You can configure resources for a job before it starts or modify them after it is published. Two resource modes are available: basic mode (coarse-grained) and expert mode (fine-grained). This topic describes how to configure job resources and provides parameter information for both modes.
Precautions
After you configure resources, you must restart the job for the changes to take effect.
Procedure
Go to the resource configuration page.
Log on to the Management Portal.
In the Actions column for the target workspace, click Console.
On the page, click the name of the target job.
On the Configuration tab, click Edit in the upper-right corner of the Resources section.
Modify the job resource settings.
Two resource configuration modes are available: basic mode (coarse-grained) and expert mode (fine-grained).
Resource mode
Description
Parameter description
Basic
Basic mode employs a static resource allocation method. You simply specify the total CPU and JVM memory required for all TaskManagers. Flink then evenly distributes these resources among the TaskManagers, guided by the
taskmanager.numberOfTaskSlotsconfiguration. This mode is generally sufficient for most simple Flink jobs.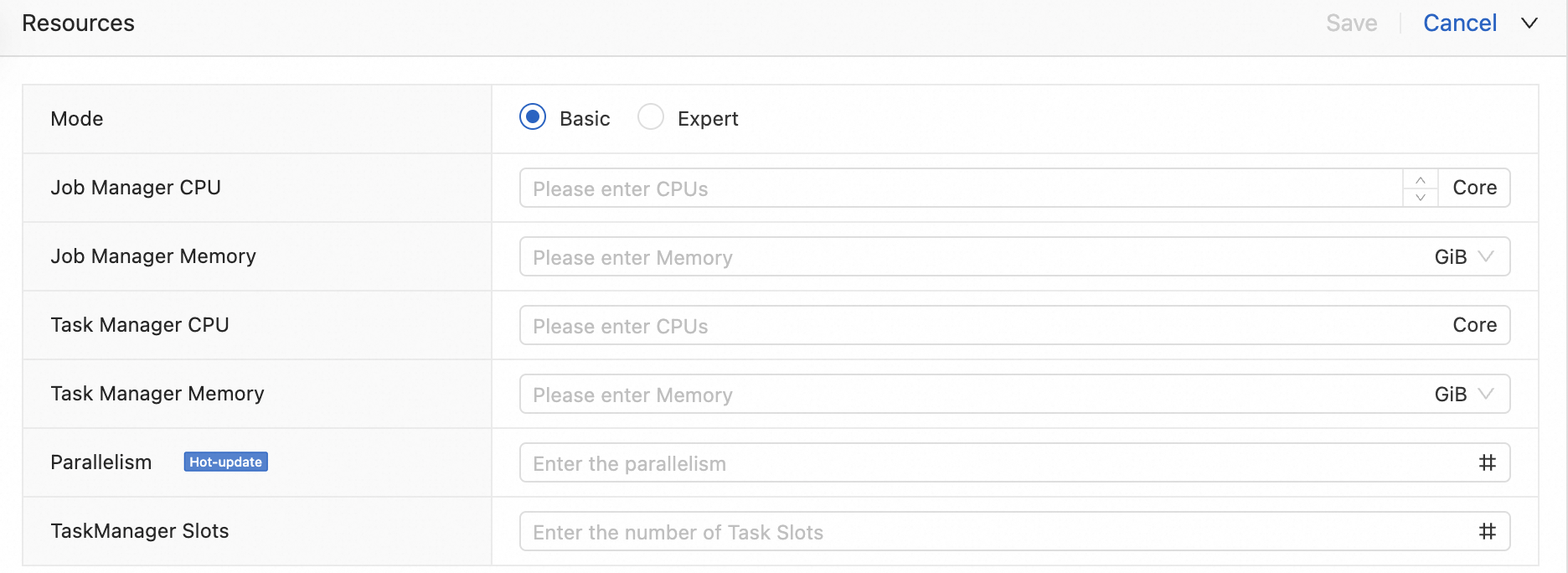
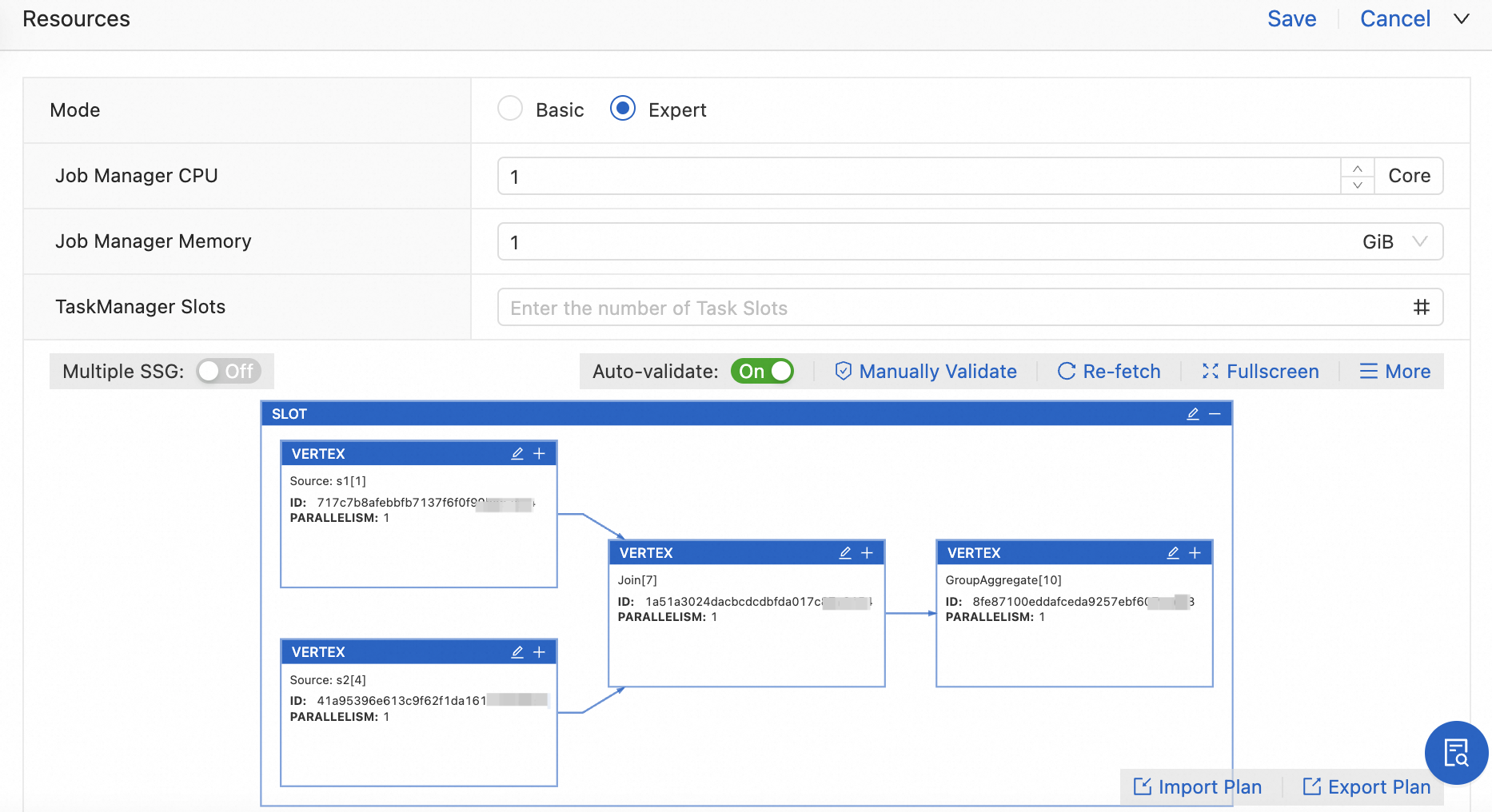
Expert
