This topic describes how to synchronize multimodal vector data from a Data Lake Formation (DLF) data source to Alibaba Cloud OpenSearch. OpenSearch can automatically extract text, image, and video data from DLF, vectorize the data using built-in models or the AI Search Open Platform, and parse its content. This process transforms unstructured data into structured vectors and synchronizes them with OpenSearch. The solution supports data formats such as Paimon, Lance, and Object Table and provides comprehensive vector index configurations, including settings for vector dimensions, distance types, and search algorithms. This helps you build efficient multimodal search applications for scenarios such as image search, text semantic search, and video search.
Prerequisites
Learn about Data Lake Formation.
You have configured a data catalog ID, a database, and a data table in DLF. They are required for data synchronization.
Add a DLF data source
On the Instance Details > Table Management page, click Add Table.
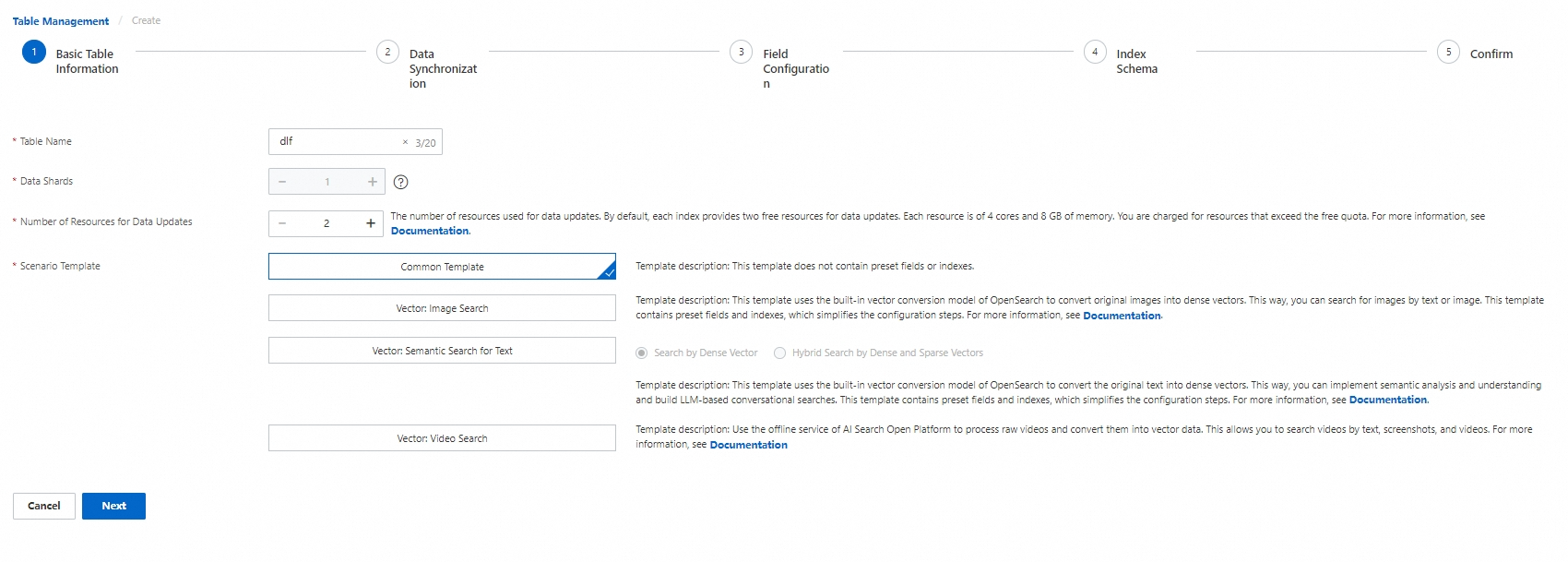
In the Basic Information step, configure the parameters and click Next.
 Configuration details:
Configuration details:
Table Name: A custom name for the table.
Data Shards: If you create multiple index tables, ensure that they all have the same number of shards. Alternatively, one index table can have a single shard while all other index tables have an identical number of shards.
Number of Resources for Data Updates: Specifies the number of resources for data updates. By default, each index includes a free quota of two resources. Each resource provides 4 CPU cores and 8 GB of memory. You are charged for any resources that exceed the free quota. For more information, see Billing of Vector Search Edition.
