This topic describes how to perform a stress test for the maximum number of connections to multiple ApsaraDB for MongoDB replica set instances of different specifications. The test is conducted by accessing the ApsaraDB for MongoDB instances from an Elastic Compute Service (ECS) instance.
Test environment
Create an ECS instance and an ApsaraDB for MongoDB instance. For more information, see Create a replica set instance and Create an ECS instance.
The following table describes the configurations of the ECS instance and the ApsaraDB for MongoDB instance used in the test.
Configuration item | ECS Instance | ApsaraDB for MongoDB instance that uses cloud disks | ApsaraDB for MongoDB instance that uses local disks |
Region and zone | Beijing Zone H | Beijing Zone H | Beijing Zone H |
Network type | Virtual Private Cloud (VPC) | VPC | VPC |
Instance category | c6e, compute-optimized instance family with enhanced performance | General-purpose and dedicated | General-purpose and dedicated |
Instance type | ecs.c6e.2xlarge | Three available instance types. For more information, see Test results. | Two available instance types. For more information, see Test results. |
Storage type | Enterprise SSD (ESSD) AutoPL disks | ESSDs | Local SSDs |
Image or engine version | Alibaba Cloud Linux 3.2104 LTS 64-bit | 4.19.91-26.al7.x86_64 | 3.10.0-327.ali2017.alios7.x86_64 |
Kernel version | N/A |
|
|
The ApsaraDB for MongoDB instance used in the test adopts the three-node architecture that consists of a primary node, a secondary node, and a hidden node.
The ECS instance and the ApsaraDB for MongoDB instance used in the test are deployed in the same zone of the same region, and the average Round-Trip Time (RTT) is 0.103 ms.
Test tool
The open-source Yahoo Cloud Serving Benchmark (YCSB) 0.17.0 tool is used in the test.
NoteYCSB is a Java tool that can be used to benchmark the performance of multiple types of databases. For more information about how to install and use YCSB, see YCSB.
A custom connection stress testing program is used in the test. For more information, see Additional information about a stress test for 96,000 connections.
Test method
- Add the primary private IP address of the ECS instance to a whitelist of the ApsaraDB for MongoDB instance. For more information, see Modify an IP address whitelist for an instance. Note You can log on to the ECS console and view the Primary Private IP Address of the ECS instance in the Network Information section of the Instance Details page.
