Fleet is a powerful solution provided by Elasticsearch to manage Fleet agents in a centralized manner. You can use Fleet to manage multiple nodes and services in Elasticsearch with ease. Fleet is composed of the Fleet server and Fleet agents. A Fleet agent is a lightweight data collection agent that is used to collect data from a source. The Fleet server is the core node of Fleet and is responsible for managing and monitoring all Fleet agents and transferring data to Elasticsearch.
Terms
Term | Description |
Fleet | Fleet is a powerful solution provided by Elasticsearch to manage Fleet agents in a centralized manner. |
Fleet agent | A Fleet agent is a lightweight data collection agent that is used to collect data from a source. A Fleet agent can run on different types of operating systems and collect multiple types of data. |
Fleet server | The Fleet server is used to transfer data that is collected by a Fleet agent from a source to Elasticsearch. |
Prepare environments
Create an Alibaba Cloud Elasticsearch cluster. For more information, see Create an Alibaba Cloud Elasticsearch cluster. In this example, an Alibaba Cloud Elasticsearch V8.5 cluster is created.
NoteThe version of the Alibaba Cloud Elasticsearch cluster must be V7.16 or V8.5.
Create an Elastic Compute Service (ECS) instance in the same virtual private cloud (VPC) as the Elasticsearch cluster. For more information, see Create an instance by using the wizard.
NoteThe ECS instance is used as the source server. A Fleet agent collects data from the ECS instance.
Create an agent policy and add integrations
Step 1: Create an agent policy
Log on to the Kibana console of the Elasticsearch cluster. For more information, see Log on to the Kibana console.
Click the
 icon in the upper-left corner. In the left-side navigation pane, choose .
icon in the upper-left corner. In the left-side navigation pane, choose . On the Fleet page, click the Agent policies tab.
Click Create agent policy. In the Create agent policy panel, configure the agent policy.
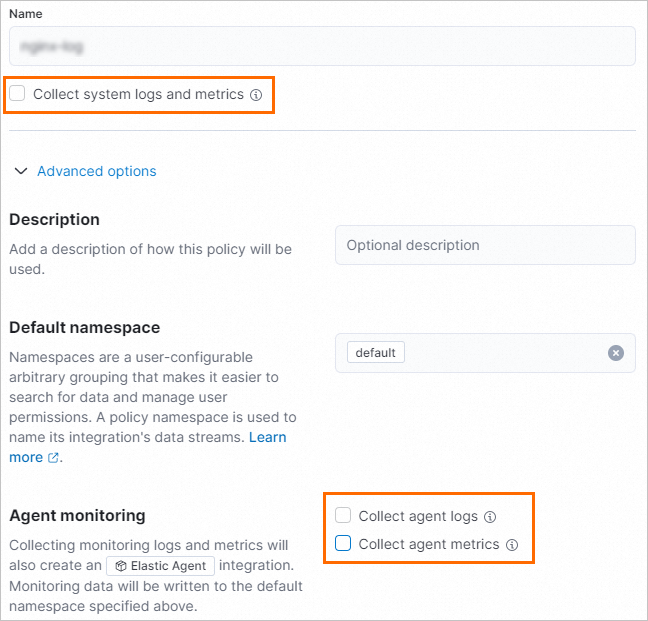
Enter the name custom-log in the Name field.
Clear Collect system logs and metrics.
Click Advanced options. In the Agent monitoring section, clear Collect agent logs and Collect agent metrics.
 Note
NoteIn this example, only custom logs need to be collected. Therefore, Collect system logs and metrics, Collect agent logs, and Collect agent metrics do not need to be selected.
Click Create agent policy.
Step 2: Add a Fleet server integration
On the Agent policies tab of the Fleet page, find the newly created agent policy custom-log and click its name.
On the Integrations tab of the page that appears, click Add integration.
On the Browse integrations tab of the Integrations page, enter Fleet Server in the search box. Then, click the Fleet Server card that is displayed.
Install the Fleet server integration.
On the Fleet Server page, click the Settings tab.
Click Install Fleet Server assets. In the Install Fleet Server message, click Install Fleet Server.
