dynamic parameters effective range: interface address, common parameters, header parameters, request body, pre-request.
Operation Example
The following example demonstrates creating an API data source using the Get DingTalk user attendance data API, to help you better understand and get started with the API data source creation operation.
This example follows the three steps described in the Procedure section of this topic: establishing API connection, parsing request results, and data synchronization settings.
Step 1: Establish API Connection
In the establish API connection phase, configure the information according to the following steps.
Configure Basic Authentication information.

Connection name: In this example, we use the business meaning of the API interface as the name, entering Get User Attendance Data.
Interface address: Obtain the request address from the API documentation page.
Request type: Obtain the request type from the API documentation page. In this example, it is POST.
Configure the Connection method.
In this example, we only need to obtain attendance data for the current day, with low real-time requirements, so the connection method is set to Extract.

Configure Pre-request.
Before calling the Get User Attendance Data interface (hereinafter referred to as the main API interface), you need to obtain an
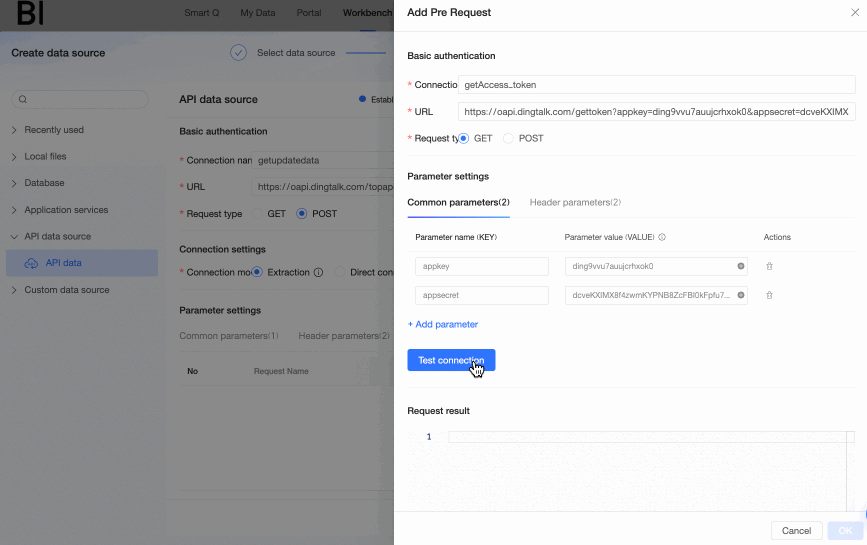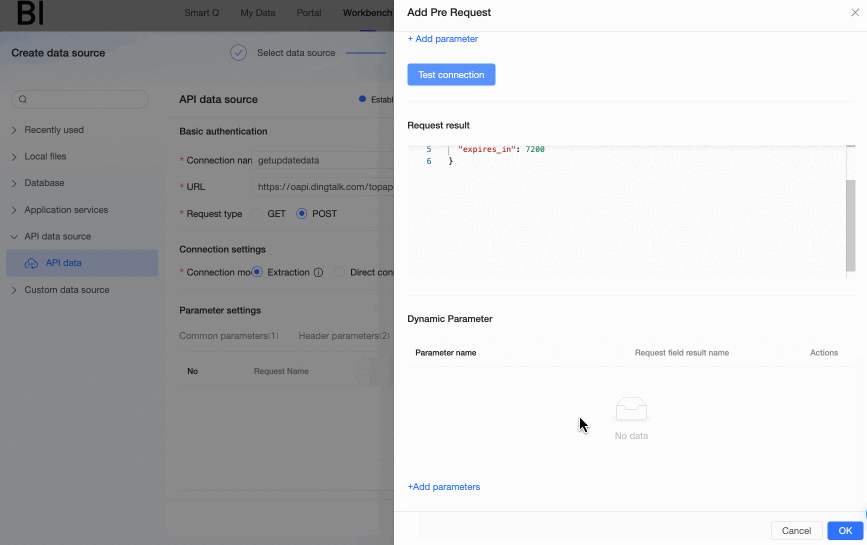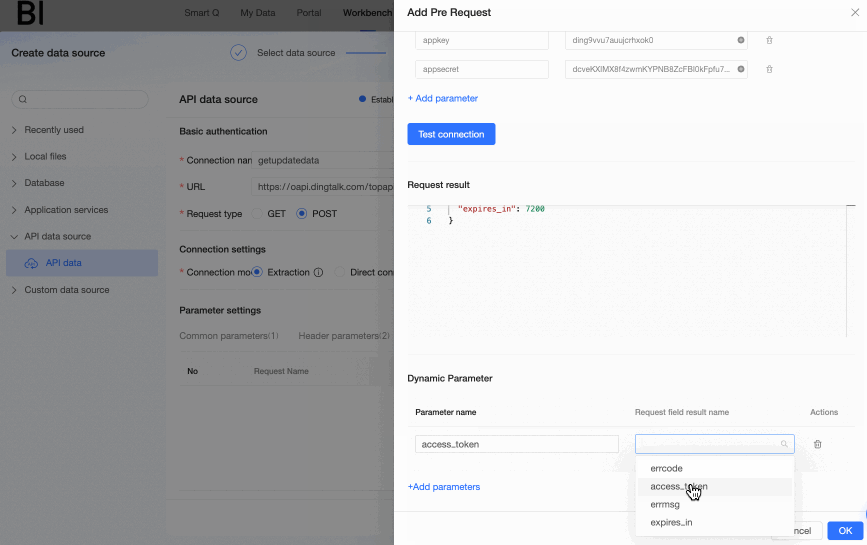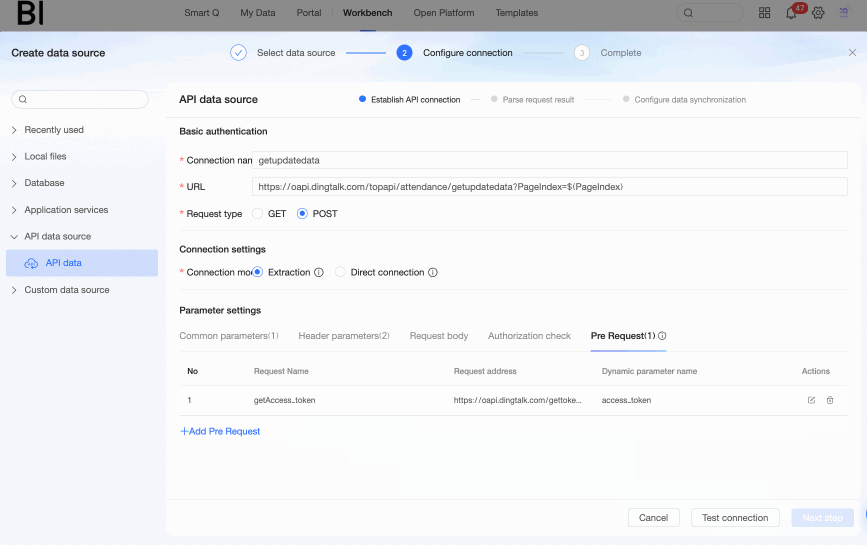
access_tokenthrough the Get enterprise internal application access_token interface and inject it into the request address of the main API interface to successfully call the main API interface to obtain attendance data. Therefore, in this example, we need to configure the step of obtaining theaccess_tokenin the pre-request and use it as a common parameter to append to the request address of the main API interface. The specific pre-request configuration operations are as follows.Click Add pre-request under the Pre-request tab.

