This document describes how to use the open-source tool DataJuicer on DLC to process large-scale multimodal data.
Background
As artificial intelligence (AI) and large models continue to evolve, data quality has become a key factor limiting model accuracy and reliability. Building more robust models requires integrating data from multiple sources, increasing its diversity, and achieving effective fusion. This places higher demands on the unified processing and collaborative modeling of multimodal data, such as text, images, and videos. High-quality data pre-processing not only accelerates training efficiency and reduces computing overhead, but it is also the foundation for ensuring model performance. Currently, a core challenge in the development of large models is how to systematically collect, clean, augment, and synthesize large-scale data to ensure its accuracy, diversity, and representativeness.
DataJuicer is an open-source tool that specializes in processing large-scale multimodal data, such as text, images, audio, and video. It helps researchers and developers efficiently clean, filter, transform, and augment large-scale datasets. This process provides higher-quality, richer, and more digestible data for large language models (LLMs).
Against this background, Platform for AI (PAI) has introduced a new job type, DataJuicer on DLC, which provides users with out-of-the-box, high-performance, stable, and efficient data processing capabilities.
Features
DataJuicer on DLC is a data processing service jointly launched by Alibaba Cloud PAI and Tongyi Lab. It allows users to submit DataJuicer framework jobs on the cloud with a single click. This service enables efficient cleaning, filtering, transformation, and augmentation of large-scale data, providing the necessary computing power for LLM multimodal data processing.
Rich operators: DataJuicer provides over 100 core operators, including aggregators, duplicators, filters, formatters, groupers, mappers, and selectors. These operators cover the entire data processing lifecycle, from data loading and normalization to data editing, transformation, filtering, deduplication, and high-quality sample selection. You can flexibly orchestrate operator chains based on your business needs.
Superior performance: DataJuicer offers excellent linear scalability and fast data processing speeds. For multimodal data processing at the scale of tens of millions of samples, it saves 24.8% of processing time compared to native nodes.
Resource estimation: DataJuicer intelligently balances resource limits and operational efficiency. It automatically tunes the degree of parallelism for operators, significantly reducing job failures caused by out-of-memory (OOM) errors. It supports resource estimation by intelligently analyzing dataset, operator, and quota information to automatically estimate the optimal resource configuration. This feature lowers the barrier to entry and ensures efficient and stable job execution.
Large-scale processing: DataJuicer leverages the distributed computing framework of PAI DLC and deep hardware acceleration optimizations, such as CUDA and operator fusion. It supports efficient processing from experiments with thousands of samples to production data at the scale of tens of billions.
Automatic fault tolerance: PAI DLC provides fault tolerance and self-healing at the node, job, and container levels. DataJuicer also offers operator-level fault tolerance to mitigate the risk of interruptions caused by infrastructure failures, such as server or network issues.
Easy to use: DLC provides an intuitive user interface and easy-to-understand APIs. It is a fully managed service, requiring no deployment or O&M. You can submit DataJuicer jobs for AI data processing with a single click, without worrying about the complexity of deploying and maintaining the underlying infrastructure.
Usage instructions
1. Select an image and framework
The image for a DataJuicer job must have the DataJuicer environment pre-installed and include the dj-process command. You can use the official image from the data-juicer repository or a custom image based on the official one.
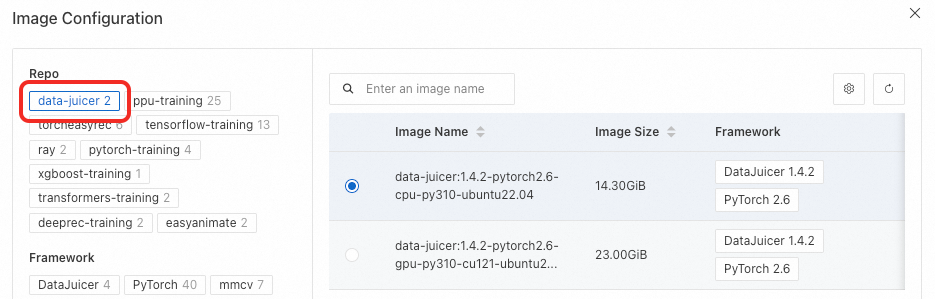
Set the Framework to DataJuicer.
