If you use a self-built task scheduling system based on the open source XXL-JOB, you may face challenges such as complex task configuration, inefficient execution, and difficult monitoring. Alibaba Cloud provides an open source solution that supports scheduled task scheduling and task sharding. This solution lets you quickly connect your self-built scheduled tasks to a task scheduling platform.
Prerequisites
A RAM user must have the required RAM permissions for XXL-JOB. For more information, see Authorize SchedulerX (XXL-JOB Edition).
Create an XXL-JOB instance. For more information, see Create an instance.
Overview of the solution
This solution describes how to use an SDK to connect Java, Go, and Python applications to MSE XXL-JOB for scheduling and executing scheduled tasks.
You implement the business logic for scheduled tasks in your code and expose a task component identified as a Bean. In the console, you then configure the name of this Bean to trigger the corresponding task logic.
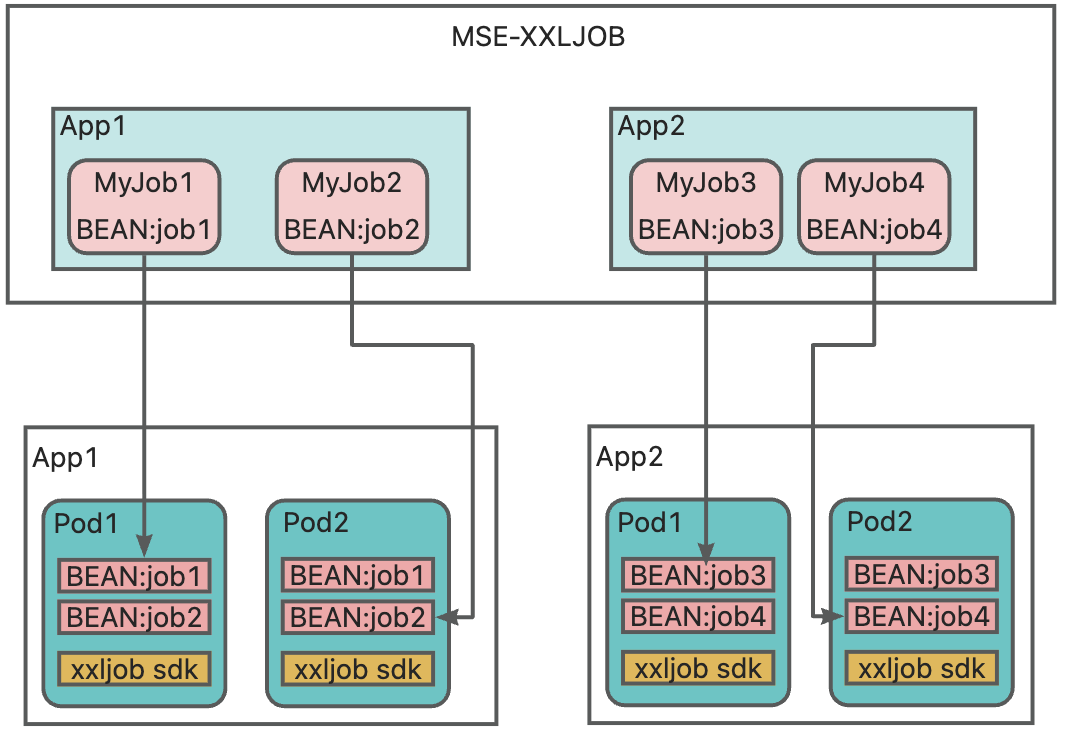
This solution includes the following steps:
Create an application: Create an application to centrally manage scheduled tasks. This improves management efficiency by making it easier to view, configure, and schedule tasks.
Develop and deploy the application: Write the code for the scheduled task, build a Docker image, and upload the image to an Alibaba Cloud image repository. This enables containerized management and deployment of the application.
Test and verify: Ensure that the connected application can be automatically scheduled and managed on the XXL-JOB platform, and that tasks execute accurately and on schedule.
Step 1: Create an application
Log on to the MSE XXL-JOB console and select a region from the top menu bar.
Click the target instance to go to its details page. In the navigation pane on the left, choose , and then click Create Application. Enter an AppName and a Name. Use the system-generated AccessToken and click OK.
Step 2: Develop and deploy the application
1. Develop an XXL-JOB task
SchedulerX (XXL-JOB Edition) supports connections from Java, Go, and Python applications. For more information, see the open source XXL-JOB demo projects:
Java version: xxl-job-executor-sample-springboot.
Go version: xxl-job-executor-go.
Python version: xxl-job-executor-python.
Java
Environment configuration: In your pom.xml file, add the Maven dependency for
xxl-job-core. For version details, see xxl-job-executor-sample-springboot.<!-- xxl-job-core --> <dependency> <groupId>com.xuxueli</groupId> <artifactId>xxl-job-core</artifactId> <version>2.2.x</version> </dependency>Initialize the executor.
@Configuration public class XxlJobConfig { private Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(XxlJobConfig.class); @Value("${xxl.job.admin.addresses}") private String adminAddresses; @Value("${xxl.job.accessToken}") private String accessToken; @Value("${xxl.job.executor.appname}") private String appname; @Value("${xxl.job.executor.address}") private String address; @Value("${xxl.job.executor.ip}") private String ip; @Value("${xxl.job.executor.port}") private int port; @Value("${xxl.job.executor.logpath}") private String logPath; @Value("${xxl.job.executor.logretentiondays}") private int logRetentionDays; @Bean public XxlJobSpringExecutor xxlJobExecutor() { logger.info(">>>>>>>>>>> xxl-job config init."); XxlJobSpringExecutor xxlJobSpringExecutor = new XxlJobSpringExecutor(); xxlJobSpringExecutor.setAdminAddresses(adminAddresses); xxlJobSpringExecutor.setAppname(appname); xxlJobSpringExecutor.setAddress(address); xxlJobSpringExecutor.setIp(ip); xxlJobSpringExecutor.setPort(port); xxlJobSpringExecutor.setAccessToken(accessToken); xxlJobSpringExecutor.setLogPath(logPath); xxlJobSpringExecutor.setLogRetentionDays(logRetentionDays); return xxlJobSpringExecutor; } }Write the task execution code. The following example uses version 2.2.x.
NoteThe XXL-JOB APIs vary by version. For more information, see the open source demo project.
@Component public class SampleXxlJob { private static Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(SampleXxlJob.class); @XxlJob("helloworld") public ReturnT<String> helloworld(String param) throws Exception { XxlJobLogger.log("XXL-JOB, Hello World, start..."); for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) { XxlJobLogger.log("beat at:" + i); TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(2); } System.out.println("XXL-JOB, Hello World, finished"); return ReturnT.SUCCESS; } }
Golang
Environment configuration: Run the following command to pull the Go version of the XXL-JOB SDK using the latest tag. For version details, see xxl-job-executor-go.
go get github.com/xxl-job/xxl-job-executor-go@{latest_tag}Write the executor initialization code.