- Connect to the ECS instance. For more information, see Create and manage an ECS instance by using the ECS console (express version).
Use the YCSB tool to load test data.
// Run the ycsb run command. ./bin/ycsb.sh load mongodb -s -p workload=site.ycsb.workloads.CoreWorkload -p recordcount=10000000 -p mongodb.url="mongodb://test:****@dds-bp13e84d11****.mongodb.rds.aliyuncs.com:3717/admin" -p table=test -threads 8Modify the following settings:
recordcount=1000000: the total amount of data loaded to the ApsaraDB for MongoDB instance.mongodb.url="mongodb://test:****@dds-bp13e84d11****.mongodb.rds.aliyuncs.com:3717/admin": the connection string of the ApsaraDB for MongoDB instance. In the test, the database account is test and the database is admin.NoteYou can obtain the endpoint in the Internal Connections - VPC section of the Database Connections page in the ApsaraDB for MongoDB console.
threads 8: the number of concurrent threads on the client used in the test.
Run the following command to perform the performance stress test:
./bin/ycsb.sh run mongodb -s -p workload=site.ycsb.workloads.CoreWorkload -p recordcount=10000000 -p operationcount=5000000 -p readproportion=50 -p updateproportion=50 -p requestdistribution=zipfian -p mongodb.url="mongodb://test:****@dds-bp13e84d11****.mongodb.rds.aliyuncs.com:3717/admin&maxPoolSize=8000" -p table=test -threads 8000Modify the following settings:
recordcount=1000000: the total amount of data loaded to the ApsaraDB for MongoDB instance.operationcount=5000000: the total number of read and write operations.insertproportion=0: the ratio of load operations.readproportion=50: the ratio of read operations.updateproportion=50: the ratio of update operations.mongodb.url="mongodb://test:****@dds-bp13e84d11****.mongodb.rds.aliyuncs.com:3717/admin": the connection string of the ApsaraDB for MongoDB instance. In the test, the database account is test and the database is admin.NoteYou can obtain the endpoint in the Internal Connections - VPC section of the Database Connections page in the ApsaraDB for MongoDB console.
When you run the preceding command, you must configure the
maxPoolSizeparameter. Otherwise, the default number of connections is 100. In this case, theMongoWaitQueueFullExceptionerror is returned during the test, and the expected maximum number of connections cannot be reached.
View the monitoring information of the ApsaraDB for MongoDB instance used in the test. For more information, see Node monitoring (previously basic monitoring).
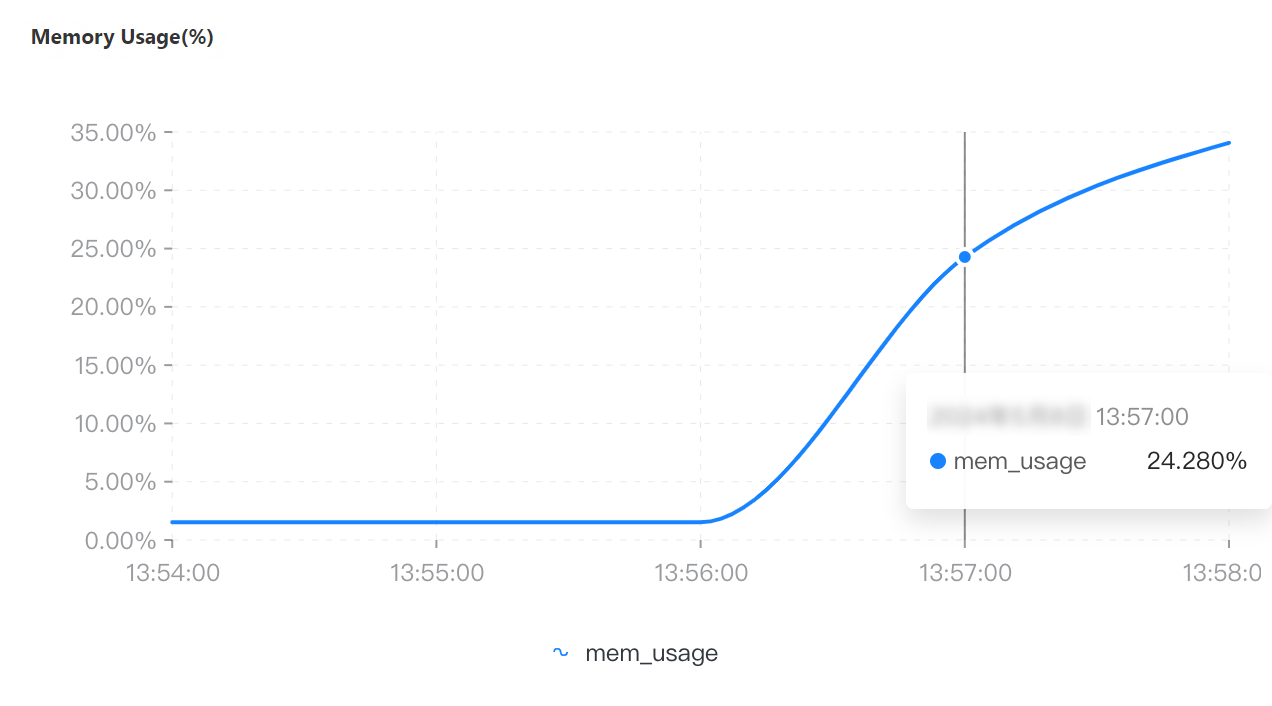
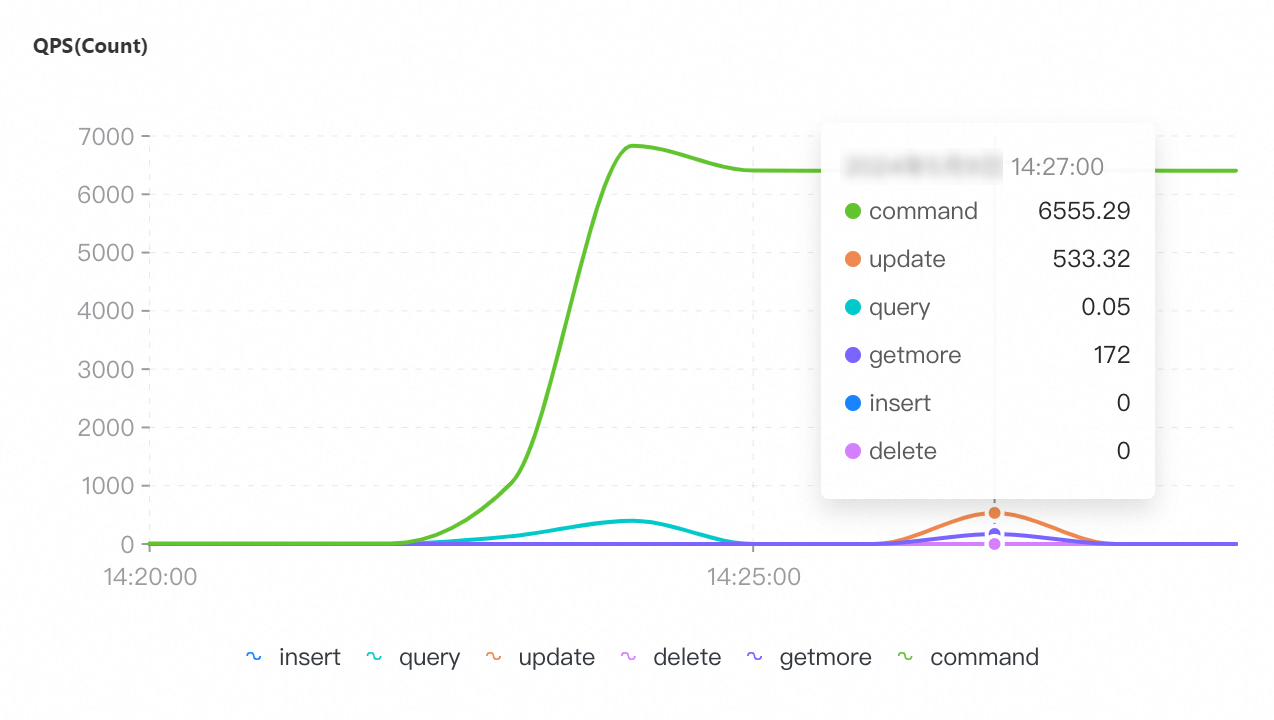
