In the Experience Center, you can visually test services such as document parsing, image content extraction, and document chunking. This helps you quickly evaluate whether the services meet your business requirements.
Features
The Experience Center provides the following services:
Service category | Service description |
Document content parsing | A general document parsing service that extracts logical structures, such as titles and paragraphs, from unstructured documents containing text, tables, and images. The service then outputs the extracted content in a structured format. |
Image content parsing | Image Content Recognition Service: Uses a multimodal large language model to parse, understand, and recognize text in images. The parsed text can be used in image search and question and answer (Q&A) scenarios. |
Image Text Recognition Service: Performs Optical Character Recognition (OCR) on images to recognize text. The recognized text can be used in image search and Q&A scenarios. | |
Document slice | A general text chunking service that splits structured data in HTML, Markdown, and TXT formats based on paragraphs, text semantics, or specified rules. It also supports extracting code, images, and tables from documents as rich text. |
Text embedding |
|
Multimodal vector |
|
Sparse text embedding This service converts text data into sparse vectors. Sparse vectors require less storage space and are often used to represent keywords and term frequencies. They can be combined with dense vectors for hybrid search to improve retrieval results. | OpenSearch sparse text vectorization service: A text embedding service for over 100 languages. The maximum input text length is 8,192 tokens. |
Dimensionality reduction | embedding-dim-reduction: A vector model fine-tuning service. You can train custom models for tasks such as vector dimension reduction. This helps reduce the dimensions of high-dimensional vectors to improve cost-effectiveness without a significant loss in retrieval performance. |
Query analysis A query content analysis service. Based on large language models (LLMs) and Natural Language Processing (NLP) capabilities, it performs intent recognition, alternate query expansion, and natural language to SQL (NL2SQL) processing on user queries. This effectively improves retrieval and Q&A performance in retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) scenarios. | A general query analysis service that uses LLMs for intent recognition and alternate query expansion on user input queries. |
Sorting service |
|
Speech recognition | Speech recognition service 001: Provides speech-to-text capabilities. It can quickly convert speech from video or audio files into structured text. The service supports multiple languages. |
Video snapshot | Video snapshot service 001: Provides video content extraction capabilities. It can capture keyframes from a video. When combined with multimodal embedding or image parsing services, it enables cross-modal retrieval. |
Large model |
|
Internet search | If your private knowledge base cannot provide an answer during a search, you can use Internet search to access more information from the Internet. This supplements your private knowledge base and allows the large language model to provide a more comprehensive response. |
Try the features
Document parsing
Log on to the Open Platform for AI Search console.
In the navigation pane on the left, select Experience Center.
For Service Category, select Document/Image Parsing (document-analyze), and then select a specific Experience Services.
To test the feature, you can use the system-provided Sample data or upload your own data using Manage data. The supported file formats are Txt, PDF, HTML, Doc, Docx, PPT, and PPTX, and the file size must not exceed 20 MB.
File: Upload local files. These files are automatically purged after 7 days. The platform does not store your data long-term.
URL: Provide the file URL and its corresponding file type. You can upload multiple URLs, with each on a separate line.
NoteSelecting the wrong data format causes document parsing to fail. Choose the correct file type based on your file's data.
 Important
ImportantEnsure that you use the web link import feature in compliance with applicable laws and regulations. You must adhere to the management specifications of the target platform and protect the legal rights of the rights holders. You are solely responsible for your actions. As a tool provider, the Open Platform for AI Search is not liable for your parsing or downloading behavior.
If you use your own data, select the pre-uploaded file or URL from the drop-down list.

Click Get Results. The system then calls a service to parse the document.
Results: Displays the parsing progress and results.
Result source code: View the Response result code. You can use Copy Code or Download File to download the code to your local machine.
Sample code: View and download the Sample code for calling the text content parsing service.

Document slice
Log on to the Open Platform for AI Search console.
In the navigation pane on the left, select Experience Center.
For Service Category, select Document Slice (document-split), and select a specific service from Experience Services.
For the test data, you can use the system-provided Sample data or select My data, enter your own data, and select the correct data format: TXT, HTML, or Markdown.
NoteSelecting the wrong data format causes document parsing to fail. Choose the correct format based on the uploaded data.
Set the Maximum Slice Length. The default value is 300, the maximum value is 1,024, and the unit is tokens.
You can configure whether to Return to sentence level slice as needed and click Get Results. The system then calls the service to segment the document.
Results: Displays the slice progress and results.
Result source code: View the Response result code. You can download the code to your local machine by clicking Copy Code or Download File.
Sample code: View and download the Sample code for calling the document slice service.
Text/Sparse embedding
Log on to the Open Platform for AI Search console.
In the navigation pane on the left, select Experience Center.
For Service Category, select Text Embedding (text-embedding), and select a specific Experience Services.
The Content Type for vectorization supports documents and queries.
You can add text for vectorization using Add Text Group or Directly Enter JSON Code.