In the Add pre-request dialog box, complete the following configuration.

Connection name: In this example, we enter the business meaning of the authentication interface, which is Get enterprise internal application access_token.
Interface address: Obtain the request address of the authentication interface through the interface documentation.
Request type: Obtain the request type of the authentication interface through the interface documentation. In this example, it is GET.
Common parameters: According to the interface documentation, the request address needs to carry
appkeyandappsecretparameters, so add appkey and appsecret in the common parameters and enter the corresponding values. After completion, the parameters will be automatically appended to the request address.Header parameters: In this example, we keep the default settings, i.e., select
Content-Typeasapplication/jsonto tell the server receiving the request that the data transmission format is JSON;Connectionaskeep-aliveto tell the server receiving the request that the current request requires a persistent connection.
Click Test connection, and you can view the return information of the current request in the Request result module. At the same time, Quick BI will automatically parse the fields contained in the request result for you. You can select fields as needed in the Dynamic parameters module to use as dynamic parameters, and reference them in the main API through the
${parameter name}method; or you can execute the pre-request without passing dynamic parameters (i.e., not setting dynamic parameters).In this example, we need to pass the
access_tokenobtained in the pre-request as a dynamic parameter to the main API, so we create the access_token dynamic parameter.NoteA maximum of 10 dynamic parameters can be added.
Configure Common parameters.
In this example, according to the main API call requirements, we need to reference the dynamic parameter access_token created in the pre-request to the common parameters of the main API through the
${parameter name}method, so click Add parameter under the Common parameters tab.NoteDynamic parameters can be referenced to the common parameters, header parameters, request body of the main API, or other pre-requests. You can choose as needed in actual operations.

Enter the parameter name, click the
 icon in the parameter value input box, select parameters as needed from the variable panel that appears, and then click the
icon in the parameter value input box, select parameters as needed from the variable panel that appears, and then click the  icon to save the configuration.
icon to save the configuration.In this example, we need to switch the variable panel to the Dynamic parameters tab, which displays the dynamic parameters already created in the current flow, and select
${access_token}.
Configure the Request body.
In this example, the request type is POST, so we need to write the request body according to the field content of the Get enterprise internal application access_token API's request parameters.
JSON format example code is as follows:
{ "work_date": "2024-11-14", "userid": "user01" }x-www-form-urlencoded format example code is as follows:
work_date=2024-11-14&userid=user01
Other parameter configurations.
In this example, header parameters and authorization verification maintain the default settings.
Click Test connection, and after success, proceed to the Next step.
Step 2: Parse Request Results
In the Parse request results section, select the required fields and adjust their field types, then click Next step.
Step 3: Data Synchronization Settings
In the data synchronization settings section, set the update cycle of this example's API data source to Manual update.

Click Finish to successfully create the Get User Attendance Data API data source.