Expert mode implements a dynamic resource allocation strategy, enabling fine-grained control over your Flink job's resources. You define the specific CPU and memory requirements for each Slot Sharing Group (SSG). Flink then accurately calculates the resource specifications needed for each slot and dynamically provisions TaskManagers and slots from the available resource pool that precisely match these requirements. For complex jobs where static (or "basic") resource allocation can lead to low utilization, expert mode significantly improves resource efficiency and helps meet demanding throughput targets by allowing precise control at the operator level.
 Note
NoteOnly SQL jobs support expert mode.
Click Save.
Restart the job.
Basic mode
Configurable parameters
These are the parameters you set in the resource configuration:
JobManager CPU
Description: The number of vCPU cores allocated to the JobManager.
Recommendation: According to Flink best practices, at least 0.5 vCPUs are required for stable operation. We recommend configuring 1 vCPU.
Limits: Minimum 0.5 vCPUs. Maximum 16 vCPUs.
JobManager Memory
Description: The JVM memory allocated to the JobManager.
Recommendation: At least 2 GiB are required for stable operation. We recommend configuring 4 GiB.
Limits: Minimum 2 GiB. Maximum 64 GiB.
TaskManager CPU
Description: The number of vCPU cores allocated to each TaskManager.
Recommendation: According to Flink best practices, at least 0.5 vCPUs are required per TaskManager for stable operation. We recommend configuring 1 vCPU.