Click Get Results to obtain the vectorization result of the text.
Results: Displays the vectorization result.

Result source code: View the response result code. You can click Copy Code or Download File to download the code to your local machine.
Sample code: View and download the Sample code for calling the text embedding service.
Multimodal embedding
Log on to the Open Platform for AI Search console.
In the navigation pane on the left, select Experience Center.
For Service Category, select Multimodal Vector (multi-modal-embedding). Then, select a specific Experience Services and select Text, Image, or Text + Image.
 Note
NoteWhen you upload a local image for embedding, the image is automatically purged after 7 days. The platform does not store your data long-term.
Click Get Results to obtain the multimodal embedding results.
Results: Displays the vectorization results.

Result source code: View the response code. You can use Copy Code or Download File to download the code to your local machine.
Sample code: View and download the Sample code to call the text embedding service.
Sorting service
Log on to the Open Platform for AI Search console.
In the navigation pane on the left, select Experience Center.
For Service Category, select Sorting Service (ranker), and select a specific Experience Services.
You can use the system-provided Sample data or input your own data.
In the Search Query field, enter text.

Click Get Results. The system then calls the sorting service to sort the documents based on the relevance between the query and the document content and output the scoring results.
Results: Displays the sorting and scoring results.

Result source code: View the response result code. You can download the code to your local machine using Copy Code or Download File.
Sample code: View and download the Sample code for calling the sorting service.
Video snapshot
Log on to the Open Platform for AI Search console.
In the navigation pane on the left, select Experience Center.
For Service Category, select Video Snapshot (video-snapshot).
You can use the system-provided Sample data or upload your own video data.
Click Get Results. The system then calls the video snapshot service to capture keyframes from the target video.
Speech recognition
Log on to the Open Platform for AI Search console.
In the navigation pane on the left, select Experience Center.
For the Service Category, select Speech Recognition (audio-asr).
For the trial, you can use the Sample data provided by the system or upload your own audio data.
Click Get Results. The system then calls the speech recognition service, which converts the audio content in the target data into structured text.
Large Language Model (LLM) services
Log on to the Open Platform for AI Search console.
In the navigation pane on the left, select Experience Center.
For Service Category, select Large model (text-generation), and then select a specific Experience Services. You can click
 to enable the Internet Search service. The system then determines whether to perform a Internet search based on the user's query.
to enable the Internet Search service. The system then determines whether to perform a Internet search based on the user's query.Enter a question and submit it. The large language model understands the question and provides an answer.
ImportantAll generated content is produced by an artificial intelligence model. We cannot guarantee the accuracy or completeness of the generated content. The content does not represent our attitudes or opinions.
The large language model's response page displays the number of input and output tokens for the current Q&A session. You can also delete the current conversation or copy the full text.
Image content parsing
Log on to the Open Platform for AI Search console.
In the navigation pane on the left, select Experience Center.
For Service Category, select Image Content Parsing (image-analyze). For Experience Services, select Image Content Recognition Service 001 or Image Text Recognition Service 001.
You can use the provided sample images or upload your own images.

Click Get Results. The system then calls the image content parsing service to understand and output the image content or recognize and output key information from the image.
Results: Displays the detection results.

