Integrate OpenSearch Vector Search Edition into your large language model (LLM) retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) service to improve answer accuracy and richness. OpenSearch supports various vector search algorithms with high performance, and provides a graphical user interface (GUI) for viewing index information and managing data.
Background information
Introduction to EAS
Elastic Algorithm Service (EAS) is a platform for online model services within Platform for AI (PAI). It supports deploying models as online inference services and AI-Web applications. EAS provides features like Auto Scaling and Blue-Green Deployment to deliver cost-effective, high-concurrency, and stable online services. EAS also provides resource group management, version control, and a comprehensive operations and maintenance monitoring system. For more information, see EAS overview.
Introduction to RAG
Generative AI has made remarkable strides in text and image generation. However, widely used large language models (LLMs) have several inherent limitations:
Limited domain knowledge: LLMs train on broad, general datasets. They struggle with deep, specialized tasks.
Information lag: A trained model is static. It cannot learn new information in real time.
Misleading output: Due to data bias and inherent model defects, LLMs may produce outputs that seem plausible but are incorrect, a phenomenon known as a model hallucination.
Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) was developed to overcome these challenges and enhance the functionality and accuracy of large models. By integrating external knowledge, RAG reduces model fabrications, improves access to recent information, and enables more personalized and accurate LLM responses.
OpenSearch overview
Alibaba Cloud OpenSearch Vector Search Edition is a fully managed, large-scale, distributed vector search service that supports various algorithms with excellent performance and high accuracy. It provides cost-effective vector index building and similarity search for massive datasets, with horizontal scaling, index merging, stream-based building, and real-time updates for immediate searchability.
Alibaba Cloud OpenSearch Vector Search Edition provides high-performance support for various typical vector search scenarios, such as retrieval-augmented generation (RAG), multimodal search, and personalized search and recommendation. For more information, see Introduction to OpenSearch Vector Search Edition.
Workflow
EAS provides a systematic RAG solution with flexible parameter configurations. You can use the RAG service through a WebUI or API calls to customize your chatbot. The core architecture of RAG consists of retrieval and generation:
Retrieval: EAS supports multiple vector databases, including open-source Faiss, Elasticsearch, Hologres, OpenSearch, and RDS for PostgreSQL.
Generation: EAS supports a rich set of open-source models, such as Qwen, Llama, Mistral, and Baichuan, and supports calls to ChatGPT.
This solution uses OpenSearch as an example to show you how to build an LLM RAG chatbot using EAS and Alibaba Cloud OpenSearch Vector Search Edition. The entire process takes about 20 minutes. The flow is as follows:
Prepare the OpenSearch vector search library
First, create an OpenSearch Vector Search Edition instance and prepare the configuration items required to associate the instance when you deploy the RAG service.
Deploy the RAG service and associate it with OpenSearch
Deploy the RAG service on the EAS platform and associate it with the OpenSearch Vector Search Edition instance.
You can connect to OpenSearch in the RAG chatbot, upload your business data files, and conduct a Q&A session.
Prerequisites
Create a Virtual Private Cloud (VPC), a vSwitch, and a Security Group. For more information, see Create a VPC with an IPv4 CIDR block and Create a security group.
Notes
This solution is limited by the server resource size and the default token limit of the LLM service, which restricts the supported conversation length. This guide helps you test the basic retrieval features of a RAG chatbot.
Prepare the OpenSearch vector search library
Step 1: Create an OpenSearch Vector Search Edition instance
Log on to the OpenSearch console. In the upper-left corner, switch to OpenSearch Vector Search Edition.
On the instance list page, create an OpenSearch Vector Search Edition instance. Key parameters are described below. For other parameters, see Purchase an OpenSearch Vector Search Edition instance.
Parameter
Description
Availability Edition
Select Vector Search Edition.
VPC
Select the created VPC and vSwitch.
vSwitch
Username
The username for the OpenSearch Vector Search Edition instance.
Password
The password for the OpenSearch Vector Search Edition instance.