package main import ( "context" "fmt" xxl "github.com/xxl-job/xxl-job-executor-go" "github.com/xxl-job/xxl-job-executor-go/example/task" "log" ) func main() { exec := xxl.NewExecutor( xxl.ServerAddr("xxxxxx"), // Request address. Obtain this from the connection configuration in the Application Management section of the console. xxl.AccessToken("xxxxxxx"), // Request token. Obtain this from the connection configuration in the Application Management section of the console. xxl.ExecutorPort("9999"), // Default is 9999 (optional). xxl.RegistryKey("golang-jobs"), // Executor name. xxl.SetLogger(&logger{}), // Custom logger. ) exec.Init() exec.Use(customMiddleware) // Set the log view handler. exec.LogHandler(customLogHandle) // Register the task handler. exec.RegTask("task.test", task.Test) exec.RegTask("task.shardingTest", task.ShardingTest) log.Fatal(exec.Run()) } // Custom log handler. func customLogHandle(req *xxl.LogReq) *xxl.LogRes { return &xxl.LogRes{Code: xxl.SuccessCode, Msg: "", Content: xxl.LogResContent{ FromLineNum: req.FromLineNum, ToLineNum: 2, LogContent: "This is a custom log handler", IsEnd: true, }} } // Implementation of the xxl.Logger interface. type logger struct{} func (l *logger) Info(format string, a ...interface{}) { fmt.Println(fmt.Sprintf("Custom log - "+format, a...)) } func (l *logger) Error(format string, a ...interface{}) { log.Println(fmt.Sprintf("Custom log - "+format, a...)) } // Custom middleware. func customMiddleware(tf xxl.TaskFunc) xxl.TaskFunc { return func(cxt context.Context, param *xxl.RunReq) string { log.Println("I am a middleware start") res := tf(cxt, param) log.Println("I am a middleware end") return res } }Write the task execution code.
package task import ( "context" "fmt" xxl "github.com/xxl-job/xxl-job-executor-go" ) func Test(cxt context.Context, param *xxl.RunReq) (msg string) { fmt.Println("test one task" + param.ExecutorHandler + " param:" + param.ExecutorParams + " log_id:" + xxl.Int64ToStr(param.LogID)) return "test done" } func ShardingTest(cxt context.Context, param *xxl.RunReq) (msg string) { fmt.Println("shardingId:" + xxl.Int64ToStr(param.BroadcastIndex) + ", shardingTotal:" + xxl.Int64ToStr(param.BroadcastTotal)) return "ShardingTest done" }
Python
Pull the dependencies. For version details, see xxl-job-executor-python.
pip install pyxxl # If logs need to be written to Redis pip install "pyxxl[redis]" # To load configurations from .env pip install "pyxxl[dotenv]" # Install all features pip install "pyxxl[all]"Write the task execution code.
import asyncio import time from pyxxl import ExecutorConfig, PyxxlRunner from pyxxl.ctx import g config = ExecutorConfig( xxl_admin_baseurl="http://xxljob-1b3fd81****.schedulerx.mse.aliyuncs.com/api/", executor_app_name="your-app-name", access_token="default_token", # If xxl-admin can directly connect to the executor's IP, you can leave executor_listen_host empty. # executor_listen_host="0.0.0.0", ) app = PyxxlRunner(config) @app.register(name="demoJobHandler") async def test_task(): # you can get task params with "g" g.logger.info("get executor params: %s" % g.xxl_run_data.executorParams) for i in range(10): g.logger.warning("test logger %s" % i) await asyncio.sleep(5) return "Success..." @app.register(name="sync_func") def test_task4(): # To view execution logs in xxl-admin, you must use g.logger for printing. By default, only logs of INFO level and above are printed. n = 1 g.logger.info("Job %s get executor params: %s" % (g.xxl_run_data.jobId, g.xxl_run_data.executorParams)) # If a sync task contains a loop, you must check g.cancel_event in each iteration to support the cancel operation. while n <= 10 and not g.cancel_event.is_set(): # If you do not need to view logs from xxl-admin, you can use your own logger. g.logger.info( "log to {} logger test_task4.{},params:{}".format( g.xxl_run_data.jobId, n, g.xxl_run_data.executorParams, ) ) time.sleep(2) n += 1 return "Success 3" if __name__ == "__main__": app.run_executor()
2. Deploy the application to Alibaba Cloud
SchedulerX (XXL-JOB Edition) supports only the Alibaba Cloud network. Therefore, you must deploy your application on Alibaba Cloud. The following example shows how to deploy a Java application to Container Service for Kubernetes (ACK).
The ACK cluster must be in the same VPC as the SchedulerX (XXL-JOB Edition) cluster.
In the root directory of the Spring Boot application, create a Dockerfile file.
# Replace with your own base image FROM reg.docker.alibaba-inc.com/xxx/xxxx-java:1.0-beta MAINTAINER your-name ENV JAVA_OPTS="" ADD target/xxl-job-executor-sample-springboot-*.jar /app.jar ENTRYPOINT ["sh","-c","java -jar $JAVA_OPTS /app.jar]Use Docker to build a Docker image and upload it to an Alibaba Cloud image repository.
docker login --username=xxx@aliyun.com registry.cn-hangzhou.aliyuncs.com --password=xxxxxx docker buildx build --platform linux/amd64 -t schedulerx-registry.cn-hangzhou.cr.aliyuncs.com/schedulerx3/xxljob-demo:2.4.1 . docker push schedulerx-registry.cn-hangzhou.cr.aliyuncs.com/schedulerx3/xxljob-demo:2.4.1In the navigation pane on the left, go to the page. In the Actions column for the target application, click Connection Configuration.
Log on to the ACK console and go to the destination cluster. In the navigation pane on the left, choose . In the upper-right corner, click Create from YAML to create a deployment. This example uses connection type 2 (restart the application using the -D parameter) for the connection configuration. Replace the JAVA_OPTS value in the YAML file to inject the JVM parameters as environment variables.