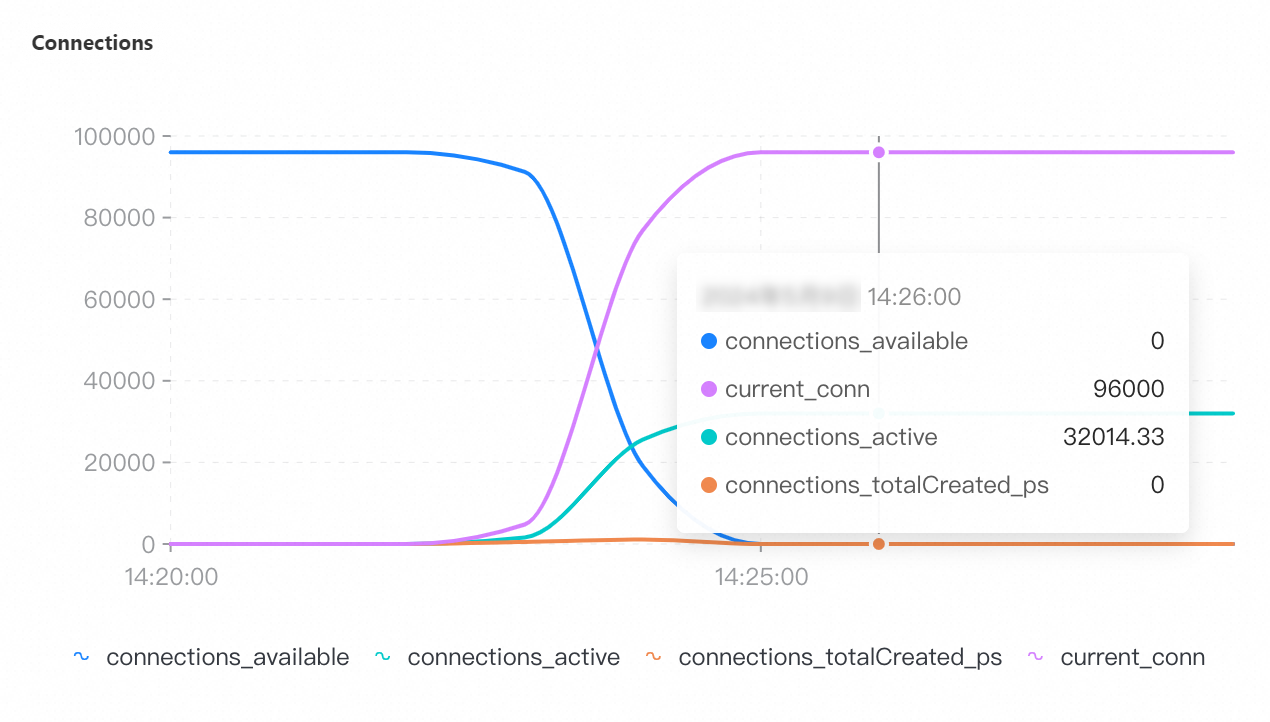
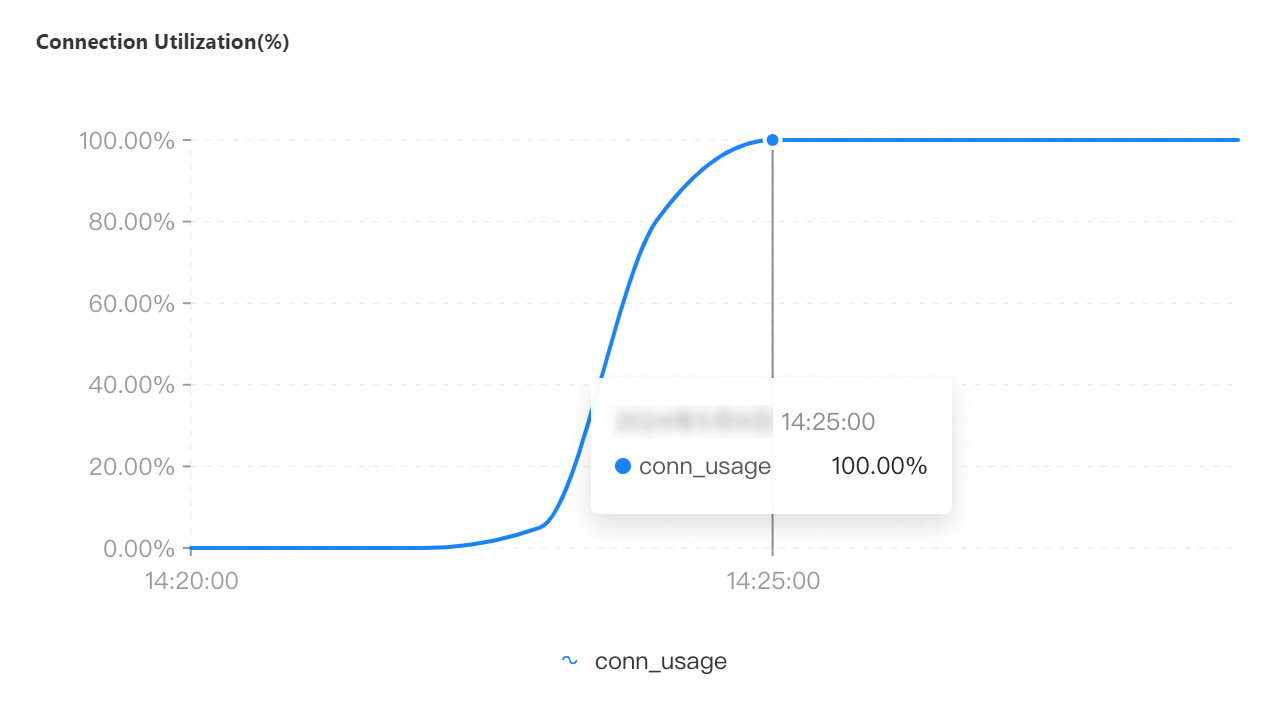
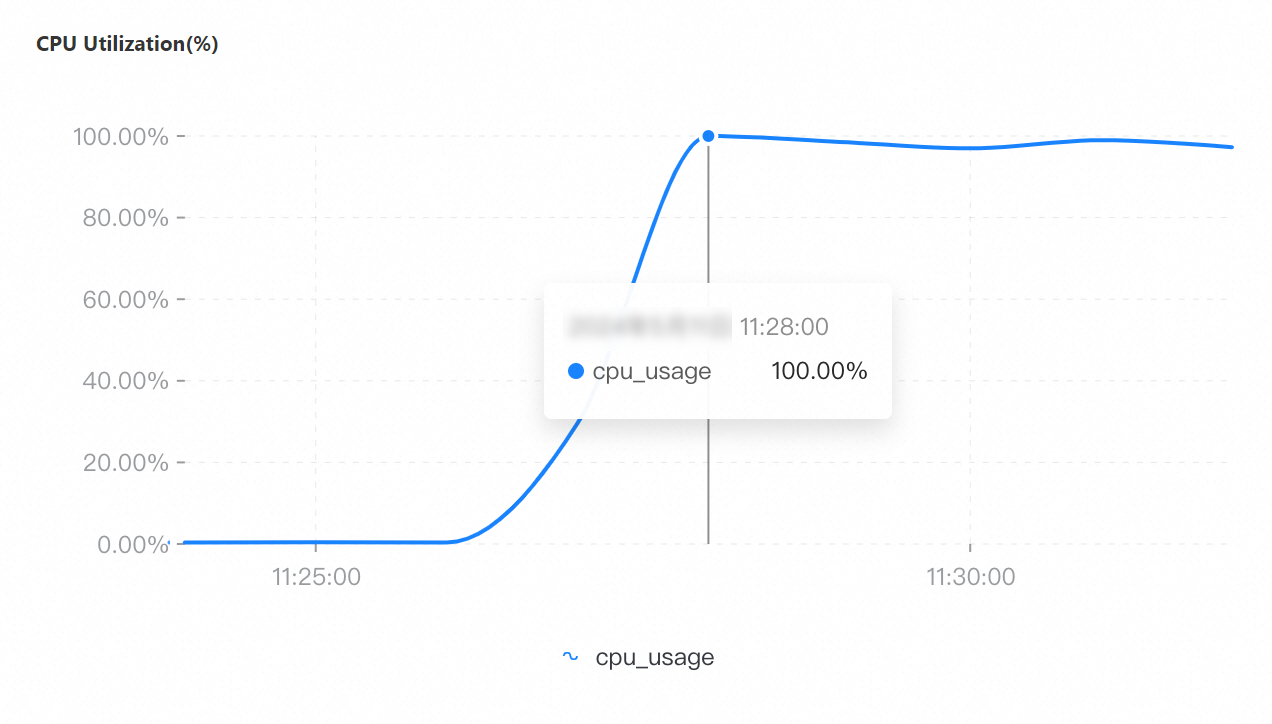
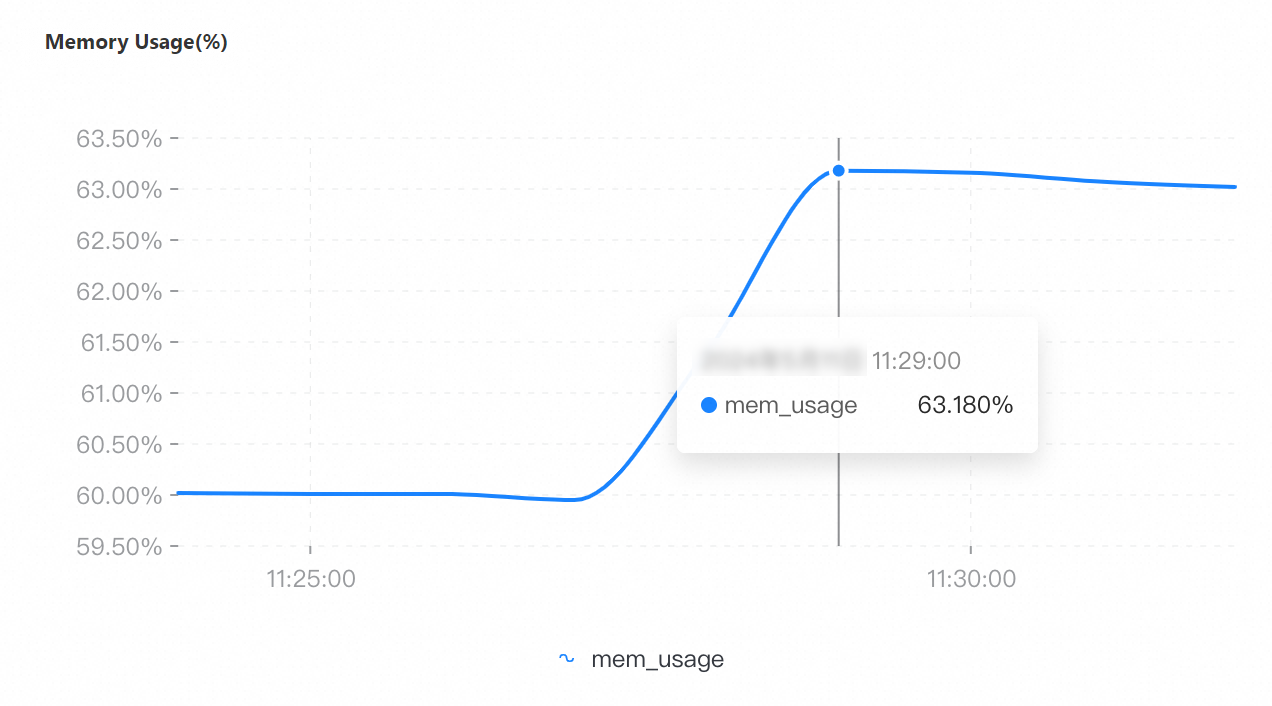
On the Node Monitoring tab, select the period of time corresponding to the test to view the CPU Utilization, Memory Usage, QPS, Connections, and Connection Utilization metrics.
Additional information about a stress test for 96,000 connections
A YCSB test depends on the Java environment. The maximum heap memory size of a Java virtual machine (JVM) is limited. If a test uses more than 20,000 concurrent threads, the Cannot allocate memory error is returned, which interrupts the test.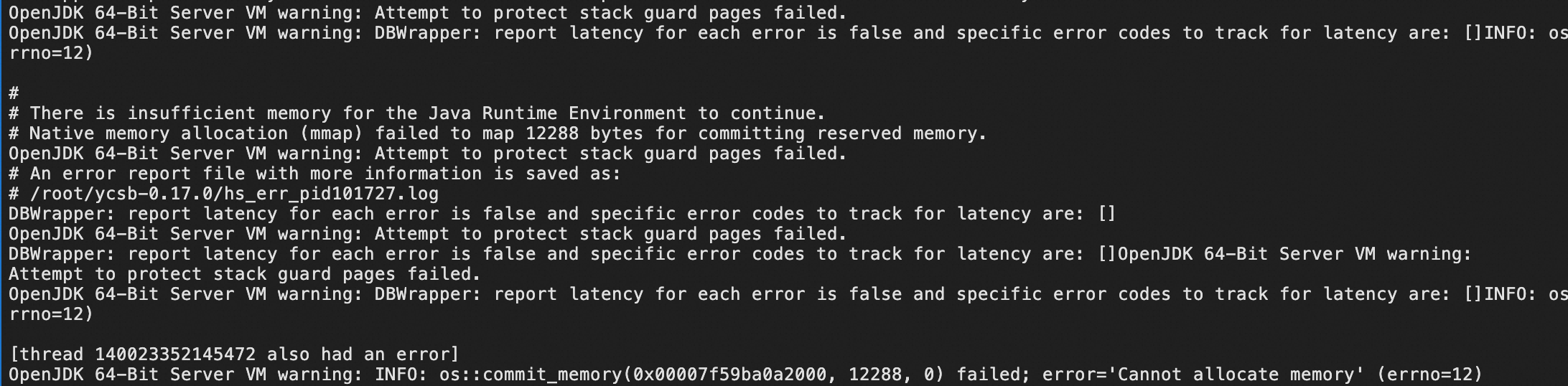
After you increase the value of the JAVA_OPTS parameter, the error still occurs. To resolve the issue, use a custom connection stress testing program. The stress testing program cyclically generates several threads. Each thread generates a MongoClient. After the MongoClient performs a query, the MongoClient maintains connections for a period of time without being released.
A single machine on which a stress testing client runs has a limited number of ports. Therefore, the machine cannot meet the requirements of stress testing for connections (up to 96,000 connections) with a specification of 32 cores and 128 GB of memory. In this case, you must run the same stress testing program on multiple machines.