Scenario Template: Vector Search Edition provides four built-in templates: Common Template, Vector: Image Search, Vector: Text Semantic Search, and Vector: Video Search. The Video Search template does not support DLF as a full data source.
In the Data Synchronization step, configure the data source. After the data source is successfully verified, click Next.
Full Data Source: Select Data Lake Formation (DLF).
Table Format: Paimon, Lance, and Object Table are supported.
Paimon is a lakehouse table format that supports real-time data updates, and both stream and batch processing.
Lance is a vector table format designed for AI that enables ultra-fast similarity searches on vectors.
Object Table is a metadata table format that lets you directly query and locate various files stored in the cloud using SQL.
Data Catalog: The ID of the target DLF data catalog that you want to access.
Database: The database in the target data catalog.
Data Table: The data table in the target database.
NoteTo use DLF data sources for existing instances, you must first upgrade the engine versions of the instances.
The Common Template and Vector: Image Search templates support the Paimon, Lance, and Object Table formats. The Vector: Text Semantic Search template supports the Paimon format.
For a Paimon primary key table, you can add, delete, modify, and query data. For a Paimon append-only table, you can only write data. You cannot modify or delete data.
Relative Path: The relative path to access files in the object table when the table format is Object Table.
Data Format: When the table format is Object Table, select ha3 or json as the data format.
Tag: A data version tag. If you specify a tag, OpenSearch uses the tagged data for the full import. If you do not specify a tag, OpenSearch uses the latest data in the table for the full import.
Paimon provides a tag feature to retain metadata and data files of specific snapshots. This prevents historical data loss due to snapshot expiration. Tags can be created automatically based on write jobs, generated periodically by processing time or watermark, or manually created, deleted, or rolled back. By configuring a data retention policy, you can control the maximum number of tags or their retention period to ensure that historical data remains queryable. For more information, see Paimon Tags.
Lance uses tags to mark specific versions in a dataset's history. This makes it easier to track dataset evolution, especially in frequently updated machine learning workflows. You can create, update, delete, and list tags. Tags do not create new versions. Instead, they exist as metadata in a separate folder. Versions with tags are not removed by the `cleanup_old_versions` operation. You must first remove the tag to remove the corresponding version. For more information, see Lance Tags.
Data Source Check: After the data source is successfully verified, you can proceed to the next step.
In the Field Configuration step, configure the fields and click Next.
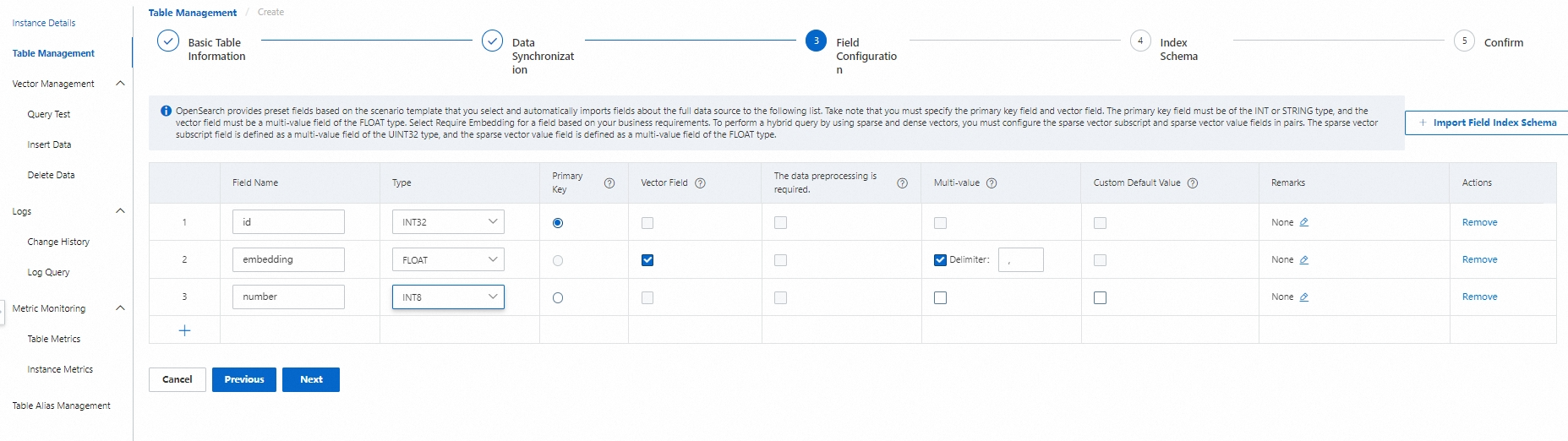
The primary key field and vector field are required. For the primary key field, set the type to int or string and select the Primary Key option. For the vector field, set the type to float and select the Vector Field option.
