This topic describes how to use the SNAT and DNAT features of a Virtual Private Cloud
(VPC) NAT gateway and an Express Connect circuit to enable a data center and a VPC
to communicate with each other by using static private IP addresses.
Scenario
The following scenario is used in this topic. An enterprise has created a VPC and
vSwitches in the China (Shanghai) region. Elastic Compute Service (ECS) instances
are deployed in the vSwitches. The data center of the enterprise is connected to Alibaba
Cloud through a virtual border router (VBR) and an Express Connect circuit. The VPC
can communicate with the data center by using Cloud Enterprise Network (CEN). The
enterprise requires the ECS instances in the VPC to communicate with the data center
by using a static private IP address.
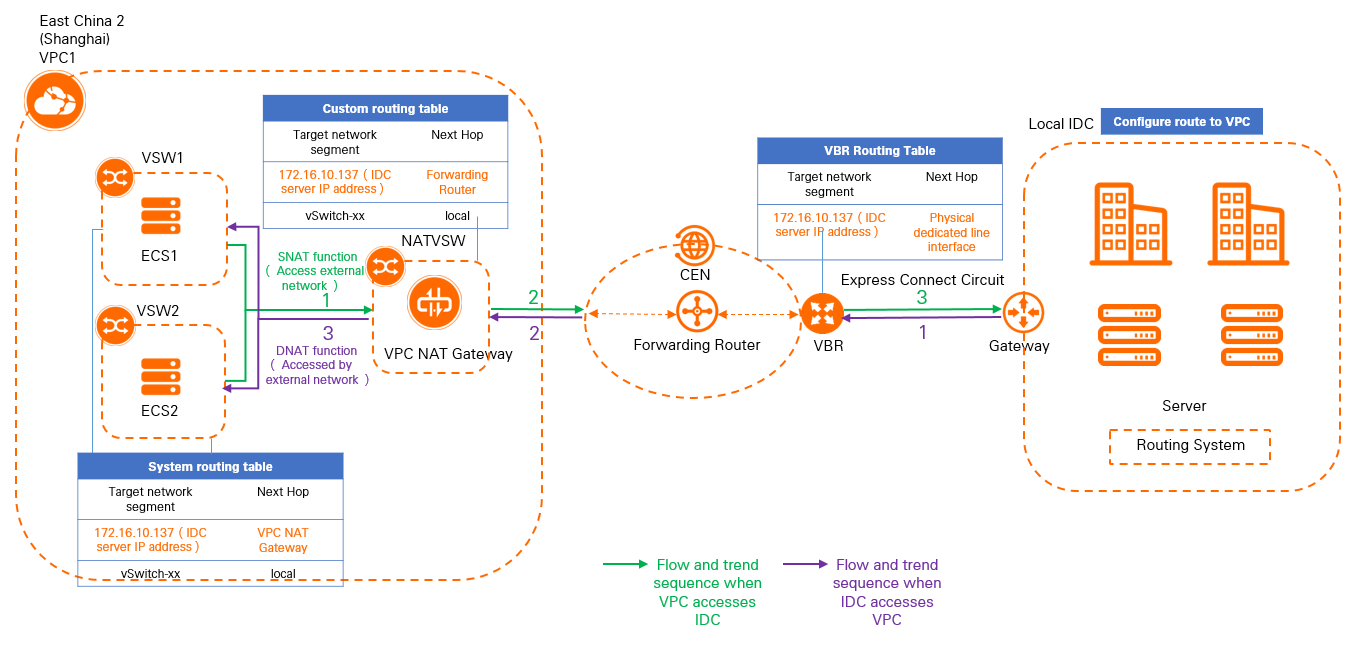
The preceding requirement can be met by using the DNAT and SNAT features of a VPC
NAT gateway. The following table describes how networks are planned in this example.
You can plan CIDR blocks based on your business requirements. Make sure that the CIDR
blocks do not overlap with each other.
| Item |
IP address/CIDR block |
| VPC1 CIDR block |
192.168.0.0/16 |
| vSwitch CIDR blocks |
- VSW1: 192.168.10.0/24
- VSW2: 192.168.20.0/24
- NATVSW: 192.168.3.0/24
|
| IP addresses of the ECS instances |
- ECS1: 192.168.10.55
- ECS2: 192.168.20.30
|
| CIDR block of the data center |
172.16.0.0/12 |
| IP address of the server in the data center |
172.16.10.137 |
| Peer IP addresses |
- VBR: 10.0.0.2/30
- Data center: 10.0.0.1/30
|
Prerequisites
- A VPC named VPC1 is created in the China (Shanghai) region and two vSwitches named
VSW1 and VSW2 are created in VPC1. VSW1 is deployed in Zone F and VSW2 is deployed
in Zone G. For more information, see Create and manage a VPC.
