Before you begin
Prepare the playbook that you want to run by using CloudOps Orchestration Service (OOS) and upload the playbook to Object Storage Service (OSS). In the following example, the playbook is used to install NGINX on Elastic Compute Service (ECS) instances.
---
- hosts: local
connection: local
become: yes
become_user: user_1
tasks:
- name: Install Nginx
yum:
name: nginx
state: installed
update_cache: trueScenario 1: Run an Ansible playbook by using its HTTPS URL
Prerequisites
The ECS instances can access the Internet.
Procedure
1. Log on to the OSS console and find the bucket in which the playbook is stored.
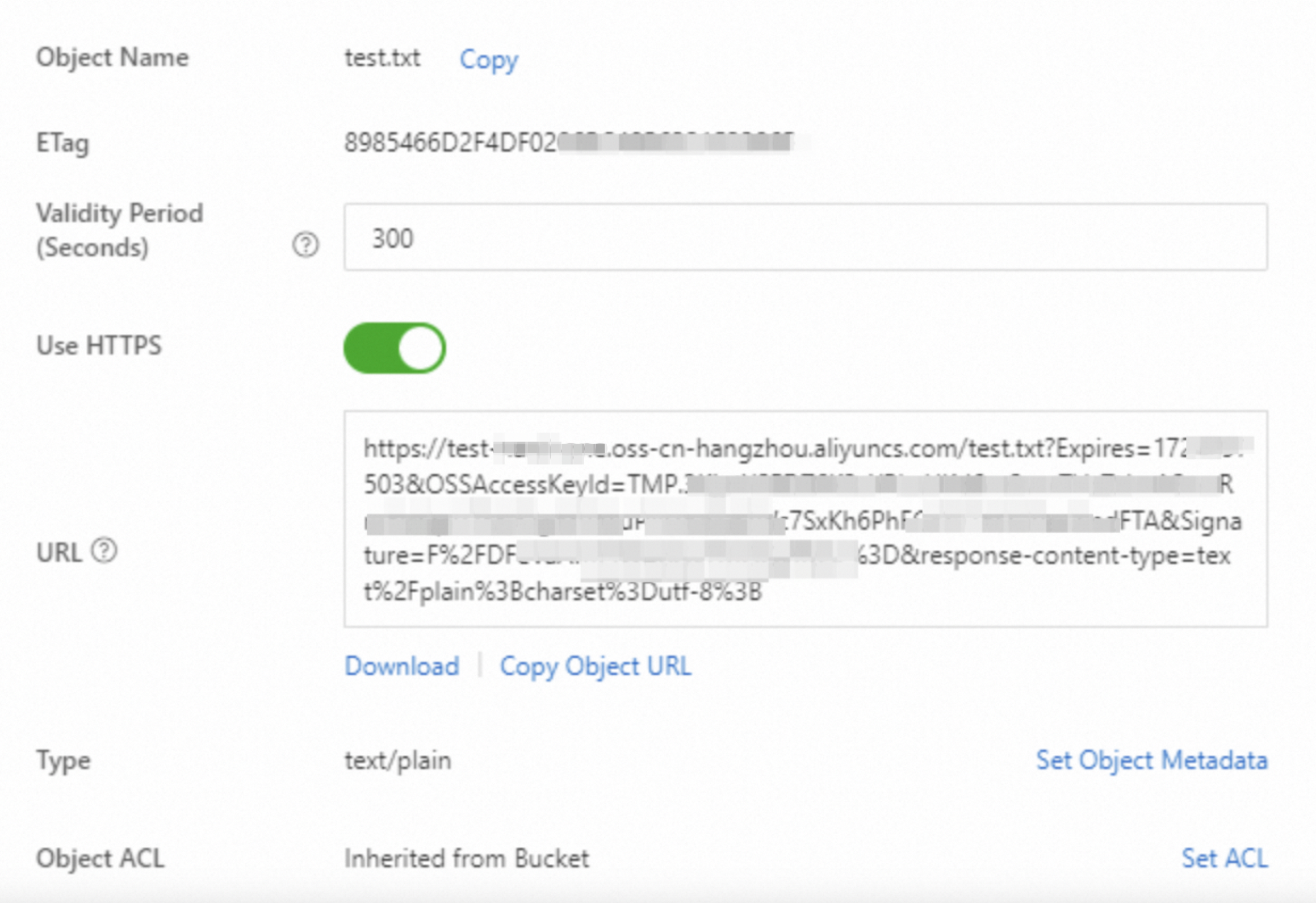
2. Click the name of the playbook. In the panel that appears, copy the URL of the playbook.
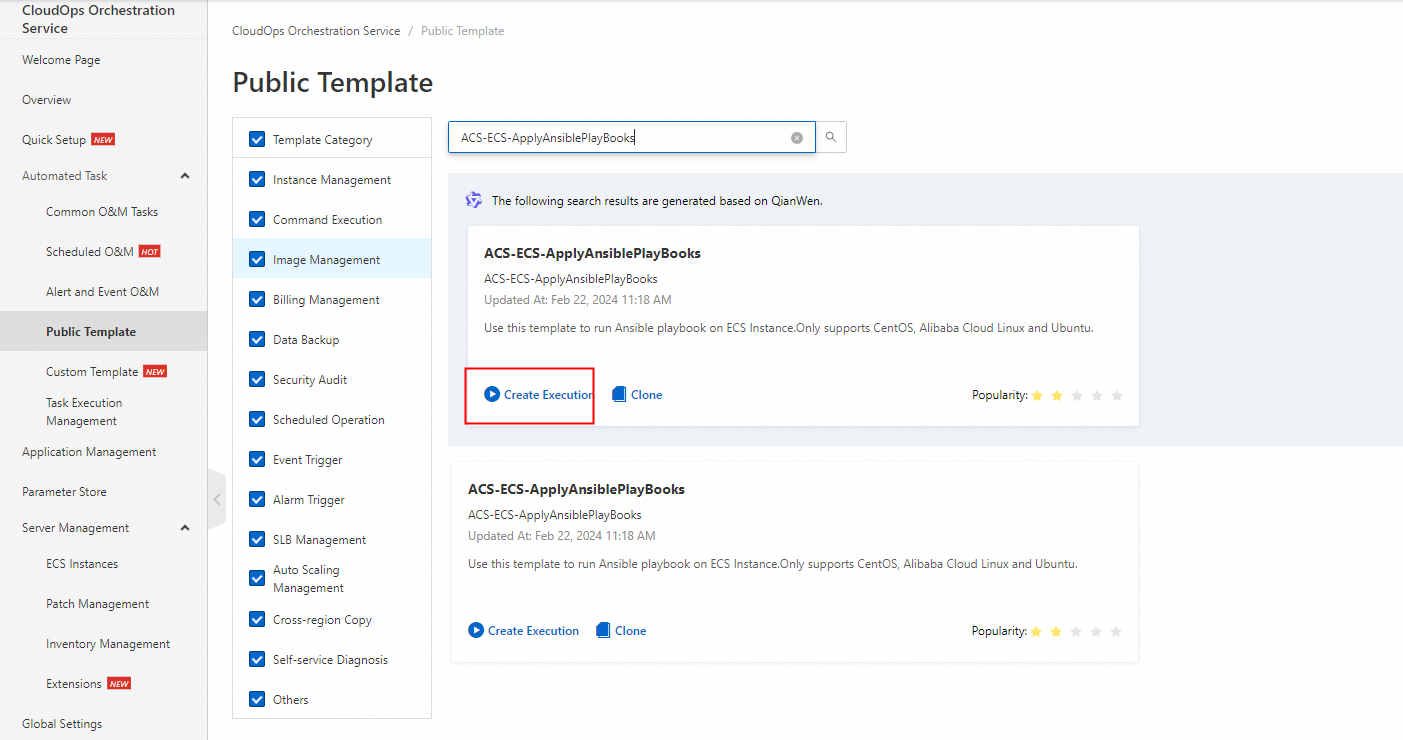
3. Log on to the CloudOps Orchestration Service console. In the left-side navigation pane, choose Automated O&M > Public Template. On the Public Template page, search for ACS-ECS-ApplyAnsiblePlayBooks. Click Create Execution.