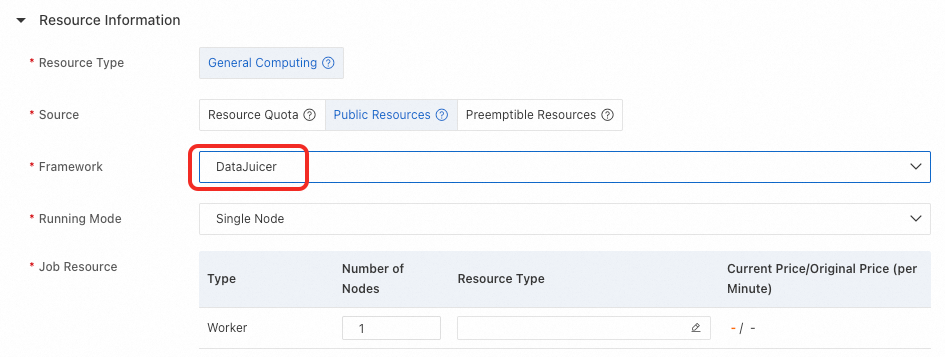
2. Configure the run mode
When you create a DLC job, you can choose between single-node and distributed run modes. Make sure the run mode matches the executor_type in the configuration file.
Single-node mode:
DataJuicer configuration file: In the configuration file, set
executor_typetodefaultor omit the field.DLC configuration:
Running Mode: Select Single Node.
Number of Nodes: Set to 1.
Distributed mode:
DataJuicer configuration file: In the configuration file, set
executor_typetoray.DLC configuration:
Running Mode: Select Distributed.
Resource Estimation: This option can be enabled only when you use a Resource Quota. When resource estimation is enabled, the system intelligently estimates the optimal resource configuration based on dataset, operator, and quota information, and then automatically runs the job. This process ensures the efficient execution of the DataJuicer data processing job. To impose a limit, you can set the maximum resource limit for the job.
Maximum Job Resource Limit: You can configure this option to set a maximum limit on the resources requested by the DataJuicer job. The total resources requested by the job will not exceed this configured limit. If you leave this field blank, the system automatically requests resources for data processing based on the resource estimation results.
Job Resources: If you do not enable resource estimation, you must manually enter the job resources.
Quantity: The number of Head nodes must be 1, and the number of Worker nodes must be at least 1.
Resource Type: The Head node requires more than 8 GB of memory. You can configure resources for Worker nodes as needed.
Fault Tolerance and Diagnosis (Optional): You can configure Head Node Fault Tolerance by selecting a Redis instance within the same Virtual Private Cloud.
3. Enter the startup command
DLC supports startup commands in Shell and YAML formats, with Shell as the default. If the command line format is Shell, the usage is the same as for other DLC jobs. If the command line is in YAML format, you can directly enter the DataJuicer configuration in the command line.

