This topic describes the job priority feature for MaxCompute subscription resources. It also explains how to enable, set, and view job priorities.
Background
Because MaxCompute subscription compute resources are limited, the system must prioritize them for important jobs during data development. For example, if certain data must be generated before 06:00, the workflow that produces this data must be able to preempt compute resources at runtime.
You can meet this requirement by setting job priorities for projects that use subscription compute resources. This ensures that high-priority jobs receive compute resources first. When a high-priority job starts, it can preempt the compute resources of low-priority jobs.
Priorities overview
Each job in MaxCompute has a priority. The priority value ranges from 0 to 9. A smaller value indicates a higher priority. High-priority jobs acquire compute resources before low-priority jobs.
Note:
MaxCompute supports setting job priorities only for projects that use subscription compute resources.
If the job priority feature is not enabled for a project, the default priority for jobs is 9. For PAI algorithm jobs, the default priority is 1.
Enable priorities
Enable priorities at the project level
Only the project owner or a user with the Super_Administrator role can enable the priority feature by running the following command.
setproject odps.instance.priority.enable=true;After you enable the priority feature, the priorities of all jobs in the project that use subscription compute resources take effect immediately. However, if you set unreasonable priorities, the job queue may become disorganized.
Check the priorities of existing jobs in Information Schema. If necessary, reset the priority to 9 for any jobs that do not have a priority of 9. Then, enable the priority feature.
Enable priorities at the quota level
After you enable the priority feature, the priorities of jobs that run on this quota take effect. This is equivalent to enabling priorities at the project level.
Prerequisites
You have purchased a subscription Standard Edition quota.
You have created a quota template and a quota plan. For more information, see Configure quotas.
Procedure
Log on to the MaxCompute console and select a region in the top-left corner.
In the navigation pane on the left, choose .
On the Quotas page, find the target quota and click Quota Configuration in the Actions column.
On the Quota Configuration page, select the Basic Configurations tab and click Edit Basic Configurations.
Select the Enable Priority option for the target level-2 quota.
NoteIf the Type for a level-2 quota is set to Interactive, the Enable Priority parameter is unavailable by default.
Click OK.
Check job priorities
View the distribution of job priorities.
Sample command:
SELECT get_json_object( REPLACE(settings, '.', '_') ,'$.odps_instance_priority' ) AS priority ,task_type ,COUNT(1) AS cnt FROM information_schema.tasks_history WHERE ds = '${bizdate}' -- bizdate is the date partition. GROUP BY get_json_object( REPLACE(settings, '.', '_') ,'$.odps_instance_priority' ) ,task_type ORDER BY cnt DESC LIMIT 100 ;The following result is returned:
+----------+-----------+------------+ | priority | task_type | cnt | +----------+-----------+------------+ | 9 | SQL | 4 | | NULL | SQL | 1 | | 2 | SQL | 1 | +----------+-----------+------------+The sample result shows three priorities: NULL, 2, and 9. Locate the jobs with a priority of 2 or NULL. A NULL value usually indicates a Data Definition Language (DDL) task, which you can ignore.
Find jobs whose priority is not 9.
Sample command:
SELECT inst_id ,owner_name ,task_name ,task_type ,settings FROM information_schema.tasks_history WHERE ds = '${bizdate}' AND get_json_object(REPLACE(settings, '.', '_'), '$.odps_instance_priority') = '${priority}' LIMIT 100 ;bizdate: The date partition. For example, 20200517.
priority: A priority value other than 9. For example, 2.