4. Click Next Step: Parameter Settings.
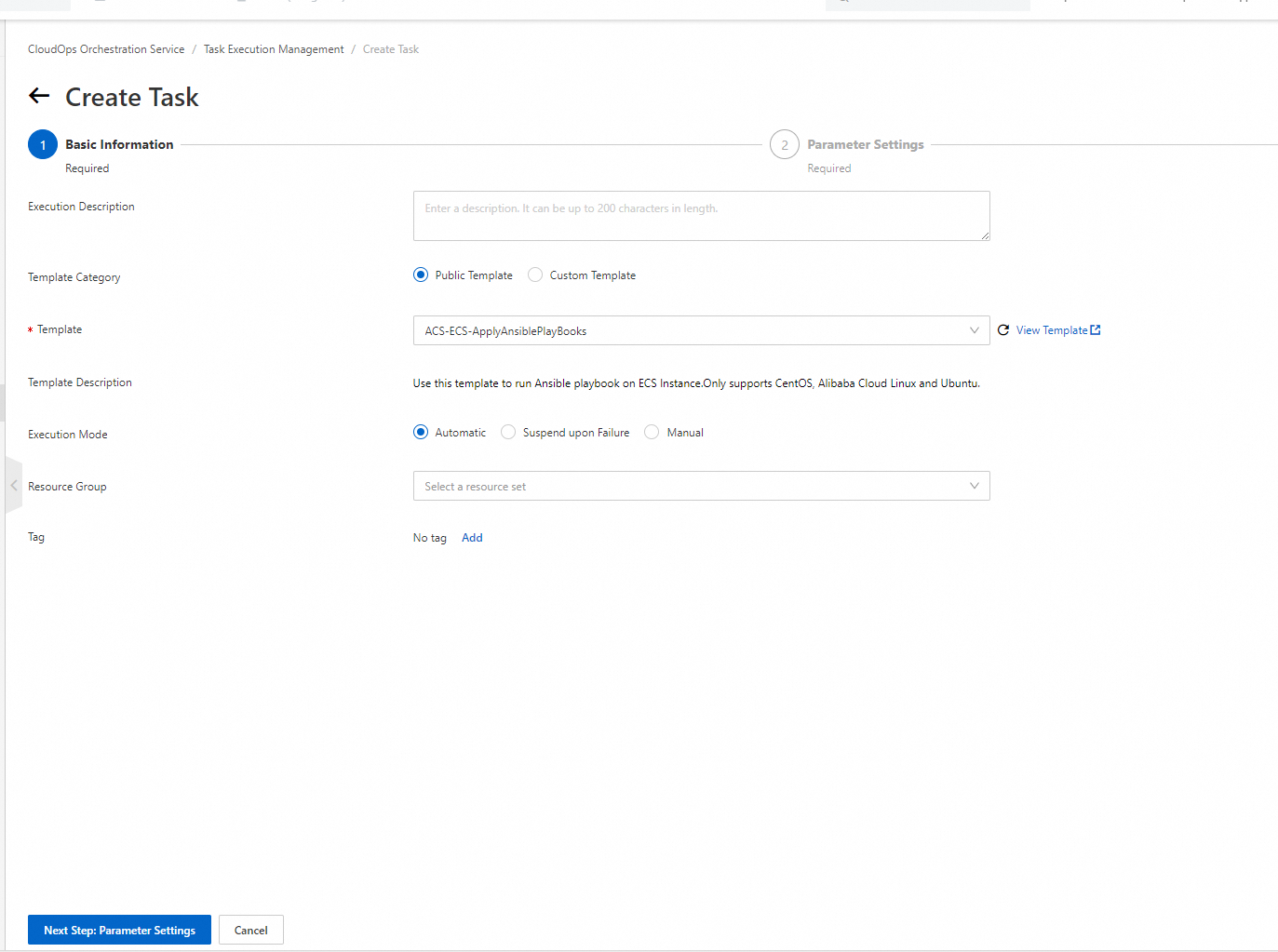
5. In the Parameter Settings step, set the SourceType parameter to https. Paste the playbook URL that you copied in OSS into the SourcePath field. For more information about other parameters, see the Template parameters section of this topic.