Step 2: Prepare configuration items
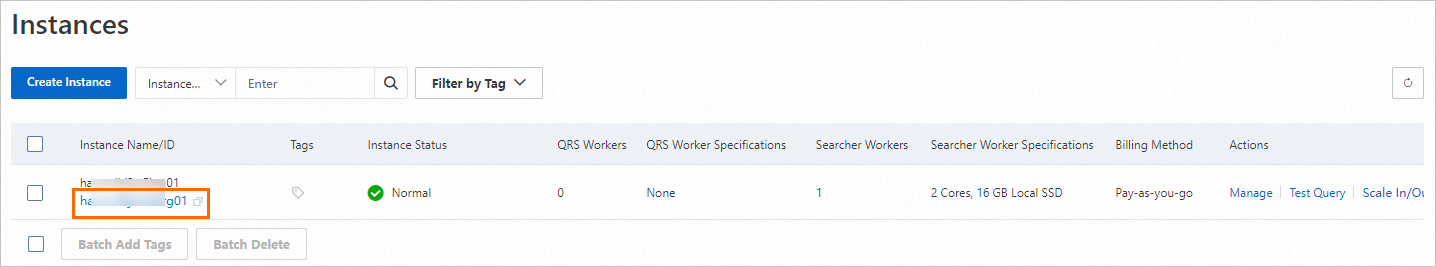
1. Get the instance ID
On the instance list page, view the instance ID of the OpenSearch Vector Search Edition instance and save it locally.
2. Prepare an index table
After the instance is created, its status becomes Pending Configuration. Configure Basic Table Information > Data Synchronization > Field Configuration > Index Schema for the instance, then wait for the index to rebuild before searching. Steps:
In the Actions column for the target instance, click Configure.
Configure the Basic Table Information parameters and click Next.
Key parameters are described below. For other parameters, see Quick Start for General-purpose Edition.
Table Name: Enter a name for the index table.
Partition: If you have purchased QRS workers, you can set this parameter to a positive integer up to 256 to improve full build speed and single query performance. If you have not purchased QRS workers, you can only set this parameter to 1.
Number of resources for data updates: Specifies the number of resources used for data updates. By default, OpenSearch provides a free quota of two update resources for each index. Each resource provides 4 CPU cores and 8 GB of memory. You are charged for resources that exceed the free quota. For more information, see Billing of Vector Search Edition for Alibaba Cloud International Website.
For Scenario Template, select General Template.
Configure the Data Synchronization parameters and click Next.
For a Full Data Source, you can choose one of three data source types based on your business needs:
MaxCompute+API: Use MaxCompute to write full data and the API to write real-time data. For more information about the parameters for this method, see MaxCompute + API data source.
Object Storage Service (OSS)+API: You can use OSS for full data writes and the API for real-time data writes. For more information about the parameters for this method, see OSS + API data source.
API: Writes both full and real-time data.
Configure the Field Configuration parameters and click Next.
Save the following sample field configuration as a JSON file. Then, click Import Field Index Schema in the upper-right corner and follow the instructions in the console to import the manifest. After the manifest is imported, the field configuration and index schema are populated from the file.
Configure the Index Schema parameters and then click Next.
Key parameters are described below. For other parameters, see General vector index configurations.
Set Vector Dimensions to 1024.
Distance Type: We recommend selecting InnerProduct.
In the configuration wizard, on the Confirm Creation page, click Confirm Creation.
You are automatically redirected to the table management page. A Status of In Use indicates that the index table is created.
3. Enable public network access for the OpenSearch Vector Search Edition instance
EAS accesses OpenSearch over the Internet, so you must configure a VPC with a NAT Gateway and elastic IP address (EIP). Enable public network access for OpenSearch and add the EIP to its whitelist. EAS can use the same VPC as OpenSearch or a different one.
Configure public network access for the virtual private cloud (VPC) that will be attached when you deploy the RAG service. For more information, see Access the Internet using the SNAT feature of an Internet NAT gateway.
View the attached elastic IP address.
Log on to the VPC console. Click the ID of the VPC instance and navigate to the Resource Management tab.
Click the attached Internet NAT gateway to go to its details page.

Click the Internet NAT gateway instance ID to go to the Basic Information page.
Click Associated EIPs to view the associated EIP and save it locally.

On the instance list page for OpenSearch Vector Search Edition, click the name of the destination instance to open the Instance Details page.
In the Network Information section, turn on the Public Access switch. In the Modify Public Access Whitelist configuration panel that appears, add the elastic IP address from the previous step to the public access whitelist.
