A global database network (GDN) is a network of multiple PolarDB clusters that are deployed in different regions. This topic describes how to view the cluster endpoints of a GDN and connect to it.
Read/write splitting and request routing
The routing of read and write requests to clusters in a GDN is determined by the database proxy configuration of each cluster. Your application does not require code changes. Simply connect to the endpoint of the appropriate cluster, and requests are automatically routed based on the following logic:
Write requests, such as
INSERT,UPDATE, andDELETEstatements, other broadcast syntax such asSETstatements, and all requests within transactions are automatically forwarded to the primary node of the primary cluster for processing.Read requests are routed by default to the read-only nodes of the local secondary cluster for nearest access. If session consistency is enabled, some read requests may also be routed to the primary node of the primary cluster to ensure data consistency.
GDN also provides a global domain name. This feature not only enables nearest access but also ensures the domain name remains unchanged after a primary cluster switchover.
Only cluster endpoints or custom endpoints with the Read/Write Mode set to Read/Write (Automatic Read/Write Splitting) support the read/write splitting service of a GDN.
The Primary Endpoint and custom endpoints with the Read/Write Mode set to Read-only do not support the read/write splitting service of a GDN.
To reduce the potential impact of replication delay between the primary and secondary clusters on your business, we recommend that when you configure a custom cluster endpoint on a secondary cluster, set Primary Node Accepts Read Requests to No and set Consistency Level to Eventual Consistency (Weak).
If your business scenario cannot tolerate latency in a secondary cluster, connect directly to the primary cluster's endpoint.
View cluster endpoints
Log on to the PolarDB console and click Global Database Network (GDN) in the navigation pane on the left.
On the Global Database Network (GDN) page, find the target GDN and click its Global Database Network ID to open the details page.
In the Clusters section, find the target secondary cluster and click View in the Cluster Endpoint column. You can view the details of the cluster endpoint in the dialog box that appears.
 Note
NoteYou can view only the endpoint information of the default cluster, which includes the Private and Public endpoints.
To view more endpoint details, click Visit the Overview page of the cluster. You are redirected to the details page of the target cluster, where you can view more endpoints in the Database Connections section.
Connect to a global database cluster
Applications in different regions can connect to a GDN using the nearest cluster endpoint. The GDN automatically performs read/write splitting. You can connect to a database cluster in several ways. The following sections provide examples of different connection methods.
Use DMS to connect to a cluster
DMS is a visualized data management service provided by Alibaba Cloud. DMS provides various management services such as data management, schema management, access control, security audit, business intelligence (BI) charts, data trends, data tracking, performance optimization, and server management. You can manage your PolarDB clusters in DMS without the need to use other tools.
Log on to the PolarDB console. Click Clusters in the left-side navigation pane. Select a region in the upper-left corner and click the ID of the cluster in the list to go to the Basic Information page. In the upper-right corner of the page, click Log on to Database.

In the dialog box that appears, enter the Database Account and Database Password that you created for the PolarDB for MySQL cluster, and click Login.

After you log on to the PolarDB for MySQL cluster, click Instances Connected in the left-side navigation pane to view and manage the PolarDB for MySQL cluster.