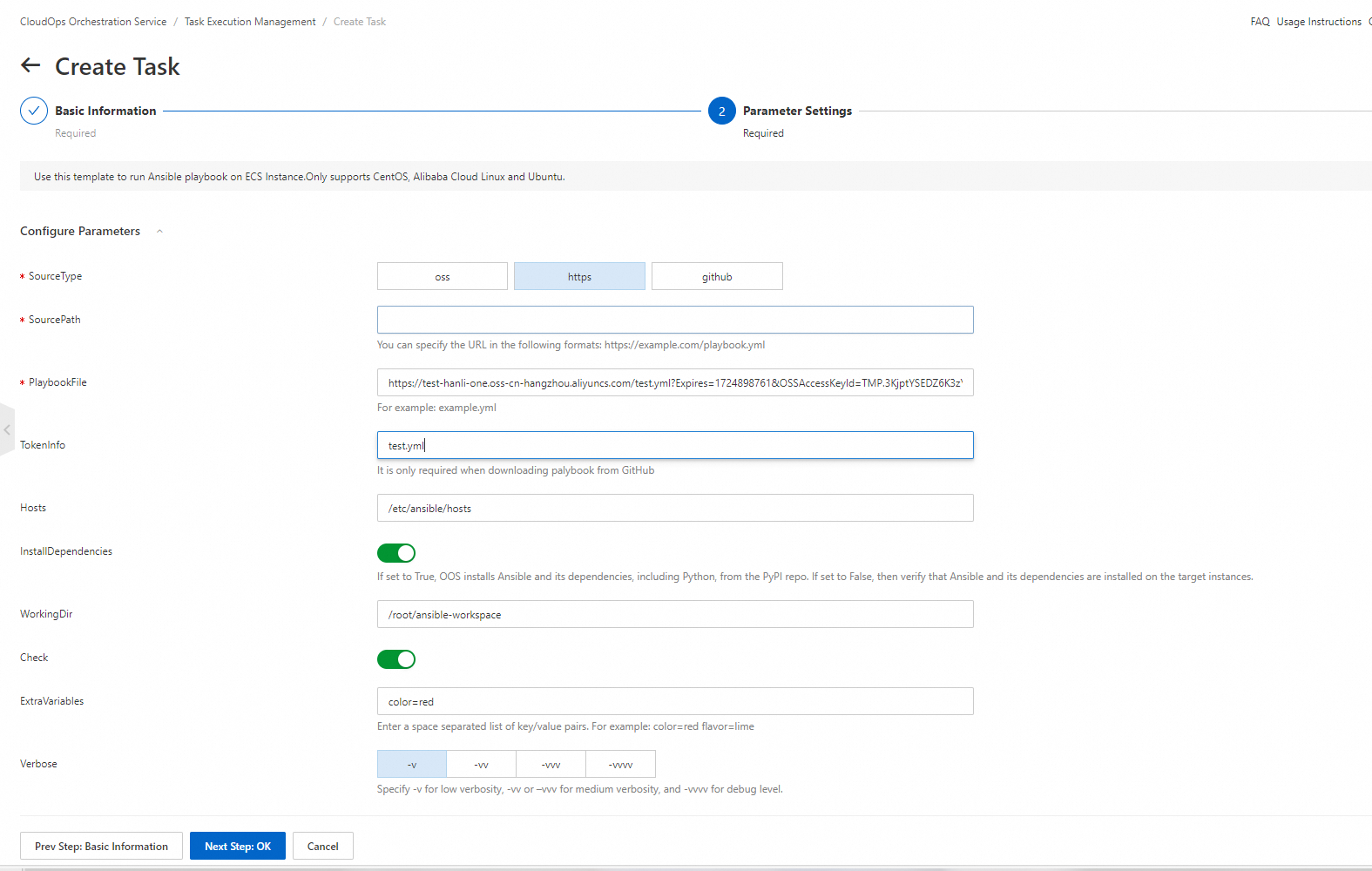
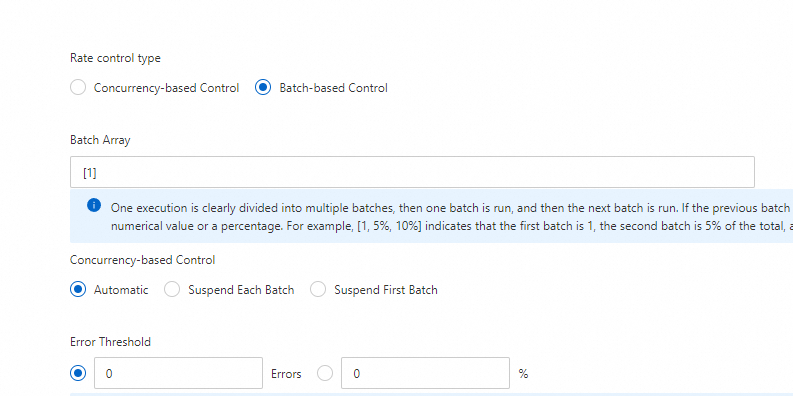
6. In the Control Options section, set the Rate control type parameter to Batch-based Control. For more information, see the Template parameters section of this topic.