You can use DataJuicer by creating a configuration file. For more information, see Create a configuration file. For a complete configuration reference, see config_all.yaml. The following figure shows a sample DataJuicer configuration:
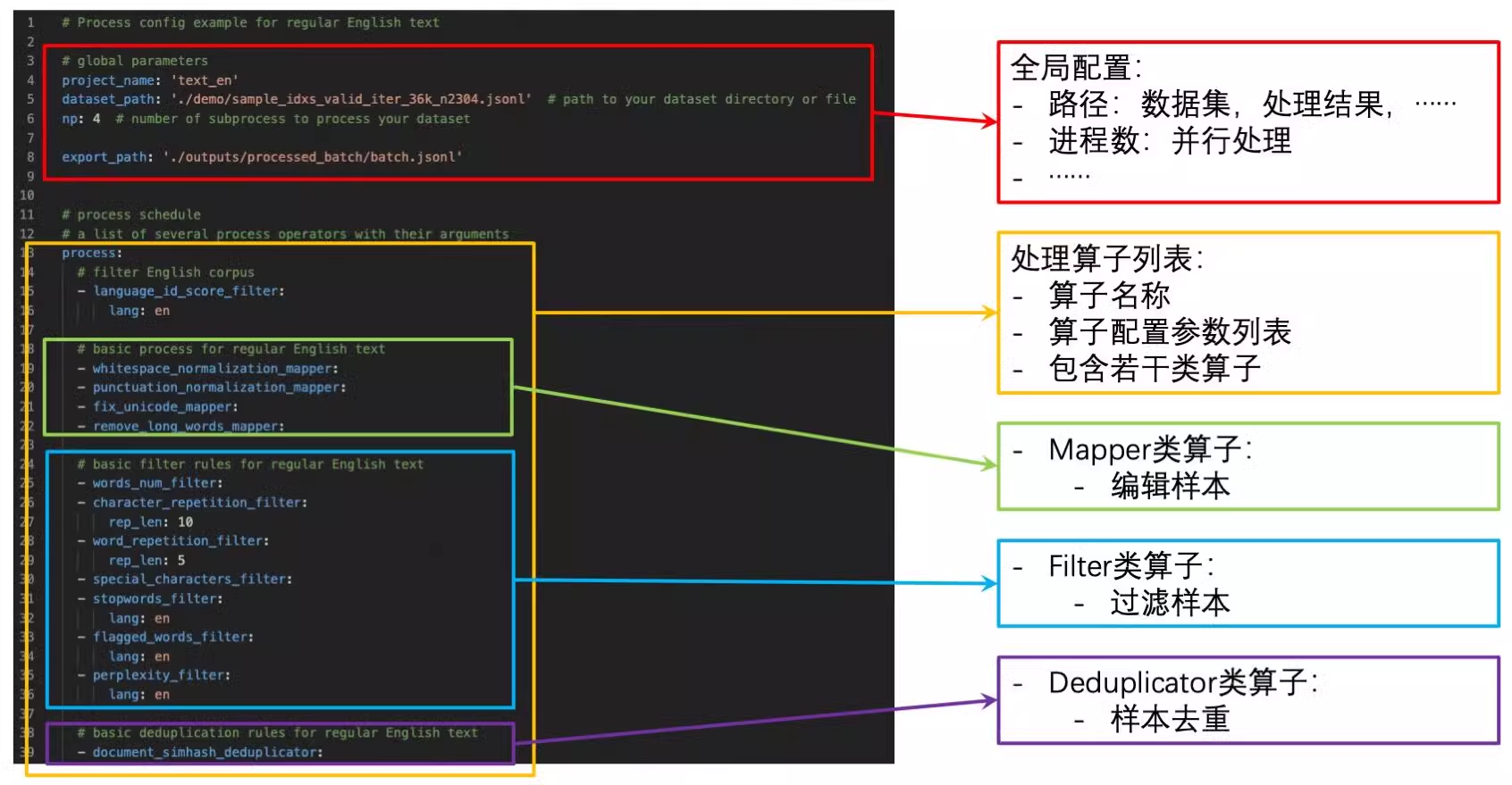
The key parameters are described as follows:
dataset_path: The path to the input data. In a DLC job, set this to the path where the data storage, such as Object Storage Service (OSS), is mounted inside the container.export_path: The output path for the processing results. For a distributed job, this path must be a folder, not a specific file.executor_type: The executor type.defaultindicates running on a single node usingDefaultExecutor.rayindicates usingRayExecutor. RayExecutor supports distributed processing. For more information, see Data-Juicer Distributed Data Processing.