Use a client to connect to a cluster
You can use a MySQL client to connect to a PolarDB cluster. MySQL Workbench 8.0.29 is used in this example. The operations by using other types of clients are similar.
Install MySQL Workbench. For more information, visit the MySQL Workbench download page.
Start MySQL Workbench and choose .
Enter the connection information and click OK.
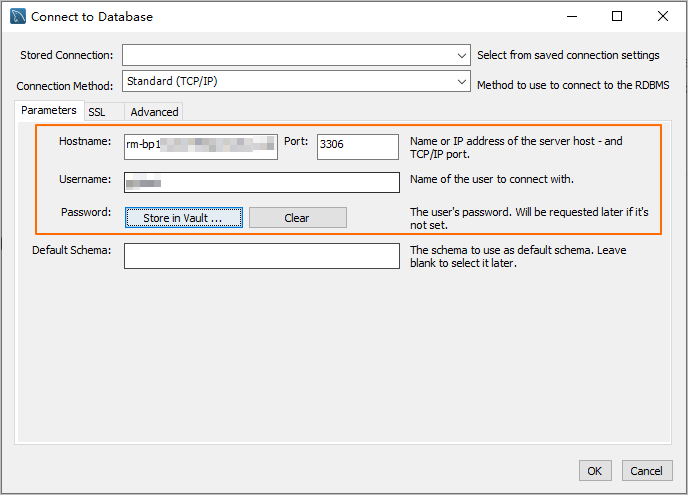
Parameter
Description
Example
Hostname
The database endpoint. For more information, see Database connection.
pc-2***.rwlb.rds.aliyuncs.com
Port
The port number that corresponds to the database endpoint.
NoteThe default port number is 3306.
3306
Username
The database account. For more information, see Create a database account.
polardb_mysql_user
Password
The password of the database account.
Pass***233
Use the CLI to connect to a cluster
If MySQL client is installed on your server, you can run commands in the CLI to connect to a PolarDB for MySQL cluster.
Syntax:
mysql -h <Endpoint> -P <Port> -u <Account> -p <Password>Example:
mysql -h pc-2***.rwlb.rds.aliyuncs.com -P3306 -upolardb_mysql_user -pPass***233Parameter | Description | Example |
-h | The database endpoint. For more information, see Database connection. | pc-2***.rwlb.rds.aliyuncs.com |
-P | The port number that corresponds to the database endpoint. Note
| 3306 |
-u | The database account. For more information, see Create a database account. | polardb_mysql_user |
-p | The password of the database account. Note This parameter is required.
| Pass***233 |
Use an application to connect to a cluster
Connecting to a PolarDB for MySQL cluster is similar to connecting to regular MySQL databases. You only need to replace the endpoint, port, account, and password of the database. The following examples show how to use applications to access a PolarDB database in some development languages:
Java
In this example, a Maven project is used to connect to the PolarDB for MySQL cluster by using the MySQL JDBC driver.
First, add the dependency of the MySQL JDBC driver to the pom.xml file. Sample code:
<dependency> <groupId>mysql</groupId> <artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId> <version>8.0.27</version> </dependency>Connect to the cluster. Replace the
<HOST>, port number,<USER>,<PASSWORD>,<DATABASE>,<YOUR_TABLE_NAME>, and<YOUR_TABLE_COLUMN_NAME>with the information of your database.import java.sql.Connection; import java.sql.DriverManager; import java.sql.ResultSet; import java.sql.Statement; public class DatabaseConnection { public DatabaseConnection() { } public static void main(String[] args) { // The endpoint, port, and database name of the PolarDB cluster to be connected. String url = "jdbc:mysql://<HOST>:3306/<DATABASE>?useSSL=false&serverTimezone=UTC"; // The database account. String user = "<USER>"; // The password of the database account. String password = "<PASSWORD>"; try { Class.forName("com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver"); Connection conn = DriverManager.getConnection(url, user, password); Statement stmt = conn.createStatement(); // The name of the data table to be queried. ResultSet rs = stmt.executeQuery("SELECT * FROM `<YOUR_TABLE_NAME>`"); while(rs.next()) { // The column name of the data table to be queried. System.out.println(rs.getString("<YOUR_TABLE_COLUMN_NAME>")); } rs.close(); stmt.close(); conn.close(); } catch (Exception var7) { var7.printStackTrace(); } } }
Python
In this example, Python3 is used to connect to the PolarDB for MySQL cluster by using the PyMySQL library.
First, install the PyMySQL library. You can run the following command to install it:
pip3 install PyMySQLConnect to the cluster. Replace the
<HOST>, port number,<USER>,<PASSWORD>,<DATABASE>, and<YOUR_TABLE_NAME>with the information of your database.import pymysql # The database connection parameters. host = '<HOST>' # The endpoint of the PolarDB cluster. port = 3306 # The default port 3306 user = '<USER>' # The database account. password = '<PASSWORD>' # The password of the database account. database = '<DATABASE>' # The name of the database to be connected. try: # Establish a database connection. connection = pymysql.connect( host=host, port=port, user=user, passwd=password, db=database ) # Obtain the cursor. with connection.cursor() as cursor: # Execute an SQL query. sql = "SELECT * FROM '<YOUR_TABLE_NAME>'" # The name of the table to be queried. cursor.execute(sql) # Obtain the query result. results = cursor.fetchall() for row in results: print(row) finally: # Close the database connection. if 'connection' in locals() and connection.open: connection.close()
Go
In this example, go1.23.0 is used to connect to the PolarDB for MySQL cluster by using the database/sql package and go-sql-driver/mysql driver.
First, install the
go-sql-driver/mysqldriver. You can run the following command to install the driver:go get -u github.com/go-sql-driver/mysqlConnect to the cluster. Replace the
<HOST>, port number,<USER>,<PASSWORD>,<DATABASE>, and<YOUR_TABLE_NAME>with the information of your database.package main import ( "database/sql" "fmt" "log" _ "github.com/go-sql-driver/mysql" ) func main() { // Database connection parameters. dbHost := "<HOST>" // The endpoint of the PolarDB cluster. dbPort := "3306" // The default port 3306. dbUser := "<USER>" // The database account. dbPass := "<PASSWORD>" // The password of the database account. dbName := "<DATABASE>" // The name of the database to be connected. // Build DSN (Data Source Name) dsn := fmt.Sprintf("%s:%s@tcp(%s:%s)/%s?charset=utf8mb4&parseTime=True&loc=Local", dbUser, dbPass, dbHost, dbPort, dbName) // Create a database connection. db, err := sql.Open("mysql", dsn) if err != nil { log.Fatalf("Failed to connect to database: %v", err) } defer db.Close() // Test the connection. err = db.Ping() if err != nil { log.Fatalf("Failed to ping database: %v", err) } // Create a cursor. var result string err = db.QueryRow("SELECT VERSION()").Scan(&result) if err != nil { log.Fatalf("Failed to execute query: %v", err) } // Print the database version. fmt.Printf("Connected to database, version: %s\n", result) // Execute an SQL query. rows, err := db.Query("SELECT * FROM '<YOUR_TABLE_NAME>'") // The name of the data table that is queried. if err != nil { log.Fatalf("Failed to execute query: %v", err) } defer rows.Close()
References
Global Database Network (GDN): Learn about GDN, its service architecture, and common scenarios.
Create a global domain name: Learn how to create a unified connection address that enables nearest access and ensures the domain name remains unchanged after a primary cluster switch.
Related API operations
API | Description |
Queries the endpoint information of a PolarDB cluster. | |
Modifies the attributes of a PolarDB cluster endpoint, including the read/write mode, whether to automatically add new nodes to the endpoint, consistency level, transaction splitting, whether the primary node accepts read requests, and connection pool settings. |