Limits: Minimum 0.5 vCPUs. Maximum 16 vCPUs.
TaskManager Memory
Description: The JVM memory (in GiB) allocated to each TaskManager.
Recommendation: At least 2 GiB are required per TaskManager for stable operation. We recommend configuring 4 GiB.
Limits: Minimum 2 GiB. Maximum 64 GiB.
Parallelism
Description: The global parallelism for the Flink job, determining the total number of concurrent tasks.
TaskManager Slots
Description: The number of task slots configured for each TaskManager (
taskmanager.numberOfTaskSlots). Each slot can run one subtask.
Resource allocation logic
The following formulas explain how configured parameters are translated into actual resource allocation and Compute Unit (CU) requirements. All calculated ratios are rounded up to the nearest integer (ceil).
Definitions and constants
1 CU = 1 vCPU (core) + 4 GiB memory
P: Configured ParallelismS_TM: Configured TaskManager SlotsCPU_TM_Configured: Configured TaskManager CPUMem_TM_Configured: Configured TaskManager Memory (in GiB)CPU_JM: Configured JobManager CPUMem_JM: Configured JobManager Memory (in GiB)DEFAULT_MAX_CPU_PER_TM: Default maximum CPU cores for a single TaskManager = 16 vCPUsDEFAULT_MAX_MEM_PER_TM: Default maximum memory for a single TaskManager = 64 GiB
Calculate total TaskManager resources
Logical number of TaskManagers (
Num_TM_Logical):Num_TM_Logical = ceil(P / S_TM)
Total TaskManager CPU required (
Total_TM_CPU_Required):Total_TM_CPU_Required = Num_TM_Logical × CPU_TM_Configured
Total TaskManager memory required (
Total_TM_Mem_Required):Total_TM_Mem_Required = Num_TM_Logical × Mem_TM_Configured
Calculate actual number of TaskManagers (Num_TM_Actual):
Flink provisions TaskManagers based on your configured resources per TM relative to default limits.
Case 1: Configured TaskManager CPU and memory are within default maximums.
Condition:
(CPU_TM_Configured ≤ DEFAULT_MAX_CPU_PER_TM)AND(Mem_TM_Configured ≤ DEFAULT_MAX_MEM_PER_TM)Num_TM_Actual = Num_TM_Logical
Case 2: Configured TaskManager CPU or Memory exceeds default maximums.
Condition:
(CPU_TM_Configured > DEFAULT_MAX_CPU_PER_TM)OR(Mem_TM_Configured > DEFAULT_MAX_MEM_PER_TM)Num_TM_Actual = MAX(ceil(Total_TM_CPU_Required / DEFAULT_MAX_CPU_PER_TM), ceil(Total_TM_Mem_Required / DEFAULT_MAX_MEM_PER_TM))
Calculate job resources
Total job CPU (
Total_Job_CPU):Total_Job_CPU = (Num_TM_Actual × CPU_TM_Configured) + CPU_JM
Total job memory (
Total_Job_Memory):Total_Job_Memory = (Num_TM_Actual × Mem_TM_Configured) + Mem_JM
Job required CUs:
Job Required CUs = MAX(Total_Job_CPU, Total_Job_Memory / 4)
Job allocated CUs:
Job Required CUs ≤ Job Allocated CUs
Calculate actual TaskManager slots (S_TM_Actual)
S_TM_Actual = P / Num_TM_Actual
Special Considerations
Exceeding default limits: By default, you cannot set TaskManager CPU or memory values that exceed their maximum limits (16 vCPUs / 64 GiB). To request values greater than these defaults, submit a ticket to support.
TaskManager slots: An equivalent parameter (
numberOfTaskSlots) can be set in the Parameters section, which takes precedence if both are configured.
Example
Let's illustrate how TaskManager count and slot count are determined:
Given:
Configured parallelism (
P) = 12Configured TaskManager Slots (
S_TM) = 4Configured TaskManager CPU/Memory are within default maximums.
Calculations:
Num_TM_Actual = Num_TM_Logical = P / S_TM = 12 / 4 = 3S_TM_Actual = P / Actual_Num_TM = 12 / 3 = 4
The results are consistent with data on the Development Console.
Expert mode
Only SQL jobs support expert mode.
After a job is deployed, if you modify the SQL code or resource configuration, regenerate the resource plan graph to ensure the job can start properly.
Configure basic resources
JobManager CPU
Description: The number of vCPU cores allocated to the JobManager.
Recommendation: According to Flink best practices, at least 0.25 vCPUs are required for stable operation.
Limits: Minimum 0.25 vCPUs. Maximum 16 vCPUs.
JobManager Memory
Description: The JVM memory allocated to the JobManager.
