This topic describes how to use Alibaba Cloud Heartbeat to check the status of Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP) and HTTP services. It can also generate visual charts.
Background information
Heartbeat is a lightweight daemon. It can be installed on a remote server to check the availability of your services on a regular basis. Heartbeat is unlike Metricbeat. Heartbeat checks whether your services are reachable but Metricbeat checks whether your services are running.
Most Beats shippers need to be installed on edge nodes. However, Heartbeat can be installed on a separate computer or even outside the network where services you want to monitor are deployed.
Heartbeat supports the following types of monitors:
ICMPv4 or ICMPv6 monitor: sends ICMP requests to check whether a service is available. This type of monitor connects to a service over ICMP. If you want to use an ICMP monitor, root permissions are required.
TCP monitor: sends or receives specific workloads to check whether a service is available. This type of monitor connects to a service over TCP.
HTTP monitor: checks whether a service is available based on specific status codes, response headers, or response content. This type of monitor connects to a service over HTTP.
NoteTCP and HTTP monitors support Secure Sockets Layer (SSL), Transport Layer Security (TLS), and some proxy settings.
Prerequisites
An Alibaba Cloud Elasticsearch cluster is created.
For more information, see Create an Alibaba Cloud Elasticsearch cluster.
The Auto Indexing feature is enabled for the Elasticsearch cluster.
For security purposes, Alibaba Cloud Elasticsearch disables the Auto Indexing feature by default. However, Beats depends on this feature. If you select Elasticsearch for Output when you create a shipper, you must enable the Auto Indexing feature. For more information, see Access and configure an Elasticsearch cluster.
An Alibaba Cloud Elastic Compute Service (ECS) instance is created in the virtual private cloud (VPC) where the Elasticsearch cluster resides.
For more information, see Create an instance on the Custom Launch tab.
ImportantBeats supports only Alibaba Cloud Linux (Alinux), Red Hat Enterprise Linux (RHEL), and CentOS.
Cloud Assistant and Docker are installed on the ECS instance.
For more information, see Install Cloud Assistant Agent and Deploy and use Docker on ECS instances.
Procedure
Log on to the Alibaba Cloud Elasticsearch console.
In the left-side navigation pane, click Beats Data Shippers.
In the Create Shipper section of the page that appears, click Heartbeat.
Install and configure a shipper.
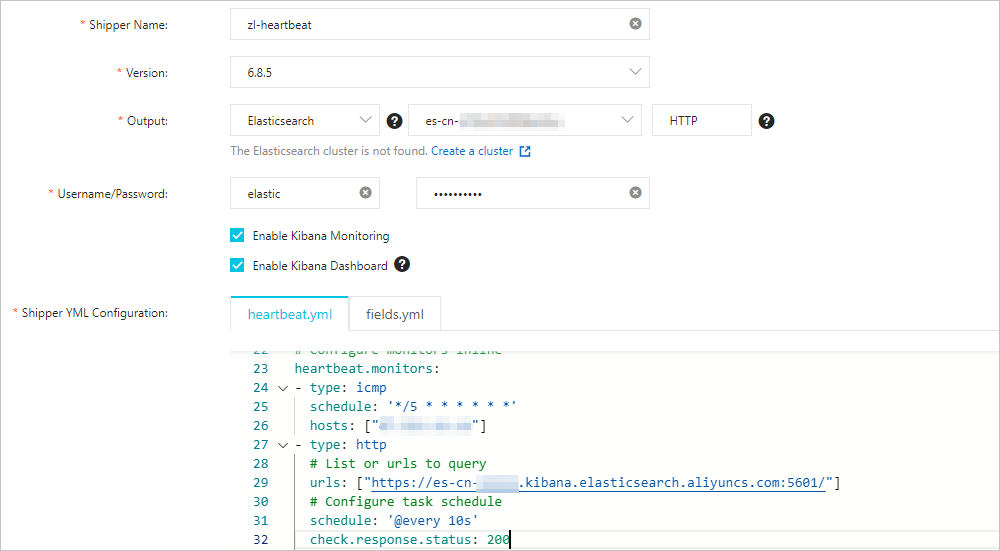
For more information, see Collect the logs of an ECS instance and Prepare a YML configuration file for a shipper. The following figure shows the configurations that are used in this example.
 Note
NoteIf you select Enable Kibana Monitoring, the system enables Heartbeat service monitoring in the Kibana console.