apiVersion: apps/v1 kind: Deployment metadata: name: xxljob-xueren-test labels: app: xxljob-xueren-test spec: replicas: 2 selector: matchLabels: app: xxljob-xueren-test template: metadata: labels: app: xxljob-xueren-test spec: containers: - name: xxljob-executor image: schedulerx-registry.cn-hangzhou.cr.aliyuncs.com/schedulerx3/xxljob-demo:2.4.1 ports: - containerPort: 9999 env: - name: JAVA_OPTS value: >- -Dxxl.job.admin.addresses=http://xxljob-xxxxx.schedulerx.mse.aliyuncs.com -Dxxl.job.executor.appname=xueren_test -Dxxl.job.accessToken=xxxxxxx
Step 3: Test and verify
1. Verify the executor connection
Go to the instance details page. In the navigation pane on the left, click Application Management. On the application list page, click the number in the executors column for the target application. You can view the addresses and online status of the connected executors.

2. Test and verify the task
Test a single-instance task
A single-instance task means that for each execution, one executor is selected from all executors in the application based on the routing policy to perform an idempotent execution.
In the navigation pane on the left, choose Task Management and click Create Task. First, complete the basic configurations. Enter a Task Name and a JobHandler Name. For Associated Application, select the target application. For Routing Policy, select Polling. Then, click Next.