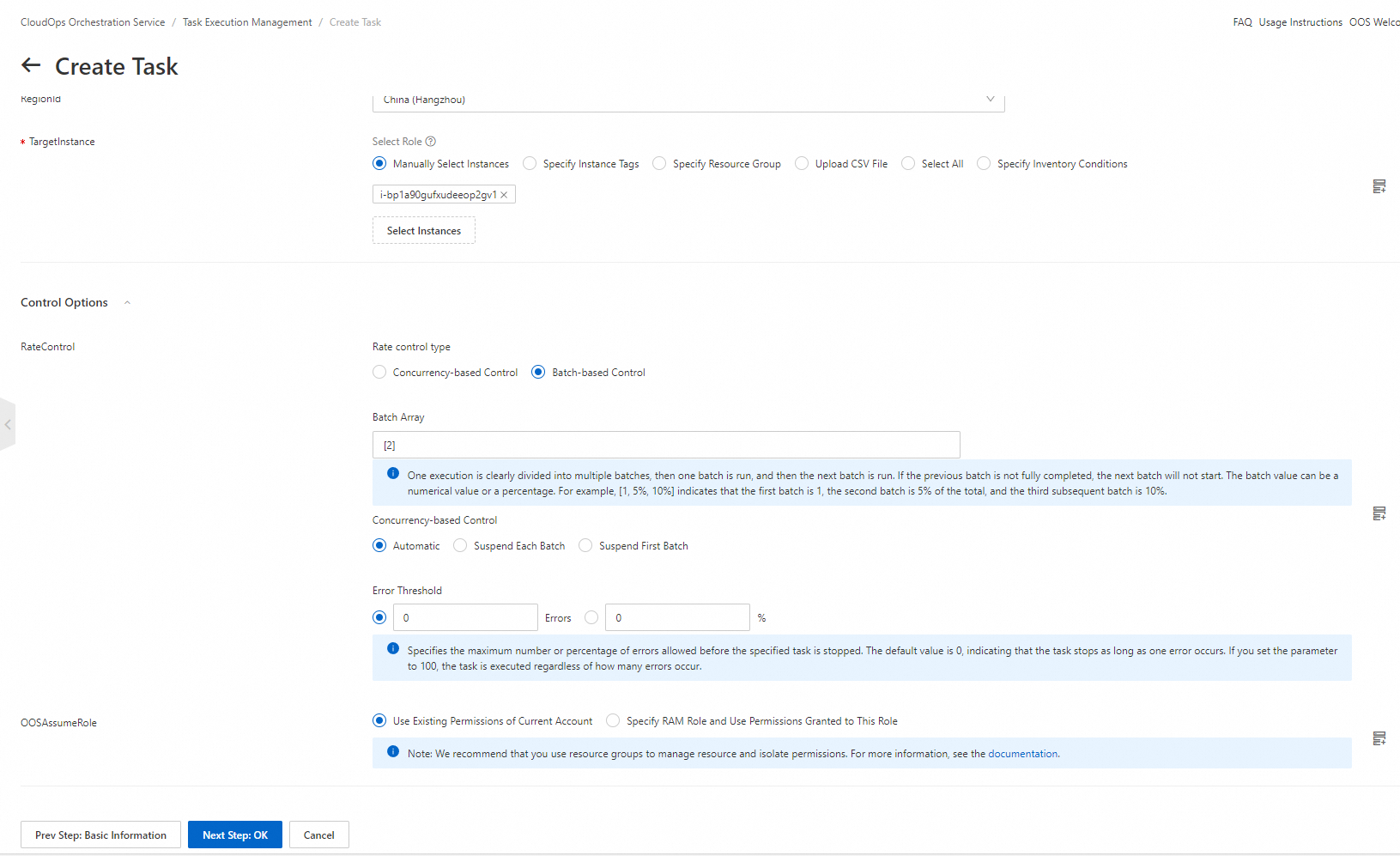
7. Confirm the parameter settings and click Create.
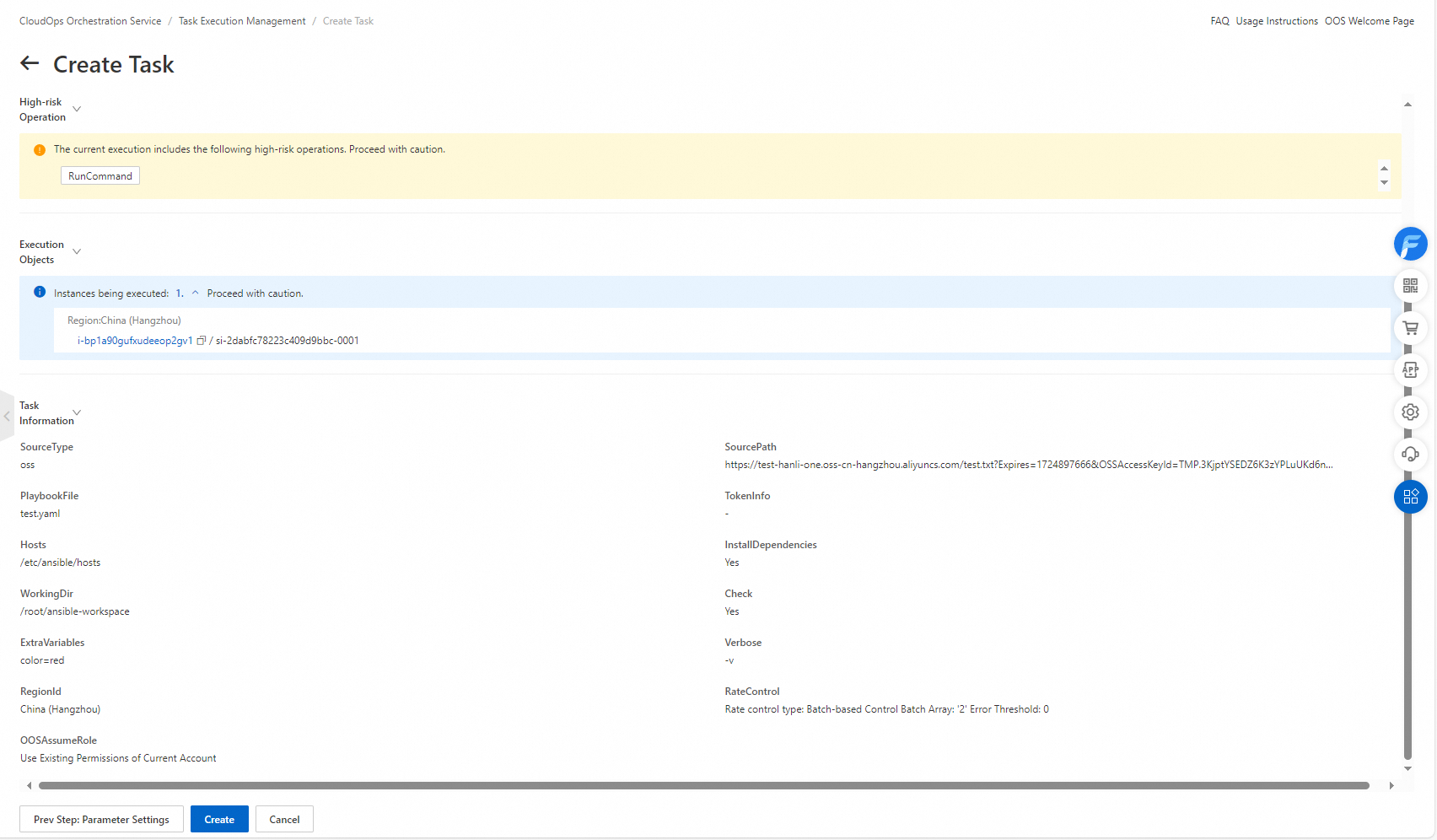
8. On the Task Execution Management page, find the execution.
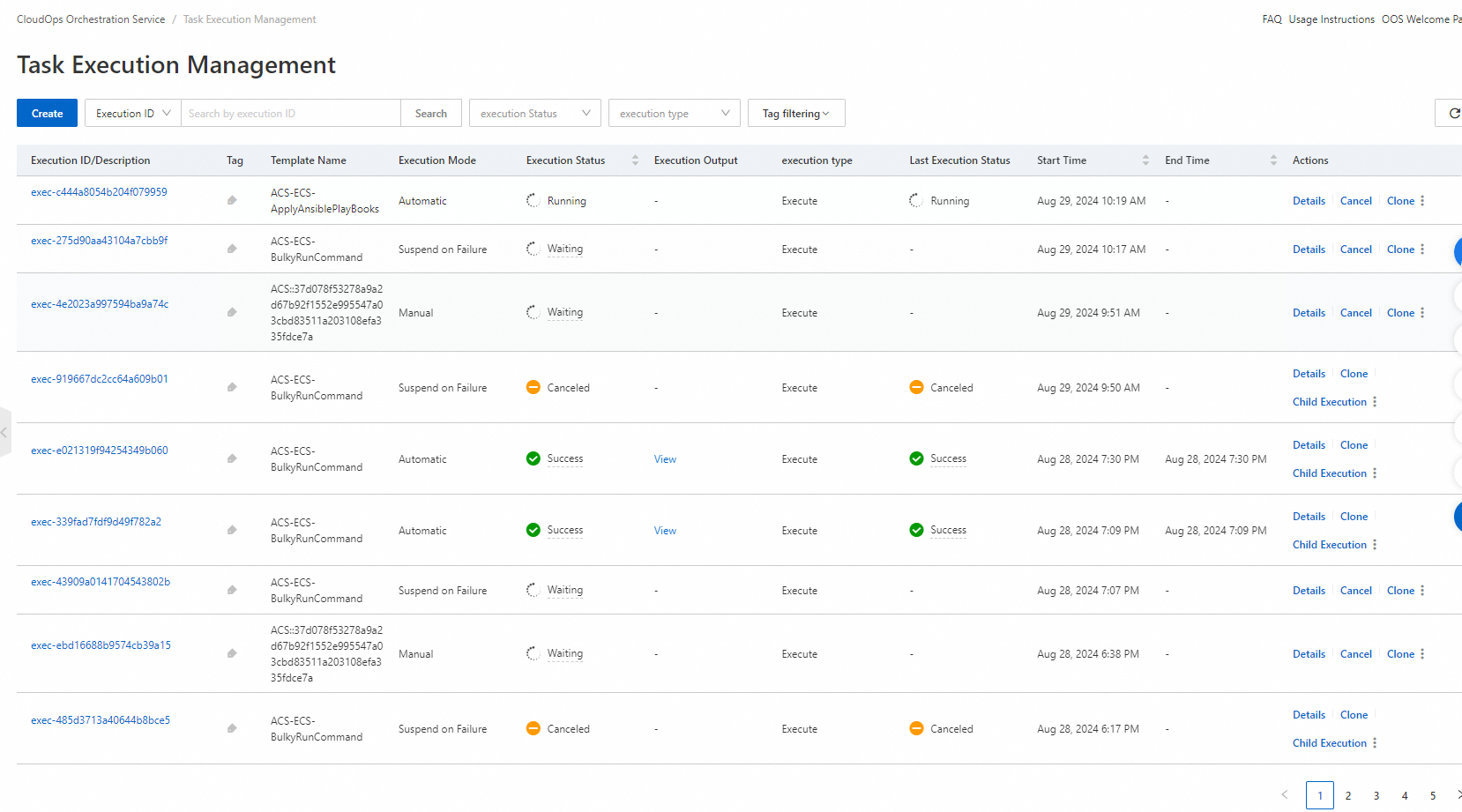
9. Click Details in the Actions column to view the status of the child execution. The execution result of the playbook is displayed on the Output tab.

Scenario 2: Run an Ansible playbook by using its OSS URL
Prerequisites
A Resource Access Management (RAM) role is created for the ECS instances on which you want to run an Ansible playbook. The RAM role has the read and write permissions on OSS. For more information, see Download files to multiple instances at a time.
Procedure