Note Before you connect an Enterprise Edition transit router to a VPC, make sure that the
VPC has at least one vSwitch in a zone that supports Enterprise Edition transit routers.
The vSwitch must have at least one idle IP address. In this example, the transit router
is created in the China (Shanghai) region. Shanghai Zone F and Shanghai Zone G support
Enterprise Edition transit routers.
- A transit vSwitch named NATVSW is created in VPC1. NATVSW is deployed in Zone H.
- Two ECS instances named ECS1 and ECS2 are created in VSW1 and VSW2. Applications are
deployed on ECS1 and ECS2. For more information, see Create an instance by using the wizard.
- An Express Connect circuit and a VBR are created. For more information, see Create and manage a dedicated connection over an Express Connect circuit and Create a VBR.
- A CEN instance is created. For more information, see Create a CEN instance.
- An Enterprise Edition transit router is created in the region where the VPC resides.
For more information about, see Create a transit router.
Procedure

Step 1: Connect the transit router to the VPC and the VBR
Connect the transit router in the China (Shanghai) region to the VBR that is associated
with the Express Connect circuit. Then, connect the transit router to the VPC that
you want to connect to the data center. This way, the VPC and the data center can
communicate with each other.
Step 2: Configure VBR routes
Add a route to the VBR. The route must point to the data center.
- Log on to the Express Connect console.
- In the top navigation bar, select the region and click Virtual Border Routers (VBRs) in the left-side navigation pane.
- On the Virtual Border Routers (VBRs) page, find the VBR that you want to manage and click its ID.
- On the details page of the VBR, click the Routes tab and click Add Route.
- In the Add Route Entry panel, set the following parameters and click OK.
| Parameter |
Description |
| Next Hop Type |
Select the next hop type. In this example, Physical Connection Interface is selected.
|
| Destination CIDR Block |
In this example, 172.16.10.137 is used, which is the IP address of the server in the data center.
|
| Next Hop |
Select the interface of the Express Connect circuit. |
Step 3: Create a VPC NAT gateway
- Log on to the NAT Gateway console.
- In the left-side navigation pane, choose .
- On the VPC NAT Gateway page, click Create VPC NAT Gateway.
- On the VPC NAT Gateway (Pay-As-You-Go) page, set the following parameters and click Buy Now.
| Parameter |
Description |
| Region |
Select the region where you want to create the VPC NAT gateway. In this example, China (Shanghai) is selected.
|
| VPC ID |
Select the VPC to which the VPC NAT gateway belongs. After you create a VPC NAT gateway,
you cannot change the VPC to which it belongs. In this example, VPC1 is selected.
|
| Zones |
Select the zone to which the VPC NAT gateway belongs. In this example, Zone H, the zone where NATVSW is deployed, is selected.
|
| vSwitch ID |
Select the vSwitch to which the VPC NAT gateway belongs. In this example, NATVSW is
selected.
|
| Name |
Enter a name for the VPC NAT gateway.
The name must be 1 to 128 characters in length. In this example, VPC_NATGW is used.
|
| Service-linked Role |
Displays whether a service-linked role is created for the VPC NAT gateway.
If this is your first time using an Internet NAT gateway or a VPC NAT gateway, you
must click Create Service-linked Role to create a service-linked role.
|
- On the Confirm Order page, confirm the information, select the Terms of Service check box, and then click
Activate Now.
When the message Order complete. appears, it indicates that the VPC NAT gateway is created.
Step 4: Add a route to the system route table of VPC1
Add a route to the system route table of VPC1. The route must point to the VPC NAT
gateway.
- Log on to the VPC console.
- On the VPCs page, find VPC1 and click its ID.
- On the details page, click the Resources tab and click the number below Route Table.
- On the Route Tables page, find the route table whose Route Table Type is System and click its ID.
- On the details page of the route table, choose , and click Add Route Entry.
- In the Add Route Entry panel, set the following parameters and click OK.
| Parameter |
Description |
| Name |
Enter a name for the route. In this example, VPCENTRY is used.
|
| Destination CIDR Block |
Enter the destination CIDR block. In this example, 172.16.10.137 is used, which is the IP address of the server in the data center.
|
| Next Hop Type |
Select the next hop type. In this example, NAT Gateway is selected.
|
| NAT Gateway |
Select a NAT gateway. In this example, the VPC NAT gateway is selected. |
Step 5: Create a custom route table and add a route
Create a custom route table for NATVSW and add a route that points to the transit
router.
For more information about regions that support custom route tables, see Regions that support custom route tables.
- Log on to the VPC console.
- In the left-side navigation pane, click Route Tables.
- In the top navigation bar, select the region to which the route table belongs.