Recommendation: At least 1 GiB are required for stable operation.
Limits: Minimum 1 GiB. Maximum 64 GiB.
TaskManager Slots
Description: The number of task slots configured for each TaskManager (
taskmanager.numberOfTaskSlots). Each slot can run one subtask.
Configure slot resources
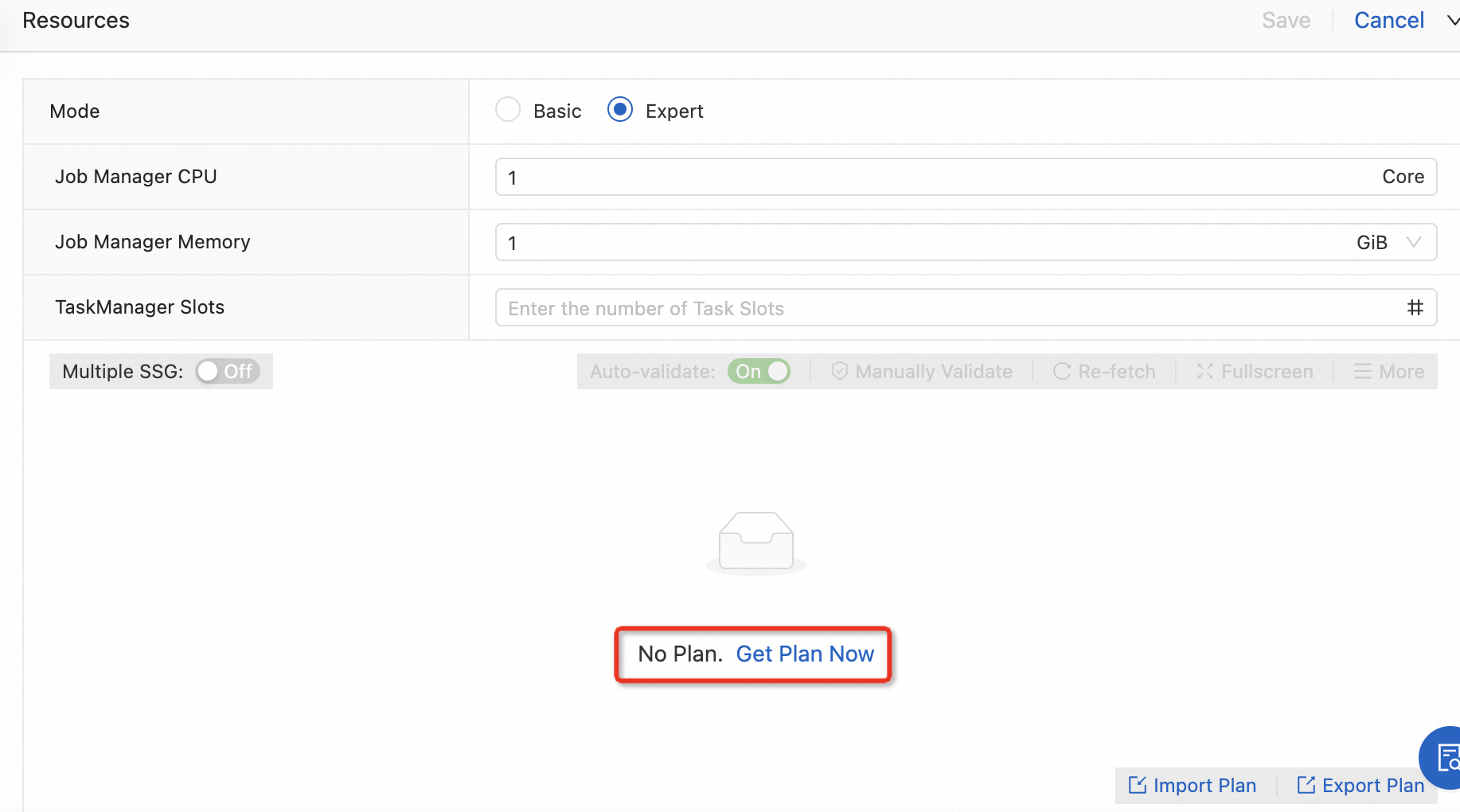
In Expert Mode, click Get Plan Now to view the resource plan graph.