Run the following Bash command to query the current port range of a machine:
sysctl net.ipv4.ip_local_port_rangeSample result:
net.ipv4.ip_local_port_range = 40000 65535Run the following command to expand the port range of a machine and then perform a connection stress test:
sudo sysctl -w net.ipv4.ip_local_port_range="10240 65535"Test results
Instance that uses ESSDs
Dedicated instance that has 4 cores and 8 GB of memory
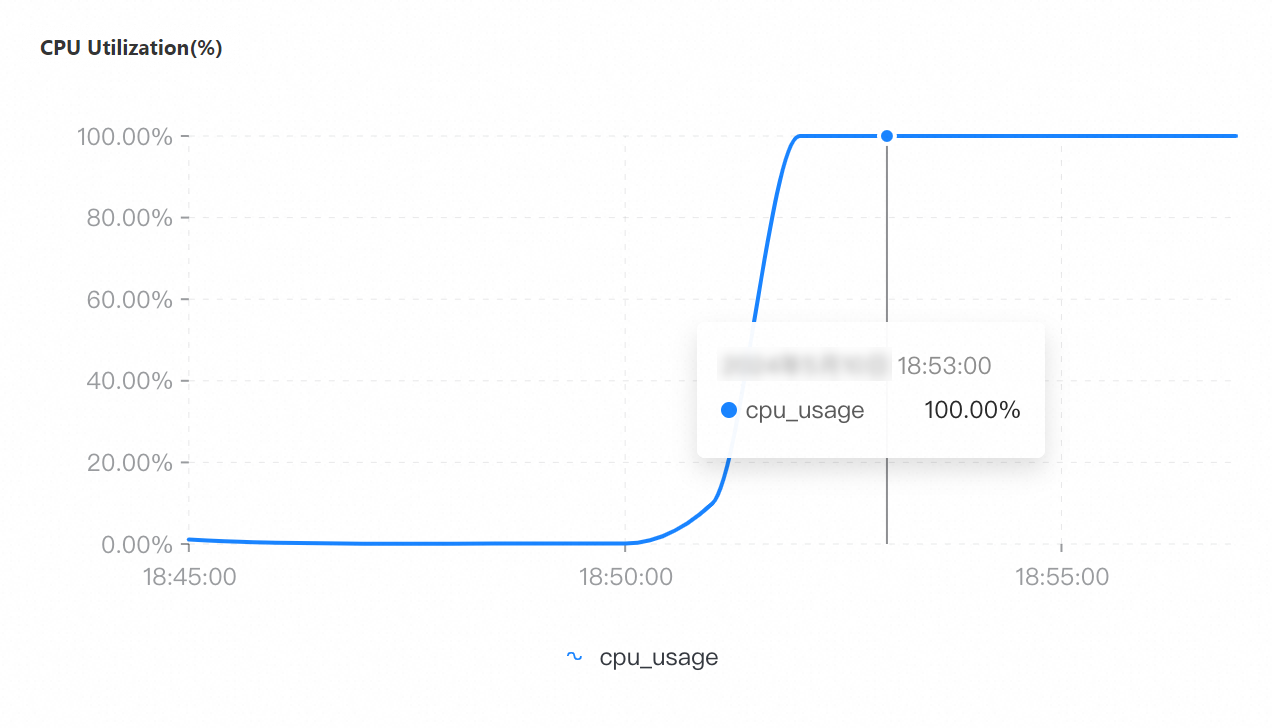
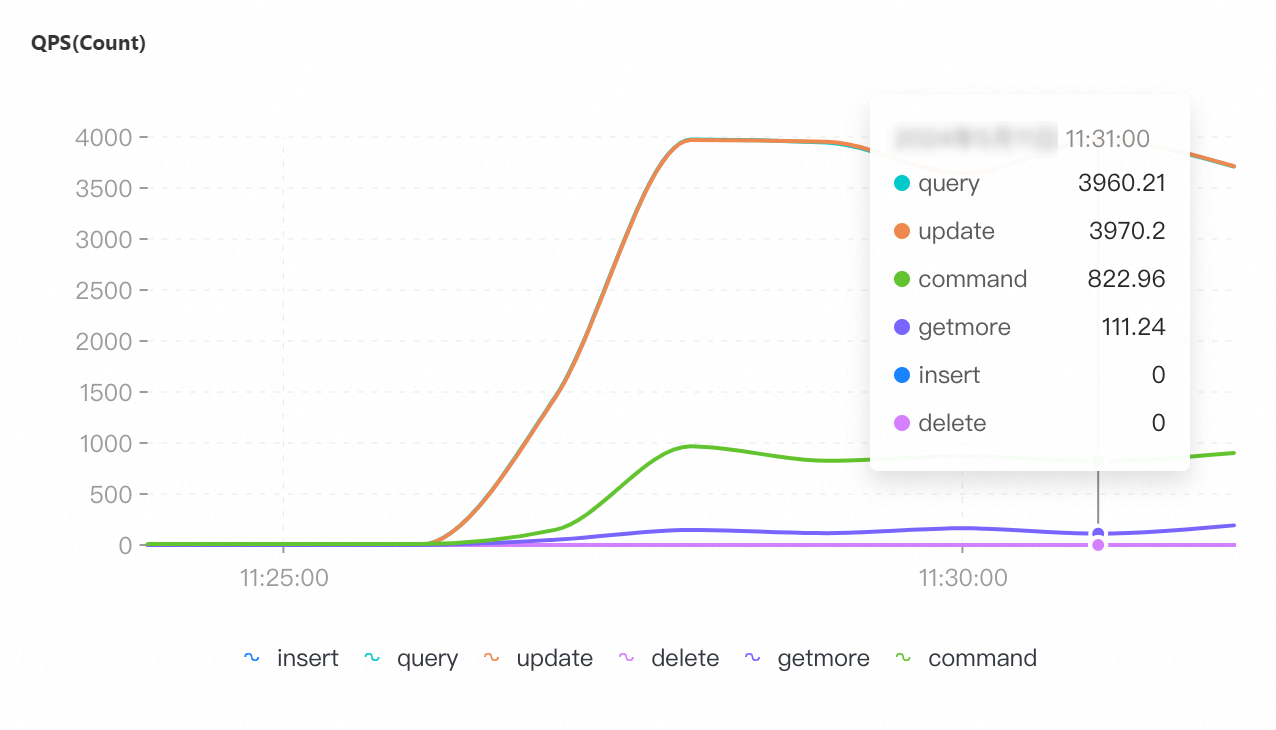
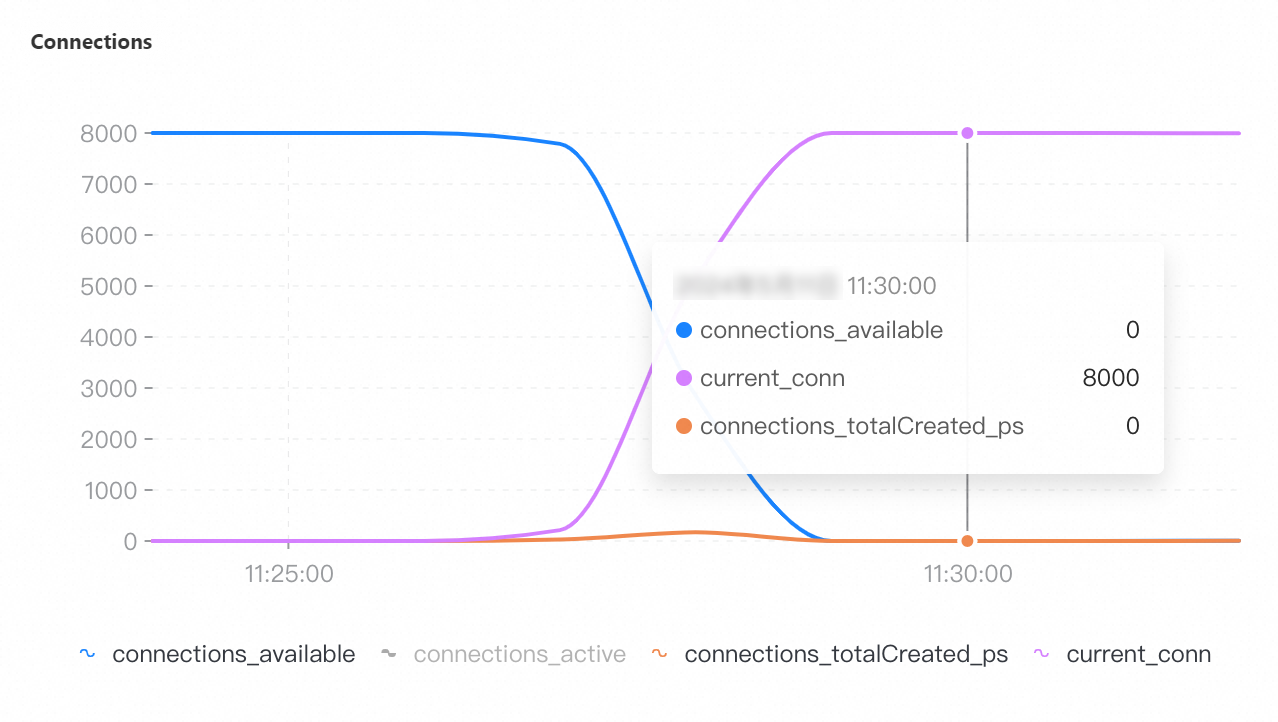
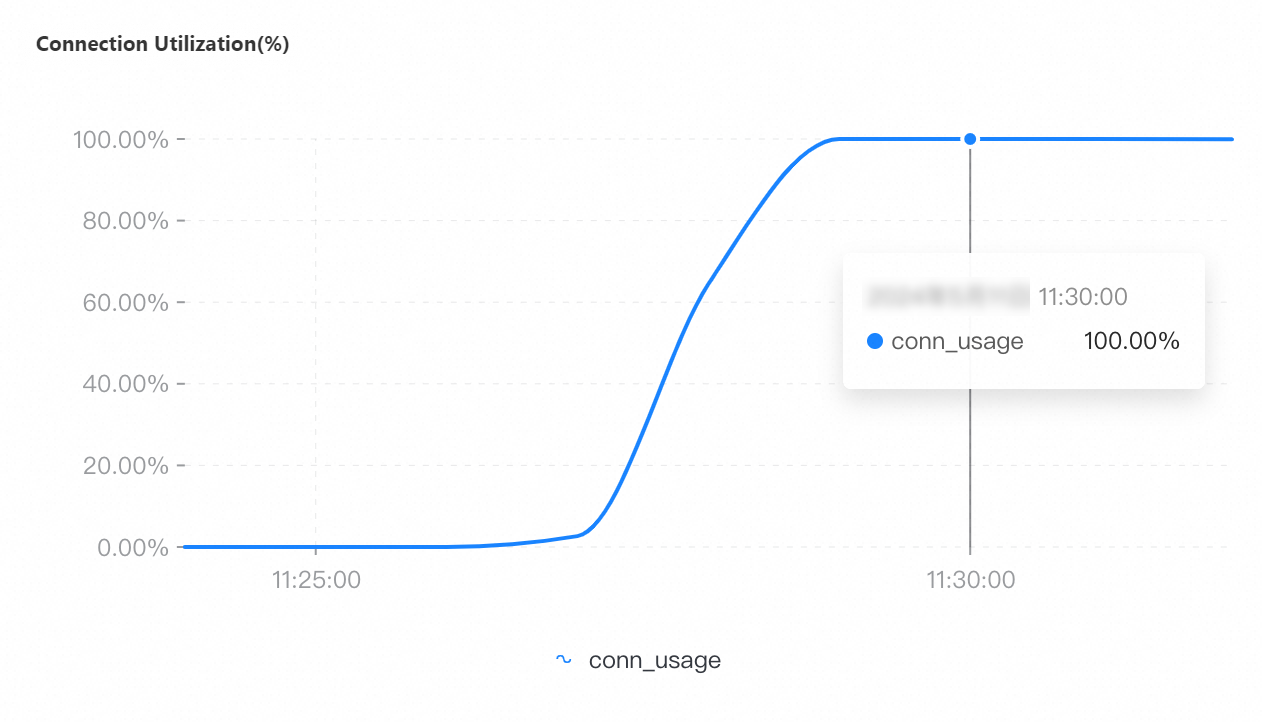
Maximum number of connections: 8,000
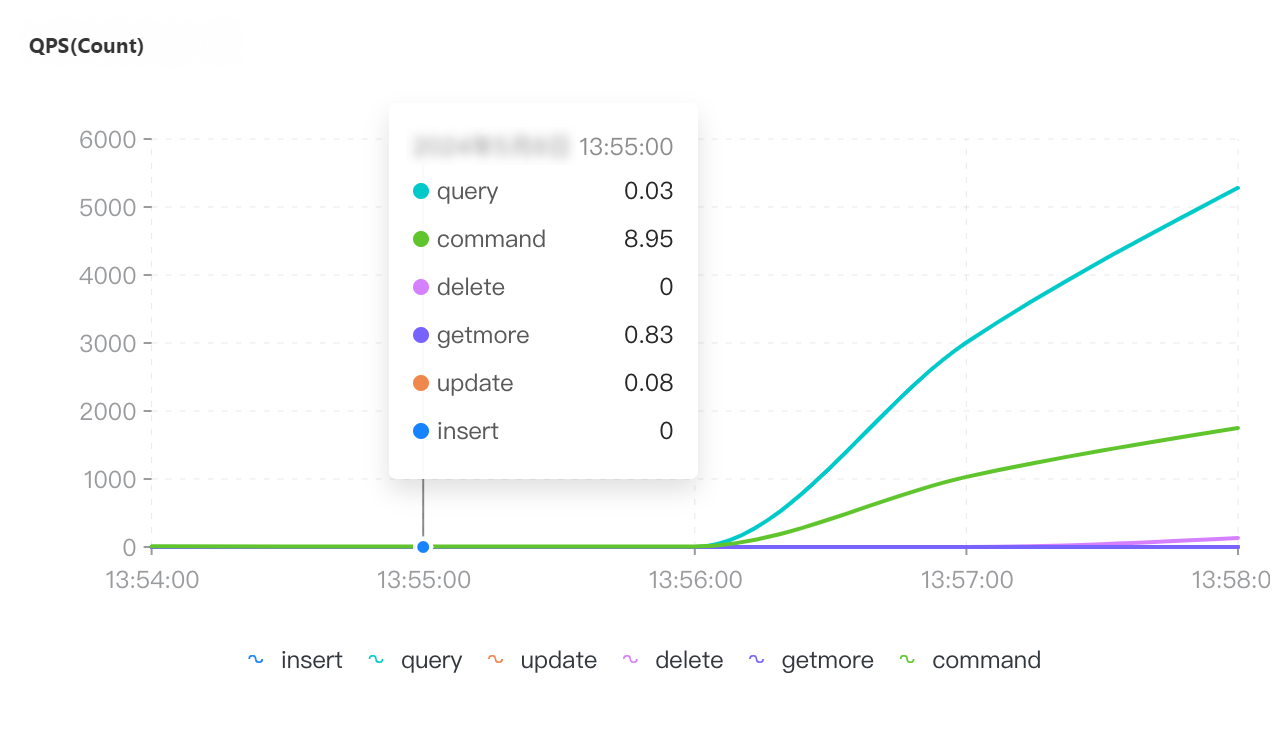
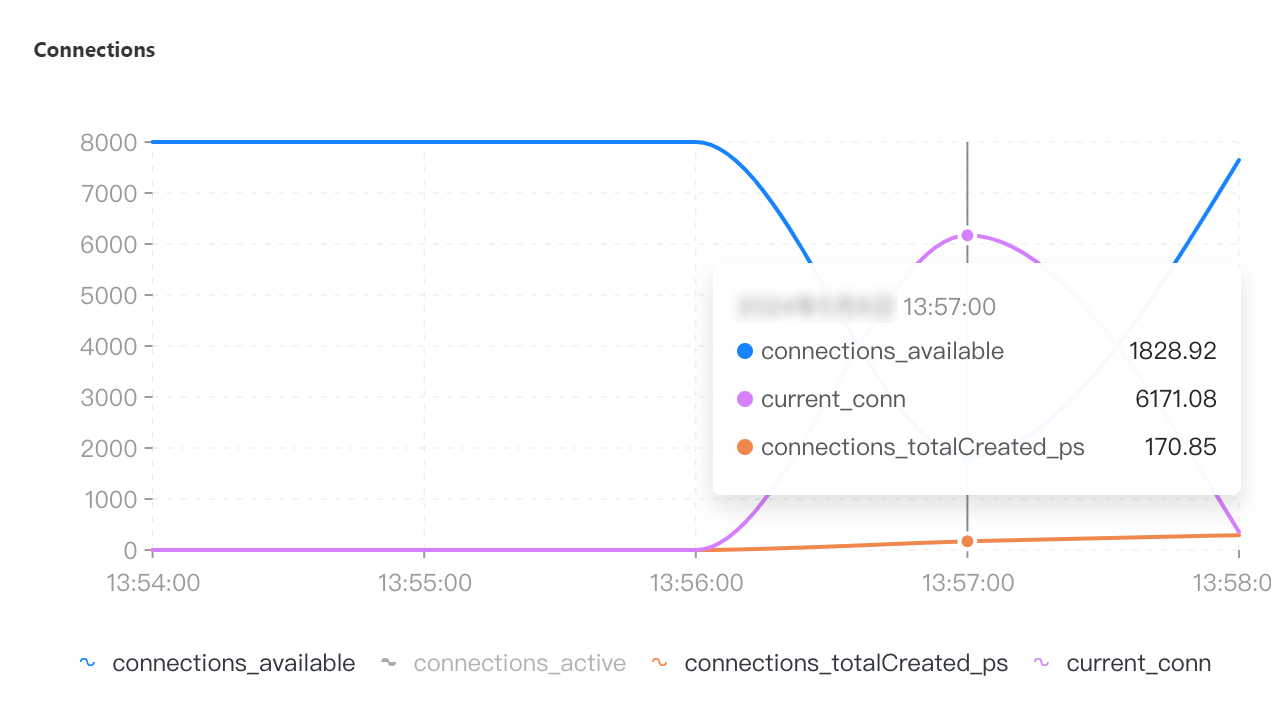
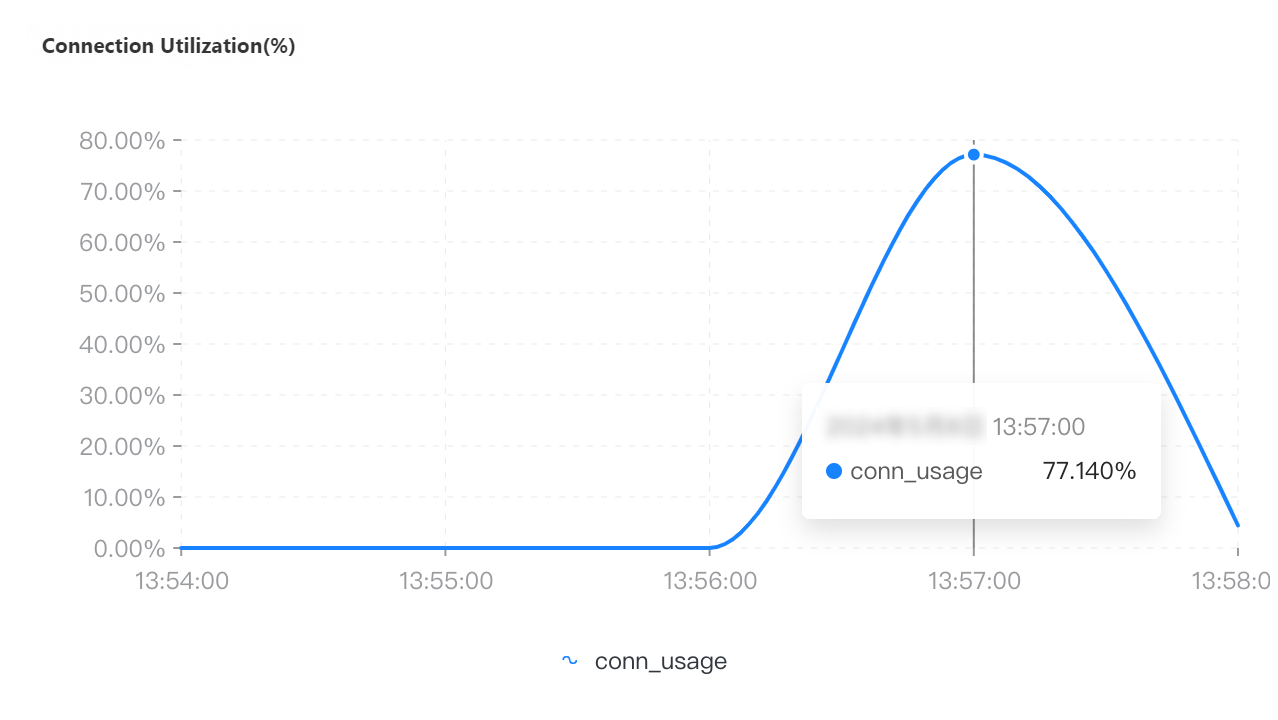
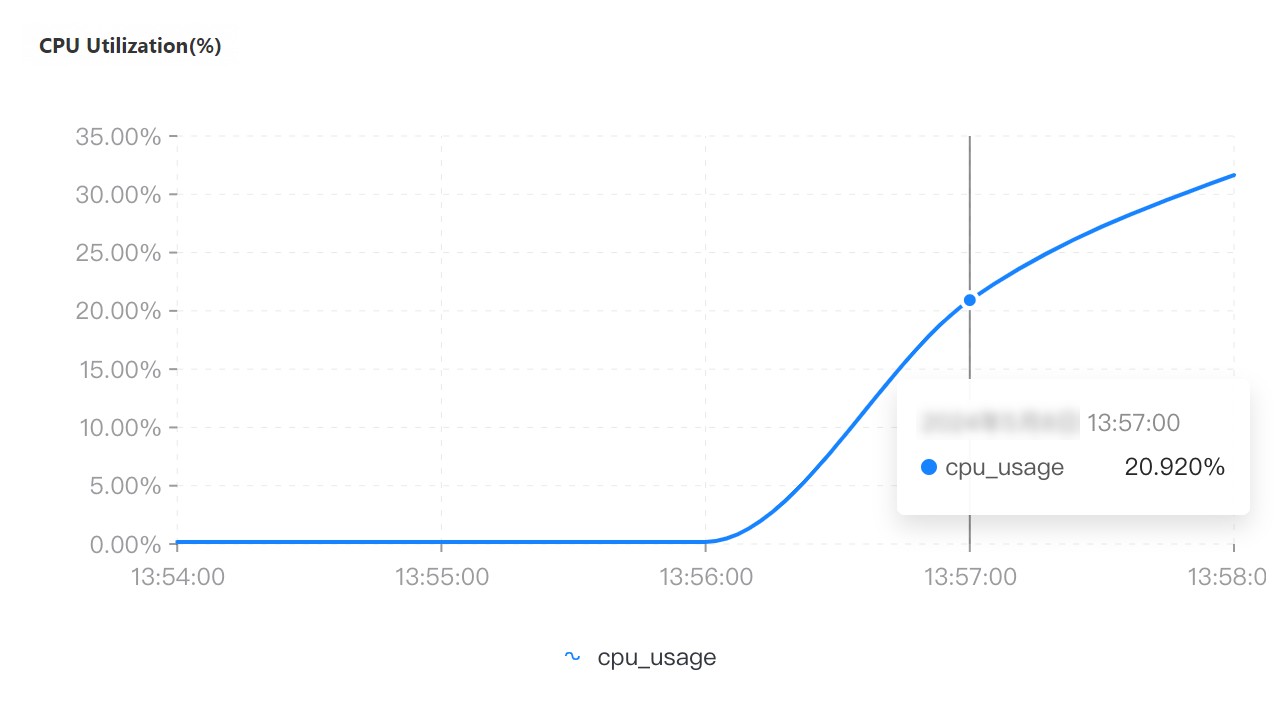
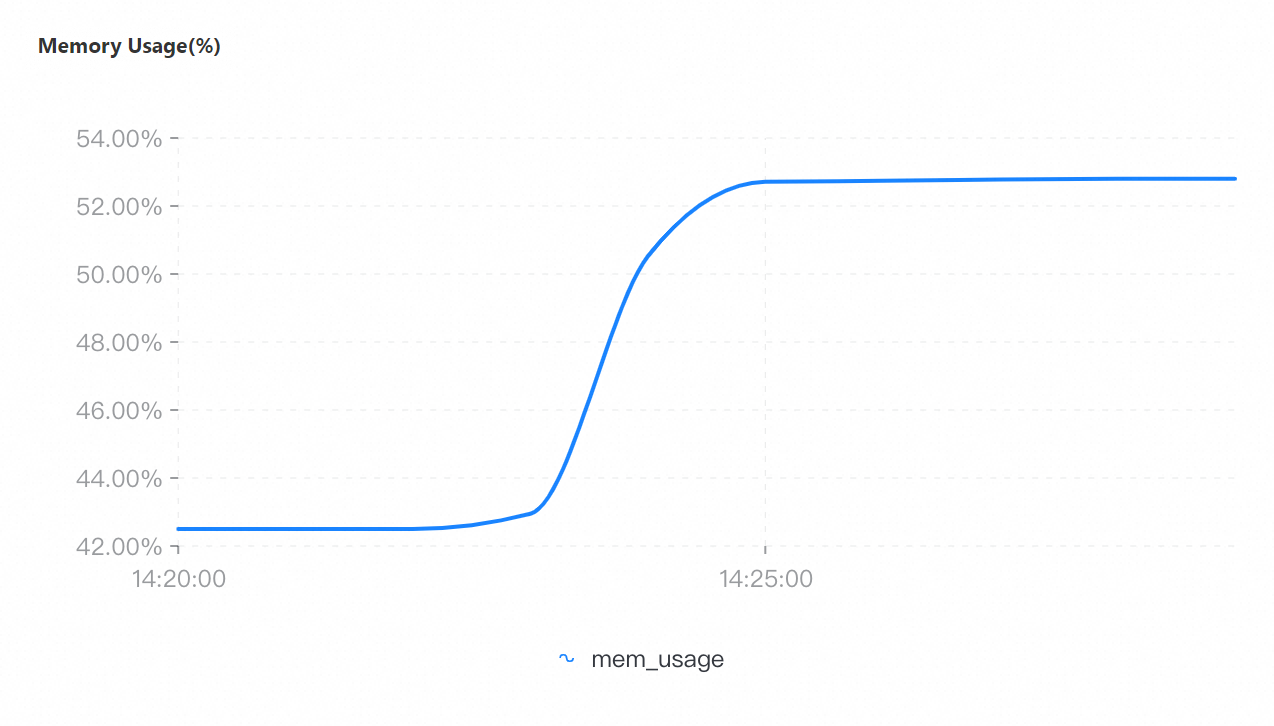
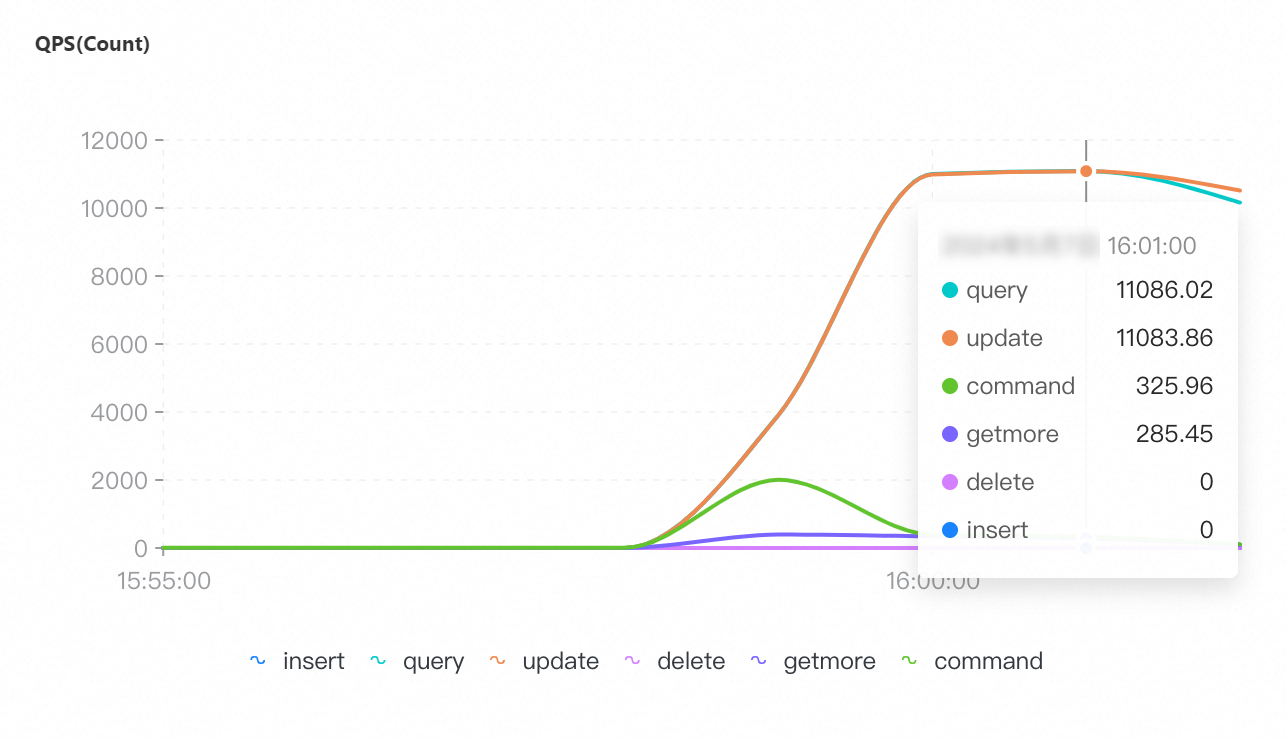
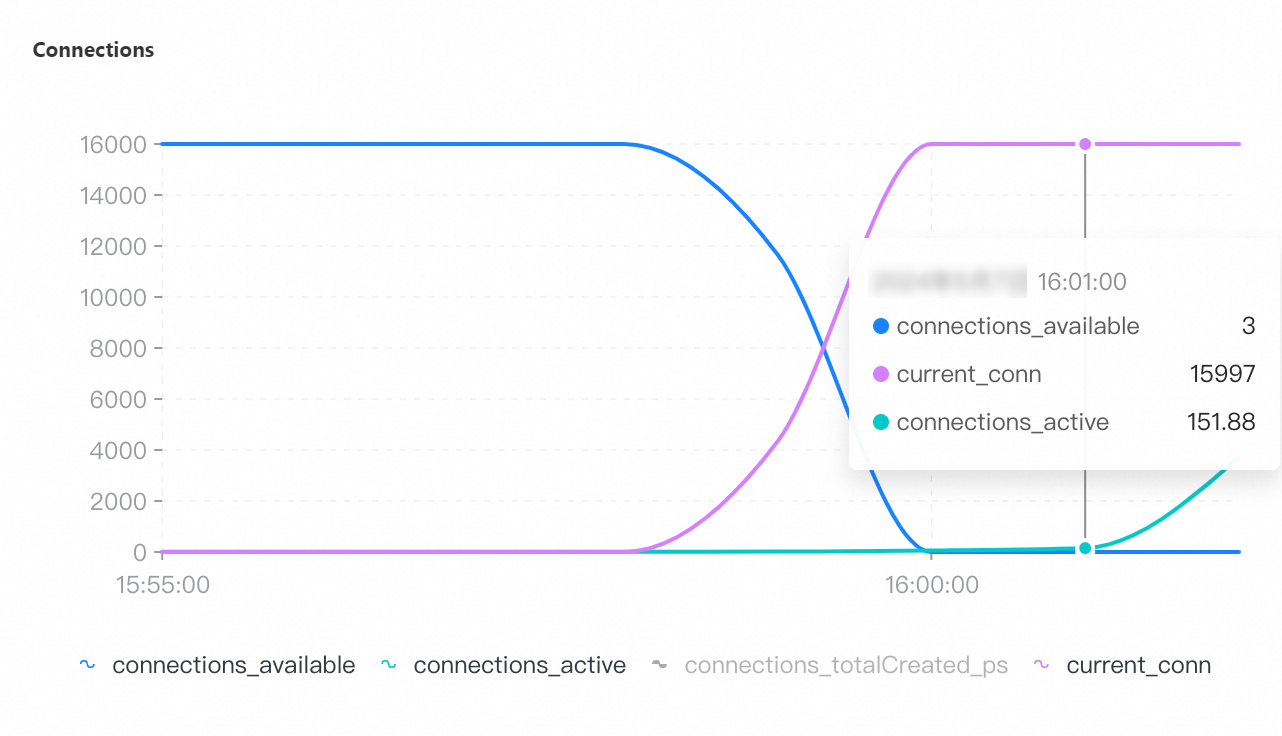
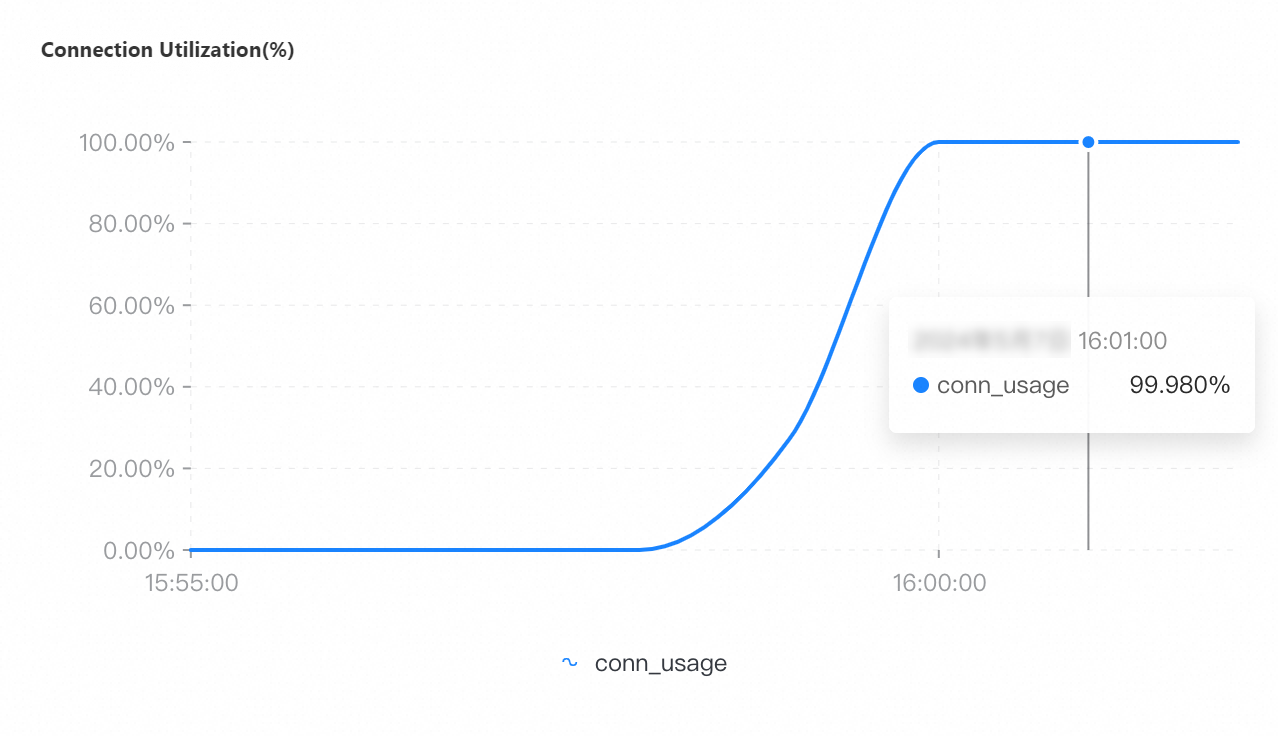
QPS | Connections | Connection utilization | CPU utilization | Memory usage |
|
|
|
|
|
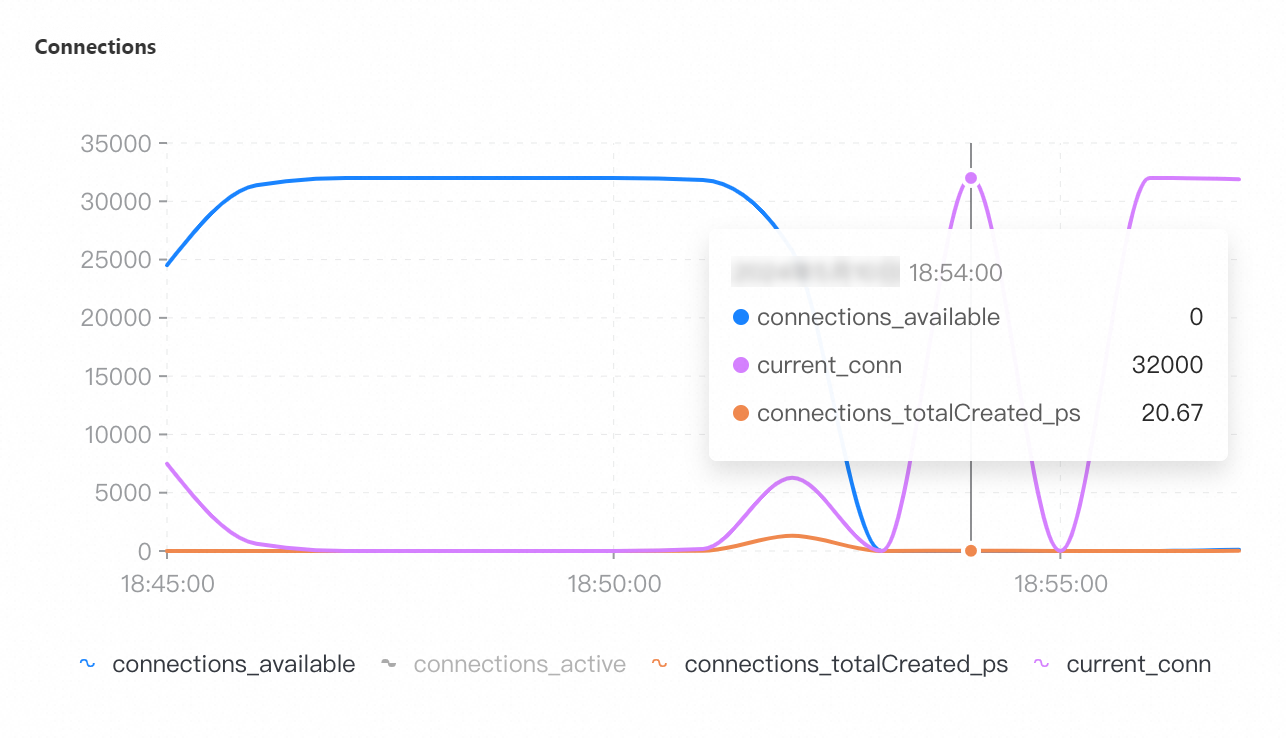
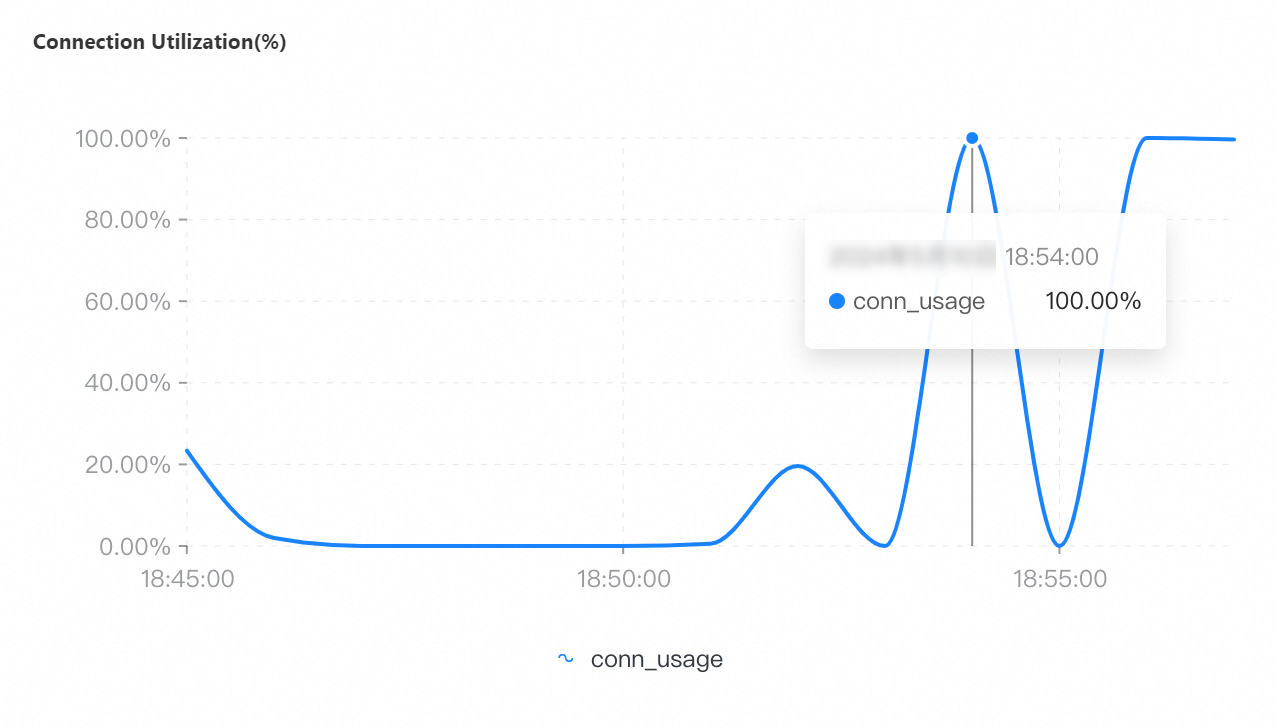