By default, the vector field is a multi-value field of the float type.
Data pre-processing required: For fields of the String type, you can select this option and click Configure to call a model to pre-process the data in the field.

Text data type
Data type: Text.
Pre-processing template: Dense vectorization, or Dense + sparse vectorization.
Service list:
After you select a pre-processing template, a list of services under the template automatically appears. This list shows the model types used in the template.
Available model sources:
Built-in models: A limited number of model types are available and can be called for free.
AI Search Open Platform: The AI Search Open Platform provides a rich set of models. You are charged based on the number of calls. For more information, see Billing methods and billable items. Before you use these models, you must first activate a workspace and an API key on the AI Search Open Platform.
Custom model: To create a custom model, go to Models > Custom Models on the Vector Search Edition page and click Create Model. For more information, see Custom Model.
Image data type
Data type: Image.
Data source: Object Storage Service (OSS), Base64 encoding, or DLF-Object Table.
Object Storage Service (OSS): Store the images in an OSS folder and specify the OSS path to import them directly.
Base64 encoding: You must first encode the images and then store them in a database or transfer them directly using an API.
DLF-Object Table: A table in the Data Lake Object Table format. You must specify the corresponding data catalog, database, and data table.
Pre-processing template: Image vectorization, Image content parsing, or Image content parsing + image vectorization.
Service list:
After you select a pre-processing template, a list of services under the template automatically appears. This list shows the model types used in the template.
Available model sources:
Built-in models: A limited number of model types are available and can be called for free.
AI Search Open Platform: The AI Search Open Platform provides a rich set of models. You are charged based on the number of calls. For more information, see Billing methods and billable items. Before you use these models, you must first activate a workspace and an API key on the AI Search Open Platform.
Custom models: You can customize models as needed. On the Vector Search Edition page, go to Models > Custom Models and click Create Model. For more information, see Custom models.
Video data type
Data type: Video.
Data source: Object Storage Service (OSS).
Pre-processing template: Video processing.
Service list:
After you select a pre-processing template, a list of services under the template automatically appears. This list shows the model types used in the template.
Available model sources:
Built-in models: A limited number of model types are available and can be called for free.
AI Search Open Platform: The AI Search Open Platform provides a rich set of models. You are charged based on the number of calls. For more information, see Billing methods and billable items. Before you use these models, you must first activate a workspace and an API key on the AI Search Open Platform.
Custom models: You can customize models as needed. On the Vector Search Edition page, go to Models > Custom Models and click Create Model. For more information, see Custom models.
If a field is missing or empty in the source data, the system automatically assigns a default value. By default, numeric fields are set to 0 and string fields are set to an empty string. You can also specify custom default values.
In the Index Schema step, configure the indexes and click Next.
