Hologres is compatible with PostgreSQL and allows you to create an auto-increment field in a table by using the SERIAL or BIGSERIAL data type.
Overview of data types
Hologres allows you to create an auto-increment field in a table by using the SERIAL or BIGSERIAL data type. The SERIAL data type indicates that the data type of an auto-increment field is INT4. The BIGSERIAL data type indicates that the data type of an auto-increment field is INT8.
In this topic, an auto-increment field of the SERIAL data type is used as an example. The following sample SQL statement shows you how to create an auto-increment field named colname by using the SERIAL data type in a table. The syntax of the sample statement also applies to the BIGSERIAL data type.
CREATE TABLE tablename (
colname serial
);Parameter descriptions:
Parameter | Description | Storage size | Valid value range |
Serial | Auto-increment field of the INT4 type | 4 bytes | -2147483648 to 2147483647 |
Bigserial | Auto-increment field of the INT8 type | 8 bytes | -9223372036854775808 to 9223372036854775807 |
Limitations
You cannot specify extra parameters of the SERIAL and BIGSERIAL data types in Hologres, including the increment step size and the default value. By default, the value of the increment step size is 1 and the default value is 1.
You cannot use the data whose data type is SMALLSERIAL in Hologres.
To create a table with fields whose data types are SERIAL and BIGSERIAL for the first time, a superuser must create the table in a database. For example, after the superuser executes the
create table test(a serial);statement, other users can create tables with fields whose data types are SERIAL and BIGSERIAL based on their business logic. Tables with fields whose data types are SERIAL and BIGSERIAL are database-level tables. If you switch to another database, the superuser must execute the preceding statement in the new database.When Flink is used for data writes or integration, only Java Database Connectivity (JDBC) mode and data integration (
insert into) mode support serial and bigserial types. DataHub does not support writing to these types.For
insert on conflictbased on a primary key, the serial type does not guarantee strictly continuous increments. If you require strict ordering, manually set the starting value of the sequence.Serial writes introduce additional lock overhead, which can reduce write performance. To mitigate this, write data in batches instead of single-row inserts. If your SQL statement is compatible with Fixed Plan, enable the following GUC parameter. This allows statements involving serial fields to use Fixed Plan for improved write performance. For more information, see Accelerate the execution of SQL statements by using fixed plans.
-- Enable the GUC parameter at the database level to support Fixed Plan writes for tables that contain serial columns. alter database <user_db> set hg_experimental_enable_fixed_dispatcher_autofill_series=on;Modifying serial parameters is restricted to Hologres V0.10 and later and
restart with.Serial writes introduce additional global lock overhead, which significantly impacts write performance. Use this feature with caution in performance-sensitive scenarios.
Example 1: Execute SQL statements to create an auto-increment field
The following sample SQL statements show you how to create an auto-increment field by using the SERIAL data type. The syntax of the sample SQL statements also applies to the BIGSERIAL data type.
// Create a table that contains the id and f1 fields.
create table if not exists test_tb(id serial primary key, f1 text);
// Insert data into the f1 field by executing the INSERT statements.
insert into test_tb(f1) values('1');
insert into test_tb(f1) values('2');
insert into test_tb(f1) values('3');
// Query the data in the test_tb table and sort the data by the id field in ascending order.
select * from test_tb order by id asc;Example 2: Connect to Hologres over JDBC and create an auto-increment field
The following sample SQL statements show you how to connect to Hologres over Java Database Connectivity (JDBC) and create an auto-increment field by using the SERIAL data type. The syntax of the sample SQL statements also applies to the BIGSERIAL data type.
package test;
import java.sql.*;
public class HoloSerial {
// Create a table that contains the id and f1 fields.
private static void Init(Connection conn) throws Exception {
try (Statement stmt = conn.createStatement()) {
stmt.execute("drop table if exists test_tb;");
stmt.execute("create table if not exists test_tb(id serial primary key, f1 text);");
}
}
// Insert data into the f1 field.
private static void TestSerial(Connection conn) throws Exception {
try (PreparedStatement stmt = conn.prepareStatement("insert into test_tb(f1) values(?)")) {
for (int i = 0; i < 100; ++i) {
stmt.setString(1, String.valueOf(i + 1));
int affected_rows = stmt.executeUpdate();
System.out.println("affected rows => " + affected_rows);
}
}
// Query the data in the test_tb table and sort the data by the id field in ascending order.
try (PreparedStatement stmt = conn.prepareStatement("select * from test_tb order by id asc")) {
try(ResultSet rs = stmt.executeQuery()) {
while(rs.next()) {
String res = rs.getObject(1).toString() + "\t" + rs.getObject(2).toString();
System.out.println(res);
}
}
}
}
// Connect to Hologres over JDBC.
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
Class.forName("org.postgresql.Driver").newInstance();
String host = "127.0.0.1:13737";
String db = "postgres";
String user = "xx";
String password = "xx";
String url = "jdbc:postgresql://" + host + "/" + db;
try (Connection conn = DriverManager.getConnection(url, user, password)) {
Init(conn);
TestSerial(conn);
}
}
}Example 3: Modify a parameter of the SERIAL data type
After you create a table by using a parameter of the SERIAL data type, a sequence named schema_name.tablename_columnname_seq is automatically generated. You can execute the ALTER SEQUENCE statement to modify the parameter of the SERIAL data type. The following part describes the procedure:
Execute the following statement to query the generated sequence. You must replace table_schema, table_name, and column_name in the statement with the actual values based on your business requirements. The table that is created in Example 1 is used in the following sample statement:
select table_name,column_name,column_default from information_schema.columns where table_schema='ods' and table_name = 'test_tb' and column_name = 'id';The following figure shows the query results.
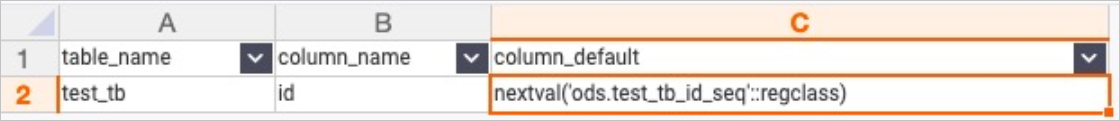 In the query results, the part that is enclosed in single quotation marks (' '),
In the query results, the part that is enclosed in single quotation marks (' '), ods.test_tb_id_seq, indicates the sequence name.After you obtain the sequence name, execute the following statement to modify the parameter of the SERIAL data type in the
restart withoptional clause.alter sequence ods.test_tb_id_seq restart with 100You can replace
ods.test_tb_id_seqand the number in the statement with other values based on your business requirements. After you modify the parameter, insert data into the table to verify the results.
FAQ
Question 1: Why am I getting a "permission denied" error when creating a table with a
serialtype?Error message:
ERROR: permission denied schema hologresCause
A superuser has not created a table that uses the serial type.
Solution
A superuser must first create a table that uses a
serialorbigserialtype (e.g.,CREATE TABLE test(a serial);). This action initializes the required sequence objects, allowing other users to subsequently create tables with these types.
Question 2: Why do I get an error when deleting and recreating a table with a
serialtype within the same transaction?Error message:
failed: error: duplicate key value violates unique constraint "hg_table_properties_pkey"Cause
Deleting and immediately recreating a table that uses a
serial(orbigserial) type within a single transaction is not supported.Solution
Do not perform the
DELETEandCREATE TABLEoperations for aserialtype table within the same transaction. Separate these operations into distinct transactions.