Click the
 icon on the SLOT box.
icon on the SLOT box.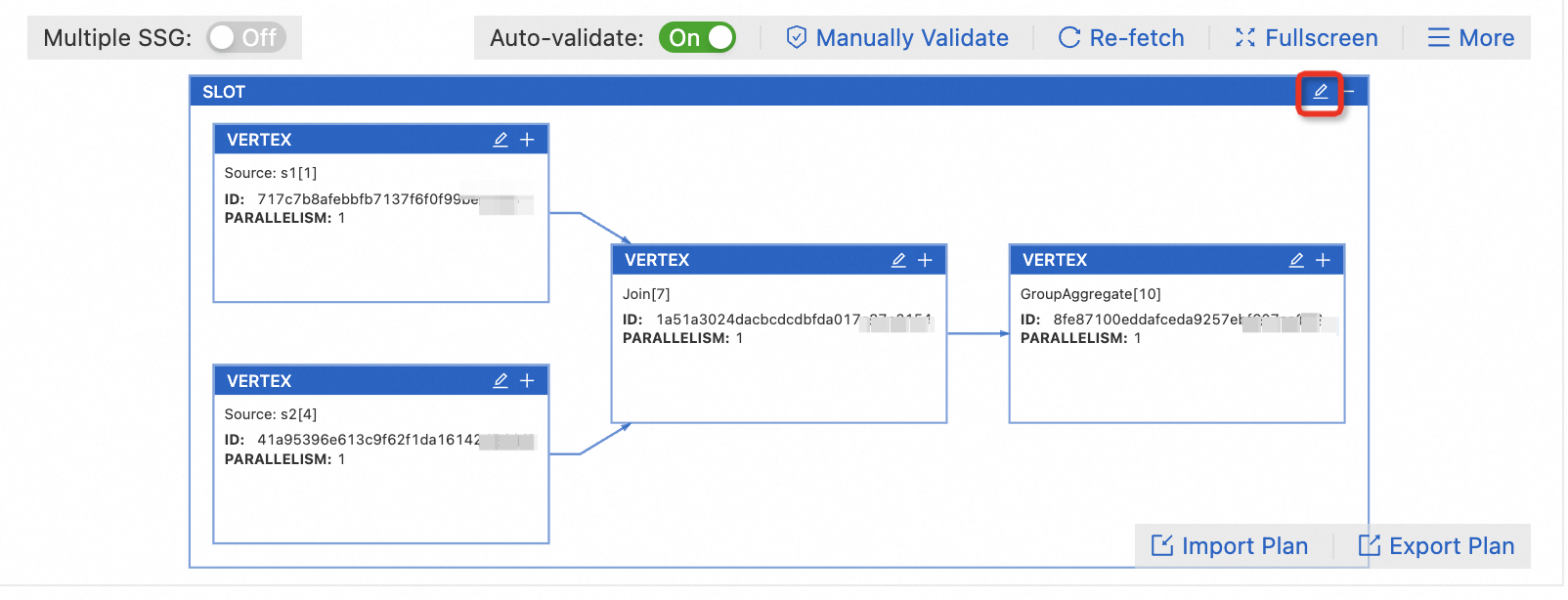
Modify the slot configuration information.
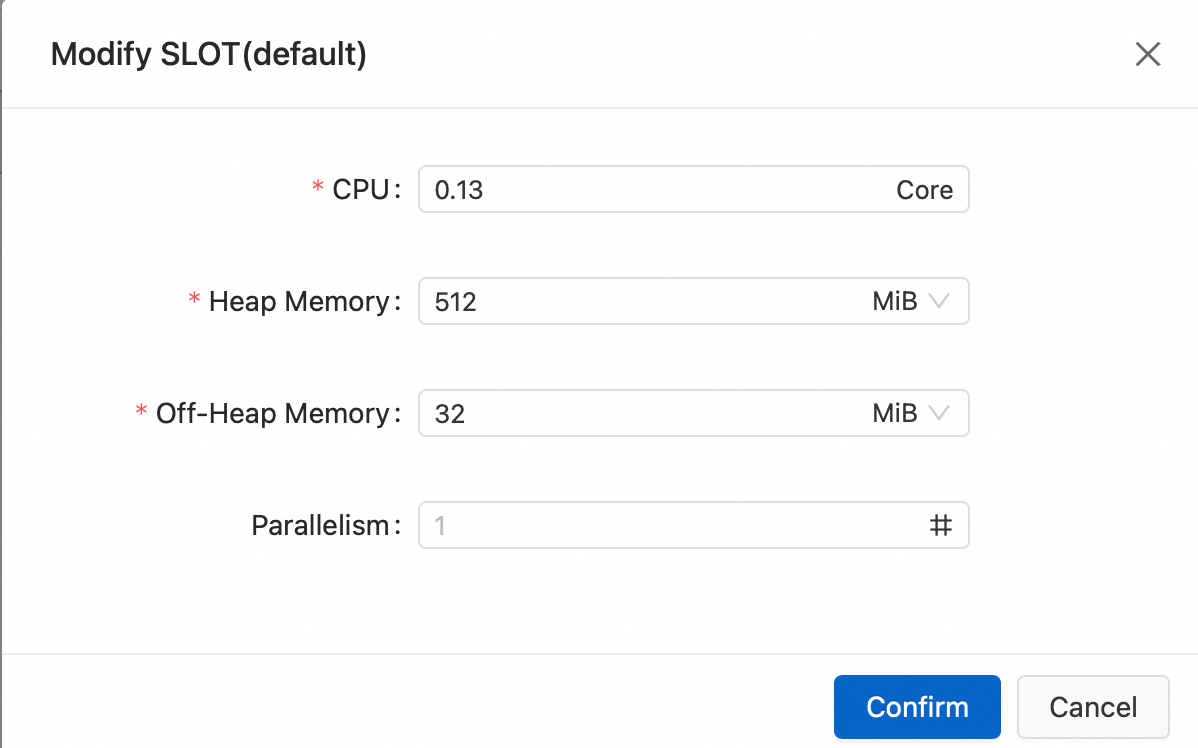
The parallelism set here is consistent for all operators within this SSG. After you complete the settings, Flink automatically performs the following operations:
Sets the same parallelism for all operators within this SSG.