1. In the Parameter Settings section, set the SourceType parameter to oss, and enter the OSS URL of the playbook in the SourcePath field, such as oss://bucket/filename. The other steps are the same as those in Scenario 1.
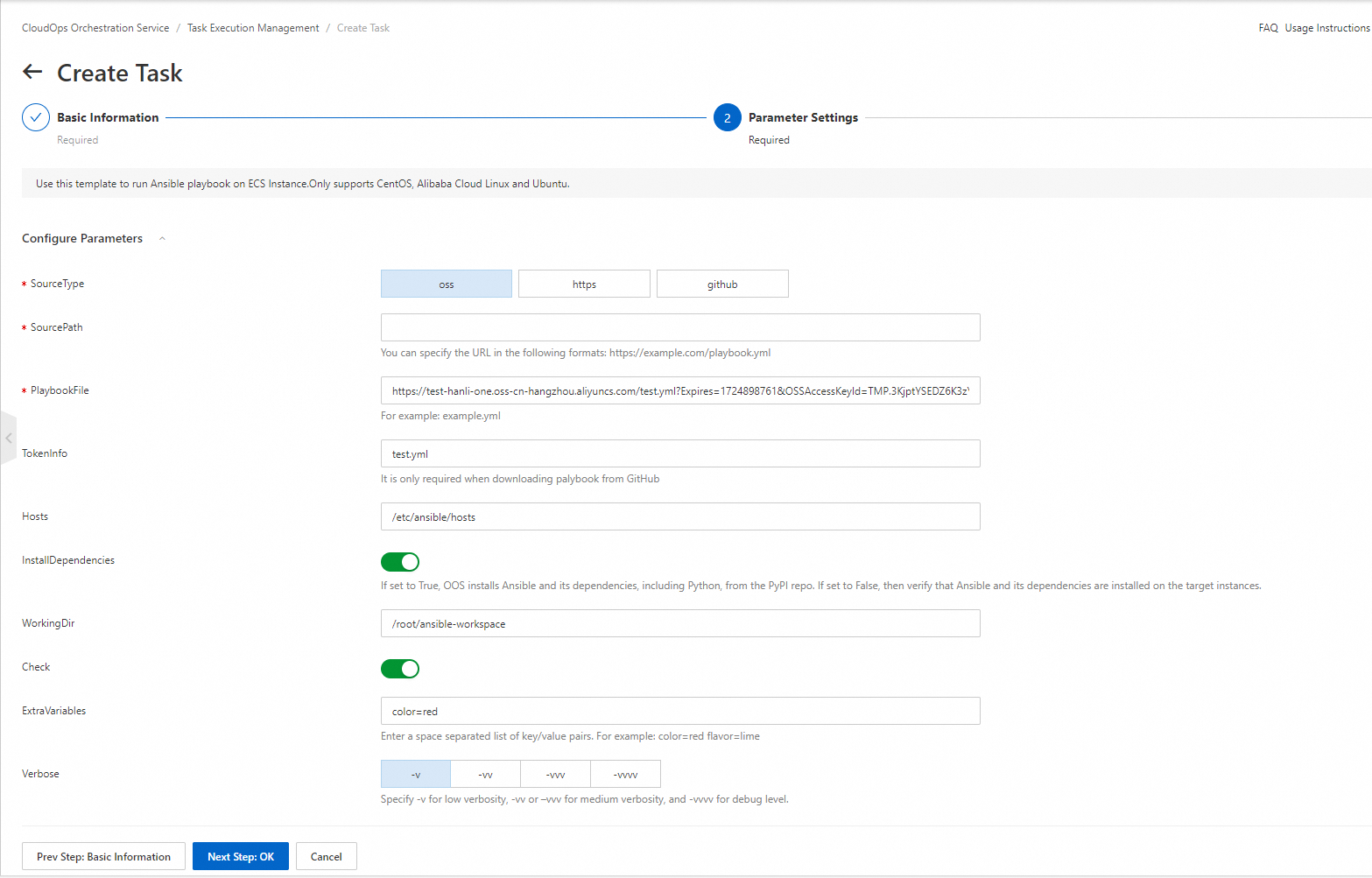
Template parameters:
SourceType: the storage type of the playbook.
SourcePath: the URL of the playbook.
PlaybookFile: the name of the playbook. Example: example.yml.
TokenInfo: the token that is used to download the playbook. This parameter is required only if you download the playbook from GitHub.
Hosts: the hosts that are used to run the playbook.
InstallDependencies: specifies whether to install the dependencies of Ansible. If you turn on the switch, OOS installs Ansible and its dependencies from Python Package Index (PyPI). Python is also installed. If