In the Network Information section, save the endpoint for Public Domain Name locally.
4. View the instance username and password
This is the username and password that you specified when you created the OpenSearch Vector Search Edition instance. You can find these credentials in the API Endpoint section on the instance details page.
Deploy the RAG service and associate it with OpenSearch
Log on to the PAI console. Select a region on the top of the page. Then, select the desired workspace and click Elastic Algorithm Service (EAS).
On the Inference Service tab, click Deploy Service. Then, in the Scenario-based Model Deployment section, click RAG-based LLM Chatbot Deployment.
On the RAG-based Smart Dialogue Deployment page, you can configure the following key parameters. For more information about other parameters, see Step 1: Deploy the RAG service.
page, you can configure the following key parameters. For more information about other parameters, see Step 1: Deploy the RAG service.
Parameter
Description
Basic Information
Version
Select LLM-Integrated Deployment.
RAG Version
Select pai-rag:0.3.5.
Model Type
Select Qwen3-1.7B-Base.
Resource Information
Deployment Resources
The system recommends a resource specification based on the selected model type. Using a different specification may prevent the service from starting.
Vector Database Settings
Vector Database Type
Select OpenSearch.
Endpoint
Set this to the public domain name obtained in Step 2. Do not include http:// or https://. For example, ha-cn-****.public.ha.aliyuncs.com.
Instance ID
Set this to the ID of the OpenSearch Vector Search Edition instance obtained in Step 2.
Username
Set this to the username you configured when creating the OpenSearch Vector Search Edition instance.
Password
Set this to the password you configured when creating the OpenSearch Vector Search Edition instance.
Table Name
Set this to the name of the index table created in Step 2.
OSS Path
Select an existing OSS storage folder in the current region. Knowledge base management is implemented by mounting an OSS path.
VPC
VPC
You can select the same VPC and vSwitch as OpenSearch.
You can also use a different VPC, but you must ensure that it has public network access and that the attached elastic IP address is added to the public access whitelist of the OpenSearch instance. For more information, see Access the Internet using the SNAT feature of an Internet NAT gateway and Configure a public access whitelist.
vSwitch
Security Group
Select a security group.
After you configure the parameters, click Deploy.
Use the RAG chatbot
The following section describes how to use a RAG-based LLM chatbot. For more information, see RAG chatbot for LLM.
1. Check the vector search library configuration
Click the name of the target RAG service, then click Web Application in the upper-right corner of the page.
Check whether the OpenSearch vector search library configuration is correct.
The system auto-configures the `default` knowledge base using the vector search library settings from the RAG service deployment. In the Vector Database Configuration section, verify the OpenSearch configuration. Update as needed and click Update Knowledge Base.
2. Upload enterprise knowledge base files
On the File Management tab of the Knowledge Base tab, upload knowledge base files.
After the knowledge base is uploaded, the system automatically stores the files in the vector database in the PAI-RAG format. For knowledge base files with the same name, vector databases other than FAISS overwrite the original files. Supported file types include .html, .htm, .txt, .pdf, .pptx, .md, Excel (.xlsx or .xls), .jsonl, .jpeg, .jpg, .png, .csv, and Word (.docx), for example, rag_chatbot_test_doc.txt.
3. Conduct a Q&A session
On the Chat tab, select a knowledge base name and an intent. Select Query Knowledge Base to use more tools. Then, you can perform knowledge-based Q&A.
Support for OpenSearch features
OpenSearch Vector Search Edition provides a GUI for managing index tables and indexes. This section explains how to view index information and perform data management tasks in the console.
Index table management
Go to the instance details page of the Alibaba Cloud OpenSearch Vector Search Edition instance.
Log on to the Alibaba Cloud OpenSearch Vector Search Edition console.
Click the ID of the instance that you created to go to the Instance Details page.
Go to the table management page to manage the index table.
In the navigation pane on the left, click Table Management.
The page displays all tables that are created for the current instance.