Allocates the required memory for the statebackend, Python, and operators based on the job's computation logic.
Source parallelism:
Ensure the source parallelism to be a divisor of the number of partitions (e.g., for a Kafka topic with 16 partitions, use a parallelism of 16, 8, or 4). This ensures even data distribution, preventing data skew.
Avoid setting source parallelism too low, as this can lead to an input bottleneck and negatively impact job throughput.
Non-source parallelism: Set higher parallelism for high-traffic operations and lower concurrency for low-traffic ones.
Heap and off-heap memory:
Only adjust them when there's a clear necessity, such as out-of-memory (OOM) errors or severe garbage collection (GC) issues.
Under normal operating conditions, adjusting these memory parameters typically does not significantly improve job throughput.
NoteClick Confirm.
Configure operator resources
By default, all operators are placed in a single SSG, so you cannot modify the resource configuration for individual operators. To set resources for individual operators, enable Multiple SSG Mode. This mode assigns a dedicated slot to each operator, allowing you to configure its resources individually. The steps to set operator resources are as follows:
(Optional) If no resource plan displays, click Get Plan Now.
Turn on the Multiple SSG switch and click Re-fetch.
The operators within the SSG are now split into individual slots.
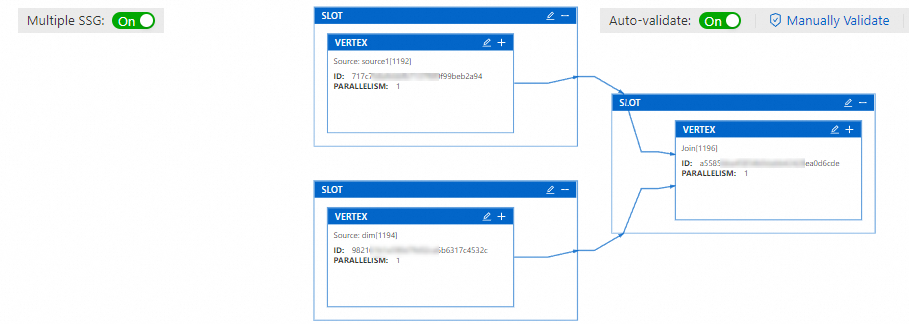
Click the
 icon on the SLOT box corresponding to the target operator, and modify the operator resources.
icon on the SLOT box corresponding to the target operator, and modify the operator resources.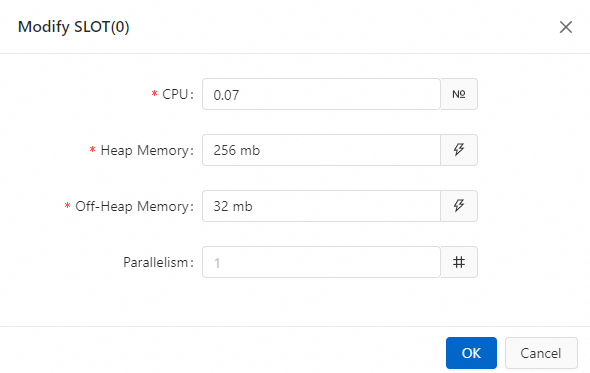
Click OK.
Configure operator parallelism, chain strategy, and TTL
Only Ververica Runtime (VVR) 8.0.7 and later versions support configuring operator TTL.
You can configure the parallelism, chaining strategy, and state TTL for a single operator.