you turn off the switch, you need to verify whether Ansible and its dependencies are installed on the specified ECS instances.
WorkingDir: the directory in which the playbook is run.
Check: specifies whether to check the execution of Ansible.
ExtraVariables: the extra variables to be passed to Ansible when the playbook is run. Separate key-value pairs with spaces. Example: color=red flavour=lime.
Verbose: specifies how detailed the execution of the playbook is recorded. A value of -v indicates the low level, a value of -vv or -vvv indicates the medium level, and a value of -vvvv indicates the debugging level.
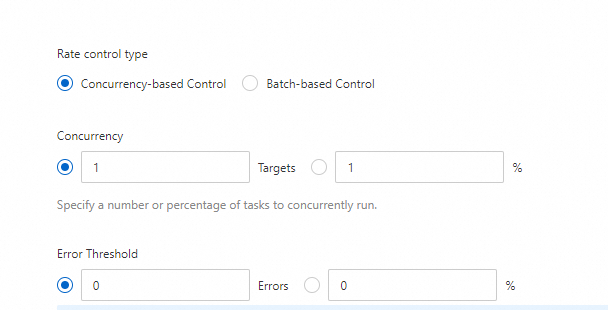
RateControl: the number of concurrent tasks.
Concurrency-based Control
Concurrency: the concurrency rate. You can specify a value or percentage. For example, a value of 1 indicates that the playbook is run on one instance each time.
Error Threshold: the maximum number or percentage of errors that are allowed before the specified task is stopped. The default value 0 indicates that only one error is allowed.
Batch-based Control
Batch Array: divides an execution into multiple batches of tasks. The tasks are run batch by batch. A batch of tasks does not start to run until the tasks of the previous batch finish running. You can specify an array that consists of numbers or percentages to specify batches. For example, [1, 5%, 10%] indicates that one task is run in the first batch, 5% of the total tasks are run in the second batch, and 10% of the total tasks are run in the third batch.