The following result is returned:
+---------+------------+-----------+-----------+----------+ | inst_id | owner_name | task_name | task_type | settings | +---------+------------+-----------+-----------+----------+ | 20200517160200907g4jm**** | ALIYUN$odps_dev_****@prod.trusteeship.aliyunid.com | console_query_task_158973132**** | SQL | {"SKYNET_ID": "21000041****", "odps.instance.priority": "2", "SKYNET_ONDUTY": "113058643178****", "user_agent": "JavaSDK Revision:33acd11 Version:0.30.9 JavaVersion:1.8.0_112 CLT(0.30.2 : 9da012b); Linux(/)", "biz_id": "210000416174_20200517_211843317416_210033365461_1_habai_test_1130586431784115_39419845061****", "SKYNET_NODENAME": "test_priority"} | +---------+------------+-----------+-----------+----------+SKYNET_ID: The ID of the scheduling node in DataWorks. If this field is not returned, the job was not submitted through DataWorks. In this case, check the owner_name and user_agent fields.
SKYNET_ONDUTY: Indicates a periodic job.
Troubleshoot job priorities.
For jobs submitted through DataWorks: If a baseline is set for a job, check whether the baseline is reasonable. If it is not, delete it. For more information, see Baseline management.
For jobs not submitted through DataWorks: Use the returned result to locate the owner and the code. Remove the priority setting from the code to restore the default priority of 9.
Set priorities
You can set job priorities in the following ways:
Method 1: Run the MaxCompute client, enter the project space, and set the job priority.
This method is often used to set the priority for temporary query jobs. Sample command:
SET odps.instance.priority=values; -- The value of values ranges from 0 to 9.Method 2: Run the MaxCompute client, enter the project space, and pass the SQL statement as a parameter to set the job priority.
This method is often used to set the priority for temporary query jobs. Sample command:
bin/odpscmd --config=xxx --project=xxx --instance-priority=x -e "<sql>"Method 3: Set the job priority using the Java SDK.
You can use this method to implement custom priority settings. For more information, see Java SDK overview. Sample command:
import com.aliyun.odps.Instance; import com.aliyun.odps.LogView; import com.aliyun.odps.Odps; import com.aliyun.odps.OdpsException; import com.aliyun.odps.account.Account; import com.aliyun.odps.account.AliyunAccount; import com.aliyun.odps.task.SQLTask; public class OdpsPriorityDemo { public static void main(String args[]) throws OdpsException { // An Alibaba Cloud account AccessKey has permissions to access all APIs, which poses a high security risk. // Create and use a RAM user for API calls or routine O&M. Log on to the RAM console to create a RAM user. // This example shows how to store the AccessKey ID and AccessKey secret in environment variables. You can also store them in a configuration file as needed. // Do not hard-code the AccessKey ID and AccessKey secret in your code. This can lead to security risks. Account account = new AliyunAccount(System.getenv("ALIBABA_CLOUD_ACCESS_KEY_ID"),System.getenv("ALIBABA_CLOUD_ACCESS_KEY_SECRET")); Odps odps = new Odps(account); // The public cloud URL. String odpsUrl = "http://service.odps.aliyun.com/api"; odps.setEndpoint(odpsUrl); odps.setDefaultProject("xxxxxxxxxx"); SQLTask task = new SQLTask(); task.setName("adhoc_sql_task_1"); task.setQuery("select count(*) from aa;"); // 5 is the job priority. Instance instance = odps.instances().create(task, 5); LogView logView = new LogView(odps); // Print the Logview to check the instance execution status. This step is optional. System.out.println(logView.generateLogView(instance, 24)); // Wait for the instance to complete. This step is optional. instance.waitForSuccess(); } }Method 4: Set the job priority using the baseline management feature of DataWorks.
This method is often used to ensure that a periodic job and its upstream jobs are prioritized when they generate data. You can use the baseline management feature to centrally set the priorities for all jobs in a data link, without having to handle each job individually. For more information about the baseline management feature of DataWorks, see Baseline management.
The baseline priorities in DataWorks can be 1, 3, 5, 7, or 8. A larger value indicates a higher priority. When you use the baseline management feature of DataWorks to set a MaxCompute job priority, the MaxCompute job priority is calculated as: 9 - DataWorks baseline priority.
NoteFor temporary queries in DataWorks, no baseline is set by default. The MaxCompute jobs that are initiated have the lowest priority, which is 9.