Configure the Schedule. Set Time Type to cron. Click Use Generator to generate a Cron Expression. This example shows a task that is scheduled to run once a day at 12:00. Then, click Next.

Configure Notifications. You can configure timeout alarms, success notifications, failure alarms, notification methods, and notification recipients. This example uses the default console configurations.

After the task is created, click Run Once in the Actions column for the target task. In the manual execution dialog box, use the Specify a Machine option to select a machine, configure the Instance Parameters, and click OK.

Click to view the task execution records.
In the navigation pane on the left, click Execution List. In the Actions column for the target execution record, click Log to view the log records for this task execution.

Test a sharded broadcast task
A sharded broadcast task means that for each execution, the task is broadcast to all executors in the application. Each executor receives a different shard number, which can be used for distributed batch processing. The open source XXL-JOB does not have an aggregation feature for sharded broadcasts. SchedulerX (XXL-JOB Edition) can aggregate and display the status of all shards for each execution.
In the navigation pane on the left, choose Task Management and click Create Task. First, complete the basic configurations. Enter a Task Name and a JobHandler Name. For Associated Application, select the target application. For Routing Policy, select Sharded Broadcast. Then, click Next.

Configure the Schedule. Set Time Type to cron. Click Use Generator to generate a Cron Expression. This example shows a task that is scheduled to run at the 10th minute of every hour. Then, click Next.

Configure Notifications. You can configure timeout alarms, success notifications, failure alarms, notification methods, and notification recipients. This example uses the default console configurations.

After the task is created, click Run Once in the Actions column for the target task. In the manual execution dialog box, use the Specify a Machine option to select a machine, configure the Instance Parameters, and click OK.

Click to view the task execution records.
In the navigation pane on the left, click Execution List. On the task execution list page, click Details in the Actions column for the target task execution. In the Shard Details section, you can view the aggregated execution status of each machine.

For each shard, click Log in the Actions column for the specified shard to view the log records for this task execution.