Click the
 icon on the target VERTEX box to expand the vertex.
icon on the target VERTEX box to expand the vertex.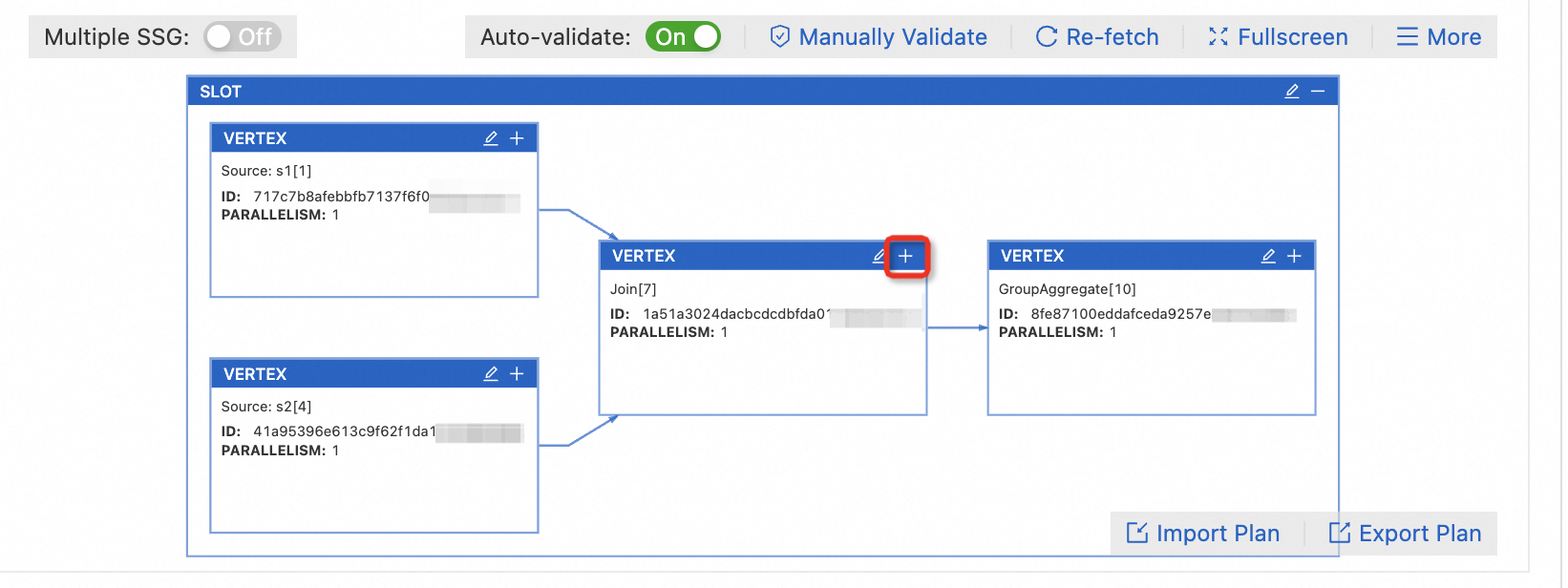 Note
NoteClick the
 icon on the target VERTEX to set the parallelism for all operators under that VERTEX.
icon on the target VERTEX to set the parallelism for all operators under that VERTEX.Click the
 icon of the operator.
icon of the operator.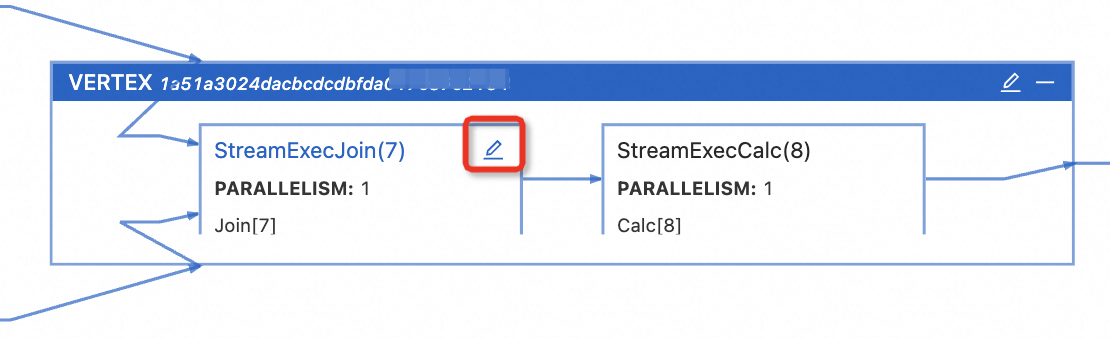
Configure the operator resources.