For DataWorks workflows, the default baseline priority is 1. The MaxCompute jobs that are initiated have a priority of 8.
Method 5: Set the job priority directly on a DataWorks node.
This method is often used to set the priority for temporary query jobs. Sample command:
set odps.instance.priority=x; -- x is the priority value.
View priorities
On the Logview 2.0 page, click the Json Summary tab. You can view the job priority in the odps.instance.priority parameter. For more information about Logview 2.0 operations, see Use Logview 2.0 to view job running information.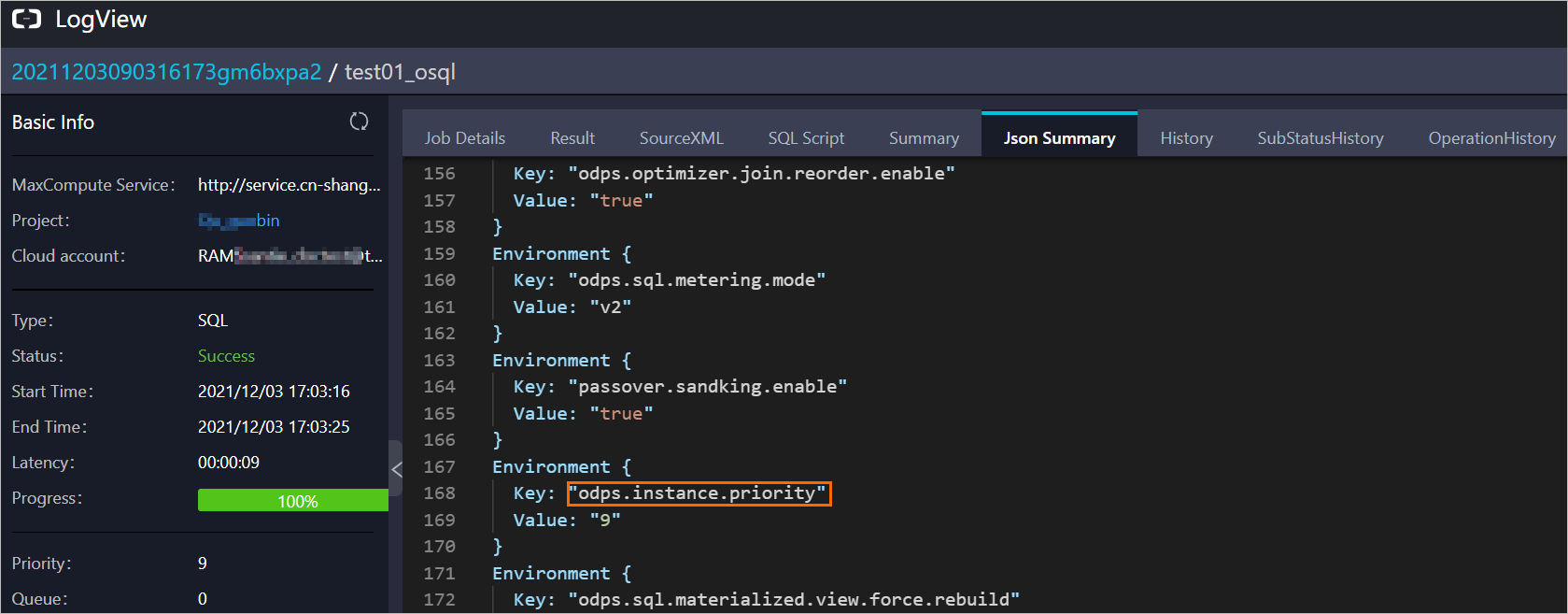
The priority displayed in XML format on the Logview page is not accurate. For projects that use the pay-as-you-go billing method, the system changes the job priority to 9. The same change applies to projects that use subscription compute resources but do not have the priority feature enabled. This occurs even if the priority value set in the XML is not 9. This change prevents unfair queuing.