This article will help you quickly get familiar with the core features of Lingma IDE, including customizing the user interface, editing code, running and debugging, as well as using the Lingma coding assistant for intelligent programming.
Getting started with workspaces
Create a folder and open it in Lingma IDE—this folder, as your workspace, will be used throughout the rest of the tutorial.
Open Lingma IDE. If it is the first time you launch Lingma, you'll see a welcome page with several beginner guides to help you get started.
From the menu bar, select to open your folder.
Click New Folder, create a new folder named "lingma demo", and then click Select Folder (or Open on macOS).
Click Yes, I Trust the Authors in the dialog box from the workspace.
NoteBecause you created this folder on your computer, you can trust the code in it.
User interface navigation
The Lingma IDE user interface consists of the following main parts:
Toolbar: Located at the top, the toolbar contains buttons for common operations, such as creating a new project, opening a file, and saving a file.
File explorer: Usually located on the left, the File Explorer displays the files and folders in the current project. You can use it to navigate and manage your project files.
Editor: This is the main area for coding. It occupies the central part of the user interface and supports features such as code highlighting and syntax checking.
Terminal: Usually located at the bottom, the terminal lets you run commands and view output and error messages.
Left sidebar: Contains different views, such as the Explorer and the Source Control view that displays Git status.
Right sidebar: Displays the AI chat interface of Lingma coding assistant. For more information, see the Lingma Intelligent Coding Assistant documentation.
Status bar: Located at the bottom of the interface, the Status Bar displays information about the current project and the files you edit.
Switch views in the Activity Bar
The Activity Bar on the left lets you switch between views.
View and edit files with the editor
Click the Explorer icon
 in the Activity Bar on the left and then the New File...
in the Activity Bar on the left and then the New File...  button to create a new file in your workspace.
button to create a new file in your workspace.Enter a file name, such as
main.py, and press Enter.You can add more files to your workspace. Lingma IDE lets you open multiple editors and arrange them as needed.
Terminal and command line
To open the terminal, click View in the menu bar and select Terminal, or press the keyboard shortcut
Ctrl+\`.You can enter a command to create a file.
echo "Hello lingma" > demo.txtThe default working directory is the root directory of the current workspace. The Explorer view automatically updates to show the new file.
To manage multiple terminals, click the drop-down arrow
 in the upper-right corner of the Terminal panel. You can then select a different shell environment from the menu.
in the upper-right corner of the Terminal panel. You can then select a different shell environment from the menu.
Command Palette
You can open the Command Palette using the keyboard shortcut
⇧⌘P(macOS) orCtrl+Shift+P(Windows), or by selecting from the menu bar. The Command Palette provides access to many commands. Extensions can also add their own commands to the Command Palette.The Command Palette supports different search operations:
With the
>symbol, you can start typing to filter and search for commands. For example, typing "move editor" shows commands for moving the editor.
If you remove the
>symbol, you can search for files. You can also use the keyboard shortcut⌘P(macOS) orCtrl+P(Windows) to go directly to file search.
NoteLingma IDE uses fuzzy matching for searches. For example, typing "odks" matches the "Open Default Keyboard Shortcuts" command.
Settings and customization
You can customize Lingma IDE by configuring its settings. Most settings can be modified in the Settings editor, but for advanced customization, you can directly edit the settings.json file.
To access the settings, you can click the user icon
 in the top-right corner of the Lingma IDE or use the keyboard shortcut (
in the top-right corner of the Lingma IDE or use the keyboard shortcut (⌘⇧,for macOS, orCtrlShift,for Windows), and select Personal Settings.By default, Auto Save is disabled. You can enable it using the Files: Auto Save drop-down menu.
Lingma IDE automatically applies the setting change, and all subsequent edits to code files are saved automatically.
Settings can be configured at two levels: User and Workspace. You can switch between these levels using the tabs in the Settings editor. User settings apply globally to all your workspaces. Workspace settings are specific to the current workspace and override any conflicting user settings.
Programming practice
Lingma IDE has built-in support for JavaScript, TypeScript, HTML, and CSS. You can add support for other languages, such as Python, by installing extensions. For this section, you will edit the main.py file that you created earlier.
Use source code management
Lingma IDE has integrated Source Control Management (SCM) and includes built-in support for Git. This section shows you how to use Git to commit the changes you made earlier.
On the left, select the Source Control view
 .
.Click Initialize Repository to create a new Git repository in your workspace. After the repository is initialized, the view displays the changes in your workspace.
You can hover over a file and click the
+icon to stage the changes.Enter a commit message, such as
Add hello function, and then click the Commit button.
Install language extensions
Lingma IDE has a rich extension ecosystem. You can install extensions to add support for new languages, debuggers, and tools to fit your development workflow.
Open the Extensions view
 .
.In the search bar, enter the keyword `python`. From the search results, install the Python Extension Pack to enable features such as syntax highlighting and IntelliSense for Python.
After the installation is complete, you must log on to your Lingma account to receive code suggestions.
ImportantSome extensions cannot be installed directly. You can go to the VS Code Marketplace to download and install them manually.
Run and debug the program
Lingma IDE has built-in support for running and debugging code. This section shows you how to use the Python extension that you installed to debug a Python program.
First, ensure that Python 3 is installed on your system. If a Python interpreter is not installed, a notification appears in the lower-left corner of the window. Click Select Interpreter to open the Command Palette, where you can select or install an interpreter.
In the
main.pyfile, pressF9on theprintline to set a breakpoint.A red dot appears in the gutter to the left of the editor, which indicates that a breakpoint is set. A breakpoint pauses the program's execution at that line of code.
Press
F5to start debugging. Select the Python debugger. The program starts to execute and then pauses at the breakpoint.Select the Python debugger:
Python DebuggerSelect the debug configuration:
Python File: Debug the currently active Python file.
The program execution pauses at the breakpoint you set.
NoteWhile execution is paused, you can check the value of a variable by hovering over it in the editor. You can also view the values of all variables in the Variables section of the Run and Debug view.
Click the Continue button
 on the debug toolbar or press
on the debug toolbar or press F5to continue execution.
Intelligent coding
The Lingma intelligent coding assistant provides features such as intelligent code generation, AI chat, multi-file modifications, and programming agents. These features help create an efficient and smooth coding experience for developers and improve development efficiency.
Code completion
At the end of the main.py file, enter the function header:
def add(a, b):Lingma automatically suggests the rest of the function. Press Tab to accept the suggestion:

Quick fix
When you call the method, an error occurs because the variables num1 and num2 are not defined. You can click the ![]() icon to automatically fix the code:
icon to automatically fix the code:

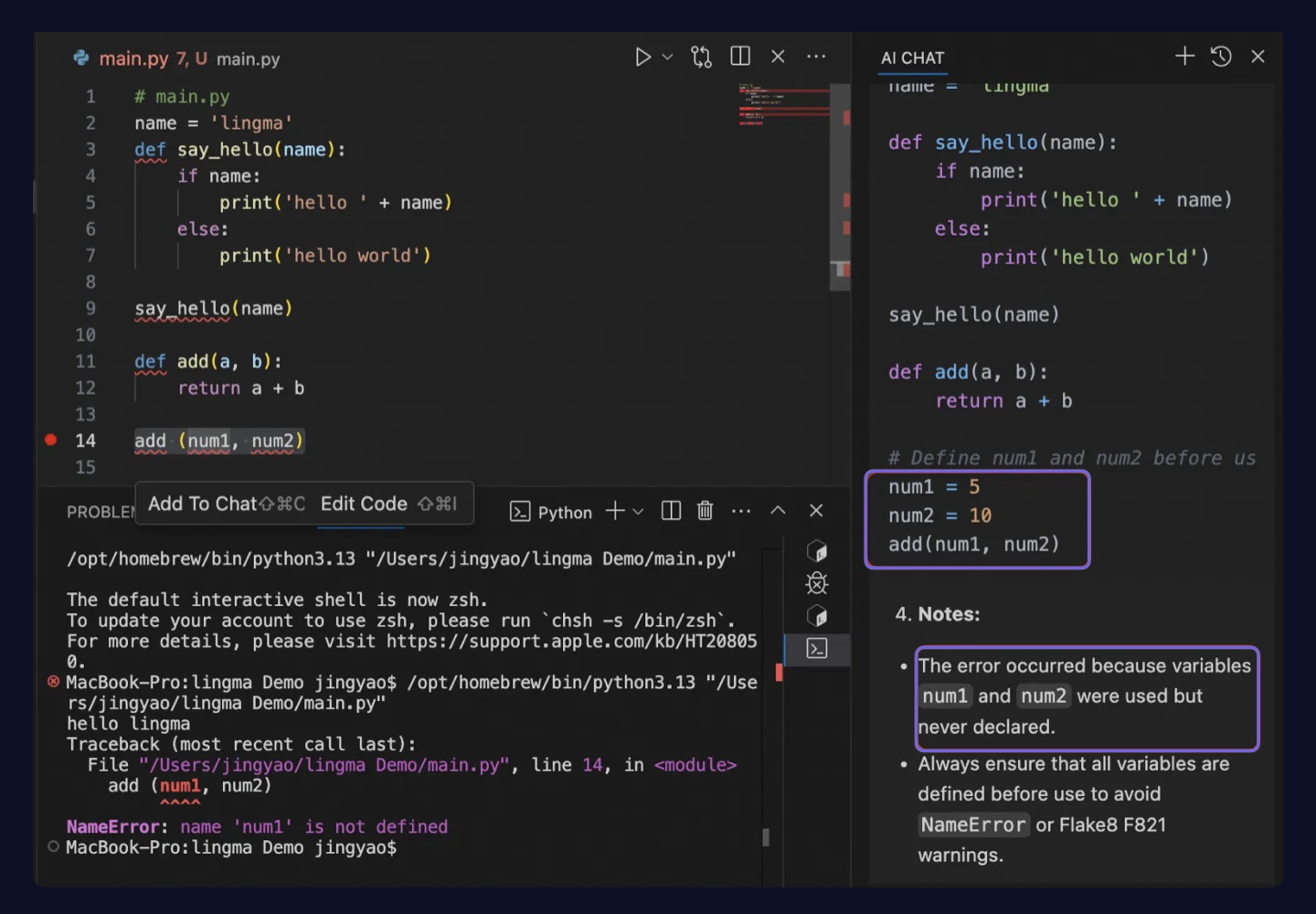
In this example, Lingma automatically fixes the issue:

For more information, see the User guide.
Keyboard shortcuts
Lingma IDE includes a set of default keyboard shortcuts. You can view them in one of the following ways:
Open the Keyboard Shortcuts editor: In Personal Settings, go to .
Use the keyboard shortcut
⌘K->⌘S(macOS) orCtrl+K->Ctrl+S(Windows).
For more information about keyboard shortcuts, see Lingma IDE keyboard shortcuts.
Set the languague to Chinese
Open the Command Palette using the keyboard shortcut
⇧⌘P(macOS) orCtrl+Shift+P(Windows), or by selecting .Enter
Configure Display Languageand press Enter.Select Chinese (Simplified) (zh-cn), and then click Restart.
After Lingma IDE restarts, the user interface is displayed in Chinese.