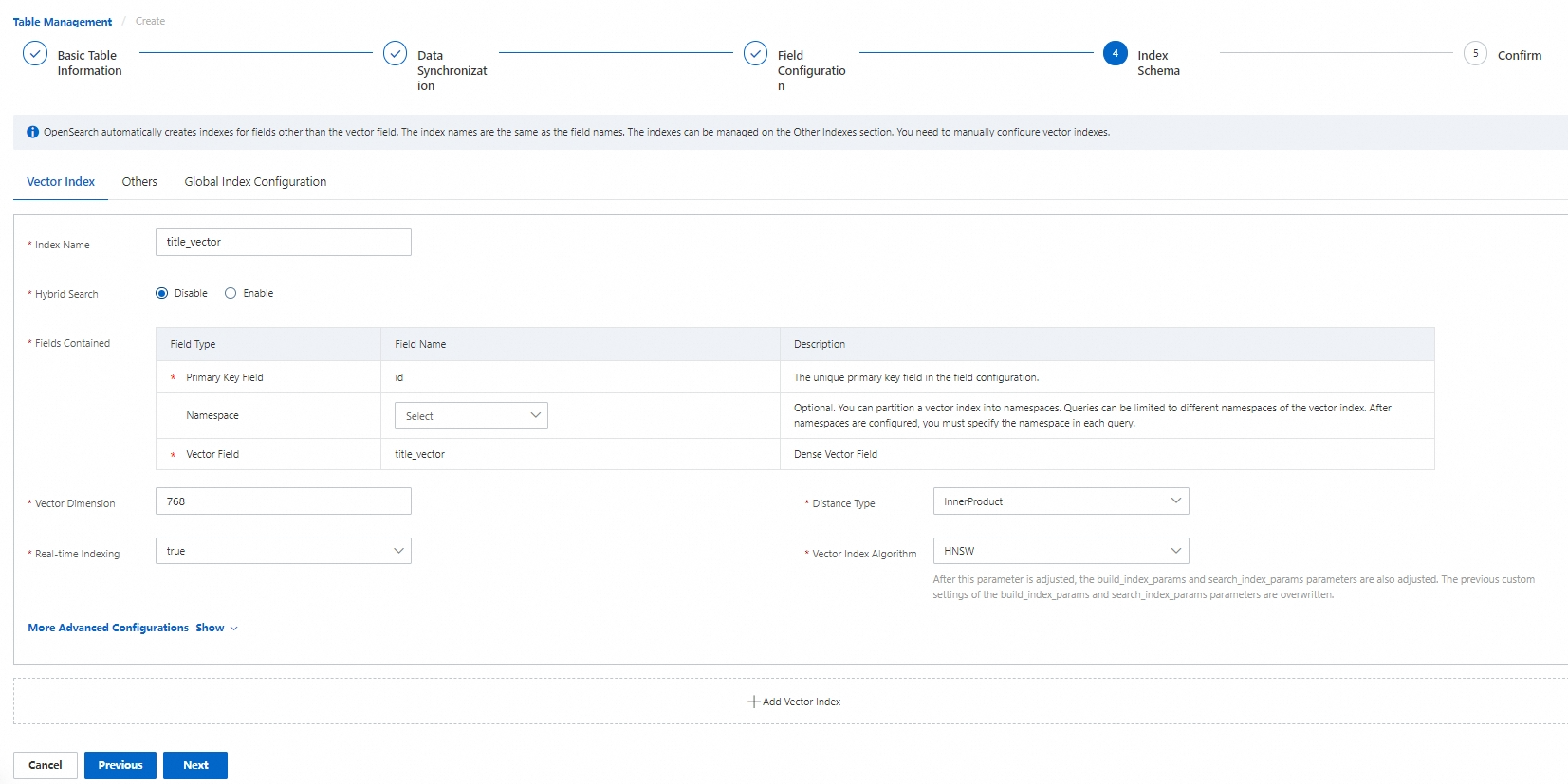
Vector Index:
Vector Dimensions: Select the vector dimensions based on the vectors generated by your model.
Distance Type: Select a distance type based on the vectors generated by your model. The system supports three distance types: Squared Euclidean, Inner Product, and Cosine.
Vector Search Algorithm: Select a vector search algorithm based on the vectors generated by your model. The system supports the following vector index algorithms: Linear, HNSW, QGraph, QC, DiskANN, and CagraHnsw.
Real-time Index: Specifies whether to build real-time indexes for incremental data that is pushed using API calls. The default value is true.
You can also click to expand and configure advanced settings. For more information about the parameters, see Common configurations for vector indexes.

Other index types: The system generates a `pk` field and a primary key index. For other non-vector fields, an index with the same name is created by default.
Global index configuration: You can configure automatic cleanup for expired documents. If this feature is enabled, a document is automatically deleted when the difference between the current time and the document's timestamp exceeds the specified expiration time.
In the Confirm step, click Confirm. The system automatically creates the configured table. You can view the table creation progress on the Change History page.
After the table status changes to In Use, you can perform a query test on the Query Test page.
Precautions
When new data is written to a Paimon table in DLF, OpenSearch automatically triggers real-time indexing for the new data. If you manually write data using API calls, data consistency issues may occur. Proceed with caution.