Result source code: View the response code. You can download the code to your local machine by clicking Copy Code or Download File.
Sample code: View and download the Sample code for calling the image content parsing service.
Query analysis
Log on to the Open Platform for AI Search console.
In the navigation pane on the left, select Experience Center.
For Service Category, select Query Analysis (query-analyze).
You can directly enter a Search Query for query intent recognition, or construct a multi-turn conversation in the Historical Message area and enter a Search Query. In this case, the model combines the multi-turn conversation and the Search Query to perform the recognition.
Turn on the Show NL2SQL service and select a created service configuration to convert natural language queries into SQL statements.
Click Get Results to view the model's performance.
Results: Displays the detection results.
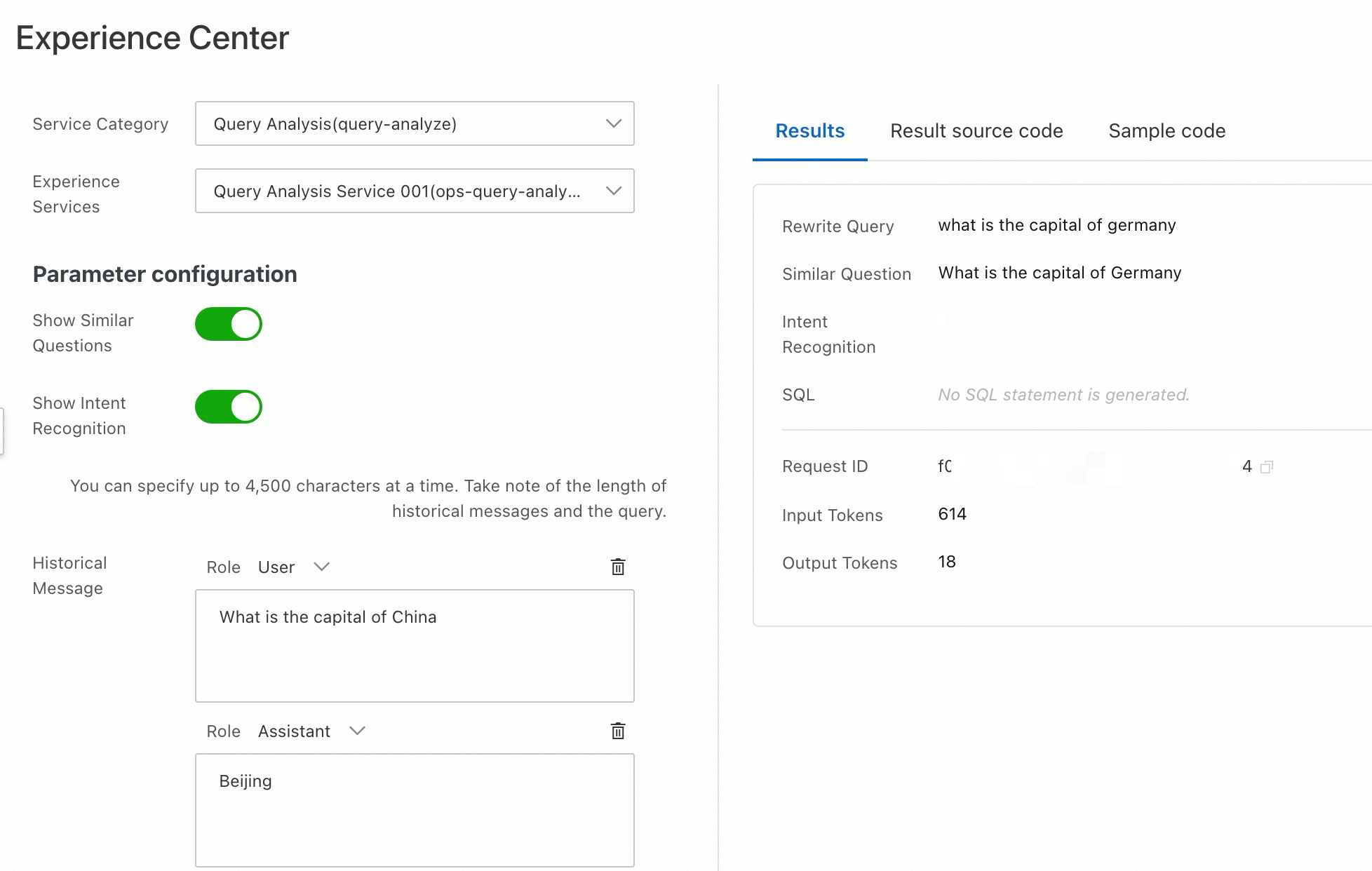
Result source code: View the response result code. You can use Copy Code or Download File to download the code to your local machine.
Sample code: View and download the Sample Code for calling the Query Analysis service.
Vector fine-tuning
Log on to the Open Platform for AI Search console.
In the navigation pane on the left, select Experience Center.
For Service Category, select Dimensionality Reduction (embedding-dim-reduction).
Select the model name (the model that you fine-tuned with your business data), specify the Produced Vector Dimension, which must be less than or equal to the dimension of the vector field selected during model training, and then Enter the original vector.
Click Get Results to view the model's performance.
For more information about how to train a dimension reduction model, see Service customization.
Internet search
You can use Internet search in the following two ways:
Directly call the Internet search service.
Enable Internet search when using an LLM.
Log on to the Open Platform for AI Search console.
Select the destination region and switch to the AI Search Open Platform.
In the navigation pane on the left, select Experience Center.
For Service Category, select Internet Search (web-search).
Enter a query in the Search Query field, such as "What to do in Hangzhou", and the results are returned.