- Perform the following operations to create a custom route table and associate the
route table with NATVSW:
- On the Route Tables page, click Create Route Table.
- On the Create Route Table page, set the following parameters and click OK.
| Parameter |
Description |
| Resource Group |
Select the resource group to which the route table belongs. In this example, All is selected.
|
| VPC |
Select the VPC to which the route table belongs. In this example, VPC1 is selected.
|
| Name |
Enter a name for the route table. In this example, NATVTB is used.
|
| Description |
Enter a description for the route table. In this example, Custom is used.
|
- Click the Associated vSwitch tab and click Associate vSwitch.
- In the Associate vSwitch dialog box, select the vSwitch that you want to associate and click OK.
In this example, NATVSW is selected.
- Perform the following steps to add a route to the custom route table:
- On the Route Tables page, find the custom route table and click its ID.
- Choose , and click Add Route Entry.
- In the Add Route Entry panel, set the following parameters and click OK.
| Parameter |
Description |
| Name |
Enter a name for the route. In this example, VPCNATENTRY is used.
|
| Destination CIDR Block |
Enter the destination CIDR block. In this example, 172.16.10.137 is used, which is the IP address of the server in the data center.
|
| Next Hop Type |
Select the next hop type. Transit Router is selected in this example.
|
| Transit Router |
Select a transit router. In this example, the VPC1 connection that you create on the
transit router is selected.
|
Step 6: Create an SNAT entry and a DNAT entry by using the default NAT IP address
Create an SNAT entry for the ECS instance to enable the ECS instance to access the
data center. Create a DNAT entry for the ECS instance to enable the data center to
access the ECS instance.
- Log on to the NAT Gateway console.
- In the left-side navigation pane, choose .
- In the top navigation bar, select the region where you want to create the NAT gateway.
- Perform the following operations to create an SNAT entry:
- On the VPC NAT Gateway page, find the VPC NAT gateway that you want to manage and click SNAT Management in the Actions column.
- On the SNAT Management tab, click Create SNAT Entry.
- On the Create SNAT Entry page, set the following parameters and click OK.
| Parameter |
Description |
| SNAT Entry |
Specify whether to create an SNAT entry for a VPC, a vSwitch, an ECS instance, or
a custom CIDR block. In this example, Specify vSwitch is selected. Then, the vSwitch to which the ECS instance belongs is selected from
the Select vSwitch drop-down list. In this example, VSW1 is selected. The vSwitch CIDR Block section displays the CIDR block of VSW1.
|
| Select NAT IP Address |
Select the NAT IP address that is used to access external private networks. The default
NAT IP address is selected in this example.
|
| Entry Name |
Enter a name for the SNAT entry. |
- Return to the VPC NAT Gateway page and perform the following operations to create a DNAT entry:
- On the VPC NAT Gateway page, find the VPC NAT gateway that you want to manage and click DNAT Management in the Actions column.
- On the DNAT Management tab, click Create DNAT Entry.
- On the Create DNAT Entry page, set the following parameters and click OK.
| Parameter |
Description |
| Select NAT IP Address |
Select the NAT IP address that is used to receive requests from external private networks.
The default NAT IP address is selected in this example.
|
| Select Private IP Address |
Specify the private IP address of the ECS instance that uses the DNAT entry to communicate
with external networks. In this example, Select by ECS or ENI is selected and the private IP address of ECS1 is selected.
|
| Port Settings |
Select a DNAT mapping method. Port mapping is used in this example. Select Specific Port, enter 22 for Frontend Port, enter 22 for Backend Port, and then select TCP for Protocol Type.
|
| Entry Name |
Enter a name for the DNAT entry. |
Step 7: Add a route to the on-premises gateway device
After you complete the preceding steps, you must add a route that points to the VPC
to the on-premises gateway device.
Add the following route that points to the VPC to the on-premises gateway device:
Note The route is for reference only. The actual route may vary based on the gateway device
vendor.
ip route 192.168.0.0 255.255.0.0 10.0.0.2
Step 8: Test the connectivity
Test whether the ECS instances can communicate with the data center.
- Log on to ECS1 in VSW1. For more information, see Connection methods.
- Ping the
IP address of the server in the data center to check whether ECS1 can access the server in the data center. In this example, the following command is used:
ping 172.16.10.137
If you can receive echo reply packets, it indicates that the connection is established.
- Log on to the server in the data center and run the
ssh root@NAT IP command. Before you run this command, replace NAT IP with the default NAT IP address
specified in the VPC NAT gateway. Then, enter the password that is used to log on
to ECS1 to check whether the server can access ECS1. In this example, the following command is used:
ssh 192.168.3.132
If you can receive echo reply packets, it indicates that the connection is established.