If you select a collection granularity at the minute level on the Node Monitoring tab, the maximum number of connections reached within the granularity cannot be displayed on the tab. The actual number of connections reaches 8,000. This can be confirmed by configuring granular monitoring or viewing the connections sub-document in the output of the serverStatus command.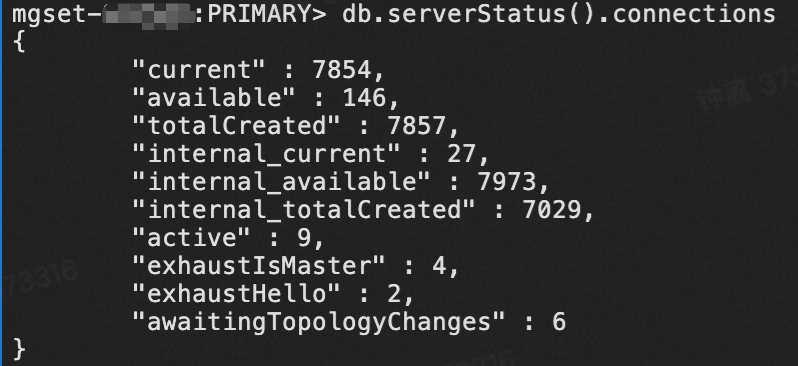
Dedicated instance that has 32 cores and 128 GB of memory
Maximum number of connections: 96,000
QPS | Connections | Connection utilization | CPU utilization | Memory usage |
|
|
|
|
|
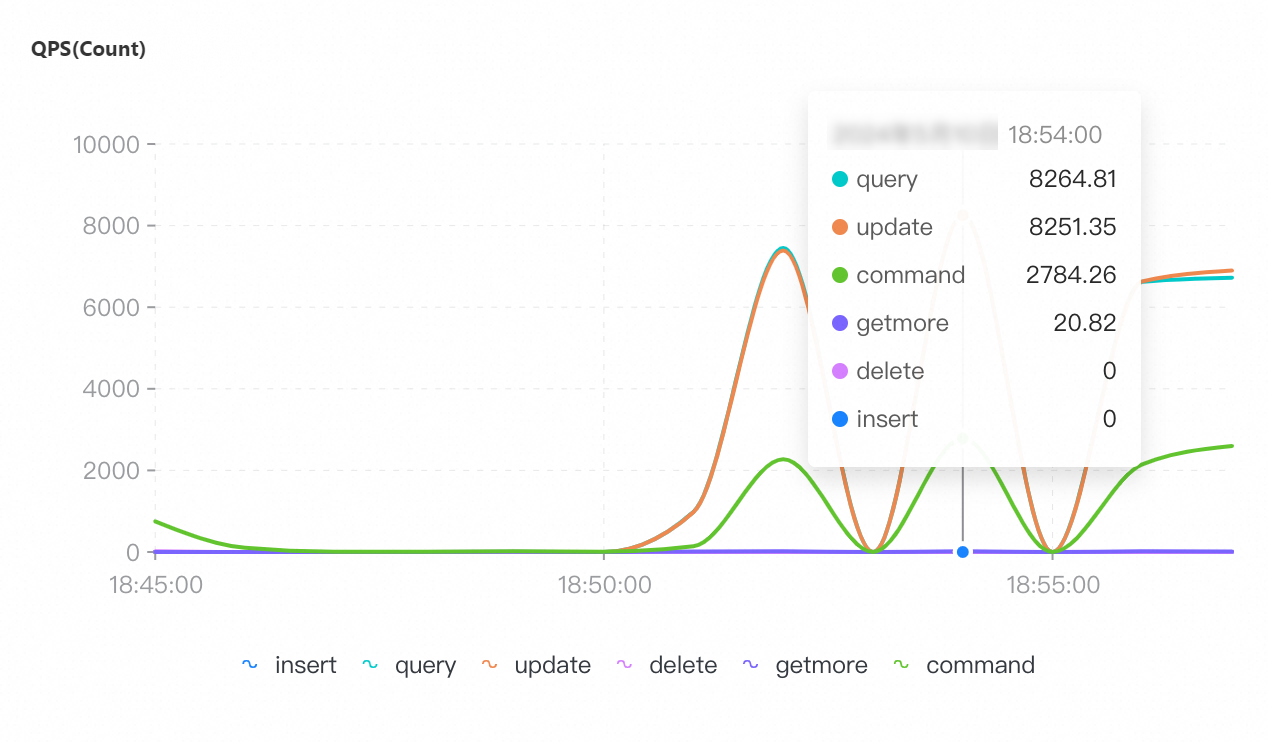
The tool used for the test when the maximum number of connections is 96,000 is different from the tools used for the tests when the maximum numbers of connections is 8,000 and 16,000. Therefore, the preceding monitoring screenshots related to QPS, CPU utilization, and memory usage have discrepancy.
General-purpose instance that has 8 cores and 32 GB of memory
Maximum number of connections: 16,000
QPS | Connections | Connection utilization | CPU utilization | Memory usage |
|
|
|
|
|
Instances that use local disks
General-purpose instance that has 16 cores and 64 GB of memory
Maximum number of connections: 32,000
QPS | Connections | Connection utilization | CPU utilization | Memory usage |