The following are examples of how to configure the startup command on DLC:
Shell format example 1: Write the configuration to a temporary file and start the task using the
dj-processcommand.Shell format example 2: Save the configuration file in cloud storage, such as OSS. Mount the file to the DLC container. Run the task by specifying the mounted configuration file path in the
dj-processcommand.dj-process --config /mnt/data/process_on_ray/config/demo.yamlYAML format example: Enter the DataJuicer configuration directly in the command line.
Use case
Processing massive video data
With the breakthrough applications of multimodal large language models (MLLMs) in fields such as autonomous driving and embodied intelligence, the fine-grained processing of massive video data has become a key technological advantage for building core industry competitiveness. In autonomous driving scenarios, models must parse multi-dimensional information in real time from video streams that are continuously fed by in-vehicle cameras. This information includes complex road conditions, traffic signs, and pedestrian behavior. Embodied intelligence systems rely on video data to build dynamic representations of the physical world to complete high-level tasks, such as robot motion planning and environmental interaction. However, traditional data processing solutions face three core challenges:
Modality separation: Video data contains heterogeneous information from multiple sources, including visual, audio, time series, and text descriptions. This requires a toolchain for cross-modal feature fusion, but traditional pipeline-based tools struggle to perform global association analysis.
Quality bottlenecks: Data cleaning involves multiple stages, such as deduplication, annotation repair, keyframe extraction, and noise filtering. Traditional multi-stage processing can easily lead to information loss and redundant computation.
Engineering efficiency: Processing large-scale video data (terabytes or petabytes) places extremely high demands on distributed computing power scheduling and heterogeneous hardware adaptation. Self-built systems often have long development cycles and low resource utilization.
The PAI-DLC DataJuicer framework provides an end-to-end solution for these challenges. Its technical advantages include the following:
Multimodal collaborative processing engine: Built-in operators for text, images, video, and audio support joint cleaning and augmentation of visual, text, and time series data. This avoids the fragmented processing of traditional toolchains.
Cloud-native elastic architecture: Deeply integrates PAI's distributed storage acceleration of hundreds of GB/s and its GPU/CPU heterogeneous resource pooling capabilities. It supports automatic scaling for jobs with thousands of nodes.
Procedure
This use case uses the video processing flow required for autonomous driving and embodied intelligence as an example. It shows how to use DataJuicer to perform the following tasks:
Filter out video clips from the raw data that are too short.
Filter out dirty data based on the Not Safe For Work (NSFW) score.
Extract frames from the videos and generate text captions for them.
Prepare the data
Using the Youku-AliceMind dataset as an example, you can extract 2,000 video data entries and upload them to OSS.
Create a DLC job
Create a DLC job and configure the following key parameters. You can leave the other parameters at their default settings.
Image Configuration: Select Alibaba Cloud Image. Search for and select
data-juicer:1.4.3-pytorch2.6-gpu-py310-cu121-ubuntu22.04.Mount storage: Select OSS.
Uri: Select the OSS folder where the dataset is located.
Mount Path: The default is
/mnt/data/.
Startup Command: Select YAML and enter the following command:
Source: Select Public Resources.
Framework: Select DataJuicer.
Running Mode: Select Distributed.
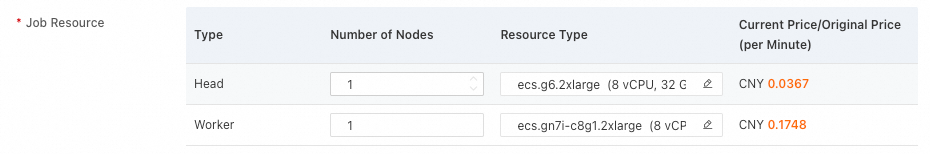
Job Resource: Configure the number of nodes and their specifications as shown in the following figure:
Click OK to create the job.