If you select Enable Kibana Dashboard, the system generates charts in the Kibana console. You do not need to configure the YML file. Alibaba Cloud Kibana is deployed in a VPC. You must enable the Private Network Access feature for Kibana on the Kibana Configuration page. For more information, see Configure a public or private IP address whitelist for Kibana.
When you configure the shipper, configure the
heartbeat.monitorsparameter in heartbeat.yml to configure monitors. The following monitor configurations are used in this example:heartbeat.monitors: - type: icmp schedule: '*/5 * * * * * *' hosts: ["47.111.xx.xx"] - type: http # List or urls to query urls: ["https://es-cn-xxxxx.kibana.elasticsearch.aliyuncs.com:5601/"] # Configure task schedule schedule: '@every 10s' check.response.status: 200Parameter
Description
typeThe monitor type. In the preceding configurations,
icmpandhttpmonitors are specified.scheduleThe task schedule. If you set this parameter to
'*/5 * * * * * *', the system runs the task at 5-second intervals. If you set this parameter to'@every 10s', the system runs the task at 10-second intervals from the time Heartbeat is started.hostsThe servers that you want to ping.
urlsThe URLs that you want to ping.
check.response.statusThe expected HTTP status code that is returned for the HTTP request. If you set this parameter to
200, the system determines that the related service is normal if200is returned.NoteFor more information, see open source Heartbeat documentation.
Select the ECS instance on which you want to install the shipper.
The selected ECS instance must meet the preceding prerequisites.
Start the shipper and check whether the shipper is installed.
Click Start.
Then, the Start Shipper message appears.
Click Back to Beats Shippers. In the Manage Shippers section of the Beats Data Shippers page, view the installed shipper.
After the state of the shipper changes to Enabled 1/1, click View Instances in the Actions column.
In the View Instances panel, check whether the shipper is installed on the ECS instance. If the value of Installed Shippers is Normal Heartbeat, the shipper is installed.
View the result
Log on to the Kibana console of the Elasticsearch cluster.
For more information, see Log on to the Kibana console.
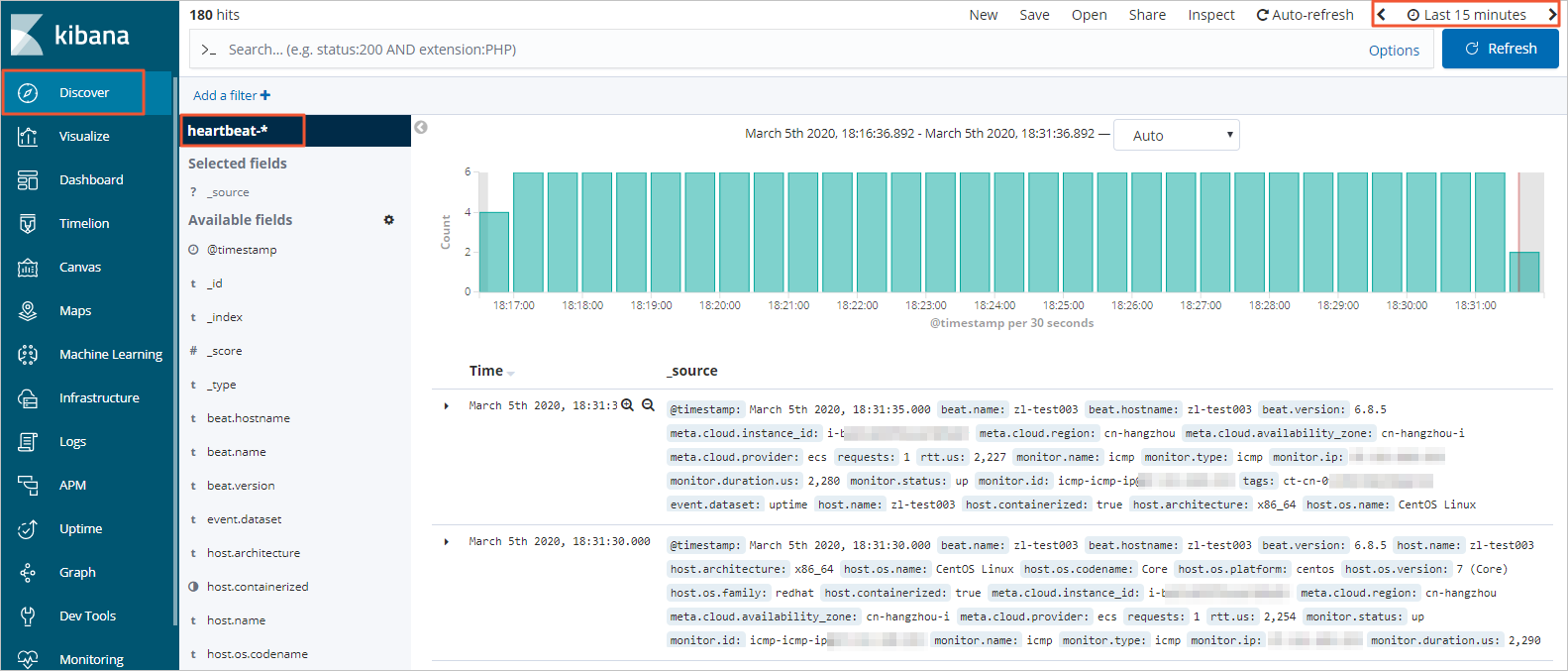
In the left-side navigation pane, click Discover. On the page that appears, select heartbeat-* from the drop-down list in the upper-left corner and specify a period in the upper-right corner. Then, view the data collected by Heartbeat within the specified period.