|
|
|
|
|
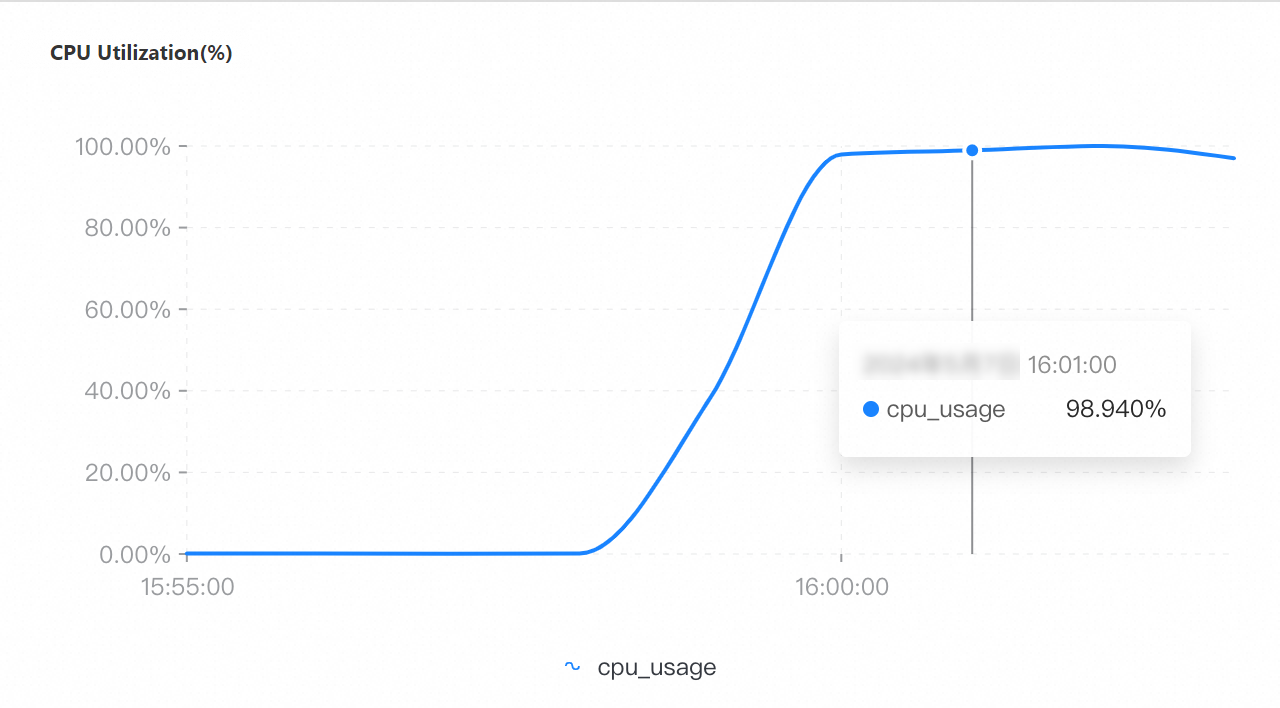
If you specify a collection granularity at the minute level on the Node Monitoring tab, the number of connections at several points in time is not monitored for a general-purpose instance that has 16 cores and 64 GB of memory due to the timeouts of collection commands caused by 100% CPU utilization. In this case, minute-level valleys occur, and the actual number of connections at the points in time remains 32,000.
Dedicated instance that has 2 cores and 16 GB of memory
Maximum number of connections: 8,000
QPS | Connections | Connection utilization | CPU utilization | Memory usage |
|
|
|
|
|
Summary
ApsaraDB for MongoDB replica set instances of different specifications and storage types can reach the maximum number of connections corresponding to their specifications.
After the maximum number of connections is reached, ApsaraDB for MongoDB rejects subsequent connections. The requests have a high latency or are stuck on your application due to the failure to establish connections.
A larger number of concurrent connections consume more resources such as CPU and memory. We recommend that you adjust the number of connections to your instance based on your business requirements.