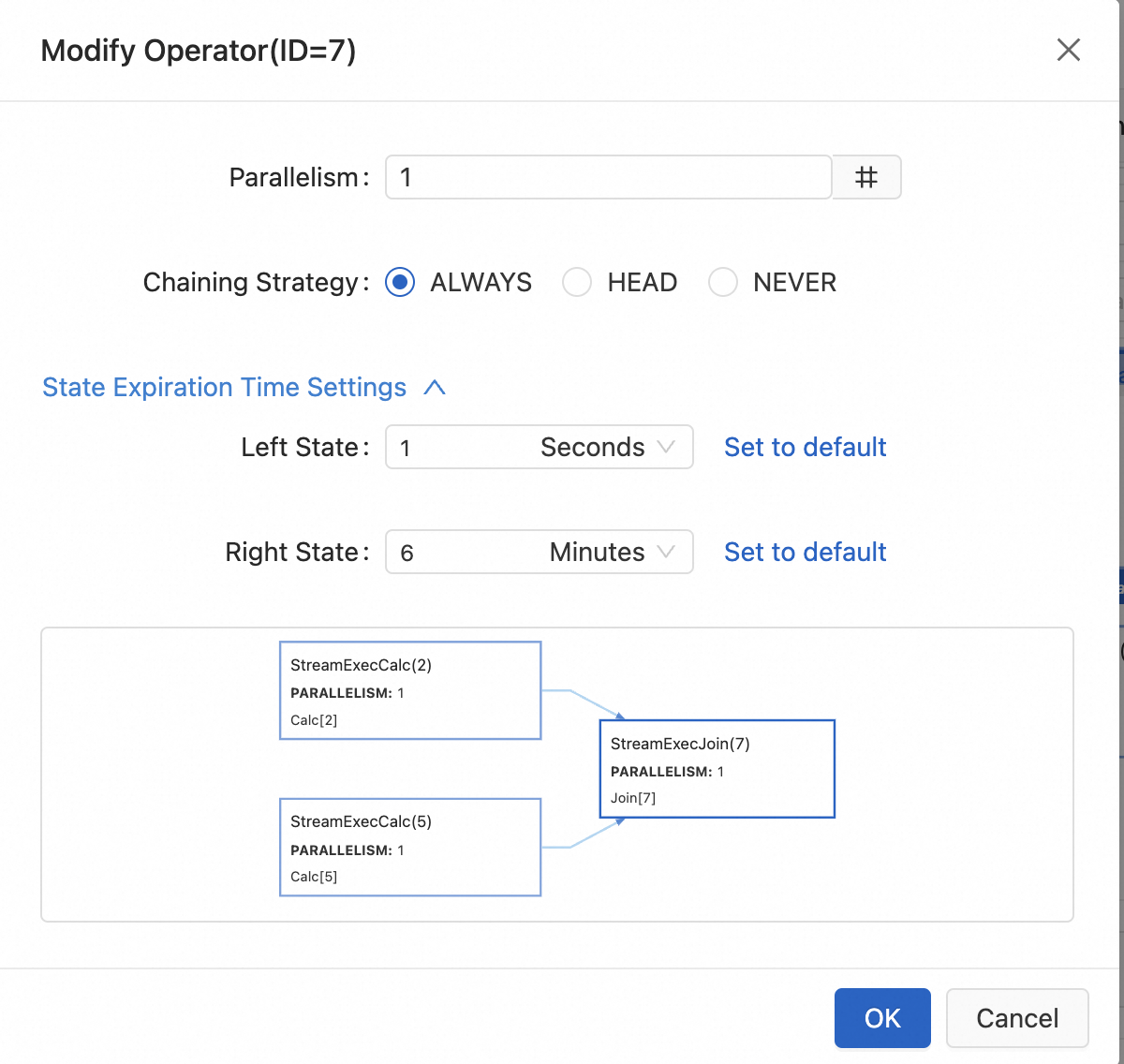
The following describes the parameters:
Parameter
Description
Parallelism
The number of parallel instances for an operator.
Chaining Strategy
Flink chains operator subtasks into a single task, improving performance by reducing data transfer and serialization overhead. Breaking chains can offer finer control over job execution. Supported strategies include:
ALWAYS (default): The operator chains with both upstream and downstream operators.
HEAD: The operator starts a new chain. It breaks the chain with upstream operators but remains chained with downstream operators.
NEVER: The operator is not chained with any upstream or downstream operators.
State Expiration Time Settings
Sets the state's TTL, configurable in seconds, minutes, hours, or days.
By default, it inherits the job's configured TTL. If no job-level TTL is set, the default is 1.5 days. See Parameters.NoteThis TTL setting:
Requires VVR 8.0.7+.
Is restricted to stateful operators.
Click Confirm.