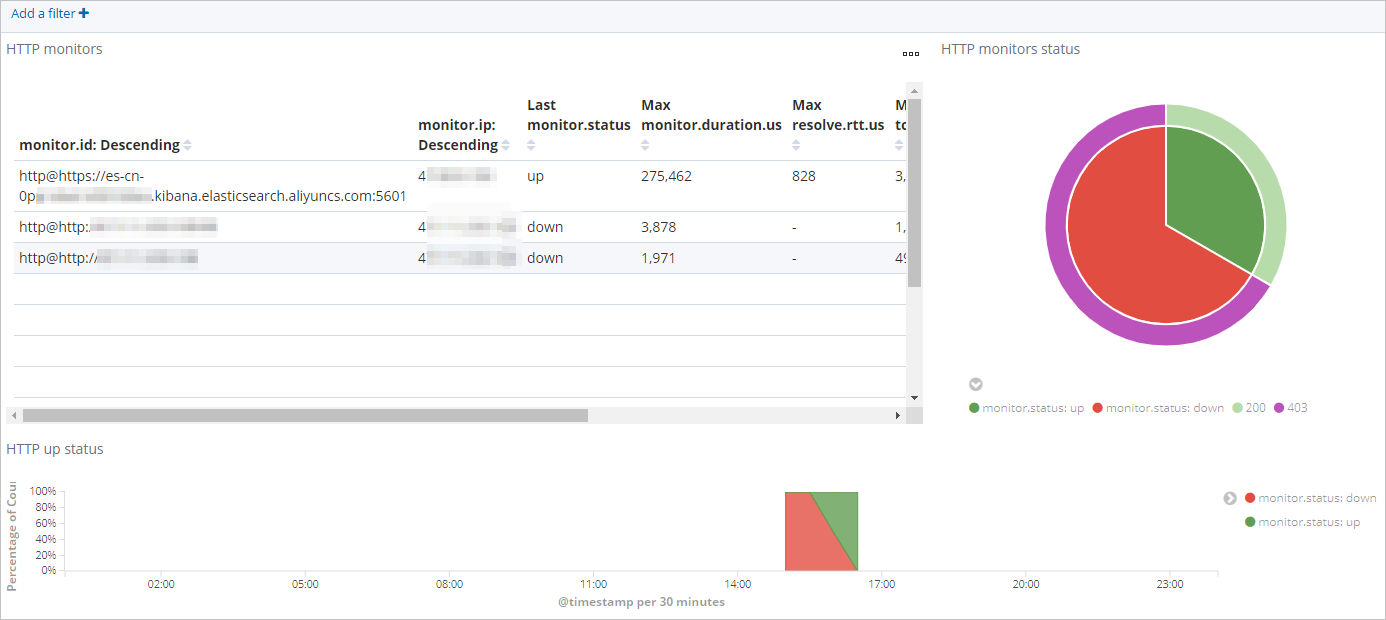
In the left-side navigation pane, click Dashboard.
In the Dashboards section of the page that appears, click Heartbeat HTTP monitoring. In the upper-right corner of the page that appears, select a period. Then, view HTTP status statistics within the specified period.