NoteAfter the integration is installed, the version of the integration is displayed on the Settings tab of the Fleet Server page.
In the upper-right corner of the Fleet Server page, click Add Fleet Server.
On the Add Fleet Server integration page, enter a name for the integration in the Integration name field in the Configure integration section and select
custom-logfrom the Agent policy drop-down list in the Where to add this integration section.In the lower-right corner of the Add Fleet Server integration page, click Save and continue. In the Fleet Server integration added message, click Add Elastic Agent later.
Step 3: Add a Custom Logs integration
On the Integrations tab of the agent policy custom-log, click Add integration.
On the Browse integrations tab of the Integrations page, enter Custom Logs in the search box. Then, click the Custom Logs card that is displayed.
Install the Custom Logs integration.
On the Custom Logs page, click the Settings tab.
Click Install Custom Logs assets. In the Install Custom Logs message, click Install Custom Logs.
NoteAfter the integration is installed, the version of the integration is displayed on the Settings tab of the Custom Logs page.
In the upper-right corner of the Custom Logs page, click Add Custom Logs.
On the Add Custom Logs integration page, configure the integration.
In the Configure integration section, enter a name in the Integration name field.
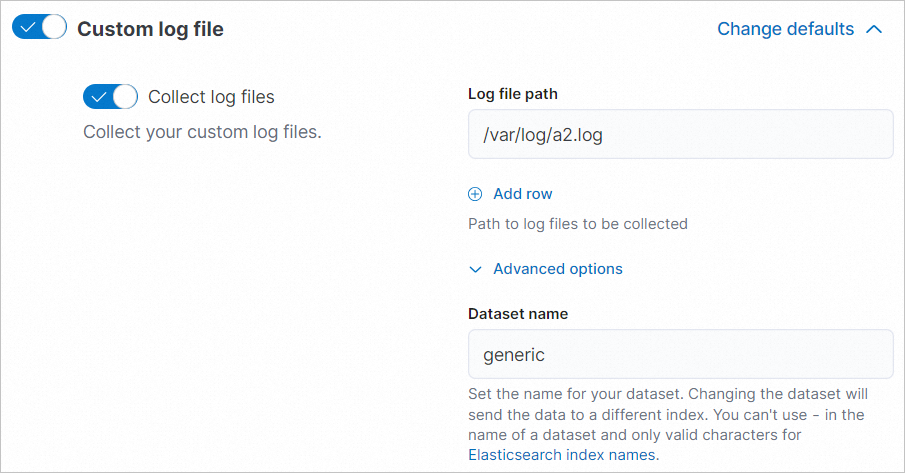
In the Custom log file section, enter the path of the ECS logs that you want to collect in the Log file path field, such as
/var/log/a2.log.Click Advanced options. Enter a name in the Dataset name field.
NoteThe dataset name determines the name of the Elasticsearch index in which the collected data is stored. You can specify a dataset name based on your business requirements. Then, the collected data is transferred to the index whose name is the same as the dataset. This can improve the flexibility of data processing and facilitate data management.
The dataset name must comply with the naming convention of an Elasticsearch index. The dataset name can contain only letters, digits, and underscores (_).
On the Existing hosts tab of the Where to add this integration section, select
custom-logfrom the Agent policy drop-down list.
In the lower-right corner of the Add Custom Logs integration page, click Save and continue. In the Custom Logs integration added message, click Add Elastic Agent later.
Add a Fleet agent
Step 1: Configure a host for the Fleet server
Log on to the Kibana console of the Elasticsearch cluster. For more information, see Log on to the Kibana console.
Click the
 icon in the upper-left corner. In the left-side navigation pane, choose .
icon in the upper-left corner. In the left-side navigation pane, choose . On the Fleet page, click the Settings tab. On the Settings tab, configure parameters for Fleet.
In the Fleet server hosts section, click Edit hosts.
In the Fleet Server hosts panel, enter the URL of the source from which you want to collect data in the Specify host URL field. The URL must be in the
https://<Private IP address of the source>:<Port number>format, such ashttps://172.16.*.***:8220. Then, click Save and apply settings. In the Save and deploy changes message, click Save and deploy.NoteIn this example, a URL that contains the primary private IP address of the ECS instance is entered. For more information about the configurations, see Fleet Server hosts.