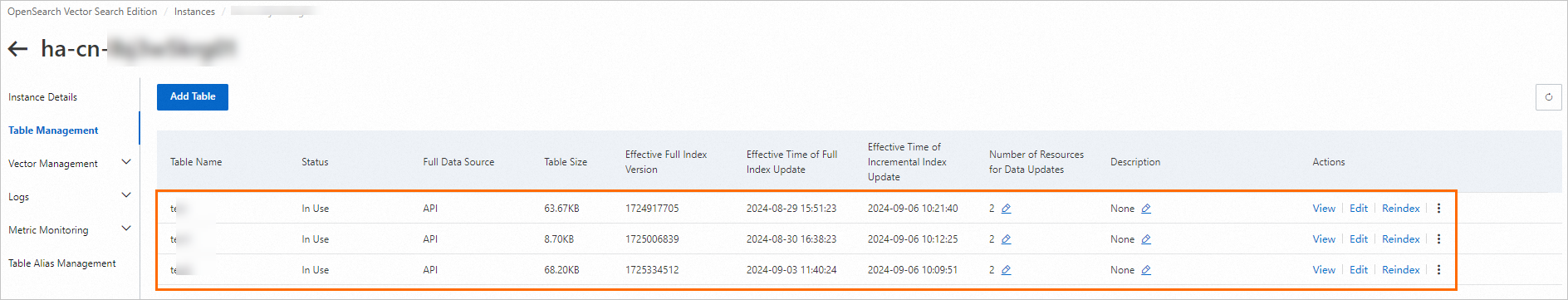
On the table management page, you can perform management operations on the index table, such as viewing field and index schemas, editing indexes, rebuilding indexes, and deleting indexes. For more information, see Table management.
Data management
Go to the instance details page of the Alibaba Cloud OpenSearch Vector Search Edition instance.
Log on to the Alibaba Cloud OpenSearch Vector Search Edition console.
Click the ID of the instance that you created to go to the Instance Details page.
Insert data.
In the navigation pane on the left, choose .
From the drop-down list on the right side of the page, select Form Mode or Developer Mode.
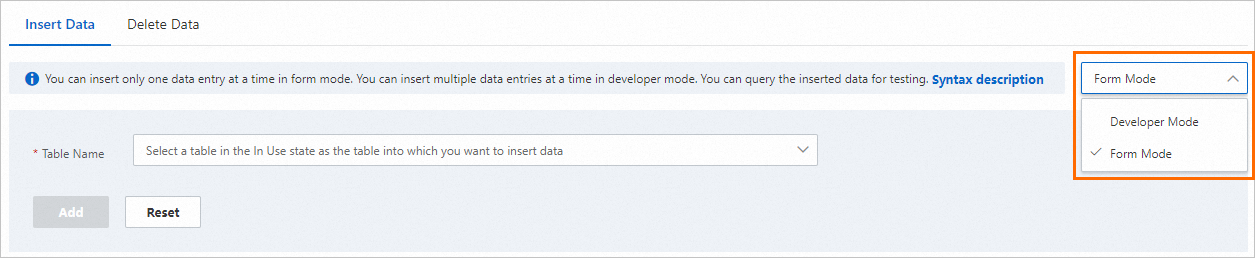
Select the name of the destination index table to which you want to add data.
Enter the data content by field or fill in the data write statement, and then click Add. For more information, see Add data.
If the execution result shows
"message": "success", the data is uploaded. You can add single or multiple data entries.
View table metric data.
In the left navigation pane, choose .
Select the name of the destination index table whose data you want to view. You can then view metrics such as the number of documents in the index and the number of successful requests per second. For more information, see Table metrics.
Delete data.
In the left navigation pane, choose .
From the drop-down list on the right side of the page, select Form Mode or Developer Mode.
Select a Table Name, enter a Primary Key, and then click Delete. For more information, see Delete data.
If the execution result shows
"message": "success", the data is deleted.
References
EAS simplifies deployment for AIGC and LLM scenarios. You can easily launch services with a single click, including deployments for ComfyUI, Stable Diffusion WebUI, ModelScope models, HuggingFace models, Triton, and TFserving. For more information, see Scenario-based deployment.
The RAG service WebUI offers a wide range of inference parameters. The RAG service also supports API calls. For more information about implementation details and parameter settings, see RAG chatbot for LLM.
The RAG chatbot for LLMs also supports association with other vector search libraries, such as Elasticsearch, or RDS for PostgreSQL. For more information, see Build a retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) chatbot using EAS and Elasticsearch, or Build a retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) chatbot using EAS and RDS for PostgreSQL.