In the Outputs section of the Fleet page, click the
 icon in the Actions column.
icon in the Actions column. In the Edit output panel, enter the URL of the Elasticsearch cluster in the Hosts field. The URL must be in the
http://<Internal endpoint of the Elasticsearch cluster>:<Port number>format, such ashttp://es-cn-uqm3auln80001****.elasticsearch.aliyuncs.com:9200.Click Save and apply settings. In the Save and deploy changes message, click Save and deploy.
Step 2: Add a Fleet agent
Add a Fleet agent to the Fleet server.
If you want to collect data from multiple source servers, you can repeat the following steps. After you add multiple Fleet agents to the Fleet server, each Fleet agent collects data from the related source server. The collected data is managed by the Fleet server in a centralized manner.
On the Fleet page, click the Agent policies tab.
On the Agent policies tab, find the agent policy custom-log, click the
 icon in the Actions column, and then select Add agent.
icon in the Actions column, and then select Add agent.On the Enroll in Fleet tab of the Add agent panel, click Add Fleet Server. In the Add a Fleet Server panel, click Advanced. In the Select a policy for Fleet Server section, retain the default value
custom-log.In the Choose a deployment mode for security section, retain the default value Quick start.
In the Add your Fleet Server host section, click Add host.
In the Generate a service token section, click Generate service token.
In the Install Fleet Server to a centralized host section, copy the code that is automatically generated and run the code in the ECS instance.
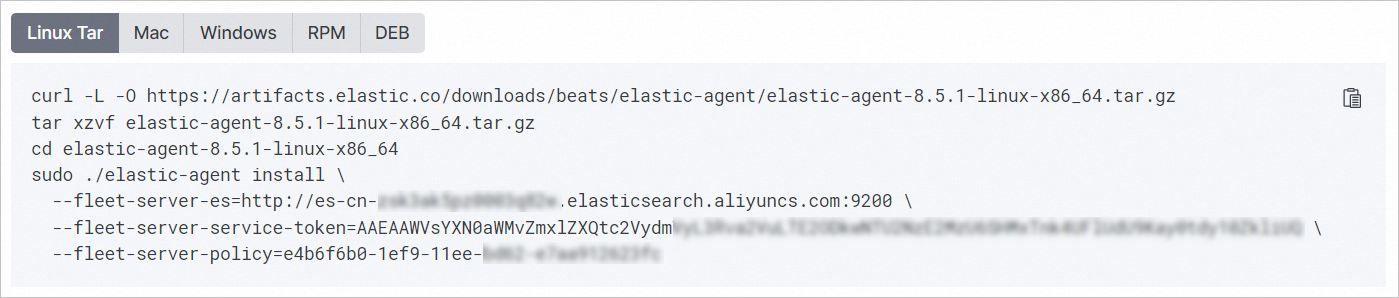
If
Successfullyis displayed after you run the code, the Fleet agent is installed on the ECS instance and is started.
View the collected data
In this example, the ECS log path /var/log/a2.log and the dataset generic are used. This section describes how to view the collected ECS log data.
You must make sure that some data is stored in the ECS log path that you specified.
View the name of the data stream on the Index Management page.
Click the
 icon in the upper-left corner and choose .
icon in the upper-left corner and choose . In the left-side navigation pane, choose .
On the Index Management page, click the Data Streams tab. On the Data Streams tab, find the data stream whose name contains
generic, such aslogs-generic-default.
View the name of the index that corresponds to the data stream in the Kibana console.
Click the
 icon in the upper-left corner. In the left-side navigation pane, choose .
icon in the upper-left corner. In the left-side navigation pane, choose . On the Console tab, run the following command to obtain the name of the index that corresponds to the data stream:
GET _data_Stream/logs-generic-defaultThe value of index_name in the returned result indicates the name of the index that corresponds to the data stream.
Run the following command to view the log data in the index:
GET <index_name>/_search { "query":{ "match":{ "log.file.path":"/var/log/a2.log" } } }